Contents
- What is Dilantin Kapseals?
- Phenytoin sodium molecular structure, IUAPC name, molecular structure weight and drug class
- Dilantin mechanism of action
- How long Dilantin stays in your body?
- What are the indications and usage of Dilantin?
- What happens if I miss a dose of Dilantin Kapseals?
- What happens if I overdose Dilantin Kapseals?
- What are some other side effects of Dilantin Kapseals?
- What is the dosage of Dilantin Kapseals?
- What are the dosage forms and strengths of Dilantin Kapseals?
- What are the contraindications of Dilantin Kapseals?
- Is Dilantin Kapseals safe in pregnancy?
- How should Dilantin Kapseals be taken?
- Can food interact with Dilantin Kapseals?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be given to a patient with blood dyscrasias?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be given to a patient with liver disease?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be given to patients with porphyria?
- Can Dialntin Kapseals be given in patient with renal dysfunction?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be given to the patient with cardiotoxicity?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be given in patients with suicidal tendency?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be taken with antacids (cimetidine)?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be taken with ethinyl estradiol?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be taken with fentanyl?
- Can Dilantin Kapseals be taken with warfarin?
- When should I see a doctor?
- How do I store and/or throw out Dilantin Kapseals?
What is Dilantin Kapseals?
Dilantin kapseals is the brand name of the extended release phenytoin capsules. Phenytoin is an anti-epileptic drug also known as an anticonvulsant. It helps in controlling the seizures by slowing down the impulses in the brain. Phenytoin does not treat all type of seizures and convulsions and your doctor can determine if it is the right medicine for you.
Each Dilantin— Extended Phenytoin Sodium Capsule, USP—contains 30 mg phenytoin sodium, USP. Dilantin in vivo performance is characterized by a slow and extended rate of absorption with peak blood concentrations expected in 4 to 12 hours as contrasted to Prompt Phenytoin Sodium Capsules, USP with a rapid rate of absorption with peak blood concentration expected in 1½ to 3 hours.
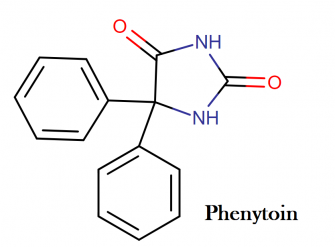
Phenytoin sodium molecular structure, IUAPC name, molecular structure weight and drug class
Molecular structure:
IUPAC name: 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione
Molecular weight: 252.268 g/mol
Chemical formula: C15H12N2O2
Drug Class:
This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenylhydantoins. These are heterocyclic aromatic compounds containing an imiazolidinedione moiety substituted by a phenyl group.
Dilantin mechanism of action
Phenytoin limits the spread of seizure activity and reducing the seizure propagation by acting on sodium channels on the neuronal membrane. Phenytoin tends to stabilize the threshold against hyper-excitability caused by excessive stimulation of reducing membrane sodium gradient, by promoting sodium efflux from neurons.
This includes the reduction of post-tetanic potentiation at synapses. Loss of post-tetanic potentiation prevents cortical seizure foci from detonating adjacent cortical areas.
How long Dilantin stays in your body?
The elimination half-life of Dilantin is 25 hours to 40 hours approximately and as a medicine takes around 5 times more to get eliminated completely from our system, Dilantin eliminated in around 4 to 5 days completely.
What are the indications and usage of Dilantin?
Dilantin is indicated for the treatment of:
- Tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures
- Psychomotor (temporal lobe) seizures
- Prevention and treatment of seizures occurring during or following neurosurgery.
What happens if I miss a dose of Dilantin Kapseals?
You should take the medicine as soon as you remember the missed dose. Never double up the dose in order to make the previous dose. If it is time for your next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose Dilantin Kapseals?
An overdose of phenytoin is so dangerous that it can prove fatal. Overdose symptoms may include twitching eye movements, slurred speech, loss of balance, tremor, muscle stiffness or weakness, nausea, vomiting, feeling light-headed, fainting, and slow or shallow breathing. Therefore seek emergency medical attention in case of the overdose of phenytoin in order to prevent the life-threatening risk.
What are some other side effects of Dilantin Kapseals?
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away:
- Dizziness
- Feeling sleepy
- Headache
- Feeling nervous and excitable
- Not able to sleep
- Hard stools (constipation)
- Upset stomach or throwing up
- Change in taste
These are not all of the side effects that may occur. If you have questions about side effects, call your doctor. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
What is the dosage of Dilantin Kapseals?
Divided daily dosage:
100 mg Dilantin as extended phenytoin sodium capsule is recommended a starting dose for adult patients who have not received any treatment previously. It should be taken by mouth three times daily.
