Contents
- What is Balziva?
- Balzivas’ active ingredients composition: molecular formula, weight, IUPAC name, drug class
- Clinical pharmacology of Balziva
- What are the indications and usage of Balziva?
- Who should not use Balziva?
- What precautions should one take while using Balziva?
- Can Balziva be given in pregnancy?
- Can Balziva be given to nursing mothers?
- What are the side effects of the Balziva?
- Can Balziva be taken with tranexamic acid?
- Can Balziva be taken with warfarin?
- Can Balziva be taken with lamotrigine?
- How to manage the co-administration of Balziva and lamotrigine?
- Can Balziva be taken with pehnobarbital?
- How to manage the combination therapy (Balziva and Phenobarbital) if necessary?
- What are some other drugs that can interact with Balziva?
- Can Balziva be taken with alcohol?
- Can Balziva be given with food?
- Can Balziva be given in case of abnormal vaginal bleeding?
- Can Balziva be given to a person suffering from hypertension?
What is Balziva?
Balziva 28 Day (norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP) provide a continuous regimen for oral contraception derived from 21 light peach tablets composed of norethindrone, USP and ethinyl estradiol, USP to be followed by 7 white tablets of inert ingredients.
Balzivas’ active ingredients composition: molecular formula, weight, IUPAC name, drug class
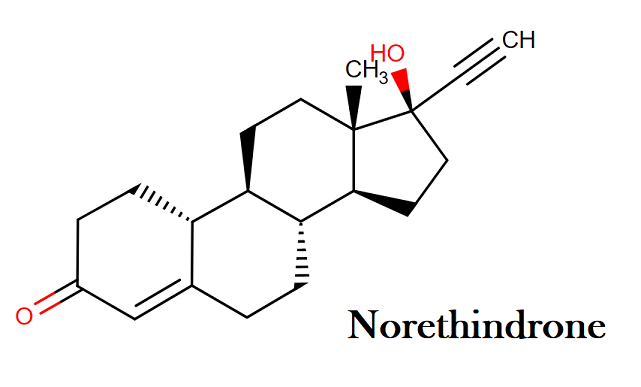
Norethindrone:
Molecular formula: C20H26O2
Molecular weight: 298.42 g/mol
IUPAC name: (1S,2R,10R,11S,14R,15S)-14-ethynyl-14-hydroxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadec-6-en-5-one
Molecular structure:
Drug class: This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as estrogens and derivatives. These are steroids with a structure containing a 3-hydroxylated estrane.
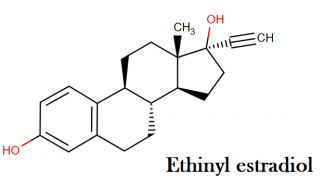
Ethinyl estradiol:
Molecular formula: C20H24O2
Molecular weight: 296.40 g/mol
IUPAC name: (1S,10R,11S,14R,15S)-14-ethynyl-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadeca-2(7),3,5-triene-5,14-diol
Molecular structure:
Drug class: This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as estrogens and derivatives. These are steroids with a structure containing a 3-hydroxylated estrane.
Clinical pharmacology of Balziva
These are oral contraceptives that act by suppressing the gonadotropins thereby inhibit the ovulation. It also makes changes in the cervical mucus and makes it thicker which make it difficult for sperm to enter into the uterus. Another mechanism of this contraceptive combination includes changes in the endometrium that reduce the likelihood of the implantation.
What are the indications and usage of Balziva?
Oral contraceptives are indicated for the prevention of pregnancy in women who elect to use this product as a method of contraception. Oral contraceptive in comparison to other methods of contraception is highly effective. The efficacy of the oral contraceptives depends upon the reliability with which they are used. The lower failure rates in the contraception can be achieved by the correct and consistent use.
Who should not use Balziva?
Oral contraceptives should not be used in women who currently have the following conditions:
- Thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- A past history of deep vein thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- Cerebrovascular or coronary artery disease
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast
- Carcinoma of the endometrium or other known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
- Cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice with prior pill use
- Hepatic adenomas or carcinomas
- Known or suspected pregnancy
- Are receiving Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for ALT elevations
What precautions should one take while using Balziva?
Balziva is a contraceptive and one can use this medication while keeping few very important things in her mind, which are as follows:
- Before using this product you must understand the fact that this product does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS-a fatal disease) or any other type of STDs (sexually transmitted diseases).
