Contents
- What is febuxostat?
- Febuxostat molecular structure, weight, formula, IUPAC name and drug class
- What is the mechanism of action of febuxostat?
- Pharmacokinetics of febuxostat
- How long febuxostat stays in your system?
- What are the indications of febuxostat?
- What are the brand names of febuxostat?
- What are the side effects of febuxostat?
- What are the contraindications of febuxostat?
- Can febuxostat be taken in pregnancy?
- Can febuxostat be taken by nursing mother?
- What are the warning or precautions should be taken while using febuxostat?
- Can febuxostat be taken with alcohol?
- Can febuxostat increase the cardiovascular risk?
- Can febuxostat be given to the patients with hyperuricemia?
- What is the duration of treatment of febuxostat?
- What is the dose of febuxostat for gout?
- Can febuxostat be given for kidney stones?
- Can febuxostat be given to a patient with renal dysfunction?
- Can febuxostat be given to the patient with hepatic impairment?
- Can febuxostat be given with azathioprine?
- Can febuxostat be taken with theophylline?
- Can febuxostat be taken with efavirenz?
- Can febuxostat be taken with dyphylline?
- Can febuxostat be taken with leflunomide?
- Can febuxostat be taken with naltrexone?
- Can febuxostat be taken with carbamazepine?
- Can febuxostat be taken with black cohosh?
- Can febuxostat cause skin rashes?
What is febuxostat?
Febuxostat is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor which is used in the treatment of gout and hyperuricemia and also used for the chronic management of this condition.
For the treatment of asymptomatic hyperuricemia, febuxostat is not recommended. Febuxostat was approved by the FDA in the year 2009 and is marketed under the brand name Uloric by Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
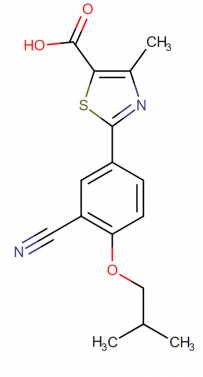
Febuxostat molecular structure, weight, formula, IUPAC name and drug class
The chemical formula of febuxostat: C16H16N2O3S
The molecular weight of febuxostat: 316.375 g/mol
IUPAC name of febuxostat: 2-[3-cyano-4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid
The drug class: Febuxostat comes under the class of organic compounds known as thiazolecarboxylic acids and derivatives. These are the compounds which contain a thiazole ring which bears a carboxylic acid group (a derivative thereof).
The molecular structure of febuxostat:
What is the mechanism of action of febuxostat?
Febuxostat reduces the serum uric acid, thereby achieves the therapeutic effect. Febuxostat does not inhibit the other enzymes which are involved in the synthesis of purine and pyrimidine. It also does not inhibit the metabolism at therapeutic concentrations.
Pharmacokinetics of febuxostat
Febuxostat is absorbed more than 49% when administered orally whereas the volume of distribution of febuxostat is 50 L approximately.
It shows around 99.2% protein binding. It is extensively metabolized by conjugation and oxidation.
It undergoes conjugation via uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase enzymes and undergoes oxidation via cytochrome P450 enzymes.
It is eliminated primarily by both hepatic and renal pathways. The elimination half-life of febuxostat is 5 to 8 hours.
How long febuxostat stays in your system?
The elimination half-life of febuxostat is 5 to 8 hours and the elimination of a drug equals to five times to that the elimination of the drug. Therefore it will be out of your system in 40 hours completely.
What are the indications of febuxostat?
Febuxostat is indicated for the management of hyperuricemia in patients with gout.
What are the brand names of febuxostat?
Febuxostat is available in market under various brand names, some common brand names are Uloric and Adenuric.
What are the side effects of febuxostat?
Febuxostat can cause some serious side effects, you should talk to your doctor immediately if see any of these side effects or if any side effect of febuxostat does not go away.
