Contents
- What is Anasarca?
- What are Anasarca symptoms?
- Can anasarca cause high blood pressure?
- What are the mechanisms of anasarca development?
- What are the causes of anasarca?
- Anasarca diagnosis
- How to differentiate anasarca from similar diagnosis (Liver cirrhosis ascites, Kwashiorkor, etc..)?
- Anasarca caused by Cirrhosis
- Anasarca caused by Heart failure
- Anasarca caused by renal failure
- Anasarca caused by severe malnutrition
- What is Clarkson syndrome? Can Clarkson syndrome cause anasarca?
- Anasarca treatment
- Diuretics for anasarca treatment
- Home remedies and diets for anasarca treatment
- What is peritoneovenous shunt? Is surgical care effective for ascites?
- What drugs should not be used by patients with anasarca?
- Difference between anasarca and ascites?
- What is scrotal edema?
What is Anasarca?
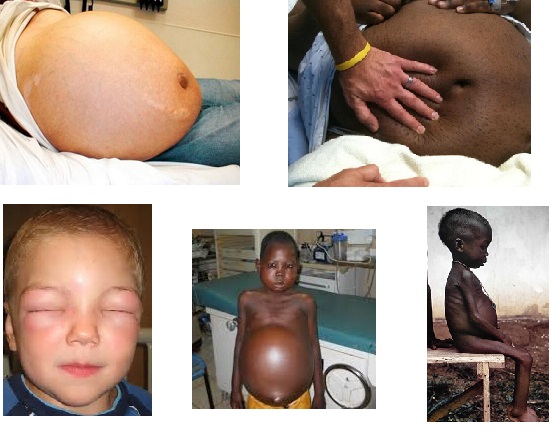
Anasarca is a medical condition characterized with a general swelling (edema) in the body, with profound subcutaneous swelling caused by effusion of fluids into the extracellular space. Quantitatively, a fluid increase of ≥3L is detected in patients who developed anasarca. Anasarca terminology comes from Greek phrases: “ana” meaning “through” and “sarca” meaning “flash”.
This condition is also called hydrosarca or dropsy. It should be known that anasarca is not a disease. It can be more precisely described as a symptom of an underlying condition such as malnutrition or rather protein deficiency. Several health issues such as liver failure, heart problems or renal failure may lead to anasarca.
Administration of exogenous intravenous fluid or chemotherapeutic drug slike doxetaxel may also cause ansarca. In anasarca, the patient looks like bloating and when the patient is pinched to the skin, it will not go back to its normal condition right away.
What are Anasarca symptoms?
Depending on underlying condition, symptoms of anasarca may be different. So, patients who have anasarca caused by renal failure may experience following symptoms:
- Nausea
- Anemia
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Cramps
- No urine output
- Swelling of the feet and ankle
- Body weakness
- Shortness of breath
On the other hand, if the cause is heart problems, patients with anasarca may experience:
- Unable to sleep at night unless sitting upright
- Shortness of breath
- Body weakness
- Decreased appetite
- Abdominal pain
If the ansarca patient is a female and the immense edema begins to develop on the lower abdominal region or the reproductive organs, they may find that they are unable to urinate and that the blood from the menstrual cycle does not flow properly. Painful cramps and massive blood clotting during the menstrual cycle can be also developed.
The most patients also suffer from abdominal pain and cramping sensations. In many cases, this could lead to a lack of appetite. Nausea and vomiting can be also present.
Most patients will also have a problem to rest at night. This is often caused because of the pain and bloating experience. In other instances, it could be a result of breathing problems. This often leads to nighttime insomnia and daytime fatigue.
Many Anasarca sufferers may also develop anemia because of the red blood cell or a hemoglobin deficiency within the blood
Some patients may also experience:
- Exaggerated leg edema when the patient is standing up.
- Periorbital edema or swelling around the eyes especially in the morning.
Can anasarca cause high blood pressure?
Due to the increase levels of fluid in the body, it is frequent for a patient with anasarca to have fluctuations in their blood pressure. In most cases the blood pressure increases. This is because the heart has to work much harder to pump blood throughout the body.
What are the mechanisms of anasarca development?
