Contents
- What is Fenofibrate
- Fenofibrate brand name
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)
- What does Fenofibrate do
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
- Chemical information of the drug
- Fenofibrate dosage strengths
- How does Fenofibrate work
- What are the recommended doses of Fenofibrate
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Fenofibrate
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Fenofibrate
- How to take Fenofibrate
- How to store the drug
- How to dispose Fenofibrate
- Does Fenofibrate has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies
- Other uses of the drug
- What special dietary precautions should I follow
- What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Fenofibrate
- Fenofibrate side effects
- Fenofibrate overdose
- Fenofibrate missed dose
- Fenofibrate drug interactions
- Does Fenofibrate have any interaction with diseases
What is Fenofibrate
- Fenofibrate is a synthetic compound, which aids to reduce blood cholesterol and triglycerides (fatty acids) levels.
Fenofibrate brand name
- The drug is available under generic name Fenofibrate and brand names TriCor, Antara, Lofibra, and Lipofen.
- The Fenofibrate is marketed by Lupin Pharma, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Northwind Pharmaceuticals, H2 Pharma and Carilion Material Management.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)
- Fenofibrate is a synthetic (man-made) pharmaceutical antihyperlipidemic agent.
What does Fenofibrate do
Why is this medication prescribed?
- Fenofibrate is an anti-hyperlipidemic class of drug, which means it reduces the amount of fatty or lipid substances such as cholesterol and triglycerides.
- Usually, Fenofibrate is used in combination of low fat diet or exercise or other drugs as adjunctive therapy to reduce elevated total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, total triglycerides and triglyceride rich lipoprotein (VLDL) ( types of fatty acids which increase the risk of heart diseases) and to increase the amount of HDL (high-density lipoprotein; a type of fatty substance that decreases the risk of heart disease) in the blood.
- The drug is usually prescribed for adult patients with primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb) and hypertriglyceridemia (Fredrickson Types IV and V hyperlipidemia).
- Fenofibric acid is the active metabolite ingredient of Fenofibrate responsible for enhancing the natural processes that expel cholesterol from the body.
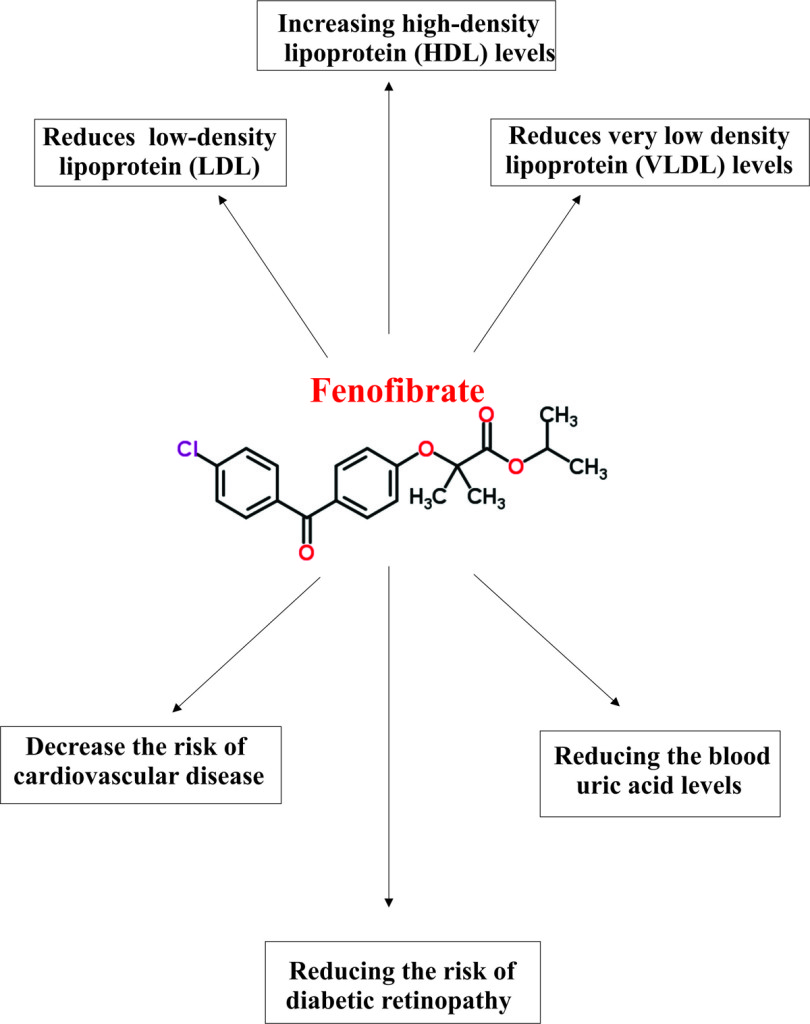
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
Fenofibrate chemically belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzophenones, a heterocyclic aromatic molecule which contains ketone attached to two phenyl groups. The detailed chemical classification of Fenofibrate is as follows.
