Contents
- What is solifenacin?
- Solifenacin IUPAC name molecular formula, weight, structure, drug class
- Solifenacin chemistry, identification and inactive ingredients
- Mechanism of action of solifenacin
- What are the pharmacokinetics of solifenacin?
- What are the possible side effects of using solifenacin?
- Toxicity of solifenacin
- Who should not take solifenacin?
- Any special dosing considerations to make during solifenacin use?
- Solifenacin use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Solifenacin use in geriatric population
- Can I take solifenacin with warfarin?
- Can I take solifenacin with digoxin?
- Can I take solifenacin with oral contraceptives?
- Can solifenacin be taken with ketoconazole?
- Can solifenacin be taken with haloperidol?
- Can solifenacin be given in patients with arrhythmias?
- Can solifenacin be given to the patients with liver injury?
- Can solifenacin be given to the patients with a renal injury?
- Can solifenacin be given to the patients with narrow angle glaucoma?
- How should solifenacin be administered?
- What are the storage conditions for solifenacin?
What is solifenacin?
Solifenacin is used for treating an overactive bladder (this is a condition in which the muscles of the urinary bladder show uncontrolled contractions and this results in the increased urge to urinate, urination frequency and bladder incontinence).
This drug is an antispasmodic which belongs to a class of antimuscarinics. Solifenacin currently only exists in generic form. This is a prescription drug which is only used in adults.
Solifenacin IUPAC name molecular formula, weight, structure, drug class
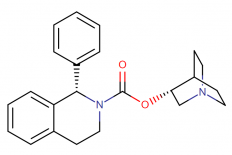
IUPAC Name: (3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-3-yl (1S)-1-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-2-carboxylate
Molecular formula: C23H26N2O2
Molecular weight:
The average weight of solifenacin is 362.473 g/mol
The weight of monoisotopic form of solifenacin is 363.199 g/mol
Solifenacin succinate weight is 480.55 g/mol
Molecular structure:
Drug class: Solifenacin belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 1-phenyltetrahydroisoquinolines, which are compounds containing a phenyl group attached to the C1-atom of a tetrahydroisoquinoline moiety.
Solifenacin chemistry, identification and inactive ingredients
Solifenacin is usually available in a mixture as solifenacin succinate. This compound is usually white in color or pale yellowish-white crystal or may be in the form of crystalline powder. This is highly soluble in water, glacial acetic acid, methanol, dimethyl sulfoxide mostly at normal room temperatures.
The formulation of solifenacin is available only in the oral dosage form and two dosage strengths are manufactured till now that is 5mg and 10mg.
Along with the active ingredient, excipients that are commonly used are magnesium stearate, lactose monohydrate, cornstarch, polyethylene glycol 8000, talc, hypromellose 2910 and titanium dioxide.
The type of ferric oxide in the formulation depends on the dosage strength to be prepared that is in 5mg tablet, yellow ferric oxide is used and in 10mg tablet red ferric oxide is used.
Mechanism of action of solifenacin
Solifenacin exerts its action in the body by acting on the muscarinic receptors. It has the specificity of being an antagonist to the M3 receptor.
Generally, all the antimuscarinic drugs are used to slow down the voluntary and involuntary contractions of the bladder.
In addition to this, the antimuscarinic drugs also control the secretions produced by the salivary glands, the ciliary muscle of gastric region and central nervous system.
There are basically five types of muscarinic receptors present out which M2 and M3 are abundantly available on the detrusor muscle.
According to some studies conducted, M3 muscle present in the detrusor muscle although small in number is responsible for the contraction of the bladder.
Some of the muscarinic receptors which also play an important role in the micturition process are present on the presynaptic nerve terminals (by regulating the release of transmitter neurons) and also on the urothelium cells present in the bladder lining.
Clinically the action of solifenacin is demonstrated to slow down or stop the contraction in the urinary bladder, reduce the detrusor pressure and cause partial emptying of the urinary bladder.
It has also been observed that solifenacin in comparison to other antimuscarinics has been more potent to enhance the volume of urine output and controls the frequency of incontinence of bladder and the urgency to urinate.
Moreover, solifenacin has poor penetration into central nervous system reducing the chances of side effects that usually occur with antimuscarinics.
It has a high distribution value in tissues other than CNS. This drug also has shown specificity to bladder muscles as compared to other muscles or salivary receptors.
What are the pharmacokinetics of solifenacin?
Absorption: Solifenacin has a very high bioavailability in the body which is approximately 90%. This shows that the drug is readily absorbed into the bloodstream.
After the drug is orally absorbed, the Cmax (which represents the peak plasma concentrations) is obtained within the time duration of 3 to 9 hours post ingestion.
This is usually obtained at a steady state ranging in between 32.3 to 62.9ng/ ml for the dosage strengths of 5mg and 10mg correspondingly.
It has thus been concluded that the plasma concentrations of solifenacin obtained shows a direct relationship to the amount of dose administered.
However, no special considerations are to be made with respect to meals for the administration of solifenacin. When a single of 10mg is given, due to the presence of food the peak plasma concentrations and AUC have increased by 3% – 4%.