There are several different pathophysiological mechanisms of anasarca development. Most common mechanisms are described below:
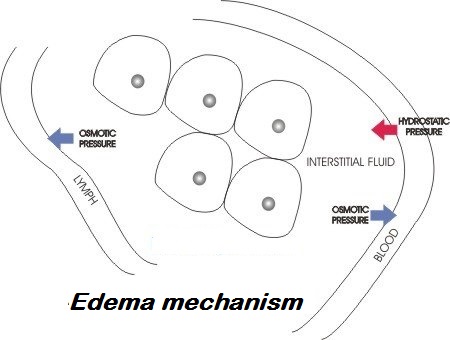
- Hypoalbuminemia and low osmotic pressure. Patients with hypoalbuminemia caused by nephrotic syndrome or some other disease have a greater chance of developing anasarca as a result of low osmotic pressure in their capillaries. The osmotic pressure is essence for keeping up the fluid within the blood vessels. When osmotic pressure is low, fluid goes out of the vessels and accumulates into the interstitium, causing edema. In the case of anasarca, the low capillary osmotic pressure is not localized, it is systemic, and may provoke generalized edema or swelling. At the beginning anasarca edema occurs in ankles, feet, and around the eyes.
- Diabetic nephropathy and glomerular blood flow obstruction. Another mechanism of anasarca development is diabetic nephropathy. Hyperglycemia and hypertension are two most common symptoms of diabetes mellitus. If untreated, the incidence of diabetes complications, such as diabetic nephropathy, increases. Uncontrolled hyperglycemia and high blood pressure may affect kidneys glomeruli by increasing the thickness of its basement membrane, causing the enlargement of glomeruli. As a result, Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules may develop. These nodules are able to obstruct the glomerular blood flow and may damage the nephrons. Proteinuria may be developed as a result of glomerular enlargement. As proteinuria becomes more serious, more nephrons become destroyed, worsening the proteinuria and the cascade goes on and on until the condition progresses to renal failure.
- Sodium retention. Excess amounts of salt (sodium-chloride) in the body causes water retention leading to more fluid in the blood to cause intravascular expansion thus increasing the hydrostatic pressure. The increased intravascular fluid volume may further lead to decrease of the osmotic pressure as a result of protein dilution.
- Fetal anasarca. Fetuses can be also vulnerable and generalized swelling may also happen intrauterine. Fetal anasarca occurs in condition called hydrops fetalis where increased permeability of capillary and obstructed lymphatic vessels may result to extravasation of fluid into the subcutaneous tissue. Fetal subcutaneous tissue appears to be 5 mm thicker than normal as a result of it.
- Ascites mechanism. Ascites is defined as accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity exceeding the volume of 25 mL. There are a number of risk factors such as hypoalbuminemia, hypotension, increased adrenaline and noradrenaline levels. However, the most convincing evidence is that ascites is caused as a result of peripheral arterial vasodilation. According to this ascites is caused by portal hypertension which leads to vasodilation. As a result, the blood volume in the arteries is descreasd. As the disease becomes worse, it begins to stimulate neurohumoral excitation, causing retention of sodium in the kidneys and expandeding plasma volume. The excess fluid enters into the abdominal cavity.
What are the causes of anasarca?
There are a various causes for anasarca. The conditions or diseases may include:
- Hookworms or ancylostomiasis
- Liver failure
- Heart failure
- Kidney failure
- Pre-eclampsia
- Chemotherapy drugs like Doxetaxel
- POEMS – Polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy syndrome
- Severe malnutrition
- Protein deficiency
- Tumors
- Amyloidosis
- Thyroid problems
- Burns
- Clarkson syndrome
- Excessive sodium intake
Anasarca diagnosis
Different diagnostic methods can be used in order to make a diagnosis of anasarca. Sometimes it is hard for even the best clinicians to diagnose anasarca, as it is sometimes similar to several other symptoms. Tests and measures that need to be performed in order to precisely diagnose anasarca are described below. These symptoms may be related to either anasarca or localized swelling, or potentially both.
- Albumin blood test. Serum albumin is most abundant plasma protein in the human body, and it is used in different functions such as maintaining osmotic pressure or as a plasma carrier protin. As described low levels of albumin in blood can lead to anasarca. This test can prove whether the patient has hypoalbuminemia, or insufficient albumin blood levels.
