Contents
- What is alendronate?
- Alendronate IUPAC name, molecular formula, weight, structure and drug class
- Alendronate identification and chemistry
- Alendronate mechanism of action
- Alendronate effects on bone resorption
- What are the indications of alendronate?
- Alendronate use for Paget’s disease
- Alendronate pharmacokinetics
- Alendronate dosage and administration
- What side are effects associated with alendronate use?
- Alendronate overdosage
- What are the contraindications of alendronate?
- Alendronate and esophageal adverse effects
- Alendronate use in renal and hepatic disease patients
- Alednronate use and jawbone issues
- Alendronate and oral contraceptives
- Alendronate and glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis
- Alendronate drug interactions
- How to use alendronate?
- Can I take alendronate if I have low calcium levels in blood?
- Recommendations for calcium and Vitamin D supplementation during alendronate use
- Can I take vitamins and minerals at the same time with alendronate?
- Can I take food at the same time with alendronate?
What is alendronate?
Alendronate is a generic name for a drug belongs to bisphosphonate group. It is a synthetic analog of pyrophosphate that binds to the hydroxyapatite present in bones.
Alendronate also acts as a potent specific inhibitor of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. As a brand name product, it is most commonly known as Fosamax.
Alendronate IUPAC name, molecular formula, weight, structure and drug class
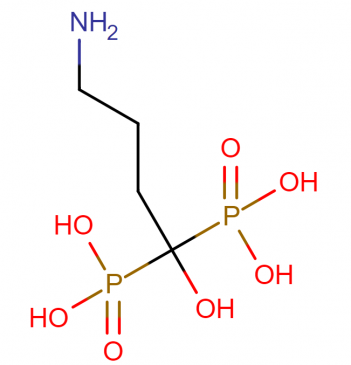
IUPAC name: (4-amino-1-hydroxy-1-phosphonobutyl) phosphonic acid
Molecular formula: C4H13NO7P2
Molecular weight: 249,097 g/mol
Molecular structure:
Drug class: Alendronate belongs to the class of organic compounds known as bisphosphonates which are organic compounds containing two phosphonate groups linked together through a carbon atoms.
Alendronate identification and chemistry
Alendronate is a white, nonhygroscopic crystalline powder which is soluble in water and very slightly soluble in alcohol and completely insoluble in chloroform. Alendronate is a nitrogen-containing, second generation bisphosphonate.
Alendronate mechanism of action
Like other bisphosphonates, affinity for bone mineral of alendronate is very high and is taken up during osteoclast resorption.
Farnesyl pyrophosphate FPP is inhibited by alendronate, which is one of the important enzymes in the mevalonic acid pathway which is involved in the formation of isoprenoid compounds that are important for post-translational modification of small guanosine triphosphate (GTP)- binding proteins.
Inhibition of this process interferes the functioning of the osteoclast.
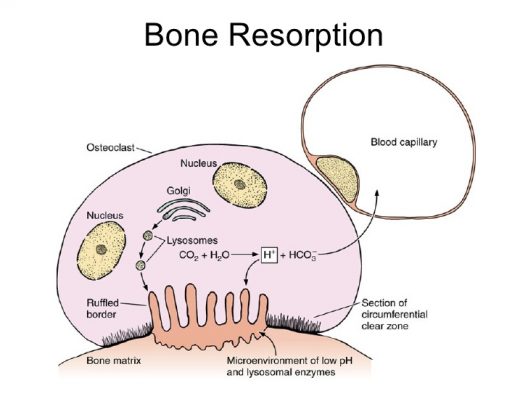
Alendronate effects on bone resorption
Osteoporosis or bone resorption is a chronic metabolic disorder which is characterized by an increased level of bone turnover, progressive loss of bone mass, microarchitectural deterioration, and increased fracture risk.
The main by-product of bone metabolism is pyrophosphate.
Alendronate is an analog of pyrophosphate that has effective inhibitory effects on bone resorption.
The alendronate is effectively adsorbed to hydroxyapatite, the crystalline form of calcium and phosphate in bone.
Alendronate works on a number of pathways to treat and prevent the bone resorption:
Remodeling
When alendronate is administered to growing experimental rats, remodeling at the ends of long bones is reduced and thus results in a reduction in the abnormal shape of bones.
Resorption
Both in vivo and in vitro studies showed the alendronate are very effective in inhibiting the bone resorption.
They act readily, and the maximum effect and its duration are related to the dose. In organ cultures of bone, treatment of alendronate used causes the inhibition of bone resorption.