Distribution: Solifenacin is widely distributed in body tissues but has shown poor penetration into the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
In vivo distribution of solifenacin is just about 98% of the plasma protein levels. Majorly, solifenacin binds with α1 – glycoprotein. An average volume of distribution of the drug is between 600 – 700L.
Metabolism: A large portion of solifenacin is metabolized by the liver. The major elimination pathway for the drug is via CYP3A4 but it is metabolized by other pathways too.
N-oxidation of quinuclidin ring and 4R-hydroxylation of tetrahydroisoquinoline ring are the major metabolic reactions that take place.
A total of four major metabolites are formed. Out of this four one is pharmacologically active metabolite which is 4R-hydroxy solifenacin and the other three have yet been marked as pharmacologically inactive metabolites which are N-glucuronide, the N-oxide and 4R-hydroxy-N-oxide of solifenacin. Further metabolic studies are still being conducted.
Excretion: According to a study conducted, when a dose of 10mg 14C-solifenacin was given to healthy people, about 69.2% of the radioactive compound was obtained in urine and approximately 23% of it was obtained in feces.
This study was made over 26 days. On average, less than 15% was obtained in urine as unchanged drug. The elimination half-life for solifenacin is between 45 – 68hours.
Among the metabolites that were formed only 4R-hydroxy-solifenacin is obtained in feces. The remaining three were excreted in urine.
What are the possible side effects of using solifenacin?
Some of the most common side effects of using solifenacin are listed below. These side effects are however mild in intensity and reversible on discontinuation of the drug. These are:
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Urinary tract infection
Serious side effects include:
- Heat stroke or heat exhaustion. This occurs in people who are living in a warm climate area. Characteristic features of this include
- Reduced sweating
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Severe allergic reactions may occur which include:
- Intense itching
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling, redness, hives, and rash
- Swelling of lips, tongue, face, eyes and lower legs
- Chest tightness and difficulty in breathing.
Toxicity of solifenacin
Solifenacin is an anticholinergic drug. Overdosage from solifenacin can possibly result in severe and drastic anticholinergic effects. The treatment should be decided accordingly.
In a research a maximum dose of solifenacin which was given to the healthy people was 100mg. but was gradually increased.
Unbearable side effects were observed when the quantity of solifenacin reached 50mg.
These side effects included dilation of pupils, blurry vision, dry skin, tremors and due to this failure to exam the area from heel-to-toe. When overdosage occurs, the patient should be immediately treated with activated charcoal.
The treatment for each symptom can be treated as follows:
- Hallucination or pronounced excitation: physostigmine can be used
- Convulsions can be treated with benzodiazepines.
- Respiratory problems: treated with respiratory depression
- Tachycardia should be treated with beta-blockers
- Mydriasis can be treated with pilocarpine eye drops or patients can be positioned in a dark room.
- Urinary retention can be treated by catheterization.
Who should not take solifenacin?
Every drug is not prescribed to every patient for a single indication. Underlying diseases or medical conditions should be considered before taking solifenacin. This is not recommended for patients who:
-
Are suffering from urinary retention.
This is due to the fact the solifenacin will exert it’s antimuscarinic effect and may deteriorate the renal function to a greater extent.
Distorted pharmacokinetic profile of the drug is seen in patients who are severely renal impaired or in whom there is a renal failure.
-
Have an abnormality in gastric retention
Solifenacin is reported to show an antispasmodic effect on the smooth muscles present in the gastric region. This, in turn, can delay gastric emptying.
All those patients with any of the disease in which gastric retention is notably changed, should not use this drug.
Moreover, it is not beneficial for the patients for the purpose of setting of ileus or colon. Generally, the use of this drug will also intensify the gastro-esophageal reflux disease.
-
Suffering from ‘controlled narrow-angle glaucoma’
The use of solifenacin has to be used with caution as it has been responsible for increasing the intraocular pressure and aqueous outflow resistance in patients who are suffering from closed-angle glaucoma.
Furthermore, the anticholinergic effect of solifenacin has also made the eyes dry with time.
-
Those are suffering from myasthenia gravis:
Solifenacin is reported to worsen up the symptoms of myasthenia gravis by acting on the cholinergic receptors.
-
Those who are allergic to any of the ingredients of solifenacin succinate formulation.
Those patients who have shown hypersensitivity to solifenacin may show angioedema. This occurs on face, eyes, lips, tongue and even on lower legs.
Angioedema is possible to occur on the ingestion of the first dose or immediately after the treatment course is finished. Swelling of the airway tract has lead to breathing difficulties.
Any special dosing considerations to make during solifenacin use?
In patients who are suffering from hepatic diseases, elimination rate is altered to a great extent. In those patients, where the hepatic function is decreased to a mild to moderate level, changes in dosage are sufficient.
It is recommended to not to exceed the adult dose from 5mg once a day. In severely damaged cases, solifenacin should be immediately discontinued.
In patients who are renally impaired, solifenacin due to its antimuscarinic effect is not advised as it will worsen the situation of urinary retention.
It may also exacerbate the situation in patients who are experiencing prostatic hypertrophy or urinary tract obstruction.
