Contents
- What is divalproex?
- Divalproex IUPAC name, molecular structure, weight, formula, drug class
- Mechanism of action of divalproex
- Pharmacokinetics of divalproex
- How long divalproex stays in your system?
- What are the indications of divalproex?
- What are the side effects of the divalproex?
- What are the contraindications of divalproex?
- Can divalproex be taken in pregnancy?
- Can divalproex be taken by nursing mother?
- Divalproex pancreatitis
- Can divalproex be used for migraine?
- Use of divalproex for schizophrenia
- Can divalproex be given to the patient with liver disease?
- Can divalproex be given to children?
- Can divalproex be given to the patients with suicidal tendency?
- Can divalproex be taken with alprazolam?
- Can divalproex be taken with aspirin?
- Can you take divalproex with estradiol?
- Divalproex and capbapenem antibiotics intereaction
- Can divalproex be given for PTSD (Post-traumatic stress disorder)?
- Divalptoex and hypothermia
- Can divalproex worsen the status of HIV-infected patients?
- Can I take alcohol with divalproex?
What is divalproex?
Divalproex is also known as sodium salt valproate and also supplied as a form of valproic acid. It is a fatty acid that possesses anticonvulsant properties.
It is beneficial in the treatment of epilepsy. Divalproex is considered to act by increasing the GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) levels in the brain or it may also act by changing the voltage-dependent sodium channel properties.
However, the exact mechanism of this drug is not known. Valproic Acid is also a histone deacetylase inhibitor and is under investigation for the treatment of HIV and various cancers.
Divalproex IUPAC name, molecular structure, weight, formula, drug class
IUPAC name: 2-propylpentanoic acid
Molecular formula: C16H31NaO4
Molecular weight: 310.405 Da
Molecular structure:
Drug class: Divalproex comes under the class of organic compounds which is known as methyl-branched fatty acids. These fatty acids have a methyl branch attached with acyl chain.
They are saturated fatty acid usually and may contain only one methyl group or more. However, it may contain branches other than methyl groups.
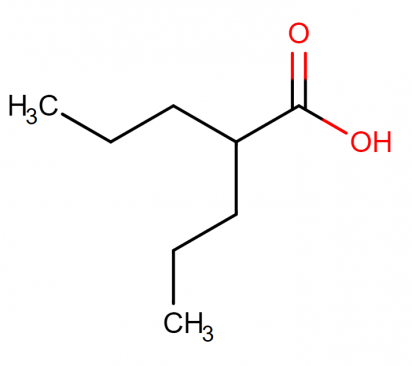
Mechanism of action of divalproex
In the gastrointestinal tract, valproic acid broke down into valproate ion which binds and inhibits GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) transaminase.
Increased concentration of GABA (an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system) in the brain may be related to the anticonvulsant activity of this drug, which acts by inhibiting enzymes that catabolize GABA or by blocking the reuptake of GABA in the nerve endings.
Valproic acid may also work by suppressing repetitive neuronal firing through inhibition of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. It is also a histone deacetylase inhibitor.
Valproic acid has also been shown to be an inhibitor of an enzyme called histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1).
HDAC1 is needed for HIV to remain in infected cells. A study revealed that patients treated with valproic acid in addition to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) showed a 75% reduction in latent HIV infection.
Pharmacokinetics of divalproex
Divalproex absorbed rapidly from the gastrointestinal tract, however, the conditions such as the formulation of this drug (such as liquid, solid or powdered form), conditions of use (like fasting or postprandial) or methods of administration can alter the rate of absorption.
In the treatment of epilepsy, these conditions are of minor importance under steady-state conditions.
In the rate of absorption of the divalproex tablet, co-administration of food has a great importance which increases from 4 hours to 8 hours as compared to the rate of absorption of the divalproex capsule which increases 3.3 hours to 4.8 hours.
Total daily systemic bioavailability (extent of absorption) is the primary determinant of seizure control as per studies.
The volume of distribution of total divalproex is 11 L/1.73 m2 and that of free valproate is 92L/1.73m2. The plasma protein binding of divalproex is from 90% at 40 µg/mL to 81.5% at 130 µg/mL.
In elderly patients, in patients with hepatic and renal diseases, the plasma free fractions occurrence is higher than expected.
The protein binding of other drugs such as phenytoin or carbamazepine is also affected by this.
The metabolism of the valproic acid takes place by the liver. 30% to 50% of an administered dose appears in urine as a glucuronide conjugate, in adult patients on monotherapy.
