Contents
- What is Atazanavir
- Atazanavir brand name
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)
- What is Atazanavir used for
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
- Chemical information of the drug
- Atazanavir strengths
- How does Atazanavir work
- Atazanavir dose
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Atazanavir
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of Atazanavir
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Atazanavir
- How to take Atazanavir
- How to store the drug
- How to dispose the medicine
- Does Atazanavir has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies
- Other uses of the drug
- What special dietary precautions should I follow
- What precautions should I follow while using Atazanavir?
- Atazanavir side effects
- Atazanavir overdose
- Atazanavir missed dose
- Atazanavir drug interactions
- Does Atazanavir have any interaction with diseases
- Where can I get more information
- Atazanavir is a drug that is in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection which can cause the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
- The drug is available under generic name Atazanavir, Atazanavir sulfate and marketed by Bristol Myers, (formerly known as BMS-232632) under brand name Reyataz.
- The drug has been placed in the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medication needed in a basic health system.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)
- Atazanavir is a synthetic (man-made) protease inhibitor (PI) class of antiretroviral drug.
- Atazanavir is an antiretroviral protease inhibitor class of drug that plays a key role in the treatment of HIV-1 infection in combination therapy with other drug such as Ritonavir.
- The drug is also used in combination of other retroviral drugs for postexposure prophylaxis of HIV infection in individuals who have had occupational or nonoccupational exposure to HIV-1.
- However, this drug does not cure the infection of Human Immunodeficiency Virus. It may reduce the possibility of the development of AIDS and also diminish the occurrence of other infections or cancer.
- Atazanavir inhibits the enzyme activity of protease by binding to its active site and lowering the quantity of virus in the infected person’s blood.
- Pharmacokinetics of Atazanavir has allowed once-daily dosing, and it is not associated with significant PI-associated dyslipidemia, lipodystrophy and elevated cholesterol levels.
- The drugs also showed no cross-resistant when boosted with other protease inhibitors.
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
Atazanavir chemically belongs to the class of synthetic pharmaceutical organic compounds which are known as Phenylpyridines. Phenylpyridines are characterized by the presence of benzene ring linked to a pyridine ring through a CC or CN bond. The detailed chemical classification of Atazanavir is described below:
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
| Class | Pyridine and derivatives |
| Sub Class | Phenylpyridines |
| Direct Parent | Phenylpyridines |
Chemical information of the drug
- Atazanavir is available as a sulfate salt which selectively brings about the inhibition of the processing of viral polyprotein precursors (Gag and Gag-Pol polyprotein) in cells infected with HIV-1 virus.
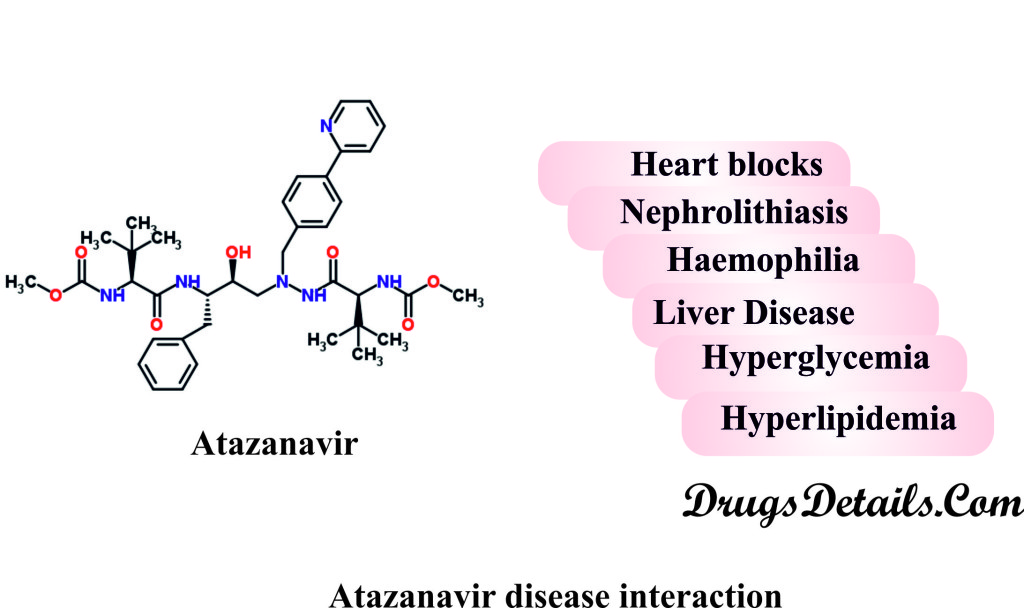
- Atazanavir is a synthetic pharmaceutical aromatic heteromonocyclic compound with a molecular formula C38H52N6O7 and molecular weight of 704.389 Da.
