Contents
What is Omeprazole
Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor that acts through blocking gastric acid secretion. The drug was approved by FDA in September, 1989 and grouped in World Health Organization’s List of the essential medications required in a basic health system.
Chemically, Omeprazole is a pro drug, which means normally it is biologically inactive agent that produces a drug only upon metabolization inside the body.
The generic name of the drug is Omeprazole, Omeprazole/Sodium bicarbonate and is available under several brand names such as Prilosec, Omesec, Prilosec OTC, Zegerid, Zegerid OTC etc.
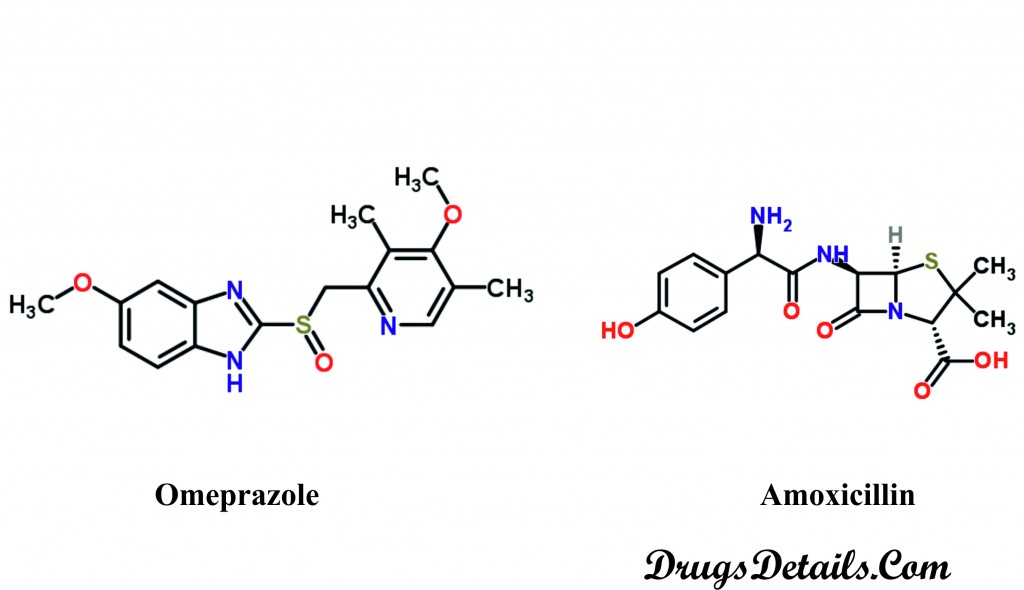
Chemically, Omeprazole belongs to a class of organic compounds known as sulfinylbenzimidazoles (containing a sulfinyl group attached at the position 2 of a benzimidazole moiety).
Prescription Omeprazole is available as a delayed-release capsule (10, 20 and 40 mg), and packets of delayed-release granules (20 and 40 mg) for suspension, whereas nonprescription (over-the-counter) Omeprazole comes in the form of a delayed-release capsule or tablet (20 mg) to be taken by mouth.
The dose of the drug depends upon the disease, age and weight. The active ingredient in the delayed-release capsule and delayed-release granule (oral suspension) are Omeprazole and Omeprazole magnesium respectively.
What is Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is a beta lactam class of antibiotic that is primarily used for the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections. Besides bacterial infections, the drug is also prescribed for skin and urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and strep throat.
The drug is commonly available under generic name Amoxicillin and marketed under the various brand names such as Amoxil, Tycil, Trimox, Amocla, Actimoxi, Moxatag, Larotid and Alphamox.
The drug was first available in 1972 and was listed on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines. Amoxicillin chemically belongs to the Penicillins class of drugs and characterized by the presence of penam ring.
The drug Amoxicillin is available in various forms such as capsule, tablets, oral solution and pediatric drops for oral uses. The recommended dose of Amoxicillin in adult is 500 mg thrice a day or 875 mg twice a day. However, the dose varies depending upon patient and diseased state.
How does Omeprazole and Amoxicillin work
The Omeprazole drug is a benzimidazole, which is a selective and irreversible proton pump inhibitor. The proton pumps are integral membrane proteins that are capable of moving protons across a biological membrane.
In stomach, proton pumps (such as hydrogen-potassium (H+/ K+) ATPase enzyme system) are present at the secretory surface of parietal cells in the stomach and involved in pronounced and long-lasting production of gastric acid or gastric juice.
The gastric acid is composed of hydrochloric acid (HCl), potassium chloride (KCl) and sodium chloride (NaCl). Omeprazole results in the suppression of gastric acid secretion by formation of a stable disulfide bond with the sulfhydryl group of the hydrogen-potassium (H+/ K+) ATPase enzyme system, thus inhibiting the final step in the acid production i.e., transport of hydrogen ions (via exchange with potassium ions) into the gastric lumen.
Due to its mode of action the Omeprazole is generally prescribed to be taken atleast one hour before meals. The drug (prescription) is prescribed either alone or in combination with other medications in therapy of acid-induced inflammation, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), stomach and duodenum ulcers, erosive esophagitis, Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (gastrin-producing tumour), and heartburn.
Similar to penicillin and other beta lactam class of drugs Amoxicillin acts against susceptible bacteria during the stage of active multiplication.
It acts on the bacteria through blocking or inhibiting the biosynthesis of cell wall mucopeptide (protein polysaccharide component of bacterial cell wall) during bacterial cell multiplication.
In bacterial cell wall Amoxicillin interacts with penicillin-binding protein 1A (PBP-1A) and inactivate it through acylation. PBP-1A enzyme is involved in crosslinking of two linear peptidoglycan strands or polymer chain.