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
| Sub Class | Benzophenones |
| Direct Parent | Benzophenones |
Chemical information of the drug
- Fenofibrate is a synthetic pharmaceutical benzophenones compound named as propan-2-yl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate.
- The compound has molecular formula C20H21ClO4 and the molecular weight of 360.83 g/mol.
- The melting point of Fenofibrate is 79-82°C.
- Fenofibrate is a white solid; granular or powder and practically insoluble in water.
- It is slightly soluble in ethanol and methanol, while soluble in acetone, ether, benzene and chloroform.
- The maximal solubility of Fenofibrate in water is ~ 0.42 mg/L at 25 °C. It is synthesized from 4-chloro-4-hydroxybenzophenone.
Fenofibrate dosage strengths
- Fenofibrate is available for oral administration in tablet or a delayed release (long lasting) capsule form.
- Fenofibrate is available in two dosage strength of 48 mg and 145 mg.
- 48 mg tablet is yellow in colour and stamped with the “a” logo and code letter “FI”, while 145 mg tablet is imprinted with the “a” logo and code letter “FO”.
- Each tablet contains sodium lauryl sulfate, sucrose, lactose monohydrate, silicified microcrystalline cellulose colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, lecithin, microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium stearyl fumarate, titanium dioxide, talc, lecithin, and xanthan gum.
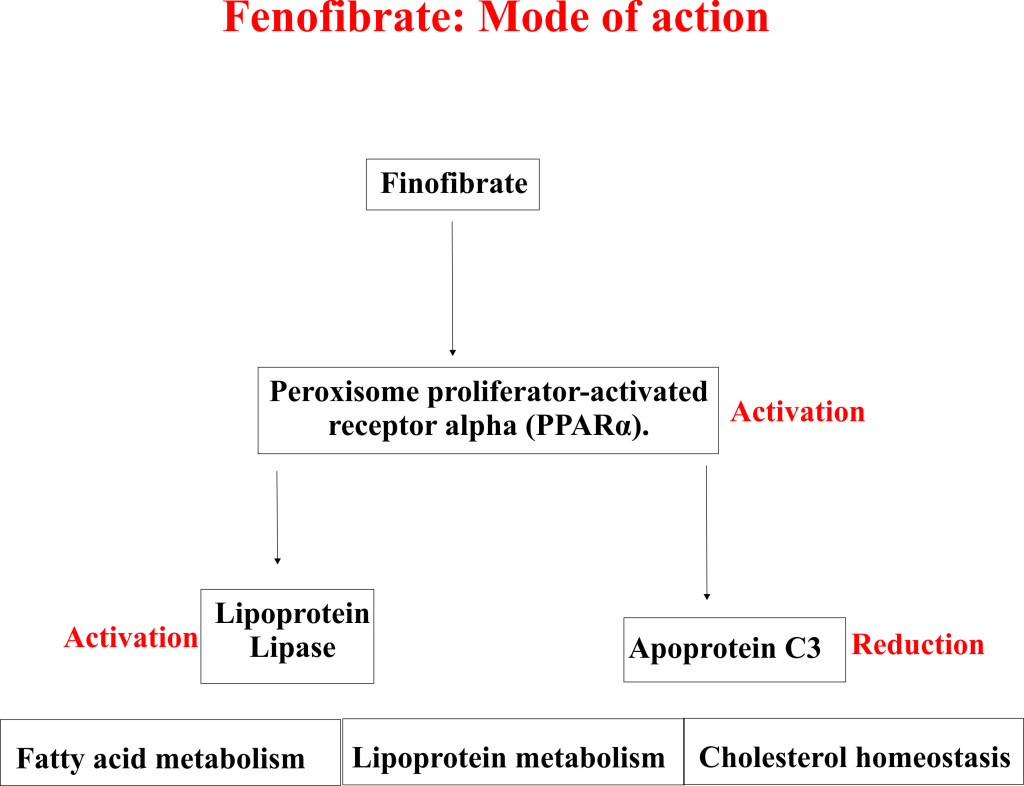
How does Fenofibrate work
How the medicine works (mode of action)?