- The Atazanavir is chemically named as methyl N-[(1S)-1-{[(2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-4-[(2S)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-N’-{[4-(pyridin-2-yl)phenyl]methyl}butanehydrazido]-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamoyl}-2,2-dimethylpropyl]carbamate.
- Atazanavir is available as free base or as sulfate (Atazanavir sulfate). Atazanavir sulfate is white to pale-yellow crystalline powder.
- The drug is slightly soluble in water and has water solubility of 4-5 mg/mL.
- The melting point of Atazanavir is 214°C -216 °C.
- Atazanavir is available in powder and capsule form for oral administration.
- Atazanavir capsule is available in different dosage of 150, 200 and 300 mg/capsule and contains crospovidone, magnesium stearate and lactose monohydrate as inactive ingredients.
- The shells of capsule contain titanium dioxide, gelatine, red black & yellow iron oxides and FD&C Blue No.2.
- Shell of capsule of 150 mg labelled with “150” mg & “3624” and capule of 200 mg labelled with “200” mg & “3631” while capsule of 300 mg is labelled with “300” mg & “3622” and all type of capsule are labelled with “BMS”.
- The ink used for printing on shell contains titanium dioxide, isopropyl alcohol, ammonium hydroxide, propylene glycol, simethicone, n-butyl alcohol, shellac and FD&C Blue No.2.
- Atazanavir powder is available in strength of 50 mg Atazanavir in 1.5 gm of powder.
- The Atazanavir powder is off white to pale yellow in color and contains aspartame, sucrose and orange-vanilla flavour as inactive ingredients.
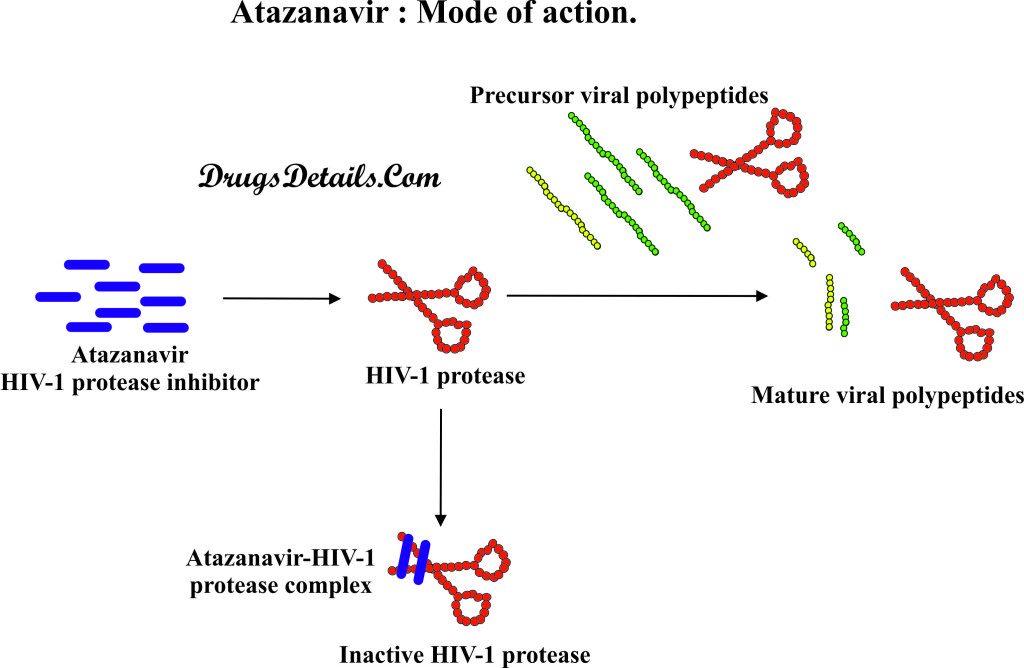
- Atazanavir is a HIV-1 protease inhibitor (PI) class of drug, which shows potent activity against Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1).
