Contents
What is azithromycin used for?
Azithromycin is belong to the class of antibiotic medications that are principally used for the treatment of wide variety of bacterial infections and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Azithromycin is basically known as a broad spectrum semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic that plays a key role in the treatment bacterial infections such bronchitis, pneumonia, skin infections and infections of ear and throat.
Besides this Azithromycin is also also used to prevent or treat the disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection. Azithromycin (in form of ophthalmic solution) is used to treat bacterial conjunctivitis (a bacterial eye infection).
The drug is marketed under generic name Azithromycin and various brand names such as Azithrocin, Azyth and Zithromax. Pfizer company is chiefly liable for the manufacturing and marketing of Azithromycin. Inspire Pharmaceuticals marketed Azithromycin as an ophthalmic solution under the brand name AzaSite.
The drug is also prescribed for the treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis caused by H. Influenza, M. Catarrhalis or S, pneumonia. Sometime it is also used to treat the infection of H. pylori and Legionnaires’ disease (inflammatory lung infection caused by Legionella). It is also prescribed for the treatment of Whooping cough. Azithromycin is a derivatives of erythromycin and available as a dihydrate salt.
The drug Azithromycin is available in different forms such as tablet and oral suspension for oral administration and ophthalmic solution. Azithromycin tablets are available in two different dosages of 250 mg and 500 mg, oral suspensions are available in two different dosages of 100 mg/5ml and 200 mg/5ml and both forms contain azithromycin dihydrate as active ingredient.
Azithromycin ophthalmic solution (AzaSite®) is available as 1% sterile solution which is an off-white viscous liquid. The dose of Azithromycin varies depending upon the age and diseased state of the patient.Pharmaceutically, Azithromycin is a semi-synthetic aliphatic heteromonocyclic antimicrobial agent with a molecular formula C38H72N2O12.
The drug is a dihydrate salt of (2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-11-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-13-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
What is Artesunate?
Artesunate (AS) is a part of Artemisinin group of antimalarial drugs that is worldwide used to treat the most deadly human disease Malaria cause by apicomplexian parasite Plasmodium. It is water soluble semi-synthetic derivative of Artimisinin. The drug is on World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system.
The drug was originally derived from Chinese herb Artemisin anua and is highly effective blood schizonticidal agent against Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum malaria. The drug is primarily used to treat multidrug resistant malaria and was shown to be highly potent than quinine. The drug is now recommended by WHO to treat all cases of severe malaria.
Besides malaria, Artesunate is also used to treat Schistosoma haematobium infection. Besides this, Artesunate is also undergoing early research and testing for the treatment of cancer. It has been observed that Artesunate has anticancer effects in experimental models and yielded promising results for the treatment of colorectal cancer.
The drug is available under various generic names (i.e. Artesunate , Artesunic Acid, ARTS, and Artesunatum) and brand names such as Amonate , Dafra, Falcigo, Ansunate, Lincoln, Activa, Artex, Artfin, Falcigo Plus, Falcinez, Larinate-MF, Plasmotrim, Pyralfin-A and Traphasunat etc.
The drug is prepared from dihydroartemisinin (DHA) by treating it with succinic acid anhydride in basic medium. The drug is available in solution form for administration by intravenous or intramuscular injection. The drug is also used orally to treat less severe forms of malaria.
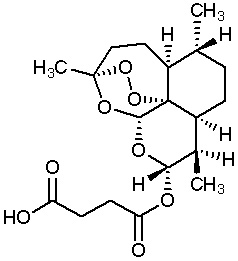
The drug is chemically known as (3R,5aS,6R,8aS,9R,10S,12R,12aR)-Decahydro-3,6,9-trimetyl-3,12-epoxy-12H-pyrano[4,3-j]-1,2-benzodioxepin-10-ol, hydrogen succinate. The empirical formula and molecular weight of Artesunate is C19H28O8 and 384 g/mol respectively. The conventional intravenous and intramuscular dose of Artesunate for treatment of severe malaria is 120 mg initially, followed by 60 mg at 4, 24 and 48 h.
How Azithromycin and Artesunate work?
Azithromycin is effective against gram positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, S. agalactiae, S. pneumonia and pyogenes, gram-negative bacteria such as Haemophilus ducreyi, H. influenza, Moraxella catarrhalis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae and some other bacteria like Chlamydophila pneumonia, Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma pneumonia. Azithromycin is a macrolides antibiotic (such as Erythromycin and Carbomycin) which acts by inhibiting the bacterial protein synthesis, quorum-sensing and formation of bacterial biofilm.
