Contents
- What is Furosemide
- Furosemide brand name
- Is Furosemide natural or synthetic
- What does Furosemide do
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
- Chemical information of the drug.
- Furosemide available strength
- How does Furosemide work
- Furosemide doses
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Furosemide
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Furosemide
- How to take Furosemide
- How to store Furosemide
- How to dispose the medicine
- Does Furosemide has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies
- Other uses of the drug.
- What special dietary precautions should I follow
- What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Furosemide
- Furosemide side effects
- Furosemide overdose
- Furosemide missed dose
- Furosemide drug interactions
- Does Furosemide have any interaction with Diseases
What is Furosemide
- Furosemide is a loop diuretic (water pill) that is employed for treating the condition of edema (excess fluid in body tissues) and hypertension (high blood pressure).
Furosemide brand name
- The drug is available under generic name
- The drug is marketed under various brand names such as Lasix, Fusid, Frumex, Rosemide, Odemase, Nicorol and Uremide etc.
Is Furosemide natural or synthetic
- Furosemide is a synthetic/man-made pharmaceutical NKCC2 (the luminal Na-K-Cl symporter present in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle) inhibitor.
What does Furosemide do
- Furosemide is widely used for treating edema (water retention) often associated with congestive heart failure, liver and kidney disorders such as hepatic cirrhosis, nephritic syndrome and renal impairment.
- It is also used for the treatment of high blood pressure ranging from mild to moderate.
- In combination with other pressure pills, it is used used in the management of severe hypertension.
- It is also sometimes prescribed for curbing high levels of potassium (hyperkalemia), calcium (hypercalcemia), and magnesium (hypermagnesemia).
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as aminobenzenesulfonamides. This is an aromatic heteromonocyclic compound that consists of a benzenesulfonamide moiety with an amine group attached to the benzene ring. The detailed chemical classification of Furosemide is as follows:
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
| Sub Class | Benzenesulfonamides |
| Direct Parent | Aminobenzenesulfonamides |
Chemical information of the drug.
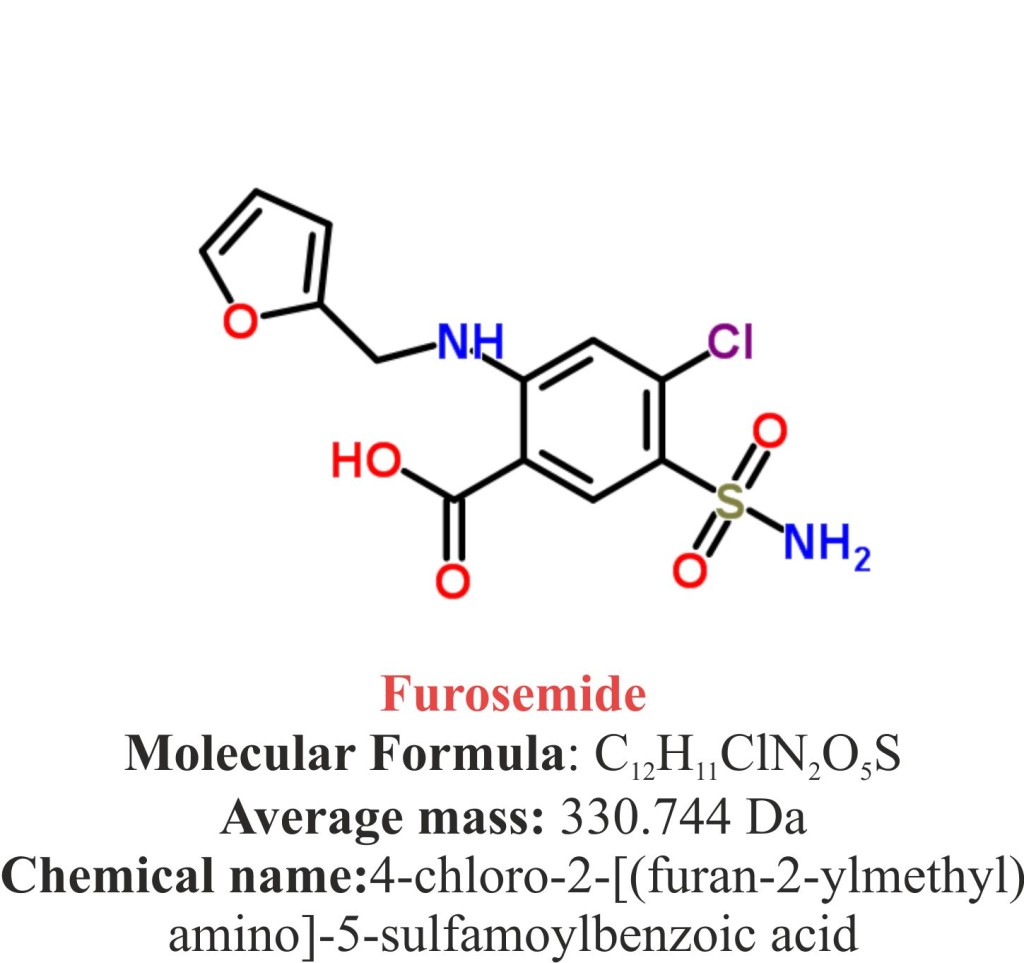
- Furosemide is a synthetic pharmaceutical organo Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds named as 4-chloro-2-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)amino]-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid.
