Contents
- What is Famotidine?
- What is Famotidine used for?
- Famotidine Molecular formula and weight:
- Famotidine drug class:
- How famotidine works in the body?
- Famotidine brand names
- Famotidine indications
- Famotidine for Helicobacter pylori eradication:
- Famotidine for gastric and intestinal ulcer disease
- Famotidine for Prevention of NSAID-induced peptic ulcers
- Famotidine for GERD
- Famotidine for Zollinger–Ellison syndrome
- Famotidine for indigestion and heartburn
- Famotidine dosage forms and strengths
- Famotidine dosage for different indications:
- Famotidine highest dose
- Famotidine Side effects:
- How to take Famotidine?
- How long does it take for Famotidine to work?
- Can I abrupt Famotidine therapy suddenly?
- Can Famotidine cause withdrawal effects?
- Precautions and warnings during Famotidine use
- Famotidine Pregnancy warnings
- Famotidine Breastfeeding warnings
- How long does Famotidine work?
- How long does Famotidine stay in your system, urine, blood, saliva?
- Can patients with renal disease take Famotidine safely?
- Can patients with liver disease take Famotidine safely?
- Famotidine absorption, metabolism and elimination:
- Can I drink alcohol while taking Famotidine?
- Can I take Famotidine with Warfarin?
- Can I take Famotidine with diazepam?
- Can I take Famotidine with antacids?
- Can I take famotidine and omeprazole or other IPP together?
- Difference between famotidine and ranitidine
- Can famotidine be bought as OTC? Difference between OTC and prescribed famotidine
- Can famotidine cause a cancer?
- Can children safely use famotidine?
- Can you give famotidine to the dogs or cats?
What is Famotidine?
Famotidine is a generic name used for a stomach acid reducer drug that belongs to the class of H2 receptor antagonist drugs. This drug works by blocking the H2 receptors in the stomach and inhibiting gastric acid secretion. By blocking the H2 receptor in the stomach, it actually inhibits the secretion of acid into the stomach and therefore the total amount of acid in the stomach decreases.
What is Famotidine used for?
The most common uses of this drug include Allergic Urticaria, Duodenal Ulcer, Duodenal Ulcer Prophylaxis, Erosive Esophagitis, GERD, Indigestion, Pathological Hyper secretory Conditions, Peptic Ulcer, Stomach Ulcer, Upper GI Hemorrhage, Urticaria, Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome. It is used for preventing ulcers in intestines and stomach. It is used for GERD (Gastro esophageal reflux disease). It is also used in Zollinger Ellison Syndrome.
It can be used for any condition which causes excessive acid production from the stomach or the reflux of acid from stomach to the esophagus. This drug works by blocking the H2 receptors in the stomach and inhibiting gastric acid secretion. By blocking the H2 receptor in the stomach, it actually inhibits the secretion of acid into the stomach and therefore the total amount of acid in the stomach decreases.
It can also be used for Allergic Urticaria, Duodenal Ulcer, Duodenal Ulcer Prophylaxis, Erosive Esophagitis, GERD, Indigestion, Pathological Hyper secretory Conditions, Peptic Ulcer, Stomach Ulcer, Upper GI Hemorrhage, Urticaria, Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome. So basically any disease which is related to or is caused by excessive amount or excessive production of acid in the stomach can be cured by the use of famotidine.
There problems basically and most commonly include ulcers such as gastric or duodenal ulcers and other diseases which may result in erosion of stomach wall. So famotidine causes inhibition of acid production and therefore can be used for any disease related to excessive acid in stomach.
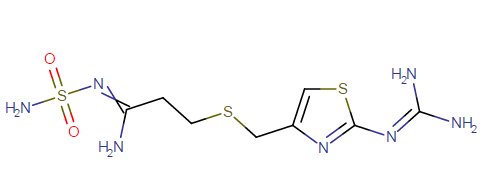
Famotidine Molecular formula and weight:
Molecular formula: C8H15N7O2S3
It contains 8 atoms of carbon, 15 hydrogen, 7 nitrogen, 2oxygen and 3 sulfur atoms.