In severe cases, the creatine clearance (CrCl) is 30ml/ minute or less, a dose which does not exceed 5mg PO can be given once daily.
Solifenacin use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
- In Pregnancy
There hasn’t been any safety studies established for solifenacin for use in pregnancy, yet it can only be used when the benefits for the mother and fetus outweigh the possible risks. This drug belongs to pregnancy category class C.
- Breastfeeding:
The prescriber should decide if solifenacin should be continued depending on the treatment duration.
It has been demonstrated that anticholinergic drugs act on the secretary receptors and are found to decrease the lactation and serum prolactin concentrations. Therefore, it is advised to not use this drug chronically.
Solifenacin use in geriatric population
With age, the body functions gradually decrease. Usually, geriatric patients have impaired renal or hepatic system. It is therefore recommended to make dose adjustments when required.
Can I take solifenacin with warfarin?
In a study conducted, when solifenacin was given to patients who were being given warfarin, it was observed the two isomers of warfarin had shown different interaction.
The R-warfarin when it was concomitantly given solifenacin, the peak plasma concentration was increased by 3% on average and the AUC reduced by 2%. Whereas when S-warfarin was administered the peak plasma concentration by 5% and AUC was increased by 1%.
Can I take solifenacin with digoxin?
Patients who were using digoxin with a loading dose of 0.25mg per day followed by 0.125mg as a maintenance dose had shown an altered pharmacokinetics when solifenacin was administered. It was observed that both the Cmax and AUC has shown a rise.
Can I take solifenacin with oral contraceptives?
In a study conducted, healthy volunteers were given 2 consecutive cycles of 21 days of oral contraceptives. This contained 30µg ethinyl estradiol and 150 µg of levonorgestrel.
When the second cycle of oral contraceptives was being administered, solifenacin was concomitantly administered. Solifenacin increased the man Cmax and AUC values for ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel.
Can solifenacin be taken with ketoconazole?
Concomitant use of solifenacin with potent inhibitors of CYP450 3A4 such as ketoconazole may significantly increase the plasma concentrations of solifenacin, which is primarily metabolized by the isoenzyme.
According to the product labeling, administration of solifenacin (10 mg) in combination with the potent CYP450 3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole (400 mg) increased solifenacin mean peak plasma concentration (Cmax) and systemic exposure (AUC) by 1.5- and 2.7-fold, respectively, compared to administration alone. Solifenacin is also associated with dose-related prolongation of the QT interval.
Can solifenacin be taken with haloperidol?
Haloperidol may provoke dose-related prolongation of the QT interval. In theory, concomitant use with other agents that can also prolong the QT interval may result in additive effects and considerably increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias including torsade de pointes and sudden death.
Haloperidol treatment alone has also been associated with a variety of reported cases of torsade de pointes and sudden death.
The majority of cases involved intravenous administration or use of higher than recommended dosages. In general, the risk of an individual agent or a combination of agents causing ventricular arrhythmia in association with QT prolongation is largely unpredictable but may be increased by certain underlying risk factors such as congenital long QT syndrome, cardiac disease, and electrolyte disturbances (e.g., hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia).
The extent of drug-induced QT prolongation is dependent on the particular drug(s) involved and dosage(s) of the drug(s).
In addition, certain agents with anticholinergic properties (e.g., sedating antihistamines; antispasmodics; neuroleptics; phenothiazines; skeletal muscle relaxants; tricyclic antidepressants) may have additive parasympatholytic and central nervous system-depressant effects when used in combination with haloperidol.
Excessive parasympatholytic effects may include paralytic ileus, hyperthermia, mydriasis, blurred vision, tachycardia, urinary retention, psychosis, and seizures
Can solifenacin be given in patients with arrhythmias?
During solifenacin use, dose-dependent prolongation in QT interval has been observed. Thus solifenacin should be used with caution in patients with a known history of QT prolongation or patients who are taking medications known to prolong the QT interval.
Can solifenacin be given to the patients with liver injury?
Solifenacin should be used with caution in patients with reduced hepatic function. Increase in half-life and AUC have been demonstrated in patients with reducing hepatic impairment.
Caution should be taken when prescribing this agent to patients with moderate hepatic impairment and the use of doses greater than 5 mg in these patients is not recommended by the manufacturer. Solifenacin is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Can solifenacin be given to the patients with a renal injury?
Solifenacin has to be used with caution in patients with kidney impairment. Increase in elimination half-life and AUC have been demonstrated in patients with severe renal impairment during solifenacin use.
Caution should be taken when prescribing this agent to patients with renal impairment. Doses greater than 5 mg in patients with severe renal impairment is not recommended by the manufacturer.
Can solifenacin be given to the patients with narrow angle glaucoma?
The use of solifenacin is contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma. Caution is advised even when using this agent in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma.
How should solifenacin be administered?
- Not more than a single tablet should be taken per day
- Do not crush or chew the tablet.
- Swallow it as a whole with water.
- Solifenacin can be taken with or without a meal.
What are the storage conditions for solifenacin?
- Solifenacin should be stored at normal room temperature of about 25°C.
- Direct exposure from sunlight should be avoided.
- It should not be placed at places accessible for children.