Contents
- What is ketoconazole?
- Ketoconazole IUPAC name, molecular formula, weight, structure and drug class
- Ketoconazole identification
- Available forms and dosage strengths of ketoconazole
- What is the mechanism of action of ketoconazole?
- Why is ketoconazole medication prescribed?
- What are the pharmacodynamics of ketoconazole?
- What are the guidelines for administrating ketoconazole?
- What are the possible side effects of using ketoconazole?
- Ketoconazole use during pregnancy and lactation
- Ketoconazole use in geriatric population
- What are some of the precautions/ warnings for the use of ketoconazole?
- Which drugs interact with ketoconazole?
- What are the storage conditions of ketoconazole?
What is ketoconazole?
Ketoconazole is one of the most commonly used antifungal medicines which are used in the treatment of certain kinds of fungal and yeast infections.
This drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1981. Ketoconazole is a derivative of azole antifungals and includes a synthetic imidazole ring in its structure.
This drug is a broadspectrum antifungal and it works by preventing the development of membrane which surrounds the fungal cells.
Ketoconazole is a prescription drug and it has a black box warning of causing liver damage and in extreme cases liver failure when used in tablet form.
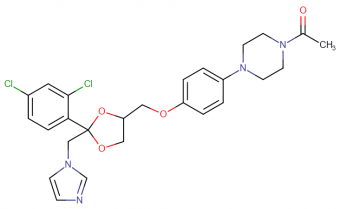
Ketoconazole IUPAC name, molecular formula, weight, structure and drug class
IUPAC Name; 1-[4-[4-[[(2R,4S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(imidazole-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethanone
Molecular formula: C26H28Cl2N4O4
Molecular weight: 531.434 g/mol
Molecular structure:
Drug class: Ketoconazole belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenylpiperazine which are compounds containing a phenylpiperazine moiety, which consists of a piperazine bound to a phenyl group.
Ketoconazole identification
This compound is a racemate which consists of equimolar quantities of (2R, 4S)- and (2S, 4R)- of ketoconazole which have chiral carbon centers on the acetal ring.
This drug is available is white to light beige colored powder which is odorless. It has more solubility in acids than in neutral solutions and alkalis.
Available forms and dosage strengths of ketoconazole
Ketoconazole is used only when prescribed by the doctor. It is available in the following dosage forms and strengths that can be used for the treating the fungal infections.
- Cream which presents in 2% of active
- Shampoo in 2% of active
- Soap in 2%
- Oral tablets – 200mg
- Gel in 2%
- Foam in 2%
The following formulation, however, can be dispensed as a non-prescription product
- Shampoo in 1%
What is the mechanism of action of ketoconazole?
Ketoconazole is a fungistatic and fungicidal imidazole compound, depending upon the concentration used. It acts on 14-α-demethylase.
This is a cytochrome P-450 enzyme required for the transformation of lanosterol to another sterol compound, ergosterol.
As a consequence of this conversion, the synthesis of ergosterol is inhibited and in turn, there is more permeability of the fungal cells.
This enhanced permeability is due to the weakening of the membrane structure and hence functional ability also decreases.
Simultaneously, the processes which are affected on using ketoconazole involve stopping of the endogenous respiration of the fungal cells, affecting on the phospholipids inhibiting the formation of mycelial forms from yeast, preventing the uptake of purine and causing the impairment triglyceride biosynthesis.
Ketoconazole also decreases the synthesis of thromboxane and other sterol compounds including aldosterone, cortisol, and testosterone.
Why is ketoconazole medication prescribed?
Ketoconazole is in the treatment of tinea corpis (ringworm: this is a fungal skin infection that is characterized by red scaly rashes on various parts of body), tinea cruris (jock itch: skin infection in the regions of groin or buttocks) tinea pedis (athlete’s foot: infection occurs on the feet and between the toes) and tinea versicolor (skin infection in which brown spots are present on the chest, back, arms, legs or neck).
This is furthermore used in treating a number of yeast infections.
Shampoo formulation which is a prescription product is used in tinea versicolor whereas non-prescription shampoo formulation is used as a prophylactic agent and also in reducing the severity of flaking, scaling, and scalp itching which occurs due to dandruff.

Ketoconazole tablets are usually prescribed for the treatment of systemic fungal infections particularly those patients who have shown no response to other therapy regimens.
The infections include blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, chromomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis.
It is important to know that the ketoconazole tablets should be avoided in the treatment of fungal meningitis as it can easily penetrate into the cerebrospinal fluid.
What are the pharmacodynamics of ketoconazole?
Absorption: Ketoconazole shows a rapid absorption. Approximately 75% of the drug is absorbed. However, it is changed to the hydrochloride salt ester just before absorption occurs.
The absorption of ketoconazole is inconsistent relying heavily on the presence of the gastric acid.
Bioavailability reduces when the gastric pH increases. The Cmax of ketoconazole is approximately equal to 3.5mcg/ml (when it is given in oral dosage form). Peak plasma time can be observed within 1 – 2 hours.