The dose of Dilantin can be adjusted up to two capsules three times a day which depends upon the conditions of the patient or to that suit to the patient’s requirements. The satisfactory maintenance dosage of Dilantin can be capsule three to four times daily, mainly for adults.
Once a day dosage:
If 100 mg dose of Dilantin (extended phenytoin sodium capsules) is given three times daily, it is beneficial in establishing the seizure control. A higher dose of 300 mg, which should be given once a day, can be considered.
Studies comparing divided doses of 300 mg with a single daily dose of this quantity indicated absorption, peak serum levels, biologic half-life, the difference between peak and minimum values, and urinary recovery were equivalent.
Once a day dosage is given to the patients who need this amount of the drug daily, and also it offers a convenience to the individual patient or to nursing personnel for institutionalized patients. A major problem in motivating noncompliant patients may also be lessened when the patient can take this drug once a day.
However, one should make the patient understand that the dose of this medication should not be missed, inadvertently. Only extended phenytoin sodium capsules (Dilantin) are recommended for once a day dosing.
Loading dose:
The loading dose is a higher dose that is given to a patient at the beginning of the treatment, before dripping down to a maintenance dose. In some adults, who require rapid steady-state serum levels, and also where intravenous administration is not desirable, some authorities advocated the oral loading dose of phenytoin is useful in such patients.
The loading dose regimen should be reserved for patients in a clinic where phenytoin serum levels can be closely monitored. The oral loading dose regimen should not be adopted in patients with kidney or liver diseases.
One gram of phenytoin capsules is divided into three doses (400 mg, 300mg, 300 mg) initially, and should be administered at two hour interval. After 24 hours of the loading dose, the normal maintenance dose can be instituted, with frequent serum level determinations.
What are the dosage forms and strengths of Dilantin Kapseals?
Dilantin extended phenytoin sodium capsules are available as:
- 30 mg: size 4 hemispherical Coni-Snap capsule with a white opaque body and pale pink opaque cap containing a white powder. The capsule is imprinted with black rectified radial print, “PD” on cap and “Dilantin 30 mg” on the body.
- 100 mg: hard, filled No. 3 capsules with a white, opaque body and a medium orange cap containing a white powder. The capsule is imprinted with black rectified radial print, “PD” on cap and “Dilantin 100 mg” on the body.
What are the contraindications of Dilantin Kapseals?
Dilantin is contraindicated in patients who are:
- Hypersensitive to phenytoin or any of its inactive ingredients, or any other hydantoins.
- History of acute hepatotoxicity attributable to phenytoin.
- Co-administration with delavirdine because of the potential for the loss of virologic response and possible resistance to delavirdine or to the class of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Is Dilantin Kapseals safe in pregnancy?
Dilantin when given in pregnant animals resulted in increased incidences of fetal malformations (teratogenicity) and other developmental toxicity such as including embryo fetal death, growth impairment, and behavioral abnormalities in different animal species at clinical doses. There are no controlled data in human pregnancy.
The use of active metabolite of phenytoin is associated with an increased risk of congenital abnormalities in an epileptic woman during pregnancy. When compared with the incidence of malformation for neonates in general population with anti-seizure medication is 10% which is approximately two to three folds in epileptic population as compared to general population.
The congenital malformations and development deformities can be increased with prenatal exposure of Dilantin. Increased frequencies of orofacial clefts and cardiac defects, dysmorphic facial features, nail and digit hypoplasia and growth abnormalities including microcephaly and mental deficiency have been reported in neonates born to epileptic women who took Dilantin or in combination with other drugs used for the treatment of epilepsy during pregnancy.
Dilantin drug comes under pregnancy category: D, US FDA pregnancy category D, if this drug is used during pregnancy, the patient should be informed about the potential harms to the fetus. An increase in seizure frequency may occur during pregnancy because of altered phenytoin pharmacokinetics.
In the management of pregnant women as a guide to appropriate adjustment of dosage, the periodic measurement of plasma phenytoin concentrations can be valuable. Original dosage can be restored postpartum. Neonatal coagulation defects have been reported postpartum which can reversible with vitamin K administration.
How should Dilantin Kapseals be taken?
Use this medicine as ordered by your doctor. Read all information given to you. Follow all instructions closely.
- Take these Dilantin kapseals at the same time of the day.
- You should not miss a dose of this medication in order to gain the most benefit.
- You should keep taking this medication even if you feel well, and you should not stop it without doctor’s consent.
- Antacids are the medication that is given to reduce the acid in the stomach, you should avoid taking Dilantin along with antacids and you should also consult with your doctor before taking such medication together.
