Contents
- What is Dyshidrotic eczema?
- What are some other names of Dyshidrotic Eczema?
- Is Dyshidrotic eczema contagious?
- Are Dyshidrotic eczema and Dyshidrosis the same?
- How Dyshidrotic eczema looks like?
- What causes dyshidrotic eczema?
- What are the symptoms of Dyshidrotic eczema?
- How is Dyshidrotic Eczema diagnosed?
- What are the complications of Dyshidrotic Eczema?
- Soaks and cool compresses for dyshidrotic eczema
- Cold and Wet compresses for dyshidrotic eczema
- Vinegar soaks for dyshidrotic eczema
- Vinegar Compress vs Vinegar Soak
- Corticosteroids creams for Dyshidrotic eczema
- How long should I use corticosteroid creams for dyshidrotic eczema?
- What corticosteroid is best for dyshidrotic eczema?
- Pramoxine for dyshidrotic eczema
- Potassium permanganate dilute solution soaks for dyshidrotic eczema
- Dapsone for dyshidrotic eczema:
- Antihistamines for dyshidrotic eczema
- Is fexofenadine the best antihistamine for dyshidrotic eczema?
- Alitretinoin for dyshidrotic eczema
- Moisturisers for dyshidrotic eczema
- Are antibiotics creams useful for dyshidrotic eczema?
- Botulinum toxin for dyshidrotic eczema
- Draining large blisters of dyshidrotic eczema in ambulance
- What systemic corticosteroids are used for dyshidrotic eczema?
- Light treatments for dyshidrotic eczema
- Appropriate diet for dyshidrotic eczema
- What should I avoid if I have dyshidrotic eczema?
What is Dyshidrotic eczema?
Dyshidrotic eczema (DE) is a skin disease in which people develop blisters on the hands and feet. In this skin condition, skin gets itchy and dry because skin cannot protect itself. Blisters that develop on the skin are small, painful, deep-seated and usually filled with fluid and lasts for 14 days to one month. After two to three weeks, when blisters clear, the skin become red, cracked and scaly.
Some triggers of DE are stress, allergies, moist hands and feet, contact with various metals and temperature rise. DE is not curable therefore some people suffers from flares that can be mild to debilitating. Severe flares on hands and feet can make the everyday task difficult. Walking can be difficult in the case of severe flare on patient’s feet.
DE is twice as common in women as men and is third most common dermatitis (skin infection) or inflammation of hands. Most of the people who suffer from DE also have atopic dermatitis (another common form of eczema). There is no cure for DE but the good news is that you can manage this disease. It is non-transferable from one person to another like all types of skin condition.
What are some other names of Dyshidrotic Eczema?
Different names for dyshidrotic eczema may include:
- Cheiropompholyx (affects the hands)
- Dyshidrosis
- Foot and Hand eczema
- Pompholyx
- Pedopompholyx (affects the feet)
- Vesicular Eczema
- Palmoplantar Eczema
- Foot and hand Eczema
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis
- Vesicular Palmoplantar eczema
Is Dyshidrotic eczema contagious?
Eczema is a very common problem in skin diseases but it is not contagious. Eczema can be caused by oral, inhalation, injectables and trans mucosal routes. Actual reasons of dyshidrotic eczema are not clear and health experts are still finding the actual cause behind this skin condition. Dyshidrotic eczema is noncontagious and it can not be spread by contact with someone suffering from it.
Skin outbreaks, allergy, infections, nutritional deficiency are some common causes of DE. Symptoms of DE are quite prominent on palms of hands and fingers. Some examples of symptoms are scaling, peeling and crusting that makes a patient feel uncomfortable to interact with others.
DE is not contagious and can not transfer from one person to another even after direct skin contact. The blisters that commonly develop in DE are filled with some fluid, and one should not worry about spreading dyshidrotic eczema with the oozed fluid from these blisters.
The blisters that develop in the DE are itchy and painful and continues itch and scratching can cause some serious pathogenic infections. These secondary infections can prove contagious and are responsible for further infections. Thus these infections should be cured properly.
Are Dyshidrotic eczema and Dyshidrosis the same?
Yes, Dyshidrosis is another name of Dyshidrotic eczema. Both are same.
How Dyshidrotic eczema looks like?