When resorption effect of osteoclast separately studied on bones and dentine slices, their effect was also inhibited by alendronate.
Alendronate does not interfere with osteoclast formation or attachment, but it may inhibit osteoclast activity and function.
Osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity
Alendronate acts not only on the direct inhibition of functioning of osteoclasts, they can also inhibit the proliferation of already produced osteoclasts.
Osteoblasts are important stimulators of osteoclast formation and activity, and many factors that stimulate bone resorption through the effect on the osteoblast.
Stimulatioin of osteoblast to produce inhibitor(s) of osteoclast formation is one of the possible mechanism of action of alendronate. Thus inhibits the bone resorption.
Studies in mice that were done with radioactive alendronate administration, indicated about 10-fold higher uptake on the surface of osteoclast than on osteoblast surfaces in bones.
After alendronate administration in rats and mice after 6 and 49 days respectively, results showed that normal bone was formed on top of the alendronate, which was incorporated into the medium.
On the other hand, the alendronate that was incorporated in the bone matrix is not pharmacologically active. Thus, a continuous supply of alendronate is required to suppress osteoclasts on newly formed resorption surfaces.
What are the indications of alendronate?
- Alendronate is indicated for the women who are suffering from postmenstrual osteoporosis and for the prevention of bone fractures which includes fractures of hip and spine (vertebral compression fracture).
- It is indicated for Paget’s disease (cellular remodeling and deformity of one or more bones)
- For the treatment and prevention of corticosteroid-associated osteoporosis with calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Alendronate is also indicated for osteogenesis imperfect in patients of 18years or older.
- On the experimental basis, it is used for dental implants coating.
- Alendronate is also indicated for the men for the treatment of osteoporosis and to prevent fractures.
- It is also indicated for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis both in men and women who are taking glucocorticoid medication equal to 7.5mg or greater of prednisone in a day and who have low BMD (bone mineral density) levels. Patient having glucocorticoid treatment should intake sufficient amount of calcium and vitamin D.
What are the indications of alendronate?
- Alendronate is indicated for the women who are suffering from postmenstrual osteoporosis and for the prevention of bone fractures which includes fractures of hip and spine (vertebral compression fracture).
- It is indicated for Paget’s disease (cellular remodeling and deformity of one or more bones)
- For the treatment and prevention of corticosteroid-associated osteoporosis with calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Alendronate is also indicated for Osteogenesis imperfect in patients of 18years or older.
- On the experimental basis, it is used for dental implants coating.
- Alendronate is also indicated for the men for the treatment of osteoporosis and to prevent fractures.
- It is also indicated for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis both in men and women who are taking glucocorticoid medication equal to 7.5mg or greater of prednisone in a day and who have low BMD (bone mineral density) levels. Patient having glucocorticoid treatment should intake sufficient amount of calcium and vitamin D.
Alendronate use for Paget’s disease
Alendronate is indicated for the management of Paget’s disease of bone. Treatment is only indicated in patients who have alkaline phosphatase at least two times the upper limit of normal, or in those who are symptomatic, or in patients who are high risk for future complications from their disease.
Alendronate pharmacokinetics
Absorption: alendronate is available in an oral dosage form. When oral doses ranging from 5 to 40mg is administered after an overnight fasting and two hours before standard breakfast, its mean oral bioavailability as compared to intravenous (IV) reference dose in women was 0.7%.
I mean, oral bioavailability of 10mg tablet (0.59%) was same as of in women (0.78%) when administered under same conditions.
Absorption of alendronate is highly affected by food and to some extent from some other medication.
So for proper absorption of alendronate, it is advised to take medication one and a half hour before meal and intake of other medication and take medicine with a full glass of water.
A study was conducted to examine the timing of the meal on the bioavailability of alendronate in which 49 postmenopausal women were evaluated.
The results of the study showed that there is approximately 40% decrease in bioavailability when 10mg of alendronate was given either 0.5 or one hours before the breakfast as compared to the dose given 2 hours before standardized breakfast.
In studies for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis, alendronate was best effective when it was administered one and half hour before breakfast. Absorption and disposition of alendronate are not dosed dependent.
Distribution: pre-clinical studies in rats show that alendronate is widely distributed in body fluid and soft tissues and it is then readily distributed again to bones.
The mean volume of distribution exclusive to bones is 28L. While plasma protein binding of alendronate is human is approximately 78%.