- Kidney and liver function tests. Your doctor may need different kidney or liver function test in order to determine if anasarca is present. Kidney function tests that should be performed are: glomerular filtration rate (GFR) or creatinine clearance rate (CCR). Liver function tests may include: liver enzymes testing such as: alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine transaminase (ALT), the direct bilirubin, and total bilirubin (TBIL).
- Urinalysis (UA). Some urinalysis can use dipsticks, and in such cases the results are seen as the color on the stick changes. Tests performed using urinalysis can include those such as the following examples: ketone bodies which are usually negative, pH which should be acidic, proteins that are usually expected, hyperthyroidism, jaundice, etc…
- Echocardiogram (ECHO) and electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Both tests of the heart, the echocardiogram which is ultrasound-based, or the electrocardiogram which represent heart electrical activity over a period of time can be useful for anasarca diagnosis.
- Blood electrolyte level test and X-ray testing can be also performed.
How to differentiate anasarca from similar diagnosis (Liver cirrhosis ascites, Kwashiorkor, etc..)?
The differential diagnosis of anasarca may include following conditions:
- Alcoholic liver cirrhosis
- Congestive heart failure
- Heart failure caused by heart cirrhosis
- Heart failure caused by thiamine deficiency
- Nephrotic syndorme
- Malnutrition
- Starvation
- Kwashiorkor
- Ascites caused by severe trauma or burns
- Hypoalbuminemia
- Eclampsia
- Hypothyroidism
When considering anasarca diagnosis, doctors will probably first look if swelling is localized or generalized in the body. If it is localized it may be because of lymphatic obstruction, venous obstruction or local trauma or burns. Usually obstruction is removed as the injury is healed and there is nothing to worry about. However if the edema/swallowing is generalized, then further steps are needed in order to confirm the right diagnosis.
If anasarca is suspected, then underlying condition should be found. In that case, laboratory tests should be performed in order to determine if hypoalbuminemia exists (albumin level of <2.5mg/dl). If hypoalbuminemia is confirmed, and generalized edema exists then the patient may either have liver cirrhosis, severe malnutrition, or nephrotic syndrome.
If the albumin levels are normal, the other common underlying cause that may lead to anasarca is heart failure and this can be detected in patients with jugular venous distention on the side of the neck or decreased cardiac output. This is due the fact that the heart fails to pump sufficient amounts of blood to systemic circulation.
If there is jugular venous distention and cardiac output are normal, then the doctor/clinician will certainly examine kidneys. If azotemia or active urine sediment are present, renal failure may be diagnosed. If renal failure is not diagnosed, anasarca may be caused by hypothyroidism or it may have iatrogenic-drug-induced nature. Some chemotherapy agents, corticosteroids, estrogens and vasodilators may be the cause of anasarca.
Anasarca caused by Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, as a sign of progressive liver failure, may be underlying condition that can lead to anasarca. Cirrhosis usually comes as a result of a chronic liver disease (hepatitis C or B virus infection) or alcoholism. Wilson disease is also often cause of cirrhosis.
As said, when cirrhosis progresses to the liver failure, anasarca can be developed. Liver is the main plasma protein producing organ. If liver cirrhosis with fibrous tissue is present, it may lead to reduced protein production.
Thus, hypoalbuminemia and low osmotic pressure may develop and fluid may leak in the interstitium. Fibrous scars of the liver tissue may make the pressure to portal vessels passing through the liver and thus increasing the hydrostatic pressure in the veins in the abdomen. This may lead to the accumulation of the fluid in the peritoneal spaces causing Ascites.
However, there are also many possible medical symptoms aside from this. As an example, spider angiomas may affect the patient too. The liver’s size can change, either increasing or decreasing. Jaundice, itching, bleeding or bruising and portal hypertension may also develop.
Anasarca caused by Heart failure
Congestive heart failure is a condition characterized by low cardiac output, and the inability of the heart to pump proper amount of blood into the bloodstream. This condition is known to be very serious, and it is the one of most common cases that leads to anasarca. When heart reduces and fails to pump the blood in the proper way, the blood flow slows down leading to venous stasis.
Venous stasis further leads to increased hydrostatic pressure and edema. Initially, edema takes peripheral part of the body such as ankles and feet, over the time progressing to the very serious anasarca with compromised heart function.