Distribution: Ketoconazole shows extensive plasma protein binding approximately 99% (in vitro) primarily to albumin protein. An only minute portion of the drug is distributed to the cerebrospinal fluid but even that is erratic.
It has been observed that ketoconazole shows a fine distribution in the regions of inflamed joint fluid, bile, saliva, sebum, cerumen, tendons, skin, and soft tissues. Ketoconazole is easily passed through breast milk.
Metabolism: This drug has been observed to undergo partial metabolism in the liver with the help of CYP3A4 enzymes to inactive metabolites.
The major and important metabolic pathways which were involved included oxidation and degradation of rings present in the compound particularly imidazole ring and piperazine ring.
Along with this, O-dealkylation and aromatic hydroxylation were also involved in the metabolism of ketoconazole. Through these pathways, ketoconazole is converted into a number of inactive metabolites.
Elimination: The major route for ketoconazole to eliminate is via bile. It is seen that greater than 50% of the drug dose of ketoconazole is excreted in the feces and approximately 13% of the drug is excreted via kidneys.
Of this 13% of the drug only about 2% – 4% of the drug remains unchanged. One of the characteristic parameters of ketoconazole is that it shows a biphasic half-life.
In the start, the half-life is around 2 hours gradually it increases and a terminal half of approximately 8 hours is obtained.
What are the guidelines for administrating ketoconazole?
When ketoconazole is prescribed orally:
The patients who are already suffering from achlorhydria, it is recommended to take the tablet with an acidic drink (preferably cola). This helps in increasing the bioavailability of the drug.
When ketoconazole is prescribed topically:
- Lotion/ cream/ ointment formulations:
These should never be administered or applied intravaginally or on the eye.
Gentle massage of cream is required on the affected side.
- OTC product – 1% shampoo
Moisten the hair with warm water. Take sufficient quantity of shampoo and rub it in between hands. Apply it on scalp and hair first covering the backside of the head, followed by the sides and in the last cover the top. Now rinse thoroughly.
- Prescription product – 2% shampoo
Carefully put sufficient quantity of shampoo on the damp skin which is affected and its surrounding zone. Massage and leave it for 5-6 minutes. Now carefully rinse using water.
In most of the cases, a single application has been proved to be sufficient.
- Gel:
This should not be used in or close to eyes, mouth, and nose or in any mucus membranous sites. As soon as the gel is gently rubbed on the affected area, it is important to wash hands.
Smoking or any other activities which involve the use of flame/ fire should be strictly prohibited while applying or even immediately after applying ketoconazole gel.
- Foam:
This should not be used in or close to eyes, mouth, and nose or in any mucus membranous sites.
Hold the foam can in an upright position and dispense a portion of foam into the cap or any other surface which is at a slightly lower temperature. It should not be dispensed straight on hands as there are chances of melting of the foam.
Gently pick up small portions of the foam from the cool surface and apply it to the affected area and rub gently.
In hairy areas, the foam can be directly applied on the affected skin.
Smoking or any other activities which involve the use of flame/ fire should be strictly prohibited while applying or even immediately after applying ketoconazole foam as this is a flammable formulation.
What are the possible side effects of using ketoconazole?
Every drug even though it is well tolerated may show up certain unwanted side effects. In a similar way, ketoconazole has the following side effects.
CNS: (mostly occurs with the use of oral tablets) moderate to severe depression, high-grade fever, headache, nervousness, dizziness, photophobia, and somnolence and in extreme cases suicidal thoughts.
Gastrointestinal: nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps and diarrhea (on taking ketoconazole orally)
Genitourinary: impotence is reported on oral administration of ketoconazole.
Hematologic: severe leucopenia and thrombocytopenia are commonly seen on oral administration, hemolytic anemia
Hepatic: one of the worst side effects of using ketoconazole that it can cause fatal hepatotoxicity.
Dermal: on topical application of ketoconazole stinging, irritation and pruritis are reported.
Other: gynecomastia along with chills and tenderness is noted.
Changes in laboratory test results:
Elevation in the lipid, alkaline phosphatase, AST and ALT levels is seen.
The levels of hemoglobin, platelets and white blood decrease.
Ketoconazole use during pregnancy and lactation
Pregnant women:
Using ketoconazole in pregnant women has not demonstrated enough adequate and well-established safety profile.
Embryotoxic and teratogenic outcomes have been demonstrated which included syndactylia and oligodactylia when ketoconazole was administered orally 2 times the maximum suggested dose amount.
Furthermore, dystocia was reported when ketoconazole was given in the third trimester orally.
When oral ketoconazole is to be prescribed to pregnant women, it should be only prescribed when the benefits are more dominant than the possible risks to the fetus.
Topical application of ketoconazole has however not be considered harmful to use in pregnant women. This drug belongs to a pregnancy category C.
Breastfeeding:
This drug is passed from mother’s milk to the baby. When a dose of 200mg of ketoconazole is used for more than 10 days by the mother, approximately 0.22mcg/ml (peak concentration) post-dose was obtained in the milk.
However, once ketoconazole was discontinued, the levels of the drug declined rapidly in the milk.
