Contents
- What is Insulin Glargine (Lantus)?
- What is the generic and brand name of the drug?
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Why is this medication prescribed?
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
- Chemical information of the drug.
- What is the available strength of the drug?
- How the medicine works (mode of action)?
- What are the recommended doses of Insulin Glargine?
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Insulin Glargine?
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug?
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Insulin Glargine?
- How to use the drug?
- How to store the drug?
- How to dispose the medicine?
- Does Insulin Glargine has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies?
- Other uses of the drug
- What special dietary precautions should I follow?
- What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Insulin Glargine?
- What are the possible side effects of this drug?
- What should I do in case of overdose?
- What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- Does Insulin Glargine have any interaction with other drugs?
- Does Insulin Glargine have any interaction with Diseases?
- Where can I get more information?
- Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases.
What is Insulin Glargine (Lantus)?
- Insulin Glargine is recombinant human insulin analogue that act as blood-glucose-lowering agent.
What is the generic and brand name of the drug?
- The drug is available under generic name Insulin Glargine and brand names Lantus , Toujeo,Abasaglar, and Basaglar
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Insulin Glargine is a synthetic bioengineered (man-made) injectable form of long-acting insulin.
Why is this medication prescribed?
- Insulin Glargine acts as a long lasting (upto 24 hour duration) insulin, which reduces the amount of sugar in the blood and urine.
- The drug is used to treat patients with type 1diabetes or diabetes mellitus type 1. In type 1diabetes the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas were non functional and unable to produce insulin.
- The drug is also used to treat type 2 diabetes or noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, (condition in which insulin is not produced in sufficient amount or not effective due to insulin resistance) to control the blood sugar level.
- Insulin Glargine is recommended in combination with other short acting insulin in case of type 1 diabetes, while in case of type 2 diabetes, insulin Glargine may be used with short acting insulin or with oral drugs used to treat diabetes.
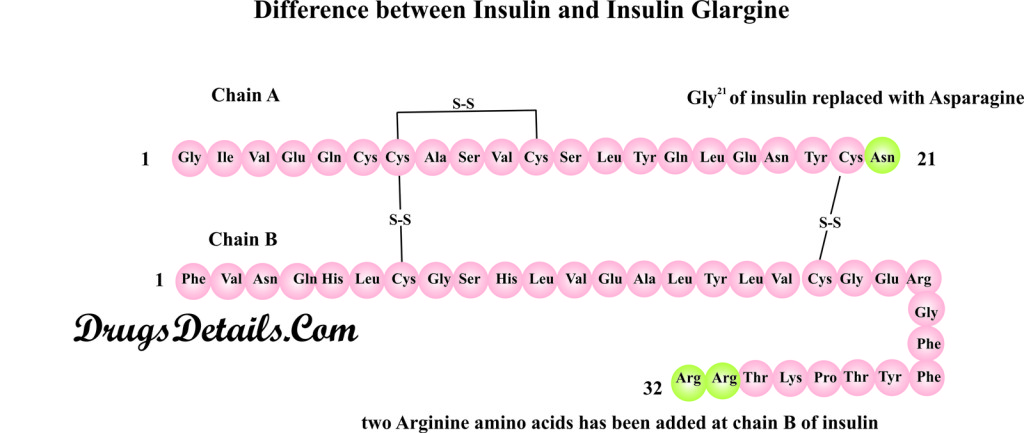
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
- Insulin Glargine chemically belongs to the class of organic compounds which are known as s Amino Acids, Peptides, and Analogues. The drug is prepared by recombinant DNA technology in non pathogenic bacteria coli. The detailed chemical classification of Insulin Glargine is described below:
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Organic Acids |
| Class | Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives |
| Sub Class | Amino Acids, Peptides, and Analogues |
| Direct Parent | Peptides and proteins |
Chemical information of the drug.
- Insulin Glargine is a bioengineered synthetic pharmaceutical recombinant protein/peptide containing two chains (chain A and B) of 21 and 32 amino acids.
- The drug (Insulin Glargine) is almost identical to that of natural insulin (protein regulates blood sugar level) and differs mainly in two aspects. First the amino acid Aspargine in chain A (A21) of insulin is replaced by Glycine amino acid and second, addition of two Arginines at C-terminus of the chain B.