- The compound has molecular formula C12H11ClN2O5S and the molecular weight of 330.744 g/mol.
- The melting point of Furosemide is 206 °C.
- Furosemide is a white to some extent yellow, fine and crystalline powder.
- It is slightly soluble in chloroform and ether; practically insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol; freely soluble in methyl alcohol; dimethylformamide; alkali hydroxides solutions and acetone.
Furosemide available strength
- Furosemide is available as tablets, liquid solution and injection.
- The tablets and solution forms are taken orally whereas injections are given either as intramuscular or intravenous.
- It is available in different dose strengths of tablet as 20, 40, and 80 milligrams, solution as 10 and 20 mg/ml, or injection as 10 mg/ml
- The 20 mg tablets are imprinted with “Lasix®20” ,40 mg tablets with “Lasix® 40” and 80 mg tablets with “Lasix® 80” on one side.
How does Furosemide work
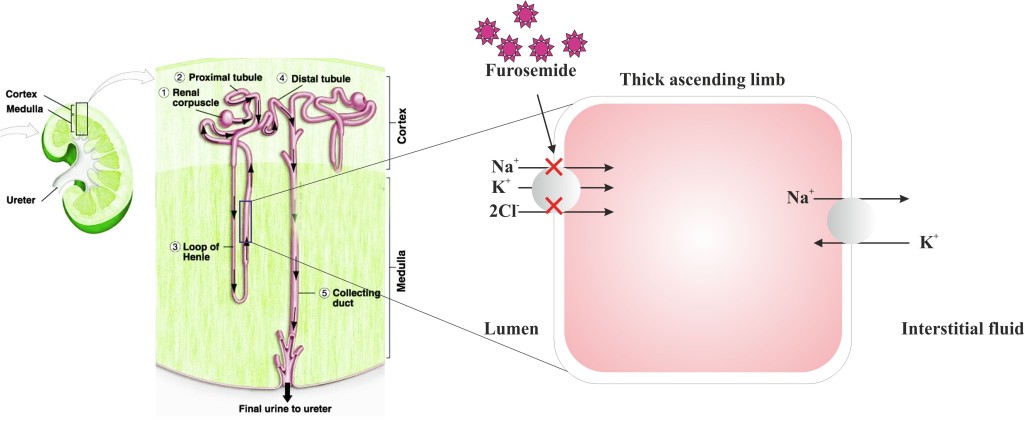
- Furosemide acts by blocking the re absorption of chloride, sodium and water from the filtered fluid in the kidney tubules.
- It achieves this by blocking the sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter present in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle in nephron.
- It competitively inhibits chloride and prevents movement of sodium from the lumen of the loop of henle to the interstitium.
- It thus decreases the osmotic gradient for water re-absorption throughout the nephron and causes a tremendous increase in the output of urine or diuresis.
Furosemide doses
What are the recommended doses of Furosemide?
The drug dosage is based on the patient’s medical state, response to treatment, and age. Children dose also includes the parameter of weight. Older people are usually given a lower dose to avoid side effects.
Edema
- The initial dose for the treatment of edema in adults is 20-80 mg given as a single dose.
- Depending on the need the same dose or an increased dose may be given 6-8 hours later.
- The doses may be raised ranging from 20-40 mg only 6-8 hours after the last dose to get the requisite diuretic effect.
- The effective amount of the drug dose may be given to the patient either once or twice daily.
- Patients with severe edema require a dose of upto 600 mg/day.
- The dose for the elderly edematous patients lies at the lower side of the dosing range.
- In pediatric patients, the initial dose is 2 mg/kg which may be increased by 1-2 mg/kg every 6-8 hours for the requisite effect.
- Children are not prescribed doses greater than 6 mg/kg.