Inactivation of PBP-1 results in complete loss of development of cross-link formation and inhibition of cell wall biosynthesis that leads to the death of the bacteria.
Amoxicillin is primarily used for the treatment of bacterial infections such as bronchitis, pneumonia, gonorrhoea etc. Besides, this the drug is also recommended to treat the infections of Salmonella and Chlamydia, Lyme disease, Streptococcal pharyngitis and Tonsillitis.
Can both Omeprazole and Amoxicillin be taken together in combination
Yes. Omeprazole can be taken in combination with Amoxicillin. Dual combination therapy of proton pump inhibitor Omeprazole with beta lactam antibiotic Amoxicillin has been widely used as an alternative to treat gastric ulcer and other diseases associated with Helicobacter pylori infection.
Omeprazole – Amoxicillin regimen is strongly recommended and widespread routine use for the treatment and prevention of reoccurrence of ulcers caused by H. pylori.
In dual therapy, Omeprazole inhibits transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen and suppressing gastric acid secretion, while Amoxicillin interrupts the synthesis of bacterial cell wall, thus cause weakening of the bacterial cell wall and cell lysis.
Amoxicillin show several advantages over other antibiotics such as high tolerability and digestibility, lack of resistance of H.pylori and potent activity and efficacy in eradicating H.pylori.
The dual therapy at a daily dose of Omeprazole (3×40=120 mg) along with Amoxicillin (750×3=1050 mg) for 14 days showed eradication rate of H. pylori over 90%. Omeprazole and Amoxicillin therapy is almost comparable to triple therapy of Omeprazole in combination with two antibiotics.
Clinical research and current scenario of Omeprazole –Amoxicillin dual therapy
- In controlled human trials Amoxicillin at a dose of 15.6 mg/kg/day (Omeprazole-Amoxicillin combined therapy) showed favourable therapeutic effects to the eradication of pylori in gastrectomized patients who were H. pylori positive.
- It has been observed that dual treatment with proton pump inhibitor Omeprazole plus Amoxicillin could cure pylori infection even after the failure to cure H. pylori infection by a usual proton pump inhibitor-based triple therapy in patients with the wt/wt homozygous extensive metabolizer genotype of CYP2C19.
- Double-blind, multicenter evaluation of Omeprazole-Amoxicillin dual therapy have revealed the cure of Helicobacter pylori infection in 67% of the patients. Besides Omeprazole, this study also revealed significant improvement in patients when Lansaprazole replace Omeprazole.
- Similarly, another double-blind trial of Omeprazole and Amoxicillin combination has revealed this therapy as a promising combination to cure Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcers. It has been noted that dual therapy at a dose of 120 mg Omeprazole daily and 25 g Amoxicillin daily showed H. pylori cure rate of around 90% and it is one of the best tolerated and most effective treatment regimens.
- Currently, Amoxicillin is also used as triple therapy forHelicobacter pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease in combination with Clarithromycin and Lansoprazole.
Safety and precautions while taking Omeprazole-Amoxicillin combination
- The usual dosing of the drug in combination may vary depending upon the efficiency and side effects of the drug in a particular individual. Therefore, it is advisable to discuss all the health related issues with your doctor before taking Omeprazole in combination with Amoxicillin.
- Omeprazole tablets, delayed release capsule or oral suspension are usually recommended at a dose of 20mg once, twice, or thrice a day before a meal.
- The Amoxicillin tablets are usually prescribed before or after food and time duration between the drug use should be 12 hours (twice daily use) to 8 hours (thrice daily use).
- Omeprazole and Amoxicillin can be taken together at the same time to treat an ulcer associated with pylori infection. However, the dose should be adjusted by professional healthcare, if needed.
- Do not use the medicine if you are hypersensitive or allergic (e.g., anaphylaxis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome) to Amoxicillin or any other penicillin antibiotic (such as Ampicillin, Dicloxacillin and Oxacillin) or substituted benzimidazoles or to any ingredient of the drug formulation.
- The Omeprazole and Amoxicillin may interact with other drugs. Therefore, care should be taken when you are taking any prescription or non-prescription medicines and herbal or vitamin supplements. It is advisable that you do not start, stop or change or take any medicine unless you have discussed with your doctor or professional consult.
- It has been observed that Omeprazole may cause a serious type of allergic reaction when used in combination with antibiotics. In case of allergic hypersensitive reactions such as itching, trouble breathing or swallowing, or any swelling of your hands, face, or mouth, it is advisable to call your doctor right away.
- Before taking Omeprazole-Amoxicillin, tell your doctor about your medical history if you have kidney disease, liver disease, asthma, liver disease, mononucleosis (also called “mono”), a bleeding or blood clotting disorder, or any type of allergy, hay fever or hives. Do not stop taking Amoxicillin until you do not finish the prescription. If you do not follow the prescription or stop taking amoxicillin too early, it may lead to the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
- The use of Omeprazole and Amoxicillin may sometimes increase the risk of Clostridium difficile-associateddiarrhea (CDAD). If you experience symptom of diarrhea that does not seem to improve seek immediate medical attention.
- Antibiotic therapy of Amoxicillin in the absence of suspected bacterial infection and discontinuation of therapy before time or too early increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
- It has been observed that colitis is occasionally caused by taking antibiotics (antibiotic associated colitis). Antibiotic therapy usually associated with reduced gut microbial flora, permits overgrowth of some of the harmful bacteria over normal gut flora. Clostridium difficile is one of such bacterial species that flourish well under antibiotic therapy. Its toxin is supposed to be a primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. Thus, antibiotic therapy with Amoxicillin and other broad-spectrum antibiotics agents should be managed cautiously in patients with a history of gastrointestinal diseases, particularly colitis.
“Can Ketorolac be taken with Tylenol?“
“Difference between omeprazole and esomeprazole“