- The drug has molecular formula C17H19N3O3Sand the molecular weight of 6063 Da.
- The melting point of Insulin Glargine is 81 °C.
- The hydrophobicity and isoelectric point of Insulin Glargine is 098 and 6.88, respectively.
What is the available strength of the drug?
- Insulin Glargine is supplied in the form of clear aqueous injectable solution to inject subcutaneously (under the skin).
- Each millilter (ml) of Insulin Glargine solution contains 100 units of (3.6378 mg) insulin glargine.
- It is available as 10 mL vial (1000 Units/10 mL), 3 mL Cartridge systems (300 Units/3 mL) and 3 mL disposable insulin device (300 Units/3 mL).
- Besides Insulin Glargine, each ml of solution contains 30 mcgzinc, 20 mg glycerol 85%, 20 mcg polysorbate 20, 2.7 mg m-cresol, and water.
How the medicine works (mode of action)?
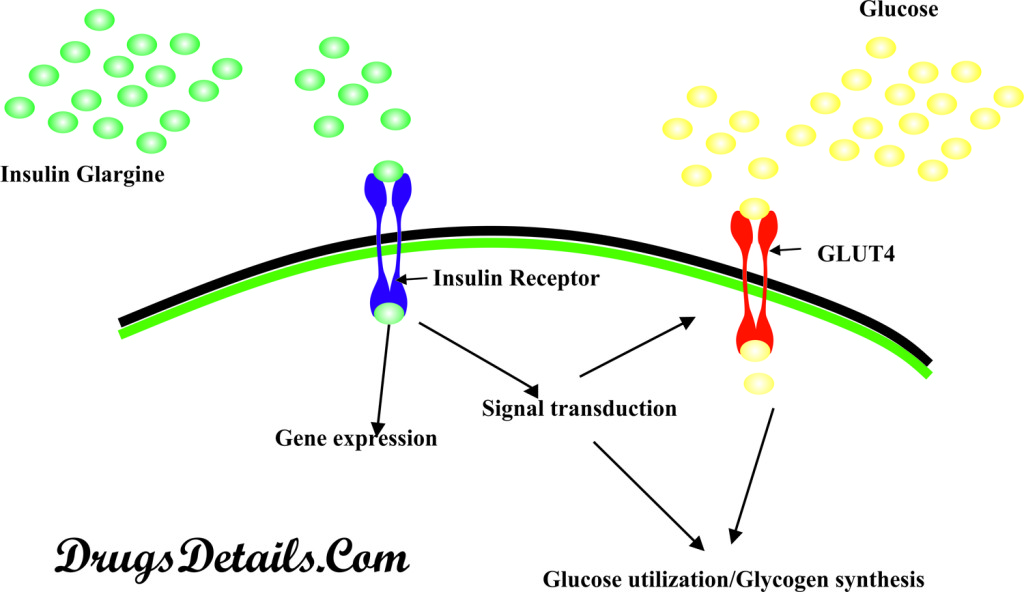
- The mode of action of Insulin Glargine is similar to that of naturally occurring human insulin produced by the pancreatic beta cells but its action lasts for a longer duration of time.
- Insulin Glargine works by replacing the insulin produced by the body, stops sugar production in liver and helps movement of sugar from the blood into other body tissues where it is used for energy.
- The long lasting action of Insulin Glargine is due to the modification in its amino acid composition which increases its solubility at pH 4 and results in formation of microprecipitates at physiological pH 7.4.
- The drug is released slowly from these microprecipitates and hence its action lasts for a longer time
- The Insulin Glargine is human insulin analogue that acts on the insulin receptors present on the cell surface. Insulin receptors are present on the surface of every cell but the density of these receptors varies according to the cell type.
- The insulin receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase, a heterotetrameric glycoprotein that consists of two extracellular alpha and two transmembrane beta sub-units. The alpha subunits have insulin binding sites whereas beta subunits are associated with tyrosine kinase activity.
- Insulin binding to the alpha subunits causes the beta subunits to phosphorylate themselves (due to activation of the tyrosine kinase activity) and hence, activation of the receptors occurs.