Metabolism: according to studies there is no evidence of metabolism of alendronate in humans as well as in humans. It eliminates from the body in unchanged form.
Excretion: alendronate is majorly excreted through renal route. In pre-clinical trials, radioactive alendronate in IV form was given to animals and approximately 50% of the radioactivity was measured in urine after 72 hours.
While there was no traces radioactivity in feces. The renal clearance of alendronate was 71ml/min and systemic clearance did not exceed from 200m./min. the terminal half-life of alendronate in humans is more than 10year (approximately 126 months).
It was noted that plasma concentration fells about 95% within 6 hours when administered in IV form.
According to these values, it is expected that after 10years of oral treatment with alendronate, the amount of drug excreted out daily from the skeleton is approximately 25% of the absorbed drug via gastrointestinal track.
Alendronate dosage and administration
- Alendronate is available in the tablet dosage form having a strength of 70 mg per tablet.
- The recommended dose of alendronate for the treatment of osteoporosis both in men and women is 70mg tablet once in a week.
- Alendronate must be taken with plain water at least one-half hour before the first food of the day, other medication or beverages because other beverages food and other medication reduce the absorption of alendronate.
- Use of alendronate in elderly patients or in patients with mild to moderate renal insufficiency (having creatinine clearance between 35 to 60ml/min), no dose adjustment is required. While use alendronate in a severe renal impaired patient (having creatinine clearance <35ml/min) is not recommended due to lack of experience.
What side are effects associated with alendronate use?
Clinical studies/ trials done on alendronate showed that it is well tolerated. The side effect occurred in these studies were of mild types and generally did not require discontinuation of therapy.
In post-market experience, following adverse events were reported.
Body as a whole: hypersensitivity reaction including urticaria and rarely angioedema. With the initiation of treatment of alendronate, some acute phase symptoms like myalgia, malaise, asthenia and rarely fever may occur. But it is only in transient phase
Gastrointestinal: with the use of alendronate gastrointestinal side effect including nausea, vomiting, esophageal ulcer, esophagitis, esophageal erosion, rarely esophageal stricture or perforation, and oropharyngeal ulceration; rarely gastric and duodenal ulcer some time sever condition may occur.
Localized osteonecrosis of the jaw, generally associated with tooth extraction with delayed healing has been reported rarely.
Musculoskeletal: bone, joint and/or muscle pain, sometimes severe; joint swelling, low energy femoral shaft fracture.
Skin: rashes occasionally due to photosensitivity, alopecia, pruritus, rarely sever skin reaction including Steven-Johnson syndrome.
Alendronate overdosage
There is no specific antidote available for the management of the overdose of alendronate.
Usually, it is advised to use antacids and milk to manage to overdose and to avoid adverse events like hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia and upper gastric problems such as upset stomach, esophagitis, gastritis, heartburn, and ulcer.
Vomiting inducing technique must be avoided due to gastric irritation and risk of gastric perforation.
What are the contraindications of alendronate?
- Alendronate is contraindicated if the patient has any of the following situations
- Hypersensitive to the drug
- Hypocalcemia (Low level of calcium in the body)
- Any abnormal condition of the esophagus that causes the slow or delayed emptying like stricture or achalasia
- The patient is unable to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes
Alendronate and esophageal adverse effects
As alendronate belongs to bisphosphonate group and like other molecules of this group alendronate also have the potential of causing local irritation in the upper gastrointestinal mucosa.
The reported esophageal adverse events from the use of alendronate include esophagitis, esophageal ulcer and esophageal erosions rarely followed by esophageal strictures or perforation.
In some cases, the severity of these esophageal disturbances caused hospitalization so a physician should warn patient to discontinue alendronate treatment and seek for a medical emergency if they develop odynphagia, dysphagia, retrosternal pain or new or worsening heartburn.
Studies say that the risk of esophageal adverse events is much more in those patients:
- Who lie down after taking alendronate
- Who fails to swallow medicine with a full glass of water
- Who continue taking medication after developing symptoms of esophageal disturbance
Therefore it is necessary to follow the dosage schedule and precaution very carefully.
Alendronate use in renal and hepatic disease patients
As alendronate is excreted mainly through kidney so in case of mild to moderate renal impaired patients dose adjustment is required.
While in severe renal impaired or kidney failure patients use of alendronate in contraindicated.
There is no evidence of metabolism of alendronate and it is eliminated in unchanged form so in hepatic impaired patient no dose adjustment is required.