Anasarca caused by renal failure
Renal failure is a serious medical condition where kidneys do not work properly in filtering and excreting waste materials from the system. It is also one of the causes that may lead to anasarca. Renal failure may lead to proteinuria, reducing the protein levels in the blood, and thus reducing coloido-osmotic pressure which may lead to edema.
The kidneys may also become unable to excrete sodium, which will retain water in the system and excesive intravascular volume leading to edema. Usually, when the plasma protein levels drop down to less of one third of the normal level, anasarca will be developed.
Anasarca caused by severe malnutrition
Severe malnutrition is another possible reason of anasarca cause. Malnutrition of certain vitamins, minerals, essential nutrients may lead to different medical issues, based upon the type of deficiency. Malnutrition itself may not necessarily lead to anasarca. However, severe protein deficiency is one possibility that can result with anasarca.
The major cause of anasarca in children is protein malnutrition also known as Kwashiorkor. Cases of Kwashiorkor occur in areas of famine or poor food supply. It is most seen in children of 1-4 years of ages in African and Southeast Asian countries.
What is Clarkson syndrome? Can Clarkson syndrome cause anasarca?
Clarkson syndrome is a rare condition where the pores in the blood capillaries increase in size and in count. This causes fluid to go out from the blood into the interstitial fluid all over the body leading to anasarca. Swelling, decreased blood pressure and failure of multiple organs can follow.
Anasarca treatment
As previously described, anasarca is not the condition by itself, it is the symptom of underlying condition, thus by treating the underlying conditions, anasarca will diminish.
The general recommendations for anasarca treatment are following:
- Water is always following sodium so patients should reduce sodium/salt intake to <500mg/day.
- If the laboratory tests detect severe state of hyponatremia (<132 mmol/L), patients should restrict water intake to <1.5L per day to prevent further lowering of sodium levels in the body, as what happens in dilutional hyponatremia when you drink a lot water.
- Resting in bed is needed for better recovery especially if the cause of anasarca is congestive heart failure or liver cirrhosis.
- Patients with swelling of the lower extremities should lie down flat on their back and should elevate their legs and feet against the wall.
- The use of compression stockings may be also helpful
- Diuretics are most commonly prescribed to reduce anasarca swelling especially if pulmonary edema, congestive heart failure or excessive sodium intake is recognized. Combination of loop diuretics with Potassium-sparing diuretics is the common therapy for best outcomes. When proper weight is achieved, diuretics dose should be reduced. Weight loss with diuretics should not be excess, and should only be 1-1.5 kg/day.
- In congestive heart failure, diuretics overuse may lead to further decreased cardiac output, azotemia and hypokalemia.
- In case of liver diseases, spironolactone which is the potassium-sparing diuretic is the drug of first choice. Thiazides or loop diuretics may be also added in combination with spironolactone. Therapy with diuretics should be closely because overuse may trigger complication like hepatic encephalopathy.
- Hemodialysis is also recommended in kidney and liver failure cases, in order to get rid of the excessive interstitial fluid.
- In patients with burns, fluid and electrolyte replacement is extremely important.
- For malnourished patients, sufficient food and fluid intake are needed to cure anasarca
- Thyroid hormone replacement therapy should be given to patients with hypothyroidism.
- Drugs that may induce anasarca should be discontinued.
Diuretics for anasarca treatment
Following groups of diuretics are most commonly used for anasarca treatment:
- Loop diuretics. Furosemide (Lasix), torasemide (Diuver) and butethamine are most commonly used loop diuretics for anasarca treatment. They are given for the excretion of excess through urination. These diuretics stimulate the kidneys loop of Henle that regulates the salt and water exretion. While thiazide diuretics are more effective in patients with normal kidney function, loop diuretics showed better responses in patients with impaired kidney function. In order to avoid excess potassium loss, loop diuretics are often combined with potassium sparing diuretics such as spironolactone.
- Potassium-sparing diuretic. Spironolactone (Aldactone) is the first choice of therapy for anasarca caused by cirrhosis. Another effective potassium-sparing diuretic is triamterene. These drugs are appropriate for anasarca treatment because they prevent potassium loss. Spironolacton is most commonly used in combination with other diuretics.
- Thiazide diuretics. Hydrochlorothiazide is most commonly used thiazide diuretic. It is very diuretic that produces synergistic response because it stimulates the different sites of the kidney for the excess water to be excreted. Because the risk of potassium loss, it is commonly used in combination with potassium-sparing diuretics.