When ketoconazole passes on to the neonates/ infants, risk for developing hepatotoxicity increases as the organs are not fully developed.
When a topical application in form of cream or gel is prescribed, care should be taken so as to avoid the ingestion of ketoconazole by the infant.
FDA has not yet approved ketoconazole as a safe and effective drug in neonates, infants or children who are younger than 2 years of age.
Ketoconazole use in geriatric population
Geriatric patients are usually already suffering from various medical illnesses, prescribing them ketoconazole will bring about drastic adverse events due to the possible drug interactions.
Ketoconazole is responsible for causing a prolonged QT interval. Due to the weakened activity of the heart, they are at a greater risk of suffering from this prolonged interval.
Ultimately, making him more prone to suffer from other medical conditions. In cases, when no other treatment line is effective, only then ketoconazole should be administered orally. Increased frequency of monitoring the vitals is advised in geriatric patients.
What are some of the precautions/ warnings for the use of ketoconazole?
Hepatotoxicity:
Patients who are suffering from acute or chronic liver disease should never be allowed to use ketoconazole in the treatment of fungal infections.
Severe cases of hepatotoxicity have caused the condition to worsen to such an in which transplant of the liver is done or even has caused the death of some patients.
It was more common in those patients who were prescribed higher doses of oral ketoconazole and even seen in patients who were using normal doses for longer durations of time.
Even though this effect is reversible on stopping of the drug but it does not always happen. Pedriatics who were using this drug had been reported to suffer from jaundice.
Thus, for using ketoconazole, it should be only used when all other treatment regimens failed to be effective or when the patient becomes intolerant to a certain drug.
During the use of ketoconazole, patients should be regularly monitored for their lab values especially when tests for ALT, AST, prothrombin time (PT), total bilirubin and alkaline phosphate.
Such patients are strictly advised to not to use alcohol. This may worsen up the condition.
QT prolongation:
Ketoconazole has been known for its action of the inhibition of metabolic hepatic isoenzymes CP3A4. Concomitant administration of oral ketoconazole with drugs which also posses the same inhibiting power will lead to an increase in the serum level of the specific drug.
As a result, the time interval for QT gets prolonged which can bring about possibly fatal ventricular arrhythmias which may be torsade de pointes.
Along with this, ketoconazole has been reported for slowing down or even stopping the metabolism of some drugs. It is advised by the FDA to prescribe ketoconazole only when the benefits outweigh the possible risks for the patient.
Females, diabetic people, those who are suffering from any thyroid disorder, malnutrition patients and alcohol addicts have a greater threat to have to prolong QT interval.
Which drugs interact with ketoconazole?
Ketoconazole interacts with a number of drugs and adversely affect their concentrations in plasma and as a result, their effectiveness is also affected.
Alfuzosin: the interaction with this drug is categorized as a severe drug-drug interaction. Both the drugs have been responsible in prolonging of the QT interval so when both are administered simultaneously, the prolongation effect is more enhances and results in a more unfortunate series of events to occur which include life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
Ketoconazole is an inhibitor of isozyme CYP3A4 whereas alfuzosin is a CYP3A4 substrate. This combination increases the serum concentrations of alfuzosin which then adversely affects the patients.
Benzodiazepines: ketoconazole when given along with benzodiazepines such as alprazolam and lorazepam, it increases the plasma concentration of these drugs, prolonging their effect particularly sedation.
When benzodiazepines are used at higher doses, chances for possible toxicity to occur also increases. Thus it is advised to keep a regular check on the patient’s vital to monitor for any signs of depression of the systems within the body.
Antacids: ketoconazole is a biphasic weak acid which requires an acidic medium for its absorption. Those medications which target the acidity of the stomach either by increasing or decreasing the pH of the medium have a direct effect on the bioavailability of ketoconazole.
Antacids decrease the acidity of the stomach and thus making the ketoconazole to absorb at a slower rate. It should be suggested to patients to ingest oral ketoconazole tablet 1 – 2 hours before antacids for maximum bioavailability.
Cisapride: this is one another sever drug interaction that is reported when coadministered with ketoconazole. The metabolism of cisapride is decreased drastically when ketoconazole is administered thus raising the plasma concentrations of cisapride.
This may cause cardiac toxicity including QT prolongation and torsade de pointes. Ketoconazole is accountable for increasing the serum concentration of cisapride by eightfold.
What are the storage conditions of ketoconazole?
Each dosage form requires specific conditions to store the product. Following are the conditions of each dosage form of ketoconazole in order to maintain its maximum stability.
- Foam and Cream:
It should not be kept at temperatures higher than 49°C.
This is a flammable product; keep away from fire and flame.
Do not directly expose it directly to sunlight.
Keep it at a normal room temperature.
This should not be kept in the refrigerator.
- Shampoo:
Do not directly expose it directly to sunlight.
Store at a temperature which should not exceed 77 °F.
- Gel:
Store at a temperature in between 59 – 86 °F
This is a flammable product; keep away from fire and flame.
“Ketoconazole oral and Lovastatin oral drug interactions”
“What is desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol used for?“