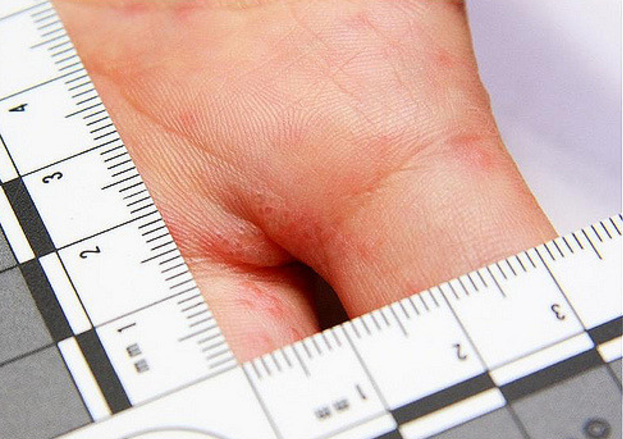
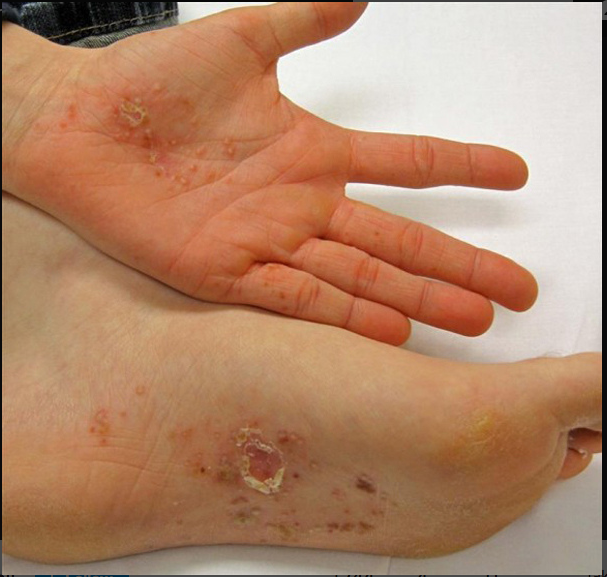
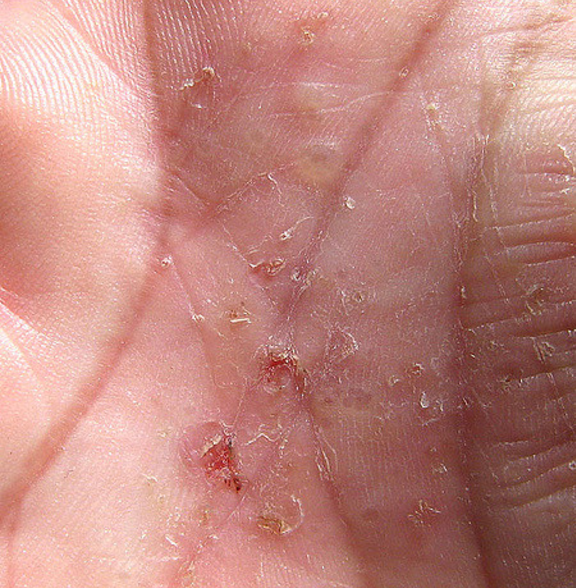
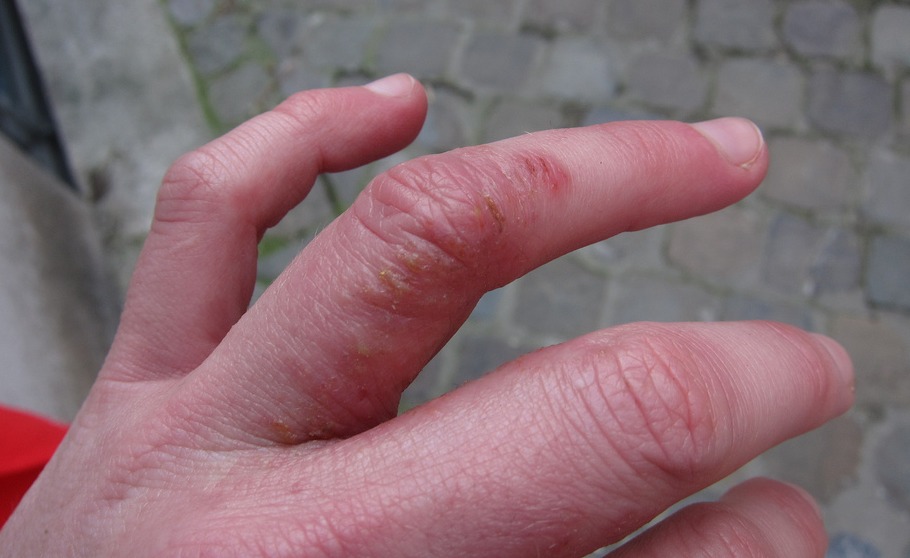
DE is the skin condition in which patient develop blisters on the palms of the hands (Refer image 3) , Sole of the feet (Image 1), Above and between the fingers (Image 2 & 4).