- Chemically Atazanavir is an azapeptide, which is a peptide analogue in which one or more of the amino residues is replaced by a semicarbazide.
- The mode of action of Atazanavir is similar to that of other drugs used for the treatment of retroviral infection.
- Atazanavir works similar to other protease inhibitor drug by inhibiting the HIV-1 protease enzyme.
- HIV-1 protease is an HIV-1 enzyme that is involved in the formation of infectious viral functional proteins (by proteolytic cleavage) from the viral polyprotein precursors.
- Atazanavir inhibits the activity of HIV-1 protease enzyme by binding to its active site. As a result of Atazanavir binding, HIV-1 protease is unable to cleave viral polyproteins precursors and development of mature infectious viral particles.
- Due to the inhibition of HIV-1 protease enzyme, processing of viral Gag and Gag-Pol polyprotein stops, which results into the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles.
- Apart from this, Atazanavir also plays an important role in increasing the number of CD4 (T) cells and help immune system to fight against HIV infection.
- The recommended dose of the drug for adults with HIV infection is usually 400 mg once a day.
- In combination therapy with the Ritonavir, the recommended dose of the drug is 300 mg once a day.
- In case of children from 6 years to less than 18 years, the recommended doses are based on the body weight and are as follows:
- 15 to less than 20 kg (33 to less than 44 lbs): 150 mg Atazanavir + 100 mg Ritonavir once a day
- 20 to less than 40 kg (44 to less than 88 lbs): 200 mg Atazanavir + 100 mg Ritonavir once a day
- 40 or more than 40 kg (88 or more than 88 lbs): 300 mg Atazanavir + 100 mg Ritonavir once a day
- In case of hepatic and renal impairment, the dosing recommendations are as follows:
- Dose in hepatic impairment: no dose adjustment required, take dose as prescribed by pharmacist or doctor.
- Dose in renal impairment: no need to alter the doses but in case of Haemodialysis 300 mg Atazanavir with 100 mg of Ritonavir should be recommended.
- Atazanavir powder is recommended for infants older than 3 months with Ritonvir. It should not be used alone.
- The usual dosing of the drug (i.e. 400 mg Atazanavir or 300 mg Atazanavir + 100 mg Ritonavir per day) may vary depending upon the efficiency and side effects of the drug in a particular individual.
- No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with hepatic impairment and renal impairment but in case of haemodialysis dose should be adjusted.
- The drug is contraindicated in case of hypersensitive response to any component of the drug.
- Atazanavir should be contraindicated with the medication of Triazolam, Dihydroergotamine, Ergotamine, Ergonovine, Midazolam and Pimozide.
- Atazanavir is not recommended for children younger than 6 year old.
- Dose adjustment is required during the medication with antacids, Didanosine or buffered Aspirin.
- Patient with phenylketonuria should use Atazanavir oral powder with aspartame.
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggested that after oral administration, Atazanavir is rapidly absorbed and has a bio-availability of approximately 60-68 %.
- When Atazanavir is taken with food, it decreases the pharmacokinetic variability and increases the bioavailability.
- It has been observed that following a 400 mg dose, maximum (or peak) plasma concentration is achieved in 150 minutes (2.5 hour) in the fasted state.
- Following absorption the majority (86%) of the drug is bound to serum proteins such as albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein.
- The drug is primarily metabolized by liver through major (monooxygenation and dioxygenation) and some minor (oxygenation, hydrolysis, dehydrogenation, glucuronidation and N-dealkylation) pathways.
- Studies with human liver microsomes also suggested that Atazanavir is extensively metabolised by hepatic cyotochrome P450, primarily the CYP3A4/ CYP3A5 isoenzymes.
- The average median half-life of Atazanavir is 7 hours except 12.1 hours in hepatically impaired patients.
- Atazanavir is mainly excreted in the feces (approximately 79%) in the form of metabolites and very little amount in the urine (13%).
- Uncharged drug account for 27% of total administered dose and excreted through feces (20%) and urine (7%).
- The Atazanavir is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: B
- Atazanavir is used for only those pregnant women who are infected with HIV-1 strain and prescribed for Atazanavir.