- The activated receptor then phosphorylates a number of intracellular proteins known as insulin receptor substrates (IRS), proteins Cbl (E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase involved in cell signalling and protein ubiquitination), APS(an adapter protein that binds cbl), Shc(an adapter protein) and Gab 1(Adapterprotein that plays a role in intracellular signalling cascades triggered by activated receptor-type kinases).
- The activity of the phosphorylated intracellular proteins get altered thereby bringing about signalling cascade and the biological response.
What are the recommended doses of Insulin Glargine?
The dose of Insulin Glargine varies from person to person and should be individualized only under the supervision of the doctor depending upon the needs of the patients. The dose is adjusted in accordance with the blood glucose measurements of the patients.
Type 1 diabetes:
- The patients’ (6 years or older) total daily insulin requirement should be calculated individually.
- The recommended initial dose of Insulin Glargine should be approximately one-third of the total daily insulin requirements to be administered subcutaneously once a day.
- The maintenance dose is adjusted according to the patient’s need and should be given once per day.
- Insulin Glargine must be co-administered with rapid or short acting insulin in order to satisfy the remainder of the daily insulin requirements.
- The use of Insulin Glargine has not been established for paediatric patients younger than 6 years of age.
Type 2 diabetes:
- The initial starting dose in patients who are presently not treated with insulin is 10 units (or 0.2 Units/kg).
- The dose should be given subcutaneously once a day and almost at the same time.
- The maintenance dose is determined based on the individual response to the drug.
- The use of Insulin Glargine is not recommended in children.
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Insulin Glargine?
- The usual dosing of the drug may vary depending upon the age and glucose levels of the patient
- The drug is contraindicated in case of pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Insulin Glargine can be given in case of breastfeeding women with diabetes Dosage adjustments are required in case of.
- Insulin Glargine is not prescribed in children less than 6 years of age with type 1 diabetes and also in paediatric patients with type 2 diabetes.
- In diabetic patients of older age, the drug should be used with caution to avoid hypoglycemic.
- Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring is required in case of co-administration of Insulin Glargine with drugs like clonidine, beta-blockers, alcohol, and lithium salts.
- Insulin Glargine dose needs to be adjusted during renal impairment because of the increased risk of hypoglycemia.
- The drug is not recommended during hepatic impairment due to increased risk of prolonged hypoglycemia (low blood sugar or glucose).
- The use of the drug is contraindicated in patients in case of hypersensitivity to Insulin Glargine or its constituents.
- The dosage needs to be adjusted during certain conditions such as:
- Obese patients, concurrent use with medications having hyperglycemic effects, pregnancy, stress, illness, trauma, or after surgery : needs higher dose
- Concurrent use of medications having hypoglycemic effects, weight loss, exercise, or low calorie diets: needs lower dose
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug?
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggest that after subcutaneous injection, insulin serum concentrations indicated a slower, more prolonged absorption and a relatively constant concentration over time (24 hours).
- No peak serum concentration is achieved for the administered Insulin Glargine.
- No data is available for the protein binding of Insulin Glargine following absorption.
- The average median half-life of Insulin Glargine is not reported in humans; however, in vitro studies in mammalian reticulocytes indicate a half life of 30 hours.
- The drug is partly metabolize in the subcutaneous depot at the carboxyl terminus of the B chain to form two active metabolites, namely, A21-Gly-insulin and A21-Gly-des-B30-Thr-insulin.
- Unchanged drug and the degradation products have been found in the blood circulation.
- The route of elimination of the drug is not known.
- The average steady state volume of distribution of Insulin Glargine is not available.
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Insulin Glargine?
- The Insulin Glargine is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: C
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies the use of Insulin Glargine in pregnant women is contraindicated and recommended only when benefit justifies the risk.
- No adequate data is available on excretion of Insulin Glargine into human breast milk.
- Despite these facts caution should be exercised when taking Insulin Glargine.
How to use the drug?
- Insulin Glargine is available as solution to be injected subcutaneously.
- Try to take the medicine at the same time every day.
- The drug is taken only once per day.
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet and take Insulin Glargine exactly as directed.
- Take the medication regularly, even if you feel well.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor. Since, the dosage is based on patient medical condition, glucose levels, age, and treatment responses.
- Do not change the brand, strength or type of insulin without consulting your doctor as it may result in change of dosage.