Famotidine molecular formula, and 3D view are given below.
Molecular weight: 337.449 g/mol
Famotidine drug class:
This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2,4-disubstituted thiazoles. These are compounds containing a thiazole ring substituted at the positions 2 and 3.
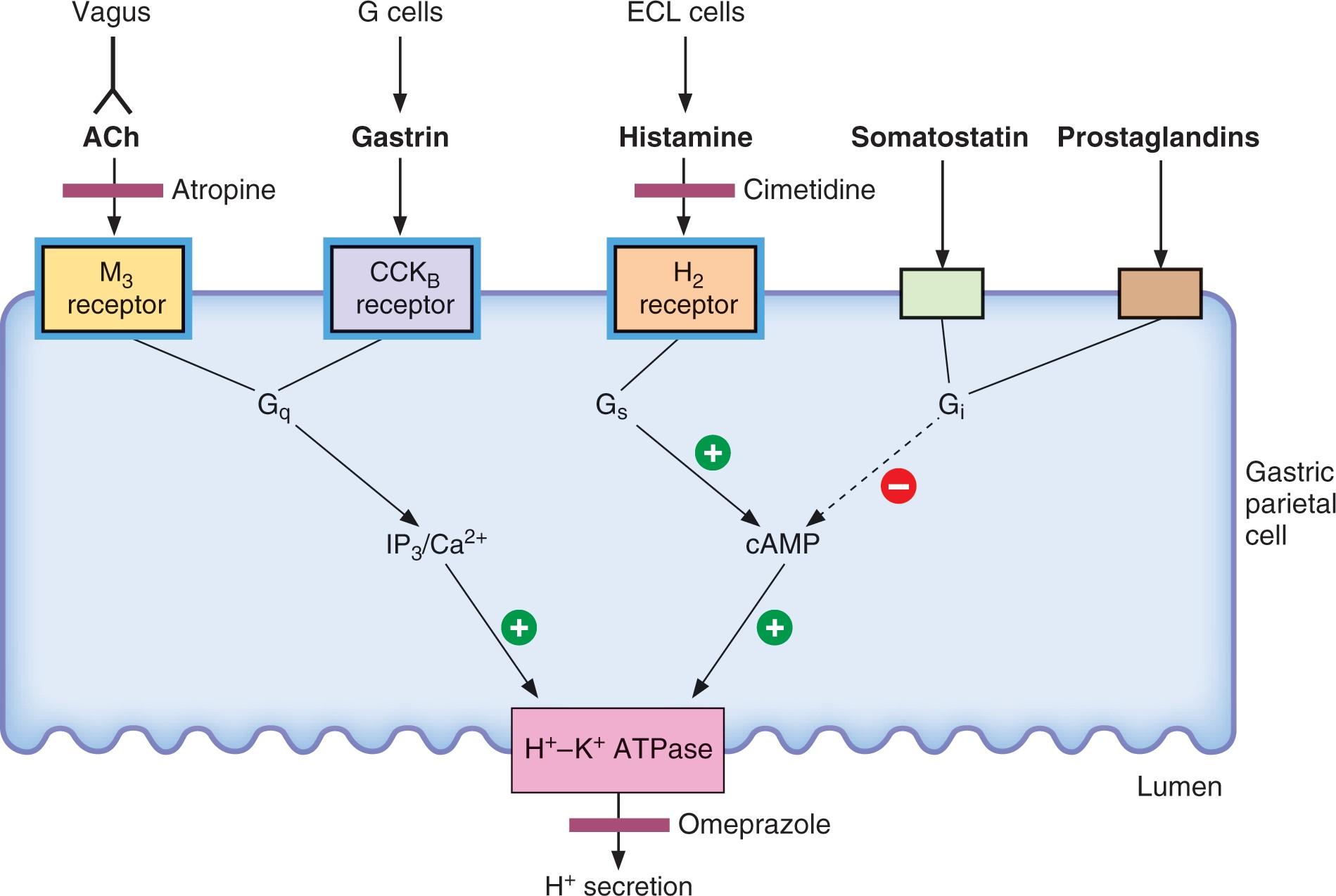
How famotidine works in the body?