Hypertension
- The initial dose for hypertension is 80 mg divided into two doses of 40 mg each per day.
- The dose of antihypertensive drugs when prescribed with Furosemide should be reduced to half.
- In geriatric patients the initial dose lies at the lower end of dosing range.
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Furosemide
- The use of the drug is contraindicated in the patients with anuria (non-passage of urine) and oliguric states (less urine output).
- The drug is also not recommended in patients who are hypersensitive to the drug.
- In case of acute renal failure the dose of the drug necessary to obtain the requisite response is 1-3 g/day.
- In hepatic impairment, the condition should be monitored very cautiously while using higher dosage.
- Drug therapy should not be introduced before the attainment of basic condition in case of electrolyte depletion and hepatic coma.
- The use of the drug should be discontinued in case of increasing azotemia(an excess of nitrogen compounds in the blood)and oliguria during treatment of severe renal disorder.
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggest Furosemide glucuronide as the only or the major bio-transformed product of Furosemide in human.
- Following absorption majority of the drug (90 %) is bound to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin.
- Plasma concentrations range from 1 to 400 μg/mL in healthy adult.
- The effect of the drug after oral administration can be seen within 1 hour which lasts from 6-8 hours. However, the peak effect exists only during the first two hours.
- Peak plasma concentrations show increment with increasing dose.
- The average half-life of the drug is approximately 2 hours.
- Only a small amount of the drug is metabolize in the liver whereas significant amount is excreted in urine following the IV injection as compared to the tablet or oral solution.
- In older people the binding of Furosemide to albumin as well as the diuretic effect of the drug gets reduced.
- The drug is mainly eliminated unchanged in the urine.
- The older patients show a significantly smaller renal clearance of Furosemide after intravenous administration as compared to younger patients.
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Furosemide
- The Furosemide is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: C.
- The knowledge regarding the harmful effects of the drug on the foetus is unknown.
- Studies indicate that Furosemide is excreted into the breast milk.
- There are also indications of the decrease of the breast milk production in the humans.
- Use of Furosemide during pregnancy requires careful monitoring of fetal growth due to the associated risk for higher fetal birth weights.
- Caution should be exercised when taking Furosemide during pregnancy and lactation.
How to take Furosemide
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet before taking Furosemide.
- It is recommended to take drug at almost the same time every day.
- Take Furosemide exactly as directed by the doctor Take the medication regularly, even if you feel well.
- This medication is to be taken orally with or without food, usually once or twice a day.
- The liquid medicine should be measured with the dose-measuring spoon or medicine cup provided with the drug.
- Doctor’s instructions should be followed very carefully regarding consumption of potassium supplements or enough salt and potassium in the diet to avoid the condition of dehydration.
- The drug should not be shared with others.
- The medication works better under certain lifestyle changes such as diet change, quitting smoking and exercise.
- Regular medical check-ups and tests such as blood tests, kidney tests, blood mineral levels should be done to check for the progress and side effects of the drug.
- In case of patients with high blood pressure, regular monitoring of blood pressure should be done while taking the drug.
How to store Furosemide
- The drug should be stored at room temperature ranging from 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) in a closed container away from direct heat, light and moisture.
- Brief excursion periods are permitted at temperatures of 59°F to 86 ° F (15 to 30 ° C).
- The drug should be kept away from the children and pets.
- The medication should not be stored in the bathroom.
- Do not freeze or store the medicine at extreme cold too.
How to dispose the medicine
- Properly throw away unused and opened, expired or no longer used container.
- Dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- The drug should not be poured in the drains or flushed down the toilet.
- Consult your pharmacist or doctor about the disposal of the medicine.
- Furosemide has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat medical complications such as fluid accumulation and swelling associated with kidney disorders, liver cirrhosis, or congestive heart failure.
- Furosemide is also used in combination with other medicines to treat fluid accumulation in the lungs.
- Furosemide can be used either alone or in combination with other medicines for the treatment of hypertension.
Other uses of the drug.
- Furosemide may also be used for other uses not listed here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special dietary precautions should I follow
- Follow a low-sodium or low-salt diet.
- Consume increased amounts of potassium-rich foods such as raisins, prunes, bananas, and orange juice in your diet.
- Follow a strict exercise and dietary routine as per the recommendations of your health care provider.
- Avoid use of alcohol beverages and smoking.
What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Furosemide
- Do not use the medicine if you are unable to urinate.
- Before using Furosemide, tell your doctor if you have any of the medical complications such as urination problems, kidney disease, cirrhosis or other liver disease, an electrolyte imbalance, enlarged prostate, high cholesterol, lupus, diabetes, or gout.