- Never share needles, syringes, or pens with others and avoid reuse of needles or syringes.
- Never dilute the drug or mix it with any other type of insulin.
- The drug should never be injected into a vein or muscle.
- Always try to rotate the injection site to avoid the accumulation of fat at the site of injection.
- Discard Insulin Glargine if it is coloured, cloudy, or consists of solid particles.
How to store the drug?
- Unopened vials, pens, and cartridge systems should be kept refrigerated between 2° and 8 °C (36 °F and 46 °F).
- Unopened vials, pens, and cartridge systems can be stored at room temperature for 28 days.
- Opened vials and cartridge systems can be refrigerated or stored at room temperature below 30°C (86°F)
- Cartridge systems inserted into the insulin delivery device and pens should be stored only at room temperature below 30°C (86°F).
- Opened vials, pens, and cartridge systems are stable for 28 days after the first use.
- Throw away any insulin that has been exposed to extreme heat or cold.
How to dispose the medicine?
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used medication.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- Consult your pharmacist for the proper disposal of the drug.
- Insulin Glargine has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2000 to control blood sugar in diabetes
(type I and type II) .
Other uses of the drug
- Insulin Glargine may also be used for other uses not listed here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special dietary precautions should I follow?
- It is recommended to follow the diet plan as directed by your doctor or dietician.
- Try to eat a healthy diet with the same amounts of the same kinds of food at about the same times every day.
- Skipping or delaying and changing the quantity or quality of food can cause changes in the amount of blood sugar.
What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Insulin Glargine?
- Do not use the medicine if you are hypersensitive or allergic to any of the ingredients.
- Before taking Insulin Glargine, tell your doctor about your medical history preferentially if you have or ever had nerve damage caused by your diabetes or any other medical problem, including liver or kidney disease.
- During pregnancy this medication is recommended only when it is essential and under doctor or pharmacist supervision.
- Since the information about excretion of drug in milk is not explored consult your doctor before breast feeding to your child.
- Consult with your doctor and pharmacist if you are taking any prescription and nonprescription medications, nutritional supplements, vitamins and herbal products such as certain cholesterol-lowering medications; angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors); medications for asthma and colds, mental illness and nausea; salicylate pain relievers; AIDS antiviral medications; diuretics; oral contraceptives; beta-blockers; sulfa antibiotics; oral medications for diabetes; diuretics; and thyroid medications etc.
- Do not share this medication with other persons having the similar kind of problems. Consult your doctor for more details.
- Do not change the brand of Insulin Glargine or syringe you are using without consulting your doctor or pharmacist as it may change blood glucose levels.
- Do not share this medication with other persons having the similar kind of problems. Consult your doctor for more details.
- Avoid drinking alcohol. It lowers blood sugar and may interfere with your diabetes treatment.
What are the possible side effects of this drug?
The use of Insulin Glargine may result in changes in the levels of blood sugar. However, sometimes, these changes may be associated with side effects. It is usually recommended to consult your doctor in case the symptoms are severe or persists for a long time. Some of the common side effects include:
- Fat accumulation
- Weight gain
- Swelling of the hands or feet
- Constipation
- Swelling, redness, pain, or itching at the site of injection
- Changes in skin texture
- Little depression in the skin (fat breakdown)
Some side effects can be serious. If case you experience these symptoms, call your doctor immediately or get emergency treatment:
- Muscle cramps
- Hives
- Weakness
- Fast pulse
- Whole body itching
- Breath shortness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Skin rashes
- Sweating
- Low blood pressure
- Swelling of the lips, eyes, tongue, face, or throat
- Trouble breathing
- Hoarseness
Severe allergic reactions are also sometimes associated with the use of Insulin Glargine. These comprise:
- Very low blood pressure
- Chest tightening or bronchospasm
- Swelling under the skin
Prolonged use of Insulin Glargine can lead to thickening of fat tissues at the site of injection.
Insulin Glargine may cause other side effects not included in the list. Consult your doctor if you have any unusual symptom while taking this medication.
What should I do in case of overdose?
Try to avoid taking the overdose of the drug.
- In case you or some other person has taken overdose of this medication contact your local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222 or emergency room immediately.
- Consult your doctor or pharmacist for symptomatic and supportive measures in any case of overdose.