Famotidine inhibits the acid secretion in stomach by blocking the H2 receptors in the stomach. Actually the H2 receptors, when activated by histamine, cause the release of acid from the stomach. Famotidine blocks the H2 receptors and thus don’t allow histamine to attach to the receptor, hence there is no acid production from the stomach.
There is one more important aspect of famotidine that it blocks the H2 receptor competitively and therefore is a strong antagonist of histamine receptors in the gut. Famotidine can be taken orally or intravenously, it has low bioavailability i.e. 40-45%. If taken orally, it gets metabolized in the liver and then after its metabolism in the liver, it starts performing its action. Famotidine starts its action in 15-60 minutes after taking it.
Therefore for people using it for the cure of ulcers, it is advised to take this drug at least 1 hour before the meal. Acid production in stomach is very high during night time therefore the patients are also advised to take this medicine before sleeping at night to reduce the amount of acid produced overnight and therefore preventing erosion of stomach wall especially at ulcerated areas of the stomach.
Famotidine brand names
Famotidine is available by the following brand names.
Pepcid, Pepcid AC, Acid reducer original strength, Acid Reducer Maximum Strength. Acid control, Acid Controller Maximum Strength, Acid Controller Original Strength, Acid Reducer Maximum Strength, Acid Reducer Original Strength, Acid Reducer-Famotidine, Fluxid, Heartburn Relief, Heartburn Relief Maximum Strength, Mylanta AR, Pepcid, Pepcid AC, Pepcid AC Chewable Tablets, Pepcid AC Maximum Strength, Pepcid AC Maximum Strength Tablets, Pepcid Oral Suspension, Pepcid RPD.
Famotidine indications
Most common indications of this drug are Allergic Urticaria, Duodenal Ulcer, Duodenal Ulcer Prophylaxis, Erosive Esophagitis, GERD, Indigestion, Pathological Hyper secretory Conditions, Peptic Ulcer, Stomach Ulcer, Upper GI Hemorrhage, Urticaria, Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome.
Other uses include the following.
- It can be used for Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer.
- Famotidine can be used for Maintenance therapy for duodenal ulcer patients at reduced dosage after healing of an active ulcer
- It can be used for Short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer. Most adult patients heal within 6 weeks or periods of more than 8 weeks.
- This drug can be used for ulcers and other diseases produced by excessive acid production in stomach such as GERD and also those diseases and ulcers which cause erosion of the gastric wall. These erosive areas can lead to further infections and diseases which maybe long-term.
- It can be used for the Treatment of pathological hyper secretory conditions (e.g., Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, multiple endocrine adenomas).
Famotidine for Helicobacter pylori eradication:
A triple course therapy is considered gold for the eradication of H.Pylori. This triple course includes an acid inhibitor with clarithromycin and metronidazole. the ideal course if of one week with the doses of the drugs as follows:
famotidine 80 mg b.d., clarithromycin 250 mg b.d. and metronidazole 500 mg b.d.
This regimen is the almost always successful for the eradication of the bacteria. The famotidine causes the suppression of acid secretion and the antibiotics eradicate the bacteria.
However the mechanisms causing the synergy between the antibiotics and acid secretion inhibitors are controversial. So basically, famotidine is used along with antibiotics to cure the infection caused by the Helicobacter pylori bacteria. The antibiotic part eradicates the bacteria whereas the famotidine inhibits acid secretion during that time, thus saving the stomach wall from ulcers and erosion.
Famotidine for gastric and intestinal ulcer disease
Famotidine is very effective for the treatment of gastric and intestinal ulcers. . This drug works by blocking the H2 receptors in the stomach and inhibiting gastric acid secretion. By blocking the H2 receptor in the stomach, it actually inhibits the secretion of acid into the stomach and therefore the total amount of acid in the stomach decreases.
It competitively blocks the H2 receptors and thus doesn’t allow the release of acid into the stomach. Therefore it is very useful especially for the prophylaxis of ulcer. By inhibiting the release of acid into the stomach it saves the wall of stomach from ulcers and erosions.