Another metabolic pathway of divalproex is mitochondrial beta-oxidation, which accounts for over 40% of the dose.
Oxidative mechanisms use to eliminate the 15%-20% of the dose. Around 3% of the drug excreted unchanged in the urine. The elimination half-life of the divalproex is 9 to 16 hours after oral administration of 250 mg to 1000 mg dose of divalproex.
How long divalproex stays in your system?
The elimination half-life of the divalproex is 9 to 16 hours, and the elimination of the drug is five times to that of the elimination half-life of the drug. Therefore the drug will be eliminated from your body in 70 to 80 hours i.e. in 3 to 4 days completely.
What are the indications of divalproex?
Divalproex is indicated for the treatment and management of seizure disorders, mania, and prophylactic treatment of a migraine headache.
In patients suffering epilepsy, the absence seizures, tonic-clonic seizures (grand mal), complex partial seizures, and the seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome can be controlled by the valproic acid.
What are the side effects of the divalproex?
Divalproex should always be administered with doctor consultation and as per doctor’s recommendation. This is the drug which can increase the risk of liver damage, therefore while taking this drug, you should look out for symptoms given below:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Persistent vomiting
- Anorexia or loss of appetite
- Pain mainly on the right side of stomach
- Dark colored urine
- Swelling that appears mainly on the face, hands, feet, and also in legs
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Divalproex is also considered responsible for suicidal actions, thought or behavior. If you suffer from any of these side effects, consult your doctor immediately.
- Suicidal thoughts, or dying
- Suicidal attempt
- Depression which is getting worse recently
- Anxiety which is getting worse with passing time
- Panic attacks
- Mood disorders
- Restlessness or shaking
- Insomnia or lack of sleepiness
You may also suffer from life-threatening pancreatitis after taking this medication. Therefore you should keep an eye on the developing symptoms and should consider emergency medical help if you see symptoms such as:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal cramps
- Stomach pain that radiates to the back or which worsen after eating
- Tenderness while pressing the stomach
Divalproex is a medication which can also cause the serious side effects such as encephalopathy (a severe or fatal brain disorder) in patients who are suffering from certain metabolic disorders, for example, urea cycle disorders.
If you develop symptoms such as unknown weakness, fatigue, vomiting, or sudden mood changes, mental changes like confusion, delirium etc., contact your doctor immediately.
One of the most common side effects of this drug is nausea, patients who take divalproex suffer from nausea at some point during therapy. Some other common side effects of divalproex are:
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Blurred or double vision
- Impaired memory
- Ear ringing
- Tremors or shakiness
- Unsteadiness
- Excessive sleepiness (somnolence)
- Baldness or hair loss
- Irregularities in the menstrual cycle
- Weight gain
- Some serious side effects of divalproex include:
- Chest pain
- Unexplained bleeding
- Easy bruising
- Irregular heartbeat
- Involuntary eye movement
- Feeling cold or shivering
- Incongruousness or feeling cold
- Rapid or heavy breathing
These are the side effects that need immediate medical attention. So, if you develop signs of serious allergic reaction such as rash, itching, hives, swelling of the face or another body part, along with dizziness, trouble breathing, contact your doctor immediately.
What are the contraindications of divalproex?
Divalproex is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to valproic acid, divalproex or to any ingredient which may be present in its formulation.
- The administration of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets in patients with hepatic disorders or any hepatic dysfunction is completely contraindicated.
- In patients with mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA polymerase or in children (aged 2 years) might be suffering from the POLG-related disorder, the use of divalproex-sodium extended-release tablets are highly contraindicated.
- In patients with hypersensitivity of the drugs, the administration of divalproex is contraindicated.
- In patients with known urea cycle disorders, the divalproex sodium extended-release tablet is contraindicated.
- In pregnant women suffering from a migraine, use of divalproex sodium extended-release tablet use as a prophylaxis of a migraine headache is contraindicated. (please see the pregnancy category for use of divalproex).
Can divalproex be taken in pregnancy?
Divalproex comes under pregnancy category-D which means there is sufficient positive evidence of human fetal risk which is observed from investigation or marketing experience of adverse reaction data of this medication in human.
However, the potential benefits of this drug may warrant the use of this drug in pregnant women despite potential risks.
The use of divalproex in pregnancy for migraine prophylaxis is contraindicated. It means that the drug should be used during pregnancy only if benefits outweigh the risk.