- Tell your doctor if you are allergic to sulpha drugs.
- Consult your doctor about your recent MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or any type of scan using a radioactive dye.
- Do not take Furosemide without consulting your doctor in case of breast-feeding.
- During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
- Do not share this medication with other persons having the similar kind of problems. Consult your doctor for more details.
- Discuss with your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and non-prescription medications and herbal products you are taking.
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to the drug or if you have any other allergies.
- In case of diabetes regular check-up of blood sugar level should be done and informed to doctor.
- Apply sunscreen and wear protective clothing when going out due to the sensitiveness provided by the drug.
- Avoid alcoholic beverages, driving, use of machinery and performing any activity requiring alertness and clear vision as the drug may cause dizziness and blurred vision.
Furosemide side effects
Some allergic reactions may occur on taking Furosemide and need emergency medical help. These include
- difficulty breathing
- hives
- swelling of lips, throat, face, or tongue
In case of a serious side effect stop taking Furosemide and call your doctor immediately or seek immediate emergency treatment:
- severe skin reaction
- clay-coloured stools, dark urine
- loss of appetite and itching
- jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- severe pain in stomach (upper part), nausea and vomiting
- rapid weight gain, swelling, less or no urination
- hearing loss, ringing sensation in ears
- low potassium resulting in muscle weakness, uneven heart rate, confusion
- cough with fever, trouble breathing, chest pain
- weight loss, numbness and body aches
- pale skin, unusual bleeding, rapid heart rate, trouble concentrating
- low calcium symptoms such as muscle tightness, stinging feeling around mouth, or contraction
- weak or shallow breathing, headache
- feeling of unsteadiness
Some less serious side effects of Furosemide include:
- constipation
- rashes
- itching
- diarrhoea
- dizziness
- stomach pain
- spinning sensation
Other side effects may also occur not listed here. Doctor should be consulted regarding side effects for the medical advice. Besides, you or your doctor may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or FDA MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online at http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch.
Furosemide overdose
What should I do in case of overdose?
- Try to avoid taking the overdose of the drug. If you overdose the drug contact with your doctor or pharmacist for symptomatic and supportive measures.
- Symptoms of overdose include fainting, dizziness, vomiting, extreme tiredness, dry mouth, very low urine output, stomach cramps, substantial sweating, extreme thirst, confusion.
- In case you or some other person has taken overdose of this medication contact your local poison control centre at 1-800-222-1222 or emergency room immediately.
- Call local emergency services at 911 in case a patient collapses or faces difficulty in breathing.
Furosemide missed dose
What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule.
- Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind not to use a double dose to make up the missed dose.
Furosemide drug interactions
Does Furosemide have any interaction with other drugs?
Some drugs may interact with Furosemide and care should be taken while taking these medications together. It is advisable that you do not alter the medication by your own and without consulting the healthcare professional.
In case of sucralfate (Carafate), take it at least 2 hours before or after taking Furosemide.
Tell your doctor about all the medications you use, especially the following:
- lithium (Lithobid, Eskalith)
- cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune)
- cisplatin (Platinol)
- methotrexate (Trexall, Rheumatrex)
- a laxative (Dulcolax, Metamucil, Milk of Magnesia, Epsom salts and others)
- phenytoin (Dilantin)
- ethacrynic acid (Edecrin)
- steroids (prednisone and others)
- heart or blood pressure medication such as ramipril, telmisartan, olmesartan, benazepril, eprosartan, lisinopril, irbesartan, amiodarone, quinapril, valsartan, and others
- an antibiotic such as cefprozil, tobramycin, kanamycin, amikacin, cefuroxime, gentamicin, streptomycin, cephalexin, neomycin
- salicylates such as aspirin, Tricosal, Dolobid, Salflex, and others
Other drugs not included in the list may also interact with Furosemide. Tell your doctor about all medications you are using including prescription, non-prescription, vitamin, and herbal products. Do not start a new medication without informing doctor.