Famotidine is mostly used for prophylaxis of ulcers. These ulcers can be gastric or duodenal in nature. By inhibiting the release of acid into the stomach, famotidine saves the gastric mucosa from erosion.
Famotidine for Prevention of NSAID-induced peptic ulcers
Famotidine has no effect on NSAID induced peptic ulcers. NSAID induced ulcers can only be cured by stopping the use of the offending agent supplemented with sucralfate and proton pump inhibitors.
Famotidine is mostly used for gastro esophageal reflux disease of ulcers. It is use for both gastric and duodenal ulcers. The inhibition of acid secretion by famotidine results in the safety of gastric mucosa from ulcers and erosion of the gastric wall.
But famotidine is not used for the cure of ulcer induced by NSAID. Famotidine is mostly used for stress induced ulcers or for conditions like Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Famotidine for GERD
Famotidine is very useful in the treatment of GERD (Gastro esophageal reflux disease). In GERD, the patient experiences heartburn and constant irritation in the chest region especially the sub-sternal region due to the constant reflux of acid from stomach back into the esophagus. This causes extreme discomfort to the patient and therefore the only remedy is to decrease the amount of acid produced in the stomach.
So famotidine is then used for this purpose. It competitively inhibits the H2 receptors and inhibits acid secretion into the stomach. Therefore it is very effective in GERD as it decreases the total amount of acid produced therefore the frequency and amount of acid reflux decreases and the patient is cured of heart burn.
Famotidine for Zollinger–Ellison syndrome
In Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, small tumors form in the pancreas or small intestine. These are called gastrinomas and they secrete gastrin hormone which eventually results in the release of acid into the stomach. Actually the gastrin hormone stimulates the parietal cells of the gastric wall to secrete hydrogen ions into the cavity of stomach and then chloride combines with and results in the formation of acid in the stomach.
Therefore gastrin hormone causes the acid production in the stomach. Therefore the end result is hyper secretory activity of the stomach which causes acidity in stomach. Famotidine is very effective in the treatment of this syndrome as it competitively blocks the H2 receptors which inhibit the acid secretion into the stomach.
No hematologic, biochemical, or clinical toxicity occurs. Famotidine appears to be the histamine H2-receptor antagonist of choice in the treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Famotidine for indigestion and heartburn
Famotidine is indicated in the case of heartburn and other related diseases which are related to excessive acid secretion in the stomach. In GERD, the patient experiences heartburn and constant irritation in the chest region especially the sub-sternal region due to the constant reflux of acid from stomach back into the esophagus.
This causes extreme discomfort to the patient and therefore the only remedy is to decrease the amount of acid produced in the stomach. So famotidine is then used for this purpose. It competitively inhibits the H2 receptors and inhibits acid secretion into the stomach.
Heartburn results due to reflux of acid from the stomach back into the esophagus. The cause of this is unusual production of acid in stomach which causes this reflux. Famotidine blocks H2 receptors and inhibits the acid secretion and is therefore used effectively for the treatment of heartburn.
Famotidine dosage forms and strengths
Injection solution
-10mg/mL
-0.4mg/mL
Oral suspension
-40mg/5mL
Tablet
-10mg
-20mg
-40mg
Tablet, chewable
-10mg
-20mg
Famotidine dosage for different indications:
When taken orally, famotidine gets metabolized in the liver and then after its metabolism in the liver, it starts performing its action. Famotidine starts its action in 15-60 minutes after taking it.
Therefore for people using it for the cure of ulcers, it is advised to take this drug at least 1 hour before the meal. Acid production in stomach is very high during night time therefore the patients are also advised to take this medicine before sleeping at night to reduce the amount of acid produced overnight and therefore preventing erosion of stomach wall especially at ulcerated areas of the stomach.
Duodenal ulcer
Acute Therapy: adult oral dosage for active duodenal ulcer is 40 mg once a day at bedtime. Most patients heal within 4 weeks. Maintenance Therapy for duodenal ulcer is 20 mg once a day at bedtime or adults and in the form of oral dose.