What causes dyshidrotic eczema?
The exact cause of DE is still not clear. As per health experts, DE may be related to seasonal allergies (such as hay fever), because blisters appear more frequently in spring allergy season.
It is also considered as more than one factor is involved in dyshidrotic eczema. A common and critical symptom of DE is excessive sweating in hands or feet that occur in patients (about 40%) suffering from this skin condition.
There are some other factors that may lead to a Dyshidrotic condition in you if:
- You have atopic dermatitis.
- You are under stress.
- You have sensitive skin.
- You wash your hands more often
- You work with cement.
- You have allergies such as hay fever.
- You receive IV immunoglobulin infusions.
- Your hands are exposed to different metals (chromium, cobalt or nickel).
What are the symptoms of Dyshidrotic eczema?
The most common symptom of DE is the appearance of blisters on hands and feet. If you are suffering from DE, you may see small, itchy and painful blisters on your fingers, toes, hands or feet.
These blisters are mainly filled with fluid and appear on edges of hands and feet. These blisters are very itchy and painful to touch and may cause the skin to flake. Sometimes, large and big blisters develop on hands or feet which are extremely painful. After three weeks, these blisters starts to dry and leave the skin dry, cracky and painful to touch. The skin may also appear thicker and spongy upon scratching.
In severe cases, larger blisters develop by merging many small blisters.
There are some characteristics of blisters in DE are:
- Small, itchy and painful, – about the width of a standard pencil lead.
- Grouped in clusters, similar to grains of tapioca.
- Filled with watery fluid.
- Small blisters merges to form larger blisters (particularly painful)
- They leave skin scaly, red, tender, cracked and painful.
- Blisters and DE recur after months or years.
How is Dyshidrotic Eczema diagnosed?
A physical examination is needed to diagnose dyshidrotic eczema. Some other test may be required such as scraping your skin and tested it for fungus type. Exposing skin patches to various patches are also done to check skin allergies and sensitivities. An allergist can diagnose DE by:
- Physical examination of your skin
- Skin biopsy in order to check out the possible cause of blisters or skin infections.
- Allergy skin testing to check if the root cause of DE is an allergy.
- Patch test to show if you have allergy to metals (nickel or chromium)
If you see blisters on your hands and feet, show these to your dermatologist, he will examine your hands, feet as well as your nails.
What are the complications of Dyshidrotic Eczema?
DE is the condition that affects mainly teenagers and adults. It may be acute, recurrent or chronic. The treatment of DE can range from self limited to debilitating. There are some complications of DE which are:
- Pitted nails
- Pain and Itching that hamper the daily working
- Bacterial infections usually caused by scratching
- Formation of large blisters by small blisters
- Excessive perspiration that limits the use of hands
- Secondary Infections
This condition sometimes becomes unresponsive to treatment, which can be frustrating for physician as well as patient.
Soaks and cool compresses for dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema is the condition in which skin becomes itchy and painful and the patient seeks immediate relief. Cold compresses and soaks are homemade alternates to get rid of itching and irritation.
Cold and Wet compresses for dyshidrotic eczema
Burning sensations and irritation can be reduced by applying cold compresses on affected areas. Cold compressions are effectively used to decrease inflammation of blisters and numb the irritated nerve endings. These compresses increase the benefits of topical creams and effectively reduces blisters.
- Before wrapping your hand or feet, soak a soft cloth in cold water and place it in the fridge for several hours.