Some common side effects of febuxostat are:
- Nausea
- Mild dizziness
- Joint pain
- Joint stiffness or swelling
- Mild skin rash
Serious side effects of febuxostat are:
Tell your doctor right away if you experience any of the following serious side effects:
- Chest pain or heavy feeling in the chest
- Pain that spreads to shoulder or arm
- Nausea, sweating, tiredness
- Dizziness
- Fatigue, numbness (mainly on one side of the body)
- A headache (that may arise all of sudden)
- Confusion
- Balance, vision or speech problems
- Stomach pain
- Fever
- Anorexia (loss of appetite)
- Dark colored stools
- Yellowing of skin and eyes
What are the contraindications of febuxostat?
One should strictly avoid taking some medications such as mercaptopurine or azathioprine with febuxostat as it can cause severe interactions (please see drug interactions).
One who have hypersensitivity to febuxostat or any of its formulation ingredients, should not take this medication.
Can febuxostat be taken in pregnancy?
Febuxostat comes under the pregnancy category C which means there are no data for febuxostat studies in human during pregnancy and as per animal studies this medication showed defects in newborn.
Therefore women who are pregnant or tried to be pregnant should not take this medication. Also, the use of febuxostat is not recommended unless the benefit outweighs the risk to the fetus.
Can febuxostat be taken by nursing mother?
The use of febuxostat by a nursing mother is generally not recommended. If necessary, one should use this medication with caution as this medication is known to get excreted in human milk. However, the effects of this medication in nursing medication is unknown.
What are the warning or precautions should be taken while using febuxostat?
Acute gout: At the beginning of the treatment of gout, febuxostat can increase the frequency of acute gout attacks, which is also known as gout flare.
In order to manage this condition, one should use prophylaxis with NSAIDs or colchicine along with febuxostat from the initial stage.
Cardiovascular events: In patients receiving febuxostat, the rate of cardiovascular events such as cardiovascular deaths, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke was higher as compared to the patients receiving allopurinol.
One should monitor the patient for signs and symptoms of the myocardial infarction and stroke.
Hepatic effects: Febuxostat can result in elevated serum transaminase concentrations. Therefore one should consider the liver function tests during therapy such as at month 2 and 4 of the therapy and then periodically.
Can febuxostat be taken with alcohol?
Alcohol can increase the levels of urate in the blood, however, it does not interact with febuxostat. The limited use of alcohol while taking febuxostat is advised.
Try to keep the recommended limits for alcohol such as 14 units per week, as part of the general treatment of gout. One should consider having alcohol free days but without saving up the units for drinking in one go.
Can febuxostat increase the cardiovascular risk?
Antihyperuricemic agents such as febuxostat and lesinurad were reported to be associated with the major adverse cardiovascular events such as cardiovascular death, non-fatal strokes and, non-fatal myocardial infarctions.
The patients with cardiovascular disease should practice caution while taking febuxostat. The patient should be monitored for signs and symptoms of myocardial infarction.
Can febuxostat be given to the patients with hyperuricemia?
No studies with febuxostat or lesinurad have been conducted in patients with secondary hyperuricemia (including organ transplant recipients).
The use of these drugs is contraindicated in patients where the uric acid formation is greatly increased, such as patients with malignant disease, tumor lysis syndrome or Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
What is the duration of treatment of febuxostat?
The dose of febuxostat is 80 mg which can be increased to 120 mg after 2 to 4 weeks if serum urate levels have not reached to <6mg/dl.
The target level of serum urate level to be achieved is <6 mg/dl. Prophylaxis treatments such as NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents) or colchicine should be used for first 6 months in order to treat acute gout attacks.
What is the dose of febuxostat for gout?
In patients who do not achieve a serum uric acid level less than 6 mg/dl, febuxostat oral should be started at 40 mg once daily and can be increased to 80 mg n order to achieve the desired level of serum uric acid after 2 weeks.
If clinically indicated, the dose of febuxostat can be increased to 120 mg once daily.
Can febuxostat be given for kidney stones?