Chemically Fenofibrate is made up of fenofibric acid linked to an isopropyl ester. The active moiety or component of Fenofibrate is fenofibric acid.
- Laboratory studies with animal models suggested that Fenofibrate acts through activation of a key protein known as peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α (PPARα).
- Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α (PPARα) principally regulates the fatty acid and lipoprotein metabolism.
- Fenofibrate lowers the blood cholesterol and other lipid levels by activating PPARα, which in turn activates lipoprotein lipase and reduces apoprotein C3.
- Active lipoprotein lipase and reduced apoprotein C3 cause dramatic degradation (lipolysis) and elimination of triglyceride-rich particles from plasma.
- Activation of PPARα also reduces very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) containing apoprotein B.
- Apart from this PPARα also enhances the synthesis of apoproteins AI, AII, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
What are the recommended doses of Fenofibrate
The Fenofibrate is available in tablet form and the dosage varies depending upon the diseases status.
The usual doses of Fenofibrate for adult patient with Hyperlipoproteinemia Type IIa (Elevated LDL) are as follows.
- Tricor (R): 145 mg (oral) once a day.
- Antara (R): 130 mg (oral) once a day.
- Lofibra (R) and others: 160 mg to 200 mg (oral) once a day with food
- Lipofen (R): 150 mg (oral) once a day with food
- Triglide (R): 160 mg (oral) once a day.
- Fenoglide (R): 120 mg (oral) once a day with food
- The usual doses of Fenofibrate for adult patient with Hyperlipoproteinemia Type IIb (Elevated LDL + VLDL) are as follows.
- Tricor (R): 145 mg (oral) once a day.
- Lofibra (R) and others: 160 mg to 200 mg (oral) once a day with food.
- Antara (R): 130 mg (oral) once a day.
- Triglide (R): 160 mg (oral) once a day.
- Lipofen (R): 150 mg (oral) once a day with food.
- Fenoglide (R): 120 mg (oral) once a day with food.
The usual doses of Fenofibrate for adult patient with Hyperlipoproteinemia Type IV (Elevated VLDL) are as follows.
- Tricor (R): 48 to 145 mg (oral) once a day.
- Lofibra (R) and others: 54 mg to 200 mg (oral) once a day with food.
- Antara (R): 43 mg to 130 mg (oral) once a day.
- Triglide (R): 50 mg to 160 mg (oral) once a day.
- Lipofen (R): 50 mg to 150 mg (oral) once a day with food.
- Fenoglide (R): 40 mg to 120 mg (oral) once a day with food.
- The usual doses of Fenofibrate for adult patient with Hyperlipoproteinemia Type V (Elevated Chylomicrons + VLDL) are as follows.
- Tricor (R): 48 to 145 mg (oral) once a day.
- Lofibra (R) and others: 54 mg to 200 mg (oral) once a day with food.
- Antara (R): 43 mg to 130 mg (oral) once a day.
- Triglide (R): 50 mg to 160 mg (oral) once a day.
- Lipofen (R): 50 mg to 150 mg (oral) once a day with food.
- Fenoglide (R): 40 mg to 120 mg (oral) once a day with food.
However, the represented dose schedule can vary according to patient response and can be changed on the basis of repeated lipid levels determination at 4 to 8 weeks interval. Treatment should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Fenofibrate
- The use of Fenofibrate is contraindicated in case of severe renal impairment as well as patient undergoing dialysis.
- The drug is also not recommended in patients with active liver disease or persistent liver dysfunction or abnormal function.
- The use of the drug is also restricted in patients who are hypersensitive to the Fenofibrate or fenofibric acid.
- In case of pre-existing gallbladder disease the Fenofibrate use is not recommended.
- The use of Fenofibrate has not been evaluated in case of hepatic impairment; however, it is necessary that the condition should be monitored very cautiously while using higher dosage.
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Fenofibrate is a prodrug, whose active chemical moiety is finofibric acid.