Benign gastric ulcer :
Acute Therapy: The recommended adult oral dosage for active benign gastric ulcer is 40 mg once a day at bedtime.
GERD :
Oral dose which is recommended is up to 20mg for almost 6 weeks. This also depends on the condition of ulcerated gastric walls or the severity of GERD.
Pediatric dose: if the age is <1 year of age: Gastro esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – 0.5 mg/kg/dose of famotidine in the form of oral suspension for up to 8 weeks once daily.
If the patients age is < 3 months of age and 0.5 mg/kg/ then the dose should be twice daily. If the patients age is 3 months to < 1 year of age. It is very important that patients should also be receiving thickened feedings.
Esophagitis:
The oral dosage is 20-40 mg and is given for 12 weeks in the cases of GERD, gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers and other diseases causing erosion of the gastric wall. Dosage may also vary according the condition of the gastric wall and the severity of GERD.
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome:
In patients with pathological hyper secretory conditions, dosage varies with the individual patient. The recommended adult oral starting dose for pathological hyper secretory conditions is 20 mg q 6 h. In some patients, a higher starting dose may be required.
Antacids may be given concomitantly if needed.
Famotidine highest dose
For gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD), the maximum dose is 40 mg. per day. For esophagitis, the maximum dose is 80 mg. per day. For Zollinger-Ellison, the maximum dose is as much as 800 mg. per day.
Famotidine Side effects:
Side effects of Famotidine are not common but the may include the following
Rare
- Bleeding gums
- Blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin
- Blood in the urine or stools
- Bloody, black, or tarry stools
- Chest pain
- Chills
- Cough or hoarseness
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Fever with or without chills
- General feeling of tiredness or weakness
- High fever
- Itching
- Joint or muscle pain
- Lower back or side pain
- Painful or difficult urination
- Pale skin
- Pinpoint red spots on the skin
- Red, irritated eyes
- Red skin lesions, often with a purple center
- Shortness of breath
- Sore throat
- Sores, ulcers, or white spots on the lips or in the mouth
- Swollen glands
- Unusual bleeding or bruising
- Unusual tiredness or weakness
- Incidence not known:
- Abdominal or stomach pain
- Anxiety
- Burning, crawling, itching, numbness, prickling, “pins and needles”, or tingling feelings
- Clay-colored stools
- Dark urine
- Depression
- Difficulty with breathing
- difficulty with swallowing
- dizziness
- dry mouth
- fainting
- false sense of well-being
- fast, irregular, pounding, or racing heartbeat or pulse
- headache
- hives
- hyperventilation
- irritability
- large, hive-like swelling on the face, eyelids, lips, tongue, throat, hands, legs, feet, or sex organs
- loss of appetite
- loss of bladder control
- loss of consciousness
- mood swings
- nausea
- nervousness
- noisy breathing
- personality changes
- puffiness or swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes, face, lips, or tongue
- rash
- restlessness
- seizures
- shaking
- skin rash
- swelling around the eyes
- tightness in the chest
- total body jerking
- trouble with sleeping
- troubled with breathing
- unpleasant breath odor
- vision changes
- vomiting of blood
- wheezing
- yellow eyes or skin
Minor Side Effects
Some side effects are very minor and the patient is not bothered with them .The side effects vanish during the therapy with. The physician may also be able to provide some tactics to overcome the side effects as different side effects may need different solutions.
The much less common side effects include the following
- Difficulty in passing stools
- Soreness of breasts in both males and females.
- Incidences which are not knows yet include:
- Stomach problems
- Skin blemishes
- Unpleasant taste
- Continuous irritating noise in the ears.
- Decrease in libio
- Difficulty in movement
- Dryness of skin
- Abnormal fear
- Loss of hair
- Thinning of hair
- Loss of hearing
- Erection problems
- mood or mental changes
- muscle cramps
- muscle stiffness
- loss of sexual activity
- pimples
- redness of the skin
- redness of the white part of the eyes
- seeing, hearing, or feeling things that are not there
- sleeplessness
- unable to sleep
- weight loss
Famotidine overdose:
- oral 2000mg\kg is lethal
- Intravenous 300mg\kg
How to take Famotidine?