Macrolides primarily act through enhancing the dissociation of peptidyl-tRNA from ribosome, thus inhibiting transpeptidation and translocation step of protein synthesis (an intermediate steps of protein synthesis). It has been observed that Azithromycin binds with the 50S subunit of ribosome and interferes with polypeptide synthesis.
Therefore, it is predicted that stimulated dissociation of peptidyl-tRNA from ribosome is the major mechanism of action of Azithromycin. Azithromycin competes for [14C] erythromycin ribosome binding site, suggesting that it binds to the same receptor as erythromycin.
However, it does not affect the synthesis of nucleic acid. The Azithromycin accumulates at very higher concentration in cells, predominantly in phagocytes and therefore delivered effectively in high concentrations to sites of infection.
Artesunate is a representative of a sesquiterpene trioxane lactone class of antimalarial whose endoperoxide bridge is essential for antimalarial activity. Artesunate is a rapidly acting blood schizonticidal class of antimalarial that is highly effective against MDR strain of Plasmodium. Several theories has been put forward about the mode of action of Artesunate, however, the precise mechanism of action is still in debate.
It has been suggested that Artesunate possibly acts through alkylation of essential parasitic protein thereby inactivating them. In several studies it has been observed that Artesunate interacts with a large number of proteins thus suggesting that it acts in a promiscuous manner. Furthermore, Artesunate also binds and interacts with heme thus causing its alkylation and generation of reactive oxygen species.
One another theory suggests that Artesunate interacts with PfATP6 (SERCA – sarco/endoplasmic reticulum membrane calcium ATPase) and thereby inhibits its function. Besides this, Artesunate is shown to accumulate within neutral lipids and cause parasite membrane damage. In one recent study, Artesunate has been shown to inhibit the essential Plasmodium falciparum exported protein 1 (EXP1), a membrane glutathione S-transferase.
Can both Azithromycin and Artesunate be taken together in combination?
Yes, both the drugs can be taken together in combination. In fact, Azithromycin and Artesunate both are used for malaria treatment. To prevent the spread of drug resistance, the World Health organization (WHO) recommend Azithromycin (an antibiotic with antimalaria activity) as an optional combination drug for antimalarial therapy.
Clinical studies indicate the safety and efficacy of using the combination of the drugs in antimalarial treatment. Clinical studies indicate that co-administration of Azithromycin and Artesunate0 is safe, tolerable and proven to be an effective prophylactic against malaria in Africa. Azithromycin has significant antimalarial activity in vitro and with a course of treatment similar to that of Artesunate.
The combination of Azithromycin plus Artesunate (AZ+AS) is potentially attractive and effective antimalarial treatment in trials of adults in Asia. The usual combination doses of Azithromycin and Artesunate are 3 days of Azithromycin (750-1000 mg twice daily) plus Artesunate (100-200 mg twice daily).
Safety and precautions while taking Azithromycin: Artesunate combination
- Azithromycin and Artesunate may interact with other drugs. Therefore, care should be taken when you are taking any prescription or non-prescription medicines and herbal or vitamin supplements. It is advisable that you do not start, stop or change or take any medicine unless you have discussed with your doctor or professional consult.
- Do not use the medicine if you are hypersensitive or allergic (e.g., anaphylaxis) to Azithromycin or any other antibiotic such as Clarithromycin, Dirithromycin, Erythromycin and Ceftazidime or to similar antibiotics, such as Ceclor, Ceftin, Cefzil, Duricef, Keflex, Omnicef, Spectracef, Suprax, or any of the drug constituents.
- Do not share the medications with other persons having the similar kind of problems. Consult your doctor for more details.
- Azithromycin and Artesunate are generally not recommended to be taken in case of pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Caution should be exercised with the use of Azithromycin oral solution and Artesunate in diabetic patients.
- Azithromycin should not be used along with antacids as they bind to the Azithromycin and prevent the absorption in intestine.
- Use of Azithromycin and Artesunate is contradictory and may not be given to pregnant mothers, patients suffering from kidney dysfunction, and patients suffering from liver malfunction.
“Can Azithromycin be taken with Imipenem?”
“Combination Antibiotics as a Treatment for Chronic Chlamydia“