- Following consumption, Fenofibrate is converted into fenofibric acid (active constituent of Fenofibrate computable in thecirculation) by acid hydrolysis.
- Fenofibrate is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal. However, due to insoluble nature the absolute bioavailability of fenofibrate cannot be determined.
- Following administration the Fenofibrate is rapidly converted to fenofibric, which is subsequently conjugated with glucuronic acid.
- Pharmacokinetic studies with Fenofibrate have shown that following oral administration about 60 % of the drug appeared in the urine, while 25% was excreted in the feces.
- The peak plasma level of the drug appears within 6-8 hours following administration of the drug.
- The bioavaility of Fenofibrate is increased significantly to 35% under fed conditions as compared to fasting.
- The peak plasma level of drug is observed after 4 hours of drug administration allowing once daily dosing.
- Following absorption the majority (~90%) of the drug is protein bound to plasma.
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Fenofibrate
- The Fenofibrate is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: C.
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies, the use and safety of Fenofibrate in pregnant women is contraindicated and recommended only when potential benefit justifies the risk.
- Laboratory animal studies have shown maternal toxicity of Fenofibrate at higher doses.
- No adequate data is available on excretion of Fenofibrate into human breast milk. However, the use of drug is not recommended in nursing mothers.
Due these facts caution should be exercised when taking Fenofibrate during pregnancy.
How to take Fenofibrate
- Fenofibrate is available in delayed/sustained release capsule form (long lasting action) for oral administration by mouth.
- Fenofibrate sold under brand names Fenoglide, Lipofen, and Lofibra are prescribed with a meal, while other brands like Fibricor, antara, Tricor, Triglide, and Trilipix are usually prescribed with or without food.
- Since food significantly increases drug absorption it is usually recommended on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after eating a meal or snack) once a day.
- It is also recommended to take drug at almost the same time every day
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet and take Fenofibrate exactly as directed on leaflet or by your health care professional.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor. Since, your doctor may decrease the dose of Fenofibrate depending upon adverse side effects or medication response.
- If you have any queries about the drug immediately consult to your doctor to explain any part you do not understand.
How to store the drug
- Fenofibrate is stored at room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
- The container should be tightly closed and away from excess heat, direct sun light and reach of children.
- Do not freeze or store the medicine at extreme cold too.
How to dispose Fenofibrate
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used container.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
- Fenofibrate has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat medical complications such as primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb) and hypertriglyceridemia (Fredrickson Types IV and V hyperlipidemia).
Other uses of the drug
- Fenofibrate may also be used for other uses not listed here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more detailed information regarding its use.
What special dietary precautions should I follow
- It is generally recommended to avoid high fat/cholesterol diet and follow a routinely exercise regimen.
- Follow a routine diet as prescribed by your dietician and avoid spicy foods.
- For more details for additional dietary information please visit National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) website (http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/public/heart/chol/chol_tlc.pdf.).
What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Fenofibrate
- First of all inform your doctor if you are allergic to any fenofibrate products or any of the ingredients present in the fenofibrate product. Ask your pharmacist or check the prescription leaflet carefully for a list of the ingredients.
- It is advisable to discuss with your doctor and pharmacist about what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, and nutritional supplements you are taking or plan to take.
- Tell your doctor if you are being treated or have recently been treated with kidney, liver, or gall bladder disease.
- Inform your doctor if you are alcoholic and have diabetes or hypothyroidism.
- Inform your doctor if you are breastfeeding or pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding.
- Inform your doctor about the surgery you have undergone, including dental surgery.
Fenofibrate side effects
Long term controlled clinical trial studies with Fenofibrate suggested that it can cause side effects, which include:
- Mild stomach pain /constipation/ diarrhea
- Back pain, pain in arm and legs
- Headache
- Heartburn
Call immediately to your doctor in case of allergic reaction or if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away.
If case you experience any of these symptoms, consult your health care provider instantly.
Fenofibrate rarely can cause breakdown of skeletal muscles, which can cause kidney failure. If you are feeling symptoms like weakness, muscles pain, unusual tiredness, dark coloured urine and fever call immediately your physician. Other serious side effects that may be serious are as follows.
- Rashes, and hives
- pain in the upper back between the shoulder blades or under the right shoulder
- Stomach pain, particularly in the upper right part of the stomach
- Breathing problems like shortness of breath or pain while breathing
- Nausea and vomitting
- Blood in cough
- Peeling skin, swelling and redness
Stop taking medicine immediately if you are feeling such symptoms.