- Cover your hands or affected areas in the cold compress for about 15 minutes for two to three times.
- You can place the crushed ice in a plastic bag to make it little longer.
- One should not soak his/her inflamed hands or feet directly in ice as it can lead to frost bite. It is beneficial in providing prompt relief but it can shock your blood vessels.
Vinegar soaks for dyshidrotic eczema
Vinegar is effective home remedy for treating Dyshidrotic eczema and is beneficial in providing relief in associate itching, scaling, and dryness. Soaking is a better option than compresses as it is less time-consuming.
Apple cider vinegar is considered best for this purpose but white vinegar also works well. White vinegar works similar to ACV (apple cider vinegar) and is cheaper in comparison of apple cider vinegar. But these soaks require you to site with a bowl, without any move, not allow you to scratch.
Follow these steps before using vinegar therapy at home:
- Dilute the vinegar before exposing it to your skin.
- Add a cup of vinegar of your choice in cold water.
- Soak the inflamed skin of hands or feet for 40 minutes.
- Repeat the procedure for best results.
Vinegar Compress vs Vinegar Soak
Cold compresses and vinegar soaks have different benefits.
Advantages:
- Cold compresses or Vinegar compress provides good coverage and allow you to be more mobile along with prompt relief.
- You can cover the compress in a plastic bag in order to avoid spillage all over on the floor.
- Vinegar soaking is also considered best home remedy for DE as it is less consuming.
- It provides prompt relief in lesser time as compared to compresses.
Disadvantages:
- Cold compresses takes much time in getting cool as it need to place in the fridge for several hours.
- Soaks makes a person immobile as one need to sit at one place with a bowl of cold water for longer periods.
Tips:
- Avoid direct exposure of vinegar to inflamed skin, as it can leave skin with a burning sensation. Always dilute the vinegar before application on to the skin.
- Always mild soaps and detergents on skin as harsh chemicals in soaps and deteregents can eczema outbreaks.
- Always use moisturiser after soak therapy as vinegar is a drying agent.
- One should wear soft clothes, eat fresh fruits and reduce stress in order to get relief from eczema and its symptoms.
- Vinegar can interact with various chemicals and medicines therefore one should always consult his/her physician before consuming vinegar.
Corticosteroids creams for Dyshidrotic eczema
Patients suffering from dyshidrotic eczema prefers ointments as they penetrate the skin better than creams. Creams are suitable for daytime application. Topical corticosteroids are the base of treatment of Dyshidrotic Eczema.
Corticosteroids are highly beneficial in treating DE as they possess anti-inflammatory properties. Corticosteroids acts by modifying the body’s immune response to diverse stimuli.
Topical corticosteroids are the first-line therapy for DE and topical ointments are more potent and greaser than creams.
Clobetasol for Dyshidrotic eczema:
It is also known as Temovate, Clobex, Cormax, Olux. Clobetasol is class 1 highly potent steroid. It is useful in the synthesis of proteins that reduces inflammation and effectively causes vasoconstriction. It effectively suppresses mitosis and is used for several episodes.
Flucinolone for Dyshidrotic eczema:
Also known as Vanos, and is a class 2 steroid. It possesses anti-inflammatory, vasoconstrictive and antipruritic properties.
Prednisone for Dyshidrotic eczema:
It is second line treatment for dyshidrotic eczema. It is highly absorbed from gastrointestinal tract. Prednisone is effective immunosuppressant and potent anti-inflammatory agent which has salt retaining properties. It acts by decreasing inflammation by reversing enhanced permeability of capillaries.
Betamethasone for Dyshidrotic eczema:
A highly effective corticosteroid that is used for severe episodes. It shows rapid action within 1 hour that stays for 72 hours. Betamethasone is available in the market under the names of Celestone, Diprolene, Luxiq and can be administered for inflammatory dermatosis. It is beneficial in reducing inflammation by reducing migration of PMN (Polymorphonuclear) leukocytes and reduced capillary permeability.
Triamcinolone for Dyshidrotic eczema:
Triamcinolone is available as Aristospan and Kenalog. It effectively decreases inflammation by suppressing migration of PMN leukocytes. This has a maximum duration of 4 to 6 weeks.
How long should I use corticosteroid creams for dyshidrotic eczema?