- Having an annual medical history and physical examination is a good medical practice for every woman who is using oral contraceptives. However, a physical examination may be deferred until after initiation of oral contraceptives if requested by the woman and judged appropriate by the clinician. The special reference should be given to blood pressure, breast, abdomen, and pelvic organs (that must include cervical cytology) in the physical examination. Appropriate measures should be taken in case of undiagnosed, persistent or irregular abnormal vaginal bleeding in order to rule out any malignancy. Proper monitoring should be done of a woman with family history of breast cancer or even who have breast nodules.
- Some progestogens (present in oral contraceptives) can increase the LDL (low-density lipoproteins) levels, therefore if a woman, who is already being treated for hyperlipidemias and opt for oral contraceptives, should be monitored and followed closely because oral contraceptives can render the control of hyperlipidemias more difficult.
- The oral contraceptives should be stopped in case a woman develops jaundice because in a patient with impaired liver function (in jaundice), can poorly metabolize such steroid hormones.
- Fluid retention can also cause the oral contraceptives. One should such medications with extra caution and only with careful monitoring of fluid retention can aggravate some other conditions.
- Women taking oral contraceptive should stop the medication in case they are becoming more significantly depressed. Such women can opt for some other method of contraception in order to rule if the symptoms of depression are drug-related. One should observe a patient with a history of depression carefully and should stop the drug if the depression recurs to a serious extent.
- Contact lens wearers who develop visual changes or changes in lens tolerance should be assessed by an ophthalmologist.
Can Balziva be given in pregnancy?
The use of Balziva or any other oral contraceptive is contraindicated when pregnancy occurs. Balziva comes under USFDA pregnancy category X. which states that one should continue the use of this medication if pregnancy is confirmed.
One should avoid administration in order to induce withdrawal bleeding as a test for pregnancy. You should also avoid administration of this medication during pregnancy as it can cause threatened or habitual abortion.
Can Balziva be given to nursing mothers?
Few adverse effects such as jaundice and breast enlargement have been noticed in the child when Balziva is taken by the mother because small amounts of oral contraceptives steroids have been identified in the milk. Oral contraceptives can also decrease the quantity and quality of breast milk when given in postpartum period as it can interfere with the lactation.
A woman should not use oral contraceptive or should consider using other methods of contraception until she has completely weaned her child. Several cases of oral contraceptive failure have been reported in association with vomiting or diarrhea, however, a cause and effect relationship has not been clearly established.
If a significant gastrointestinal disturbance occurs in any woman receiving contraceptive steroids, the use of a backup method of contraception for the remainder of that cycle is recommended.
What are the side effects of the Balziva?
Every medication has some side effects and Balziva is no different. It can also cause some side effects, few of them could be serious and you should see medical help immediately in such conditions. Few side effects that Balziva can cause are:
- When you are on these contraceptives pills, you may notice some irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting can also occur. It could be a minor staining between your menstrual cycles to breakthrough bleeding like the normal flow in your periods. During first few months of use of these contraceptives, you can see irregular bleeding but it may also occur after you been on such pills for some time. You should not worry about such kind of vaginal bleeding as it is temporary and it does not indicate any serious problem. You should take your contraceptive medications on time. Contact your gynecologist, if you see frequent and heavy bleeding which lasts for more than a few days.
- Balziva can cause gastrointestinal side effects which could be unpleasant such as nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, bloating or change in appetite or eating habits.
- You should contact your doctor if you notice a change in your vision or an inability to wear your lenses (in case you wear lenses).
- Oral contraceptives such as Balziva can also cause edema also called as fluid retention. You may notice swelling of fingers, ankles or may notice a sudden rise in your blood pressure. You should contact your doctor in case of fluid retention.
- A spotty darkening on the face (known as Melasma) is can also occur as side effects of Oral contraceptives such as Balziva.
- Balziva and other oral contraceptives can cause many other side effects such as a change in appetite, headache, nervousness, depression, dizziness, loss of scalp hair, rash, and vaginal infections.
You should seek medical help if any of these side effects start bothering you or even if they create disturbance in your daily routine.
Can Balziva be taken with tranexamic acid?
No, Balziva should never be administered with tranexamic acid; even the concurrent administration of both the medications is highly contraindicated. There is no sufficient and proved clinical data is given on the use of tranexamic acid along with hormonal contraceptives.
The co-administration of both is contraindicated because tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic agent, the use of tranexamic acid along with Balziva or other oral contraceptives can enhance the risk of thrombotic events such as thromboembolism as well as arterial thromboses (for example – stroke, myocardial infarction).
In women aging 35 or more or even those who are smokers or obese, the risk is pretty higher. When clinical trials are taken for safety and efficacy of tranexamic acid in the treatment of menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding), the women who are using hormonal contraception are excluded from the study.
However, there have been postmarketing reports of venous and arterial thrombotic events in women who have used tranexamic acid during treatment with combination hormonal contraceptives.