As per the US FDA category D, this medication can be used for manic episodes associated with bipolar disorders. Moreover, the use of this medication is not recommended in the pregnancy.
In case women get pregnant while receiving this drug or in case a pregnant woman take this medication, she should be alerted to the potential harmful effects to the fetus.
Can divalproex be taken by nursing mother?
While breast feeding, there are no adverse events were noted while using this medication by a nursing mother. The reason behind this is low levels of this drug in breastmilk and infant serum.
Theoretically, breastfed infants are at risk for drug-induced hepatotoxicity, so infants should be monitored for jaundice and other signs of liver damage.
UK: A decision should be made to discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. US: Caution should be exercised when valproate is administered to a nursing woman. Excreted into human milk: Yes (at a concentration ranging from 1% to 10% of maternal serum levels).
Divalproex pancreatitis
Cases of life-threatening pancreatitis have been reported in both children and adults receiving valproate.
Some of the cases have been described as hemorrhagic with a rapid progression from initial symptoms to death. Cases have been reported shortly after initial use as well as after several years of use.
Patients and guardians should be warned that abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and/or anorexia can be symptoms of pancreatitis that require prompt medical evaluation.
If pancreatitis is diagnosed, valproate should ordinarily be discontinued. Alternative treatment for the underlying medical condition should be initiated as clinically indicated.
Can divalproex be used for migraine?
Divalproex is the first anticonvulsant medication for a migraine headache and has been approved by the FDA as a migraine prophylactic agent.
When tried on a group of patients with a migraine or cluster headaches, divalproex showed relief from headache pain and migraine headache in such patients and even those patients continued this therapy for 3 months.
However, some patients also reported some negative side effects such as weight gain, nausea, vomiting, somnolence, tremor, alopecia, disequilibrium, and rashes.
Therefore few people left the therapy due to such side effects. Overall, it was reported that divalproex was an effective and well tolerated prophylactic treatment for a migraine and cluster headache both as monotherapy and polytherapy.
Use of divalproex for schizophrenia
Divalproex is a fast acting agent which appears to be safe and effective in conditions like schizophrenia. Divalproex was proved to be well tolerated and effective in agitated or violent psychotic persons.
Divalproex has been reported to produce calmer response and less dangerous hospital course for such patients. Along with such effects, it appears to produce no adverse events.
Can divalproex be given to the patient with liver disease?
In patients with the hepatic disease or significant hepatic dysfunction, the use of valproate derivatives such as divalproex is highly contraindicated. In patients treated with such agents, the fatal hepatotoxicity can occur.
In children (less than 2 years of age), or in patients who are on multiple anticonvulsants and those with congenital metabolic disorders, or in patients with mental retardation or with any other organic brain disease, the risk appears to be at greatest.
In patients with risk factors for valproate-related hepatotoxicity, the divalproex should be given with extreme caution.
The patient may suffer from the nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, weakness, lethargy, facial edema, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and loss of seizure control, however, these symptoms may appear after 6 months of treatment.
One should closely monitor the patients for such symptoms, if they suffer from significant hepatic dysfunction, the therapy should be stopped immediately.
Before initiating this therapy, the patient should undergo liver function test which should be continued thereafter, especially during first 6 months of the therapy.
However, clinicians should bear in mind that transient, dose-related, asymptomatic elevations in serum transaminase, amylase and ammonia levels may commonly occur and often return to normal with or without dosage adjustment.
Can divalproex be given to children?
Children under the age of two years are at a considerably increased risk of developing fatal hepatotoxicity, especially those on multiple anticonvulsants, those with congenital metabolic disorders, those with severe seizure disorders accompanied by mental retardation, and those with organic brain disease.
When Divalproex sodium extended-release tablets are used in this patient group, it should be used with extreme caution and as a sole agent.
The benefits of therapy should be weighed against the risks. The incidence of fatal hepatotoxicity decreases considerably in progressively older patient groups.
Can divalproex be given to the patients with suicidal tendency?
Increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior is generally increased in the patients taking antiepileptic drugs. In patients with depression or other psychiatric disorders, the therapy with antiepileptic drugs should be administered with precaution.
One should keep the fact in their minds is that the antiepileptic drugs are usually associated with morbidity, mortality, suicidal behaviors and thoughts therefore despite being treated for untreated illness, the patient should be assessed for the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
This medication can worsen the signs of depression, unusual changes in mood or behavior, or suicidal thoughts, therefore the caregivers, patients, and families should be alerted for the same.