- Dilantin contains phenytoin which interacts with food also, therefore if it is given through a feeding tube, therefore stop feeding tube for 2 hours before giving this medication. One can restart feeding after 2 hours of Dilantin.
- Do not break or crush Dilantin Kapseals, swallow the whole kapseal.
- Many other drugs interact with this medication, the efficacy of Dilantin kapseals can be lowered or even side effects of this medication can be increased when taken with other medications. The side effects of this drug when interacting with other drugs can be life-threatening or severe. Therefore always let your doctor knows about all other medications that you are taking, which may include OTC drugs, vitamins, herbal products etc.
- Talk with your doctor before you drink alcohol or use other drugs and natural products that slow your actions.
- Certain lab tests may also be affected by this drug, therefore, let your lab worker know that you are already taking this medication.
- If you have a seizure problem, you should follow the laws about driving.
- You should see a dentist often and should take care of your teeth.
- Talk to your doctor before switching to any other brand of this medication, sometimes inactive ingredient that may be present in other brands of same medicine can interact and can cause side-effects.
- Let your doctor know before stopping this medication because of you may be at higher risk of developing seizures again. You should stop this medication gradually and that is also under proper observation of a doctor.
Can food interact with Dilantin Kapseals?
When phenytoin (Dilantin) taken along with food, it can cause moderate interaction. A nutritionally complete feed can reduce the phenytoin level when the suspension is given with it. This could lead to a loss of seizure control. The feeding should be done two hours before or after the phenytoin dose. You can also give the diluted phenytoin suspension (diluted in water), and after administration, you should flush the tube with water.
By this way, the absorption of medication became easier for the body. One should check the phenytoin levels before starting and after enteral feedings. The effects of phenytoin may also alter when using this medication with food.
There are many symptoms of toxicity or worsening of seizures can occur, therefore you should contact the doctor immediately, such symptoms include twitching eye movements, slurred speech, loss of balance, tremor, muscle stiffness or weakness, nausea, vomiting, feeling light-headed, fainting, and slow or shallow breathing.
You may need a dose adjustment or special test to use these medications safely if your doctor does prescribe these medications together. You should always tell your doctor about other medications that you use including vitamins and herbs. Also before making any changes in therapy, talk to your doctor.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be given to a patient with blood dyscrasias?
Dilantin in a patient with blood dyscrasias can cause major interaction. Use of hydantoin anticonvulsants is associated with hematologic toxicities, thrombocytopenia, leucopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia and rarely hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia and pure red cell aplasia.
In patients with coexisting blood dyscrasias or bone marrow depression, the phenytoin or hydantoin anticonvulsants therapy should be used with extra precautions. Before initiating the therapy, one should perform complete blood counts, including platelets and it should be done regularly after several months.
For the anticonvulsants like mephenytoin, the blood count should be counted after 2 weeks on a low dosage as per manufacturer’s instructions. The blood count should be repeated after another 2 weeks when a full dosage is reached, then monthly for a first year and every 3 months thereafter. Marked depression of blood counts may be indication for withdrawal of hydantoin therapy.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be given to a patient with liver disease?
Hydantoin anticonvulsants are primarily metabolized by the liver. In patients with, liver disease, both metabolic activity, and plasma protein binding may be altered significantly that results in elevated drug levels and increased risk of toxicity. In patients with impaired hepatic function, hydantoin anticonvulsants therapy should be used with caution.
Reduced dosages and slower titration may be necessary. The use of hydantoin is associated with hepatotoxicity, therefore periodic monitoring of liver function is recommended. If the evidence of liver damage is observed, the hydantoin therapy should not be continued and also should not be re-administered. The use of hydantoin is also associated with risk of hepatic failure and death.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be given to patients with porphyria?
When hydantoins including Dilantin taken by the patients suffering from porphyria, it can cause potential hazards to them, however, the exacerbation of porphyria is rarely noticed with the use of phenytoin.
The phenytoin therapy should be used with caution in a patient with porphyria. Due to the structural similarities of ethotoin and mephenytoin (other hydantoin anticonvulsants), the precaution should be observed while using these agents also.
Can Dialntin Kapseals be given in patient with renal dysfunction?
In patients with renal impairment, the plasma protein binding of phenytoin may be significantly decreased, which later results in increased free drug concentrations and elevated risk of toxicity. This effect is proportional to the degree of renal impairment and qualitative differences in serum albumin as well as qualitative difference in the ability to bind phenytoin.