Topical Steroids (TCS) are the mainstay of treatment of dyshidrotic eczema and is first line therapy for eczema. Steroids are highly potent, and higher strength is needed for disease control, still, their potency is based on patient’s response to treatment.
- One should not apply TCS for more than two to four weeks and frequency should also be reduced to twice weekly use.
- An effective and safe treatment plan should be made by your healthcare provider, in which daily use of TCS should be restricted, especially on sensitive areas.
- Careful monitoring and good communication is needed to ensure restricted usage of TCS.
- One should follow the treatment plan by heart and should not ask for multiple refills.
What corticosteroid is best for dyshidrotic eczema?
Clobetasol is considered best corticosteroid for dyshidrotic eczema. It is super-potent corticosteroid that suppresses mitosis, enhance the protein synthesis that are beneficial in reducing inflammation and cause vasoconstriction.
Pramoxine for dyshidrotic eczema
The main concern in treating dyshidrotic eczema is to relieve itch and pain associated with it. Pramoxine is an effective agent that helps in relieving itch as well as pain. Pramoxine is widely used surface anaesthetic because it combines effectiveness with low system toxicity. It is proved to exhibit low sensation for itch and pain sensitisation.
Pramoxine is an antihistamine that blocks nerve conduction by inhibiting depolarisation of neurons. It is available as 1% or 2.5% cream or ointment.
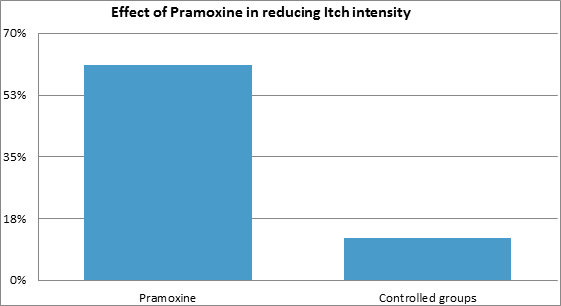
A study showed that the pramoxine shows a maximum reduction in itch intensity as compared to controlled groups.
Pramoxine : 61% reduction in Itch intensity associated with DE.
Controlled groups: 12% reduction in Itch intensity associated with DE.
A combination of pramoxine and hydrocortisone named PRAMOSONE is highly effective in treating eczema as hydrocortisone produces anti-inflammatory properties and pramoxine is an topical anaesthetic. It reduces redness, swelling, blisters, itching and irritation as well as reduces pain on affected area by blocking transmission of nerve impulses.
Potassium permanganate dilute solution soaks for dyshidrotic eczema
Potassium permanganate is an oxidising agent that possesses disinfectant and astringent properties. It is highly useful for conditions like eczema and blistering skin conditions.
As potassium permanganate is an effective disinfectant and its baths are beneficial in treating dyshidrotic eczema and fluid filled blisters associated with eczema.
- The exact ratio of dilute solution of potassium permanganate for soak is 1:10000 and it should be of pink colour (as shown above).
- A tablet of 400mg is also available in the market which should be diluted in 4litres of water.
- The tablet should be dissolved in hot water before soaking your hands into the bath.
- One should take bath in this solution for 2 times a day to dry out oozing sores and fluid filled blisters.
- Wet soaks of potassium permanganate can be made by soaking cotton strips in this solution (1:10000).
- These soaks should be wrapped on hands or feet for 20 to 30 minutes.
- As potassium permanganate possesses astringent properties, it helps in drying out the blisters.
Dapsone for dyshidrotic eczema:
Dyshidrotic eczema is also known as Pompholyx in which oedema fluid accumulates inside visible blisters. There is no specific cause of this skin condition, the treatment is done by means of soaks and compresses with antibacterial agents. Chronic and relapsing eczema can be treated by corticosteroids but the result remains unsatisfactory mainly in relapsing cases. therefore dyshidrotic eczema treated with Dapsone including chronic and relapsing cases.
Dapsone is the drug that is mainly used to treat laprosy and is proved highly beneficial in management of dermatoses. Dapsone was tried in dyshidrotic eczema where it showed very effective due to involvement of polymorphs or immune complexes.
- Initially a dose of 4mg/kg/day is given in two divided dose to 76 patients, till the clearance of lesions occurred.