- Aquaretics or antagonists of vasopressin V2-receptor promote excretion of water without electrolytes and therefore, this therapy might be beneficial in patients with ascites and hyponatremia. Although study results have been promising aquaretics still await approval by the FDA
Home remedies and diets for anasarca treatment
- Since loop and thiazide diuretics will excrete potassium, except the potassium-sparing diuretics such as spironolactone or triamterene, patients need to intake foods rich in potassium including: bananas, orange juice, potatoes, and tomatoes.
- Alfalfa plant contains chlorophyll which is a potent detoxifier. A recommended 2,000 to 3,000 mg per day is also recommendable.
- Proteins that may help edema reduce may include: eggs, skinless chicken or turkey, broiled white fish, cottage cheese, low-fat yogurt and kefir
- High fiber diet is also a remedy for edema
- Patients with post-surgical edema should intake horse chestnut, as it may reduce the problem
- Rose hips is rich with bioflavonoids thus it might be helpful for edema treatment
- Mild exercise and saunas may be helpful, since sweating can lessen edema
- Hawthorn berries, juniper, uva ursi and horsetails are natural diuretics and may increase the urine output
- It is also important to avoid taking of alcohol, animal proteins, beefs, chocolates and some dairy products that may slow reduction of edema or even promote it
- Salt intake should be lessened because it increased the incidence of water retention in the body.
- Wearing support hose for pitting edema is also recommendable
- Patients with heart failure should limit fluid intake. Excessive fluid intake can promote edema and may also cause breathing difficulties.
- Dandelion Leaf and Ginkgo – enhances the circulatory system and improve blood flow to our body.
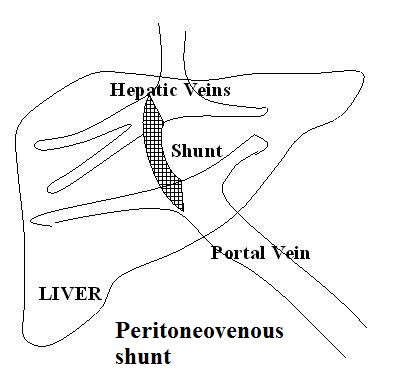
What is peritoneovenous shunt? Is surgical care effective for ascites?
The peritoneovenous shunt is an alternative treatment for patients with intractable ascites. This procedure is known as a megalymphatic shunt that revenues the ascitic fluid from interstitium to the central venous system. Beneficial effects of this procedure are: increased cardiac output, increased renal blood flow, glomerular filtration rate and urinary volume, increased sodium excretion and decreased plasma renin-aldosterone-angiotensin system. The AASLD recommends considering peritoneovenous shunting for patients with refractory ascites who are not candidates for paracentesis, transplant, or TIPS.
What drugs should not be used by patients with anasarca?
Different medicines may cause edema. Thus, therapy with such medicines should be abrupted in the case of anasarca. These medicines may include:
- NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen and naproxen)
- Calcium channel blockers (diltiazem, amplodipine)
- Corticosteroids (betamethasone, prednisone, methylprednisolone)
- Pioglitazone and rosiglitazone
- Pramipexole
- Vasodialtators
- Doxetaxel chemotherapy drug
Difference between anasarca and ascites?
Anasarca is defined as generalised edema while ascites is defined as an accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, frequently symptomatic of liver disease.
What is scrotal edema?
When one of the testicles is swollen compared to the other one, the pull of gravity results in increased pain and discomfort, particularly when standing. The normal scrotum is anatomically on the front side, while the edematous scrotum swells between the upper legs to the hind side. The scrotum is now an obstacle to movement from one place to another, thereby changing the patient’s normal posture and pattern
There are quite a number of causes of anasarca in the testicles. Some of them are:
- Liver cirrhosis
- Renal failure
- Heart failure
The condition may present with the following symptoms:
- Testicular Lump
- Groin Swelling
- Tender Testes
- Abdominal Pain
- Pain
- Fever
- Pain In Testicle
- Groin Pain
- Feels Hot to Touch
- Pain In Urethra
- Painful Ejaculation
- Lower Abdominal Pain
“Plantar Fasciitis (Policeman’s heel): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Pictures”