In patients with impaired renal function, the phenytoin therapy should be used cautiously. The dosing of phenytoin should be considered in such patients because the therapeutic and toxic plasma phenytoin levels may be lower than normal patients. Alternatively, the unbound phenytoin concentration is recommended to monitor.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be given to the patient with cardiotoxicity?
In patients with sinus bradycardia, sino-atrial block, 3rd degree AV block, and, Adam-stokes syndrome, the intravenous administration of phenytoin or fosphenytoin (prodrug of phenytoin) is contraindicated. In elderly patients, the parenteral phenytoin is associated with severe cardiotoxic reactions related to depression of atrial and ventricular conduction and ventricular fibrillation.
When the drug was administered too rapidly, hypotension and cardiovascular collapse have also been reported. Therefore extra caution should be taken in patients with hypotension or in patients with severe myocardial insufficiency when Dilantin therapy is given via intravenous route in elderly patients. The dose should be adjusted as per patient’s cardiovascular status and rate of injection should not pass the recommendations given by the manufacturer.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be given in patients with suicidal tendency?
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior is observed to be increased by antiepileptic drugs. In patients with depression or other psychiatric disorders, therapy with antiepileptic drugs should be used cautiously.
Epilepsy and many other conditions for which antiepileptic drugs are given associated with morbidity and mortality and also it increases the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior, therefore, the patient should be carefully assessed against the risk of untreated illness.
The emergence or worsening of signs and symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts or behavior can occur in such patients, therefore, patients, caregivers, and families should be altered for the same.
The treatment withdrawal or dosage reduction should be considered for clinically significant or persistent symptoms that may occur. The treatment should be discontinued in case of a patient have symptoms of suicidal ideation or behavior.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be taken with antacids (cimetidine)?
One should generally avoid the concurrent administration of Dilantin kapseals and antacids such as cimetidine (a known acid reducer). The plasma concentration of phenytoin can be increased with concurrent administration of phenytoin and cimetidine. This occurs due to inhibition of the isoenzymes responsible for the metabolic clearance of phenytoin by cimetidine.
Cimetidine in dosage 1000 to 1200 mg/day can increase the phenytoin plasma levels that may be ranging from 13% to 300% and also phenytoin toxicity developing in same. There have also been rare reports of severe and life-threatening thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, and cutaneous reactions including toxic epidermal necrolysis in patients receiving phenytoin and cimetidine, with or without glucocorticoids.
The relativity of these events is pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic remain unknown. The phenytoin serum levels do not significantly affect with cimetidine at a dose of 400 mg/day for two weeks. Seizure frequency has not been reported to be increased at this dose of cimetidine when taken with long-term phenytoin therapy.
In patients who are under treatment of phenytoin therapy, the use of cimetidine should be avoided. One should opt for safer alternatives such as other H2-receptor antagonists or proton pump inhibitors. These agents (including omeprazole) are safer alternatives because they do not interact with phenytoin in pharmacokinetic studies, and very rare interaction of these drugs have been noted till now.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be taken with ethinyl estradiol?
One should generally avoid the concurrent administration of phenytoin and ethinyl estradiol. An additional contraception is usually recommended. The coadministration of ethinyl estradiol with certain anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, eslicarbazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and primidone) can reduce the efficacy of contraceptive hormones.
The women who receive oral contraceptives with anticonvulsants can suffer from menstrual abnormalities including breakthrough bleeding, amenorrhea, irregular menses and also unintended pregnancy. There is around 65% chances of menstrual irregularities associated with this combination have been reported.
Some anticonvulsants can accelerate the clearance of contraceptive hormones as well as decrease the plasma concentrations of unbound (active) hormones due to induction of hepatic CYP450 enzymatic activity and hormone-binding globulin capacity.
When Dilantin is given with concomitant therapy with enzyme-inducing anticonvulsants in women using hormonal contraceptives, they should be advised about the intended risks that include breakthrough bleeding and unintended pregnancy. One should use alternative or additional methods of birth control for 2 weeks after short-term anticonvulsant therapy and 4 weeks after long-term anticonvulsants therapy.
If a combination oral contraceptive pill is used, a regimen containing at least 50 mcg of ethinyl estradiol per day or equivalent should be considered. Although breakthrough bleeding is not necessarily indicative of low ethinyl estradiol serum levels or increased risk of ovulation, some clinicians suggest that women who experience breakthrough bleeding during enzyme-inducing therapy may be prescribed an increased dose of ethinyl estradiol above 50 mcg daily by combining more than one formulation of the contraceptive pill if necessary.