The use of tranexamic acid for the treatment of menorrhagia in the women receiving oral contraceptives is strictly contraindicated because of potential risk of thrombosis.
If a patient experience the severe signs and symptoms of blood clots (like chest pain, shortness of breath, hemoptysis, hematuria, sudden loss of vision, and pain, redness or swelling in an extremity), they should consider medical help immediately in order to prevent serious consequences that may occur after concurrent administration of Balziva and Tranexamic acid.
Can Balziva be taken with warfarin?
One should generally avoid the concurrent administration of Balziva and warfarin. The therapeutic effects of the oral anticoagulants such as warfarin can be diminished when taken along with estrogen-containing drugs.
The plasma levels of clotting factors such as fibrinogen, prothrombin and factor VII and VIII can be increased by estrogens in a dose-dependent manner that can result in increased risk of thromboembolism, stroke, or myocardial infarction. Smoking or lack of exercise can increase the risk.
In patients receiving anticoagulant therapy (such as warfarin) should avoid the use of estrogen-containing drugs. They should avoid the concurrent administration of these drugs until benefits are anticipated to outweigh the risks.
If the combination is prescribed, the close and clinical monitoring is recommended. Patients should be advised to promptly notify their physician if they experience potential signs and symptoms of blood clots such as chest pain, shortness of breath, sudden loss of vision, and pain, redness or swelling in an extremity.
Can Balziva be taken with lamotrigine?
One should not take Balziva and lamotrigine altogether because concurrent administration of lamotrigine with estrogens or progestins may decrease the plasma concentrations and pharmacologic effects of lamotrigine due to induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation.
As per one study of a group of investigators cited seven suspected cases of this interaction in women treated with oral contraceptives that contained either ethinyl estradiol in combination with desogestrel or norethindrone or norethindrone alone.
It showed that the contraceptives reduced plasma levels of lamotrigine by 41% to 64%, and a deterioration in seizure control was observed several days to two months after initiation of contraceptive use, necessitating an increase in lamotrigine dosage or discontinuation of the contraceptive. The dose reduction was also required in some cases where lamotrigine toxicity was reported due to contraceptive discontinuation.
A pharmacokinetic study also reported similar reductions in lamotrigine plasma levels in patients on combination oral contraceptives, with lamotrigine clearance 2.5 times greater than in controls.
There are many other facts that support the interaction are changes in hormone levels are known to influence the pharmacokinetics of glucuronidated drugs in humans, and elimination of lamotrigine is significantly increased during pregnancy.
However, a population pharmacokinetics study in patients newly diagnosed with epilepsy and receiving oral lamotrigine monotherapy for up to 48 weeks found no significant effect of the oral contraceptive use or dose on the oral clearance of lamotrigine.
Lamotrigine also has been shown to have little or no effect on the pharmacokinetics of contraceptive hormones, although measurement of serum FSH, LH, and estradiol has indicated some loss of suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis. The clinical significance is unknown. Measurement of serum progesterone indicated no hormonal evidence of ovulation.
How to manage the co-administration of Balziva and lamotrigine?
When estrogen or progestin medications are added or withdrawn from the therapy, the pharmacologic response and plasma levels of lamotrigine should be monitored closely. The detailed dosage recommendations should be considered before manufacturer’s labeling.
If a patients suffer from loss of seizure control or lamotrigine toxicity (such as ataxia, nystagmus, increased seizures, irregular heartbeat, and changes in mental status), they should report to the doctor immediately.
In patients receiving oral contraceptives, gradual transient increases in lamotrigine levels will occur during the pill-free week for women not also taking an enzyme-inducing drug (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, primidone, rifampin).
The increase in lamotrigine levels will be greater if the dose of lamotrigine is increased in the few days before or during the pill-free week. Although diminished contraceptive efficacy has not been reported, the possibility should be considered. Patients should be instructed to promptly report changes in their menstrual pattern.
Can Balziva be taken with pehnobarbital?
Balziva should not be administered along with barbiturates or Phenobarbital, the use of this combination is generally not recommended. The additional contraception is recommended. As there are certain anticonvulsant medications such as carbamazepine, eslicarbazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and primidone that decrease the efficacy of oral contraceptive hormones.
The women who received oral contraceptives along with anticonvulsant reported to suffered from menstrual abnormalities like breakthrough bleeding, amenorrhea, irregular menses and an unintended pregnancy.
Sometimes the menstrual abnormalities are observed as higher as 65%. Some anticonvulsants can reduce plasma concentration of active hormones and also can enhance the clearance of the contraceptive hormones due to induction of enzymatic activity.