Febuxostat is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor which is effective in lowering the serum urate concentration and uric acid excretion via urine in a patient suffering from gout.
A study was done on febuxostat and allopurinol for checking their efficacy in reducing 24-hour urinary uric acid excretion and also in preventing the stone growth or even new stone formation.
As a result, the urinary uric acid excretion was found higher in case of febuxostat as compared to the allopurinol.
However, there was no significant change was noticed in the stone size, stone number, or renal function. With any of the drug, no new safety was noted in this study.
Therefore in stone formers with higher urinary excretion, febuxostat can lower the 24-hour urinary uric acid after 6 months of treatment. However, after a 6 months period, there was no change in stone size or number of kidney stones.
Can febuxostat be given to a patient with renal dysfunction?
Patient with impaired renal function or renal dysfunction should use this medication with precaution, as there is no sufficient data given on the use of febuxostat in such patients. In patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, no dose adjustment is required.
Can febuxostat be given to the patient with hepatic impairment?
Just like renal dysfunction studies, there is no sufficient data given about he efficacy of febuxostat in hepatic impaired patients, therefore precaution is required in such patients. In patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, no dose adjustment is necessary.
Can febuxostat be given with azathioprine?
The concurrent administration of azathioprine and febuxostat is highly contraindicated.
The concentration of xanthine oxidase substrates (such as azathioprine, mercaptopurine, and theophylline) can be increased due to co-administration of febuxostat. Also, it can lead to toxicity. Febuxostat is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
The mechanism and studies have been studied with allopurinol (another xanthine oxidase inhibitor) instead of febuxostat, still one should consider the similar effects of allopurinol before taking these medications concurrently.
Concurrent use of xanthine oxidase inhibitor (febuxostat and allopurinol) along with mercaptopurine or azathioprine can result in severe bone marrow suppression and other toxicities.
Allopurinol at higher doses (600 mg/day or more) can increase the theophylline concentrations when co-administered with azathioprine or mercaptopurine.
Therefore one should not use febuxostat along with mercaptopurine, azathioprine or theophylline.
Can febuxostat be taken with theophylline?
The pharmacokinetics of the febuxostat can be interfered due to co-administration of theophylline. The mechanism behind this is known to be the inhibition of the xanthine oxidase.
Co-administration of the theophylline and febuxostat can result in 6% increased peak plasma concentrations of the theophylline along with 6.5% increase in systemic exposure (AUC). However, such changes were not considered significant.
However, as per the study, the urinary excretion of 1-methylxanthine (a major metabolite of theophylline) was increased up to 400 fold. The safety of this metabolite for long-term exposure has not been evaluated.
Therefore when co-administered with febuxostat, there is no need for dose adjustment of theophylline. However, one should practice the precaution because the safety of the theophylline metabolite exposure (for the long term) is unknown.
Can febuxostat be taken with efavirenz?
When febuxostat is co-administered with efavirenz, it can cause hepatotoxicity which can increase the risk of liver injury. During postmarketing use, efavirenz was reported to be associated with hepatotoxicity.
Management of interaction: The risk of hepatic injury should be considered when efavirenz is used in combination with other agents that are potentially hepatotoxic (e.g., acetaminophen; alcohol; androgens and anabolic steroids; antituberculous agents; azole antifungal agents; ACE inhibitors; cyclosporine (high dosages); disulfiram; endothelin receptor antagonists; interferons; ketolide and macrolide antibiotics; kinase inhibitors; minocycline; nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents; other HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors; proteasome inhibitors; retinoids; sulfonamides; tamoxifen; thiazolidinediones; tolvaptan; vincristine; zileuton; anticonvulsants such as carbamazepine, hydantoins, felbamate, and valproic acid; lipid-lowering medications such as fenofibrate, lomitapide, mipomersen, niacin, and statins; herbals and nutritional supplements such as black cohosh, chaparral, comfrey, DHEA, kava, pennyroyal oil, and red yeast rice).