For emergency contraception in patients who have used a hepatic enzyme inducer in the past 4 weeks, a non-hormonal emergency contraceptive (e.g., copper intrauterine device) is considered preferable. If this is not possible, some authorities recommend that the usual dose of levonorgestrel (1.5 mg) should be doubled to 3 mg and taken as a single dose as soon as possible (within 72 hours of unprotected sexual intercourse). However, there are no data on efficacy, compliance, or side effects of this regimen.
For women with the etonogestrel subdermal implant, the addition of a barrier method is recommended during concomitant use and for 28 days after discontinuation of hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs. It is recommended to remove the implant and to prescribe a non-hormonal method in women who require long-term treatment with hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs.
No precautions or recommendations are available for women using hormone-releasing intrauterine systems, but a significant interaction with these systems is thought to be unlikely due to their local action. Injectable progestin-only contraceptives are also thought to be unaffected by enzyme-inducing drugs.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be taken with fentanyl?
One should monitor the patient closely if he had administered the combination of phenytoin and fentanyl. Phenytoin can reduce the plasma concentration of opioids (butorphanol, fentanyl, hydrocodone, and oxycodone) which are metabolized by CYP450 3A4. Reduced efficacy or withdrawal symptoms may occur in patients maintained on their narcotic pain regimen following the addition of an enzyme-inducing anticonvulsant.
Anticonvulsants such as phenytoin should not be stopped abruptly because the discontinuation of the anticonvulsant may increase opioid plasma concentrations which can lead to fatal respiratory depression due to potentiating the risk of overdose.
When an enzyme-inducing anticonvulsant is added or withdrawn from the therapy, the pharmacologic response of opioid should be monitored closely. The dose of the opioid need to be adjusted and is necessary.
The ambulatory patients should be counseled to avoid hazardous activities that require mental alertness and motor coordination because the combinations of phenytoin and fentanyl have the potential for additive central nervous system depressant effects.
Can Dilantin Kapseals be taken with warfarin?
When phenytoin is taken along with warfarin, it can cause moderate interaction. Anticoagulants like warfarin increase the elimination half-life of phenytoin as well as the serum concentrations. The mechanism behind this is known as the inhibition of the CY450 metabolism. The prothrombin time has been increased initially, but anticoagulant effects can be reduced thereafter with the addition of phenytoin to warfarin therapy.
The serum concentration of phenytoin should be monitored in patients receiving the phenytoin concurrently with warfarin and whenever the dosage is changed or discontinued. Any signs of bleeding (e.g., pain, swelling, headache, dizziness, weakness, prolonged bleeding from cuts, nosebleeds, bleeding of gums from brushing, red or brown urine, or red or black stools) or hydantoin toxicity (e.g., drowsiness, visual disturbances, change in mental status, seizures, nausea, or ataxia) should be advised to report promptly to their doctor.
When should I see a doctor?
Some people may have very bad or even deadly side effects when taking a drug, however, the chances are rare. Such conditions are alarming and need medical attention immediately. You should see your doctor right away if you also see some dangerous side effects of Dilantin kapseals. Such side-effects are:
- Signs of an allergic reaction, like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing or talking; unusual hoarseness; or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Trouble walking
- Feeling confused
- Slurred speech
- Swollen or sore gums
- Severe muscle pain
- Trouble controlling body movements, twitching, change in balance, trouble swallowing or speaking
- If seizures are worse or not the same after starting this medicine
- A burning, numbness, or tingling feeling that is not normal
- Not able to control eye movements
- Shakiness
- Call your doctor right away if you have swollen glands; fever; rash; chest pain; unable to pass urine or change in the amount of urine passed; or signs of liver problems like dark urine, feeling tired, not hungry, upset stomach or stomach pain, light-colored stools, throwing up, or yellow skin or eyes. Sometime severe and deadly effect has happened in people taking drugs for seizures like this medicine (Dilantin Kapseals).
- Certain blood problems have been reported with this drug, however they were rare. This can lead to bleeding problems or infections which were deadly sometimes. Tell your doctor right away if you have signs of infection like fever, chills, very bad sore throat, ear or sinus pain, cough, more sputum or change in color of sputum, pain with passing urine, mouth sores, or a wound that will not heal. Tell your doctor right away if you have any unexplained bruising or bleeding, or if you feel very tired or weak.
How do I store and/or throw out Dilantin Kapseals?
- Store at room temperature.
- Protect from light or keep it away from direct sunlight.
- Store in a dry place. Avoid storing this medication in a bathroom.
- Keep all drugs in a safe place. Keep all drugs out of the reach of children and pets.
- In case of disposing this drug safely, check with your pharmacist about how to throw out unused drugs.
“Is Senna a laxative or a stool softener? Is Senna good for weight loss?“