Fenofibrate overdose
- Overdose usually occurs when someone by mistake or deliberately takes more than the prescribed limit of this medication.
- There is no specific treatment for Fenofibrate overdose. In case of overdose, contact with your doctor or emergency room immediately. Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
Fenofibrate missed dose
What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule. Keep in mind to take the missed dose only on an empty stomach.
- Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind to not use a double dose to make up a missed dose.
Fenofibrate drug interactions
It has been observed that Fenofibrate may interact with or increase or decrease the effect of following drugs. Caution should be taken when co administrating the Fenofibrate with one of the following drugs.
- Anticoagulants (Coumarin): It has been observed that Fenofibrate potentiate the effectiveness of coumarin-type anticoagulant as measured by PT/INR test (prothrombin time test, used to monitor the effectiveness of the anticoagulant). Caution should be given when Fenofibrate is given in conjunction with coumarin anticoagulants. It is usually advisable to keep low dosage of anticoagulants to maintain the PT/INR at the desired level. Since high PT/INR may cause unexpected bleeding complications.
- Immunosuppressants: The primary route of Fenofibrate elimination from body is renal excretion. Therefore, it is not recommended for patients suffering from moderate to severe renal problems. Immunosuppessants (such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus) generally potentiate nephrotoxicity and decreases serum creatinine clearance. As a consequence, serum creatinine level rises and can cause deterioration of renal function. The benefits and risks of using Fenofibrate tablets in conjunction with immunosuppressants and other potentially nephrotoxic agents should be carefully considered under the professional supervision.
- Bile Acid Binding Resins: Bile acid binding resins bind with other drugs and thus impede the absorption of the drug, if used simultaneously. To avoid it, it is usually recommended to take Fenofibrate at least 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours after a bile acid binding resin consumption.
- Control trial and case studies suggests that co-administration of Fenofibrate with colchicines may cause myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, therefore caution should be taken when prescribing Fenofibrate with colchicine.
- Besides this, a large number of other drugs such as diuretics (water pills), hormonal contraceptives ( patches,birth control pills, implants, and injections), beta blockers, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (cholesterol-lowering agents) can also interact with Fenofibrate.
- This list do not comprises all the drugs that interact with Fenofibrate and there are many other drugs that can interact with Fenofibrate. If you start any new medication, first consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Does Fenofibrate have any interaction with diseases
It has been observed that following medical conditions (disease) may also interact with Fenofibrate:
- Hepatotoxicity, (biochemical abnormalities of liver function)
- Hepatitis (Hepatocellular, chronic active, as well as cholestatic) and, rarely, cirrhosis
- Liver disease or unexplained, persistent elevations of serum transaminases
Where can I get more information
Your pharmacist can provide more information about Fenofibrate.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- Fenofibrate is a PPAR-alpha agonist widely recommended for treatment of hypercholesterolemia, lipid abnormalities in patients with cardiovascular disease, including Type 2 diabetes and/or metabolic syndromes.
- Studies with Fenofibrate revealed that it reduces postprandial VLDL and LDL particle concentrations, oxidative stress and inflammatory response.
- Fenofibrate has very effective and promising results in preventing progression of diabetes-related microvascular complications as observed in Intervention for Event Lowering in Diabetes (FIELD) study.
- Recent studies have shown a growing interest in use of Fenofibrate in the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- The combination therapy involving the use of Fenofibrate/ Statin for optimising reduction in the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients suffering with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome is undergoing. Data are also awaited from the ongoing Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) study to assess the outcome benefits of this approach.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
- Fenofibrate: MedlinePlus Drug Information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a601052.html.
- Fenofibrate | C20H21ClO4 | ChemSpider. chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.3222.html.
- DrugBank: Fenofibrate (DB01039). www.drugbank.ca/drugs/db01039.
- Safety Information > Tricor (fenofibrate) tablets. fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/ucm342600.htm.
- Fenofibrate | C20H21ClO4 – PubChem. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/fenofibrate.
- The role of Fenofibrate in clinical practice. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17935056.
- Fenofibrate: a review of its use in primary dyslipidaemia, the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17209672.
- Fenofibrate: treatment of hyperlipidemia and beyond. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19018684.
Read about,
“Furosemide, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
“Warfarin, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