Does Furosemide have any interaction with Diseases
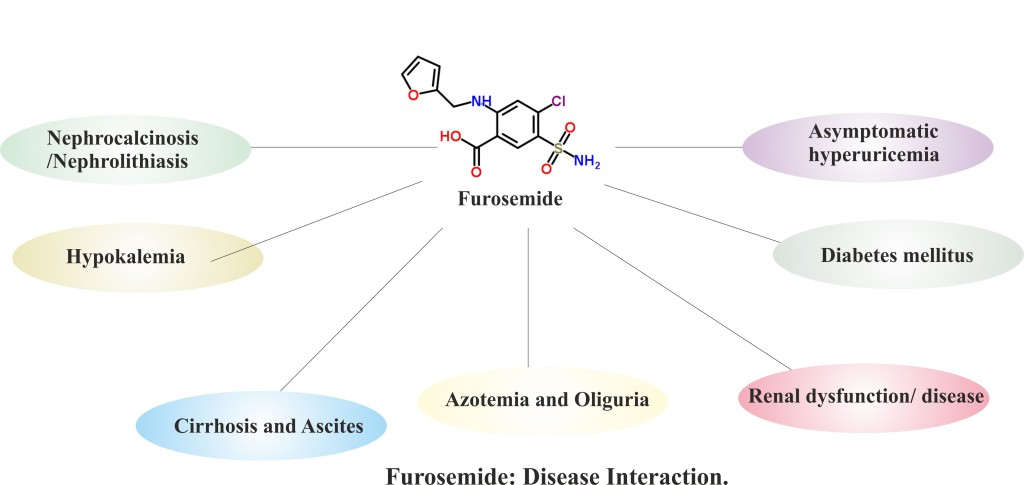
Furosemide may interact with one or more of the following diseased state:
- In patients suffering with hepatic cirrhosis and ascites, Furosemide therapy is best introduced in the hospital. Sudden change in fluid and electrolyte balance requires strict observation during diuresis. Supplemental potassium chloride or aldosterone antagonist may help in prevention of hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
- Use of Furosemide may be stopped in case of increased azotemia and oliguria that occur during treatment of severe progressive renal disease.
- Furosemide can lead to a higher incidence of deterioration in renal function in patients at high risk for radiocontrast nephropathy.
- Hypokalemia (lower than normal potassium level in your bloodstream) may set in with Furosemide, when cirrhosis is present, or during concomitant use of ACTH, corticosteroids, licorice in large amounts, or prolonged use of laxatives.
- The administration of Furosemide in patients of urinary retention may result in increased production and retention of urine. Thus, these patients require careful monitoring, especially during the initial stages of treatment.
- Patients suffering with diabetes mellitus should be informed about the increase in blood glucose levels by the intake of Furosemide.
- Furosemide effect may get attenuated and its ototoxicity initiated in patients with hypoproteinemia (e.g., associated with nephrotic syndrome).
- Asymptomatic hyperuricemia can occur and gout may rarely be triggered.
- Furosemide may result in reversible elevations of BUN (blood urea nitrogen) associated with dehydration, which should be avoided, particularly in patients with renal insufficiency.
- In premature infants Furosemide may increase the development of nephrocalcinosis/nephrolithiasis, therefore renal ultrasonography should be performed and renal function monitored.
Where can I get more information
- Your pharmacist or health care provider can provide more information about Furosemide.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
Furosemide belongs to a class of medicines known as loop diuretics that helps the body to get rid of extra salts and water.
- Furosemide is used for the treatment of edema often associated with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease in adults and pediatric patients.
- As an adjunct therapy Furosemide is used for the treatment of cerebral or pulmonary edema requiring rapid diuresis (IV injection).
- Furosemide is also used in management of severehypercalcimia in combination with adequate rehydration.
- Furosemide is also used along with albumin in nephrotic syndrome to reduce edema.
- Furosemide is recommended for high blood pressure when other diuretics fail to control.
- Furosemide can be used either alone (as a diuretic) or as a combination tablet along with other diuretics such as spironolactone, triamterene, or amiloride. It is sometimes prescribed as a combination tablet with a mineral called potassium.
- Furosemide is used along with albumin to increase diuresis in chronic kidney diseases with hypoalbuminemia.
- Furosemide may be prescribed in adults for the treatment of hypertension either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases.
- DrugBank: Furosemide (DB07799). http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00695.
- Furosemide | C12H11ClN2O5S | ChemSpider. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.3322.html.
- Furosemide Medline plus information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a682858.html.
- Furosemide – National Library of Medicine – PubMed Health. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0000793/.
- Furosemide – oral, Lasix. http://www.medicinenet.com/furosemide-oral/article.htm
- http://www.drugs.com/furosemide.html.
- Drugs and medications. Furosemide. http://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-5512-8043/furosemide-oral/furosemide-oral/details#.
- Furosemide (Lasix) Uses, Dosage, Side Effects. http://www.drugs.com/furosemide.html.
- http://reference.medscape.com/drug/lasix-furosemide-342423#0
- Safety Information > Lasix (furosemide) tablets. http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/ucm232345.html.
“Memantine, drug class, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
“Fenofibrate, drug class, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