Alednronate use and jawbone issues
Jawbone problem due to use alendronate is one of the serious problems facing the patient. The doctor should check mouth before patient start this medication.
Before any dental work is done inform the doctor about the use of this medication. Have a regular dental checkup and keep the teeth and gums to avoid and prevent the jaw bone problem.
If jawbone problem develops in someones due to this medication then seek for a medical emergency.
Alendronate and oral contraceptives
Before starting treatment, the hormonal levels both in men and women should be ascertained and suitable substitute considered.
A bone mineral density test should be done at the initiation of therapy and repeated after regular intervals of up to 6 to 12 months.
Alendronate and glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis
Alendronate has been shown to be efficient in the management of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in patients with a medium BMD which was 1.2 standard deviations below the mean for healthy young adults.
One study that lasted 2 years established the efficacy of alendronate. The increase in BMD is much greater in the first year of therapy as compared to the second year of treatment when there is a small increase in bone mineral density.
However, the efficacy of alendronate beyond two years has not been studied. The efficacy of alendronate in respect to fracture prevention has been demonstrated for vertebral fractures.
Alendronate drug interactions
The concomitant use alendronate with calcium supplements, antacids, and other oral medications will interfere the absorption of alendronate.
Therefore patient must take other oral medication at least one-half hour after the alendronate dose.
Use of Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is associated with gastrointestinal irritation so caution is required when NSAIDs are used with alendronate.
Two clinical trials were conducted in which concomitant use of alendronate and HRT (estrogen + progesterone) was evaluated in postmenopausal osteoporosis women.
Results show that combine use alendronate and HRT causes a greater increase in bone mass and decrease the risk of bone turnover as compared to either alone treatment.
In these trails, safety and tolerability profile of combined therapy were consistent as of in individual treatment.
No other drug interaction was observed in clinical studies and trials.
How to use alendronate?
For better delivery of alendronate and to avoid potential esophageal disturbance, it should be taken only upon rising for the day at least for one-half hour before the first meal of the day with full glass of plain water and it is instructed not lay down for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication and until after the first meal of the day.
Alendronate should not be taken at night. Not following this instruction may cause increased risk or severity of potential esophageal adverse events.
Can I take alendronate if I have low calcium levels in blood?
Patients who have hypocalcemia should not use bisphosphonates as they are contraindicated in that case. These drugs may increase bone mineral density.
At the beginning of therapy, a short-term reduction in serum calcium and phosphate levels usually develops because of the inhibition of bone resorption, especially in Paget’s disease patients, in whom the pretreatment rate of bone turnover may be greatly elevated.
Hypocalcemia and mineral metabolism disturbances, such as vitamin D deficiency, should be treated before the initiation of therapy. Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D should be ensured throughout the course of treatment.
Recommendations for calcium and Vitamin D supplementation during alendronate use
Recommend patients to take supplemental calcium if their dietary intake is inapropriate. Patients who are at increased risk for vitamin D insufficiency such as those over the age of 70 years, chronically ill or nursing home-bound may need vitamin D supplementation.
Patients with GIT malabsorption diseases may need higher doses of vitamin D supplementation and also a measurement of 25-hydroxyvitamin D should be considered. Patients treated with glucocorticoids need to receive adequate amounts of calcium and vitamin D.
Can I take vitamins and minerals at the same time with alendronate?
Alendronate and multivitamin with minerals should not be taken orally at the same time. Products that contain aluminum, magnesium, calcium, iron, and/or other minerals may interfere with the alendronate absorption and reduce its effectiveness.
You should take multivitamin with minerals at least 30 minutes after the alendronate dose. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns.
It is important to tell your doctor about all other medications you use, including vitamins and herbs. Do not stop using any medications without first talking to your doctor.
Can I take food at the same time with alendronate?
Food can reduce the alendronate absorption and bioavailability, which may furhter lead to reduced blood levels of the drug and possibly reduced effectiveness.
Patients should take alendronate in the morning, at least 30 minutes before meal or before they drink anything or take any other drug.
Patients should take each dose with a full glass of water, and use only plain water (exclude mineral or vitamin water).
Patients should not take alendronate if they can’ sit upright or stand for at least 30 minutes. Alendronate can cause stomach or esophagus irritation and ulcer, thus patients will need to stay upright for at least 30 minutes after taking it.
Patients should talk to their doctor or pharmacist if they have questions on how to take this medication.
It is important to tell their doctor about all other drugs they use, including vitamins and herbs. They should not using any medications without first talking to their doctor.