- Then reduced the dose to 2mg/kg/day for a period of 2 weeks,
- Complete clearance of lesions associated with dyshidrotic eczema is noticed in just 4 to 18 days.
- Whereas when the same test is done on placebo and saline compresses, only 3 cases showed clearance of lesions.
Antihistamines for dyshidrotic eczema
Few symptoms associated with dyshidrotic eczema are itching, pain and pruritus. Antihistamines are effective in treating pruritus. A metabolite of loratadine, Desloratadine is tricyclic antihistaminic which is selective for the H1 receptor. The dose for adults and children is 5 mg orally. There are no side effects are noted, it rarely causes pharyngitis or dry mouth. Some examples of effective antihistamines in the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema are:
- Loratadine inhibits peripheral histamine H1 receptors
- Hydroxyzine shows antihistamine activity in subcortical region of CNS
- Pramoxine blocks nerve conduction (explained above also)
Is fexofenadine the best antihistamine for dyshidrotic eczema?
Fexofenadine can’t cure dyshidrotic eczema but it may easy symptoms related with the allergy. It can also be used as a test for dyshidrosis. Test is performed by following:
- Take 180 mg per day for 5 days and it has half life of 14 hours.
- Fexofenadine is 3rd generation over the counter anti histamine which can taken in a enhanced dose of 90 mg every 12 hours.
- Take the fexofenadine, if the itch goes, it is dyshidrosis.
- If continues itch and skin become red and inflamed than it is more likely to be a contact allergy.
To relieve the symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema, one should take fexofenadine and cover hands/feet in a cream made up of castor oil and zinc oxide overnight.
Alitretinoin for dyshidrotic eczema
Alitretinoin is an effective retinoid that is effective for chronic hand eczema:
- A novel and standard treatment for chronic hand eczema or pompholyx
- Alitretinoin is a unique pan agonist (the agents that acts on more than two isomers of the receptor) retinoid
- It possesses immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Oral alitretinoin have high efficacy rates of 28% to 89%, higher tolerability profile and shows improved quality of life.
Alitretinoin side effects:
- Redness, rash, pain, burning, itching, stinging, or tingling at the application site may occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
- Remember that your doctor has prescribed this medication because he or she has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
- Tell your doctor right away if any of these unlikely but serious side effects occur: blistering/crusting/oozing/peeling of the skin, severe burning/stinging of the skin, swelling of the skin.
- A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, seek immediate medical attention if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.
Moisturisers for dyshidrotic eczema
Moisturisers are most effective and easily available treatment for dyshidrotic eczema. But the wrong type of moisturiser can even flare up the eczema and will not help you to control the symptoms associated with eczema. Moisturisers that have higher oil content are best suited for dyshidrotic eczema. The best moisturisers are the ointments, creams because they are greasier, and contain more oil.
One, who has eczema, should carry moisturiser every time with them to ensure reapplication throughout the day. The moisturiser should be applied on your hands and feet or the affected area, immediately after washing.
There are some points that one should remember while using moisturisers for treating eczema.
- Lock in the moisture of the skin by applying a thick layer of moisturiser within three minutes of bathing.
- Apply as directed, if you are using a prescribed ointment or if it contains any corticosteroid.
- Always moisturise your skin before going to bed at night, as it will help you to retain moisture for a longer time.
- Choose the moisturiser that is free from fragrance and dye in order to avoid any kind of irritation.
- Avoid chances of contamination of container by minimizing the use of your hands while taking the moisturiser out of the container.
- Apply the moisturiser in downward strokes; avoid stroking up and down or in circular motions.
- Do not remove the excess moisturiser from your skin, as it will be absorbed after some time.
- Whenever you wash your hands with water, do not forget to apply moisturiser
- Wear cotton gloves on your hands and cover your feet (in the case of itching and pain on your feet) after application of prescribed ointment before going to bed.
Are antibiotics creams useful for dyshidrotic eczema?
Antibiotics are second line treatment of dyshidrotic eczema. It is mainly used for impetigo due to infection.
Dicloxacillin for dyshidrotic eczema
Dicloxacillin is an effective antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by blocking penicillin binding proteins. Dicloxacillin can be used as initial therapy for staphylococcal infections.