What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule.
- Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind to not use a double dose to make up a missed dose.
- Avoid taking more than one dose in a 24-hour period unless directed by your doctor.
Does Insulin Glargine have any interaction with other drugs?
There are a number of drugs that brings about a change in the glucose metabolism and requires insulin dosage to be adjusted and close monitoring of glucose levels. These include:
- Drugs that increase the risk of Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar or glucose): The blood glucose lowering effect of Insulin Glargine may be enhanced in presence of certain drugs that increases the chances of hypoglycemia. These include:
- Fluoxetine
- Salicylates
- Anti-diabetic products
- Pramlintide
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Pentoxifylline
- Angiotensin converting enzyme (ace) inhibitors
- Fibrates
- Disopyramide
- Propoxyphene
- Somatostatin analogs
- Sulfonamide antibiotics
- Angiotensin II receptor blocking agents
Dose adjustment and increased glucose monitoring is required in case of co-administration of Insulin Glargine with these drugs.
- Drugs that reduce the blood glucose lowering effect of Insulin Glargine : The blood glucose lowering effect of Insulin Glargine may get decreased in case of its co-administration with following drugs:
- Danazol
- Somatropin Protease inhibitors
- Oral contraceptives (estrogens, progestogens)
- Antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine and olanzapine)
- Corticosteroids
- Thyroid hormones
- Sympathomimetic agents (e.g., terbutaline, albuterol, epinephrine)
- Protease inhibitors
- Glucagon
- Isonazid
- Diuretics
- Niacin
- Phenothiazines
The administration of these drugs with Insulin Glargine requires dose adjustment and enhanced glucose monitoring.
- Drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect of Insulin Glargine: When Insulin Glargine is co-administered with the following drugs, the glucose lowering effect of the drug may get increased or decreased.
- Lithium salts
- Alcohol
- Beta-blockers
- Clonidine
- Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed by hyperglycemia.
Dose adjustment and increased glucose monitoring is required when Insulin Glargine is co-administered with these drugs.
- Drugs that may affect signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia: The signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia may get reduced or absent when Insulin Glargine is co-administered with
- Guanethidine
- Beta-blockers
- Reserpine
- Clonidine
Does Insulin Glargine have any interaction with Diseases?
There are some diseases that are known to interact with Insulin Glargine. These are renal dysfunction, liver disease and cancer. In first two cases lower initial dosages, careful monitoring of plasma glucose levels and dosing adjustments may be needed.
- Renal impairment: Patients with renal impairment have reduced insulin metabolism and therefore, a reduction in the Insulin Glargine dose may be required in such cases.
- Liver impairment: Patients suffering with hepatic impairment are characterized by reduced capacity for gluconeogenesis and reduced insulin metabolism. Hence, a reduction in the Insulin Glargine dose may be required in these patients.
- Cancer: there are increased risk of cancer in patients who take Insulin Glargine.
Where can I get more information?
Your pharmacist or health care provider can provide more information about Insulin Glargine.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
Insulin Glargine is represented as an insulin analogue for controlling blood glucose levels in diabetic patients.
- Studies indicate the effectiveness and safety of Insulin Glargine in treatment of type I and type II diabetes.
- No clinical data is available to establish the cardiovascular safety of Insulin Glargine.
- Clinical studies indicate the potential of Insulin Glargine for the development of antibodies in diabetic patients. In type 1 diabetes patients, 79% of patients and in type 2 diabetes patients, 25% of patients receiving drug once a day were positive for anti-insulin antibodies (AIA).
- Current studies also provide the possibility of the development of cancer in patients who take Insulin Glargine.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases.
- DrugBank: Insulin Glargine (DB00047). http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00047.
- Insulin Glargine (rDNA origin) Injection. Medline plus information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a600027.html.
- TOUJEO (Insulin Glargine injection) – Food and Drug Administration. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/206538lbl.pdf.
- Insulin glargine – Medscape . http://reference.medscape.com/drug/lantus-toujeo-insulin-glargine-999003.
- Evolution of insulin: from human to analog. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25282010.
- Insulin Glargine. The most studied basal insulin. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24475676.
Read about,
“Fondaparilux, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action”
“Moxifloxacin, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