Pharmacokinetic studies have found that normally recommended dosages of anticonvulsants ( such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin) can individually reduce ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel systemic exposure (AUC) by a third or more.
How to manage the combination therapy (Balziva and Phenobarbital) if necessary?
Women should be advised to use concomitant therapy with enzyme-inducing anticonvulsants and they should also be advised of breakthrough bleeding and unintended pregnancy that may occur while using this combination. After short-term (i.e. 2 weeks) or long-term (>4 weeks) anticonvulsant therapy, alternative methods of contraception should be used. If a combination oral contraceptive pill is used, a regimen containing at least 50 mcg of ethinyl estradiol per day or equivalent should be considered.
Although breakthrough bleeding is not necessarily indicative of low ethinylestradiol serum levels or increased risk of ovulation, some clinicians suggest that women who experience breakthrough bleeding during enzyme-inducing therapy may be prescribed an increased dose of ethinyl estradiol above 50 mcg daily by combining more than one formulation of the contraceptive pill if necessary. A nonhormonal emergency contraceptive is preferable for emergency contraception in patients who have used a hepatic enzyme inducer in the past 4 weeks.
If this is not possible, some authorities recommend that the usual dose of levonorgestrel (1.5 mg) should be doubled to 3 mg and taken as a single dose as soon as possible (within 72 hours of unprotected sexual intercourse). However, there are no data on efficacy, compliance, or side effects of this regimen.
For women with the etonogestrel subdermal implant, the addition of a barrier method is recommended during concomitant use and for 28 days after discontinuation of hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs. It is recommended to remove the implant and to prescribe a nonhormonal method in women who require long-term treatment with hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs.
No precautions or recommendations are available for women using hormone-releasing intrauterine systems, but a significant interaction with these systems is thought to be unlikely due to their local action. Injectables progestin-only contraceptives are also thought to be unaffected by enzyme-inducing drugs.
What are some other drugs that can interact with Balziva?
There are many drugs that can interact if take concomitantly with Balziva or other oral contraceptives. The administration of such drugs along with Balziva should be avoided. The drugs that can interact with oral contraceptives or Balziva are
Rifampin: The concurrent administration of rifampin along with Balziva can cause breakthrough bleeding and menstrual irregularities. The efficacy of rifampin also been reduced when administered along with oral contraceptives or Balziva.
HCV combination therapy: One should not use Balziva with HCV combinations (containing ombitasvir / paritaprevir / ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir) as it has potential to elevate ALT levels.
Can Balziva be taken with alcohol?
In patients taking oral contraceptives, the central nervous system effects and levels of alcohol in blood may be increased. However, there is no sufficient data is reported and given reports are contradictory. The enzyme inhibition may be the mechanism behind it.
Can Balziva be given with food?
The bioavailability of estrogens can be increased with coadministration with grapefruit juice. The proposed mechanism is inhibition of the first-pass metabolism in the gut wall induced by certain compounds present in grapefruits.
The peak plasma concentration and AUC (area under the curve) of ethinyl estradiol can be increased by 37% when administered along with grapefruit as compared to herbal tea. However, the safety profile of the ethinyl estradiol is likely to get unaffected with the grapefruit juice.
Can Balziva be given in case of abnormal vaginal bleeding?
In patients suffering from abnormal and unknown vaginal bleeding, the use of estrogen is strictly contraindicated. Prolonged use of estrogen has been reported to be associated with dose-related risk of endometrial carcinoma.
The addition of progestin can offset the risk but may not be completely abolished. In order to rule out endometrial malignancy (if it is there), proper diagnostic tests should be done and then one should initiate estrogen therapy. If vaginal bleeding develops during estrogens therapy, similarly diagnostic tests should be done along with cessation of estrogen therapy.
Can Balziva be given to a person suffering from hypertension?
In patients with hypertension, the contraceptives and estrogen use can increase the risk of myocardial infarction and strokes. The blood pressure can get elevated and hypertension can attenuate with the use of estrogens (including progestogens). In patients receiving high doses of oral contraceptives, see high progestational activity, therefore, significant blood pressure elevation has been reported in such patients.
The duration of the therapy and patient’s age also contribute as a great factor in elevating the blood pressure. In patients with preexisting hypertension, therapy with estrogens should be administered with precaution.
The cardiovascular status and blood pressure of the patient should be noticed and estrogen therapy should be withdrawn as necessary. In patients of age, 35 or above or those who are hypertensive or even those who smoke should consider other options for contraception.
“How many times is it safe to take “Emergency contraception” Plan B?”
“How does the nexplanon (Birth control implant)prevent pregnancy?“