A dosage reduction or treatment withdrawal should be considered in case of persistent symptoms. The treatment should be immediately stopped in case patient show suicidal ideation.
Can divalproex be taken with alprazolam?
One should generally avoid taking divalproex and alprazolam together because benzodiazepines such as alprazolam can enhance the teratogenic effects of the valproate in the infant of women suffering from epilepsy.
Administration of both drugs concurrently is associated with adverse effects to the fetus. As per one study, valproate is known to displace the diazepam from the plasma protein binding sites and also it can inhibit its metabolism.
Valproate can also interact with other benzodiazepines in the similar fashion.
In pregnancy, the use of both these medications is contraindicated and should not be used until the benefits outweigh the risk.
The clinical evidence of benzodiazepines toxicity such as excessive sedation should be observed closely in case valproate and benzodiazepines are administered by a normal patient.
Can divalproex be taken with aspirin?
Let your doctor know that you are already taking divalproex before he prescribes you aspirin. In order to take both these medications safely, you may need a dose adjustment.
If you are taking aspirin for a longer period of time, you may need to check the level of divalproex because small single doses of aspirin may be unable to produce any significant effects.
If you have symptoms such as drowsiness, pain, nausea, vomiting, or stomach pain, you should notify your doctor promptly.
In case you are taking other medications such as vitamins or other herbal medications, let your doctor know about all medications. Also, avoid stopping this drug without doctor’s consent as it can also cause withdrawal symptoms.
Can you take divalproex with estradiol?
One should generally avoid concurrent administration of divalproex with estradiol because the combination of both medications can cause loos of seizures control, and several changes in behavior such as tremors, poor muscle coordination, and increased seizures.
You should report your doctor promptly to you see any adverse reaction produced after concurrent administration of both these medications.
When both these medications are administered concurrently, the pharmacological response should be monitored and if required the dosage should be adjusted.
If you experience any symptoms such as seizure control loss, valproic acid toxicity (like tremors, ataxia, nystagmus, increased seizures, or even change in mental status), they should contact their doctor immediately.
In women at pill-free week, if the dose of divalproex or valproic acid is increased, the level of valproic acid can be increased in the body.
Divalproex and capbapenem antibiotics intereaction
Carbapenem antibiotics (for example, ertapenem, imipenem, meropenem; this is not a complete list) may reduce serum valproate concentrations to subtherapeutic levels, resulting in loss of seizure control.
Serum valproate concentrations should be monitored frequently after initiating carbapenem therapy. Alternative antibacterial or anticonvulsant therapy should be considered if serum valproate concentrations drop significantly or seizure control deteriorates
Can divalproex be given for PTSD (Post-traumatic stress disorder)?
There is no sufficient data is given for the administration of divalproex sodium for the treatment of PTSD, therefore you should always consult your doctor before taking this medication for a post-traumatic stress disorder.
Divalptoex and hypothermia
Hypothermia, defined as an unintentional drop in body core temperature to < 35° C (95° F), has been reported in association with valproate therapy both in conjunction with and in the absence of hyperammonemia.
This adverse reaction can also occur in patients using concomitant topiramate with valproate after starting topiramate treatment or after increasing the daily dose of topiramate.
Consideration should be given to stopping valproate in patients who develop hypothermia, which may be manifested by a variety of clinical abnormalities including lethargy, confusion, coma, and significant alterations in other major organ systems such as the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Clinical management and assessment should include examination of blood ammonia levels.
Can divalproex worsen the status of HIV-infected patients?
There are in vitro studies that suggest valproate stimulates the replication of the HIV and CMV viruses under certain experimental conditions. The clinical consequence, if any, is not known.
Additionally, the relevance of these in vitro findings is uncertain for patients receiving maximally suppressive antiretroviral therapy.
Nevertheless, these data should be borne in mind when interpreting the results from regular monitoring of the viral load in HIV infected patients receiving valproate or when following CMV infected patients clinically.
Can I take alcohol with divalproex?
Alcohol can increase the nervous system side effects of divalproex sodium such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating. Some people may also experience impairment in thinking and judgment.
You should avoid or limit the use of alcohol while being treated with divalproex sodium.
Do not use more than the recommended dose of divalproex sodium, and avoid activities requiring mental alertness such as driving or operating hazardous machinery until you know how the medication affects you.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns.
“Can you eat after taking Nystatin? Can Nystatin be used on the face?“