It comes as a tablet and also as a suspension. It is usually taken 15-60 minutes before meals and at bedtime. It is usually taken 2-4 times a day. If it is being taken as suspension, then make sure to shake the liquid well for 10 seconds before taking it. If it is being taken in the form of tablet, then swallow it with a glass of water. Milk is not recommended with this. Do not take over the counter tablet for longer than 2 weeks.
How long does it take for Famotidine to work?
Famotidine, an H2 antagonist can be taken orally or intravenously, it has low bioavailability i.e. 40-45%. If taken orally, it gets metabolized in the liver and then after its metabolism in the liver, it starts performing its action. Famotidine starts its action in 15-60 minutes after taking it. Therefore for people using it for the cure of ulcers, it is advised to take this drug at least 1 hour before the meal.
Acid production in stomach is very high during night time therefore the patients are also advised to take this medicine before sleeping at night to reduce the amount of acid produced overnight and therefore preventing erosion of stomach wall especially at ulcerated areas of the stomach.
It usually takes about 15-60 minutes for famotidine to work but maximum effect occurs in 1-3 hours. In case of GERD of heartburn, take famotidine almost 60 minutes before the meal so it sets into action. In case of ulcers, this drug needs to be taken for 2 weeks.
Can I abrupt Famotidine therapy suddenly?
Famotidine can be abrupted suddenly because it is a reversible blocker.
Can Famotidine cause withdrawal effects?
Withdrawal effects are most commonly seen in males aged between 40-49 years and have been using the drug for at least one month or more. Generally these effects are not observed. These are very rare to be observed. Mostly famotidine has no effects if it is intake is abruptly stopped.
Precautions and warnings during Famotidine use
- If the patients are aged between 18 and 60 and has no other conditions and are not using any other drugs, then following side effects maybe experienced.
- Diarrhea and constipation associated with headache may also be seen.
- People who have the following issues may experience more effects than the others.
- Heart diseases, liver problems, kidney problems and seizures.
Famotidine Pregnancy warnings
In case of pregnancy, use only if clearly needed. This drug is able to cross the placental membrane but until now there have been no incidences of teratogenic effects. AU TGA pregnancy category: B1. US FDA pregnancy category: Loratadine is not formally assigned to a pregnancy category.
Famotidine Breastfeeding warnings
The use of this drug in breast feeding is still controversial. Mostly it is recommended that during breastfeeding, either the drug should be stopped or breast feeding should be stopped
How long does Famotidine work?
Usually the Effect lasts for 10 to 12 hours after a single dose. Usually this drug is used for around one month for acid peptic diseases.
How long does Famotidine stay in your system, urine, blood, saliva?
Famotidine would be eliminated from the system in around 36-48 hours after stopping it. however if there are side effects due to this drug, then it will take 3-4 days for the side effects to disappear.
Can patients with renal disease take Famotidine safely?
In patients with moderate, (if creatinine clearance is 50ml per minute or if there is severe creatinine clearance <10 mL/min, longer intervals between doses or lower doses have to be used to adjust for the longer elimination half-life of famotidine.
Can patients with liver disease take Famotidine safely?
The effects of famotidine on liver have not been proven to be significant. in some rare cases, there have been reports of elevated serum ALT levels. In these cases, onset has been observed after 1 to 14 weeks and the pattern of elevated enzymes has been typically hepatocellular.
Famotidine absorption, metabolism and elimination:
When famotidine is taken orally, it is incompletely absorbed and its bioavailability is 40-45% only. Its first pass metabolism is very low and minimal. Fifteen to twenty percent of famotidine in the body in plasma is protein bound.
Its elimination half-life is 2.5-3.5 hours. Famotidine is eliminated by renal , which is (65 to 70%) and metabolic, which is (30 to 35%) routes. 30% of oral dose and 70% of IV dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged compound.
Can I drink alcohol while taking Famotidine?
Drinking alcohol while taking famotidine can be very dangerous as it can worsen the condition of stomach. This can increase the erosive areas of stomach or duodenum due to ulcers.