Patients should be advised to seek medical attention if they experience potential signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity such as fever, rash, itching, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, malaise, right upper quadrant pain, dark urine, pale stools, and jaundice.
Monitoring of liver function tests should occur before and during treatment, especially in patients with underlying hepatic disease (including hepatitis B or C coinfection) or marked transaminase elevations.
The benefit of continued therapy with efavirenz should be considered against the unknown risks of significant liver toxicity in patients who develop persistent elevations of serum transaminases greater than five times the upper limit of normal.
Can febuxostat be taken with dyphylline?
Before using febuxostat along with dyphylline, you should consider talking to your doctor. The way by which dyphylline broke down in the body get changed when it is administered with febuxostat.
This can lead to enhanced levels of a byproduct of dyphylline. Currently, the potential effects (if any) of having increased levels of the byproduct are unknown.
In case you experience increased side effects, contact your doctor immediately. In case you use any other medications such as herbs and vitamins, let your doctor know about them too. You should also not stop this medication without prior consultation with your doctor.
Can febuxostat be taken with leflunomide?
Leflunomide is known to cause liver problems, and if it is concomitantly used with other drugs that may also affect the liver such as febuxostat, the risk may be increased.
Because leflunomide can stay in your blood for a prolonged period after the last dose, interactions with other drugs may occur for some time even after you have stopped taking it.
Patients should also avoid or limit the use of alcohol while being treated with these medications. Call your doctor immediately if you have fever, chills, joint pain or swelling, unusual bleeding or bruising, skin rash, itching, loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark colored urine, light colored stools, and/or yellowing of the skin or eyes, as these may be signs and symptoms of liver damage.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns. It is important to tell your doctor about all other medications you use, including vitamins and herbs. Do not stop using any medications without first talking to your doctor.
Can febuxostat be taken with naltrexone?
Concomitatn use of naltrexone with drugs known to provoke hepatotoxicity such as febuxostat may potentiate the risk of liver injury.
Naltrexone, especially in larger than recommended doses (more than 50 mg/day), has been related with hepatitis, hepatocellular injury and elevations in liver transaminases and bilirubin.
Other potential causative etiologies identified include preexisting alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B and/or C infection, and concomitant usage of other hepatotoxic drugs.
Can febuxostat be taken with carbamazepine?
Potent inducers of UGT enzymes vmay increase the metabolism of febuxostat and decrease its therapeutic efficacy. Febuxostat undergoes extensive metabolism by both conjugation via UGT enzymes including UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7, and oxidation via cytochrome P450 enzymes.
The relative contribution of each isoenzyme and the clinical significance is unknown. Conversely, increased plasma levels of febuxostat may occur after a potent UGT inducer is discontinued.
Can febuxostat be taken with black cohosh?
Concomitant use of black cohosh (Cimicifuga racemosa rhizome) with febuxostat may induce the risk of hepatotoxicity and theoretically increase the risk of liver injury.
Black cohosh has been suspected in rare cases of liver toxicity ranging from abnormal liver function tests and jaundice to various forms of hepatitis and hepatic failure requiring transplantation.
The onset has typically been within the first 3 months after initiation of black cohosh. Although approximately half of the cases resulted in hospitalization, most improved or resolved following discontinuation of the product.
Many of the cases were not well documented with respect to the specific herbal formulation and dose used or timeframe of treatment in relation to onset of reaction, or they were complicated by multiple confounding factors.
Some of the cases also involved products containing multiple herbal or other medicinal substances.
Can febuxostat cause skin rashes?
Febuxostat theoretically can reduce the cross-allergenicity because it has a chemical structure different from that of allopurinol.
The structural differences between the two allow the febuxostat for consideration in a patient who has a great need for allopurinol but also had a very severe allergic reaction.
As the study was done on a very small number of patients, so if the patients are to be treated with febuxostat, a close observation is needed.
“What is the best medicine for overactive bladder?”