Cephalexin for dyshidrotic eczema
It is also available in the market under the name of Keflex. It primarily acts against skin flora. Cephalexin is an effective first generation cephalosporin that possesses bactericidal activity as it inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis thereby stops bacterial growth.
Erythromycin (E.E.S., Erythro RX, Ery-Tab) for dyshidrotic eczema
It comes as Ery-tab or E.E.S. and it is used for the treatment of staphylococcal infections. It also acts against bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Botulinum toxin for dyshidrotic eczema
Botulinum toxin is another effective treatment for dyshidrotic eczema as it affects the nerves in the skin. Botulinum toxin is a potent inhibitor of ACh (Acetylcholine release) which is responsible for production and release of sweat, thereby reducing the moisture in the skin. Sweating of hands in dyshidrotic eczema can also be inhibited effectively by tap water iontophoresis
A study was done in order to check the effect of botulinum toxin on the patients with dyshidrotic eczema. The DASI (Dyshidrotic Eczema Area and Severity Index) score have been checked and results were incredible:
- When given topical therapy alone, the DASI score changed from 28 to 17.
- When given adjuvant botulinum toxin along with corticosteroid therapy, the DASI score changed from 36 to 3.
Complete inhibition of itching and vesiculation is noted with the combination of Botulinum toxin and corticosteroids. No relapses have been reported in this treatment.
Therefore, it is concluded that Botulinum toxin is antipruritic that not only inhibits acetylcholine but also interacts with substance P.
Draining large blisters of dyshidrotic eczema in ambulance
In dyshidrotic eczema, small and itchy blisters develop on the hands and feet. Sometimes these small blisters combine to form large blisters, which cause extreme pain and itching.
Some patient drains the blisters to get rid of itch and pain because itch vanishes immediately after draining the fluid out from the blisters. Sometimes the blisters are quite large and dermatologists may drain these large blisters to relieve pain and itching.
After draining the blisters will heal within few days. Afterward, skin starts to dry and peel and ultimately heals completely. There are several treatments are available in the market for getting relief from itch and they should be considered before draining the blisters.
What systemic corticosteroids are used for dyshidrotic eczema?
When topical steroids and phototherapy become refractory in the case of hand eczema, systemic immunosuppressive therapy is considered.
Systemic glucocorticosteroids are given in the case of actual flares but they are not suitable for longer periods.Cyclosporin also proves to be useful for a shorter duration.Some promising agents for long term relief are methotrexate, mycophenolate, and mofetil. These drugs are well tolerated without any side effects. Retinoids are also systematically used for the treatment of hand eczema. e.g. etretinate and acitretin.
Light treatments for dyshidrotic eczema
Exposing the skin to the Ultra violet light for a specific period of time or a prescribed amount of time is used to treat skin effected with dyshidrotic eczema. It is proved that more than 90% of patients showed excellent results within 6 to 8 weeks of treatment.
The light treatment should be taken under medical supervision in a hospital or a clinic.
- UVA -1 treatment reported to be beneficial for dyshidrotic eczema and therapeutic response.
- Light therapy shows a significant reduction in DASI (Dyshidrotic Eczema Area and Severity Index) that lasts for 6 weeks after last treatment.
- UVA therapy for hands and feet is beneficial for the improvement of eruption and pruritus when taken for 2-3 times per week.
- A topical application is also available in the market as a combination of 8-methoxypsoralen plus UVA (bath-UVA)
- Topical ointment is considered as preferred method for treatment of dyshidrotic eczema as compared to oral PUVA.
- UVB (Ulta voilet B) is used for treatment of chronic hand eczema.
Appropriate diet for dyshidrotic eczema
When you are suffering from dyshidrotic eczema, do not forget to change your body habits.
- Avoid acidic foods and try to take food that brings the acid to alkaline.
- Avoid sugar, wheat, rice, wine, coffee and any other acidic food.
- Take apple cider vinegar to make body alkaline.
What should I avoid if I have dyshidrotic eczema?
One who have any kind of allergy, he/she should avoid food that is high in histamine, because histamine signals the mast cells and your digestive system can also drain some histamine from the food that you eat. An elevated level of histamine in the blood can worsen the allergic condition.
Things to be avoided are sauerkraut juice, stale fish, soy fermented products, sea fish, blue cheese, non synthetic soy sauce, vine, and bear.