Can I take Famotidine with Warfarin?
Warfarin is metabolized by cytochrome p450 and any drug which alters the effect of cyt. p450 will result in disturbances when taken with warfarin. Famotidine has no effect on cyt.p450. Since there are no direct interactions between these two drugs, they can be taken together safely.
Can I take Famotidine with diazepam?
Diazepam is metabolized by cytochrome p450 and any drug which alters the effect of cyt. p450 will result in disturbances when taken with diazepam. Famotidine has no effect on cyt.p450 so it can be taken with diazepam.
Can I take Famotidine with antacids?
Famotidine is shown to improve its results when used with antacids because the antacids are also helpful in ulcers and GERD as they neutralize the acid of the stomach therefore these can be used with famotidine.
Can I take famotidine and omeprazole or other IPP together?
Yes, taking famotidine with other PPI like omeprazole is very beneficial. Studies have shown that the effect of famotidine increases and the therapeutic effect of both drug increases. The combination of famotidine with other PPIs is quite useful in GERD and ulcers and is much more effective than the single drug therapy.
Difference between famotidine and ranitidine
Famotidine which is an H2-receptor antagonist with a thiazole nucleus is approximately 7.5 times more powerful than ranitidine. Therapeutic trials indicate that famotidine 20 mg or 40 mg at night time before sleep is as effective as standard doses of cimetidine and ranitidine for healing duodenal ulcers.
Like ranitidine, famotidine does not have antiandregenic effects or substantially inhibit the hepatic metabolism of drugs. Because of its increased anti secretory potency and lack of ant androgenic effects at higher doses, famotidine may be the H2-receptor antagonist of choice in treating Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Difference between famotidine and omeprazole
Famotidine is and H2 blocker whereas omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor. Famotidine stops the acid production by blocking H2 receptors whereas omeprazole stops acid production by blocking the proton pump in the stomach and therefore stopping the movement of hydrogen ion. Famotidine is basically used for heartburn and zollinger ellison syndrome whereas omeprazole is mostly used for ulcers.
Can famotidine be bought as OTC? Difference between OTC and prescribed famotidine
Yes, famotidine is available as an OTC drug in 20mmg form. This 20mg OTC should be taken not more than twice daily. It should be taken at least one hour before meal and at bed time. OTC drug is available in mostly 10mg or 20mg form whereas prescribed drug is available in 40mg form. Also, if the doctor has prescribed, famotidine can be taken up to 4 times a day.
Can famotidine cause a cancer?
There has been no incidence of cancer linked to the use of famotidine. Therefore it can be safely said that famotidine does not cause cancer. Rather famotidine is used to cure Zollinger ellison which is a case of carcinoma.
Can children safely use famotidine?
Yes, the safe dose for children is 0.5 mg\kg for children. Maximum dose should never exceed 40mg\day.
Can you give famotidine to the dogs or cats?
Famotidine is very effective for the treatment of gastric and intestinal ulcers. . This drug works by blocking the H2 receptors in the stomach and inhibiting gastric acid secretion. By blocking the H2 receptor in the stomach, it actually inhibits the secretion of acid into the stomach and therefore the total amount of acid in the stomach decreases.
It competitively blocks the H2 receptors and thus doesn’t allow the release of acid into the stomach. Therefore it is very useful especially for the prophylaxis of ulcer. By inhibiting the release of acid into the stomach it saves the wall of stomach from ulcers and erosions.
Famotidine is mostly used for prophylaxis of ulcers. These ulcers can be gastric or duodenal in nature. By inhibiting the release of acid into the stomach, famotidine saves the gastric mucosa from erosion.
Famotidine can be used for cats and dogs to reduce stomach acid production. Famotidine works in animals the same way it works in humans. It is FDA approved. The dosage for dogs and cats is 0.25 to 0.5 mg per pound (0.5 to 1.0 mg/kg) every 12 to 24 hours.
“Is lansoprazole (Prevacid) or omeprazole (Prilosec) same thing?“
“Difference Between Omeprazole and Esomeprazole“
“Can zanaflex cause heartburn?“