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies the use of Atazanavir in pregnant women is contraindicated and recommended only when benefit justifies the risk.
- Laboratory animal studies have shown no adverse effect of Atazanavir on fetus.
- Studies support the excretion of the drug into animal milk. However, no adequate data is available on excretion of Atazanavir into human breast milk.
- HIV infected women and women who use the medication of Atazanavir should not breastfeed the baby.
- Despite these facts caution should be exercised when taking Atazanavir.
- Atazanavir is available in capsule form for oral administration by mouth and usually recommended once a day with snacks or food.
- It is usually recommended not to chew or open or split the capsule.
- Atazanavir is also available in the powder form and used always with the combination of Ritonavir. Do not take the Atazanavir powder without Ritonavir.
- The powder of Atazanavir can be taken with food products (such as applesauce or yogurt) or liquids such as water, or milk.
- Precautions should be taken to mix the powder well and to take full dose of the drug.
- While taking or mixing the Atazanavir in water it is usually prescribed to take snacks or meal immediately after the consumption of powder mix.
- In case of infants Atazanavir powder can be mixed in infant formula and can be given using dropper or oral dosing syringe. Avoid mixing or use of baby bottle for the powder dosing.
- It is usually recommended to take the drug at the same time daily and the time duration between the drug uses should be at least 24 hours.
- Atazanavir is taken with water (one glass or more) at same time each day.
- It is advisable to take Atazanavir exactly as directed and not to take more than one capsule daily.
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet and ask your pharmacist for any information or any part you are unable to understand.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor, since the dosage is based on patient medical condition, treatment responses and usage with other drugs.
How to store the drug
- Atazanavir is stored at 25°C (77°F) and excursion permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
- The container should be tightly closed and kept away from excessive heat, direct sun light and reach of children.
- Do not freeze or store the medicine at extreme cold temperature.
- Medicine should not be stored in the bathroom.
How to dispose the medicine
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used container.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- Atazanavir should not be disposed in the household garbage, sink or in wastewater.
- The drug has received it official approval for the treatment of infection of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) on 20 June 2003 by U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- The drug was first protease inhibitors approved for once-daily dosing (rather than multiple dosing) and do not cross-resistant with other protease inhibitors (used for boosting the effect of Atazanavir).
- In year 2009, the US FDA issued a warning regarding use of Atazanavir with proton-pump inhibitors i.e. Asomeprazole (Prilosec), Rabeprazole (Aciphex) or Esomeprazole (Nexium). According to US FDA the concomitant use of Atazanavir with proton pump inhibitors significantly reduces the absorption and effects of Atazanavir.
Other uses of the drug
- Atazanavir may also be used for preventing the infection of HIV in peoples who are accidentally exposed.
- Atazanavir may also be used for other cases not mentioned here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special dietary precautions should I follow
- Alcoholic beverages, grapefruit, or grapefruit juice should be avoided.
- Alcohol consumption can also enhance some side effects of the drug.
- Do not use the medicine if you are hypersensitive or allergic to any of the ingredients. Consult with your doctor and pharmacist if you are taking any prescription and non-prescription medications or herbal products.
- Before taking Atazanavir, tell your doctor about your medical history preferentially if you have any kind of liver disease, renal disorder, heart disease, eye disorders, bleeding disorders, or blood pressure problems.
- During the treatment of Atazanavir, if the symptoms of other infections develop, consult to your doctor immediately.
- Avoid sharing razors, toothbrushes, medicine needles and unprotected sex.
- Use of Atazanavir may increase the body weight. Consult your doctor in case of any query.
In addition to the associated benefits, Atazanavir administration is accompanied with some side effects few of them are more common, others less common whereas some are more serious. It is always recommended to consult a doctor if you encounter any of the side effects.
Some common side effects of Atazanavir are as follows. If these symptoms persist tell to your doctor:
- Fever
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Mild rash
- Headache
- Depression
- Muscle pain
- Stomach pain
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Numbness, burning, pain, or tingling of hands or feet
Atazanavir may cause serious side effects. On appearing of these symptoms immediately contact to your doctor and get emergency treatment:
- Blood in urine or dark colored urine
- Dizziness
- Erection that lasts longer than 4 hours
- Irregular heartbeat
- Light-colored bowel movements
- Loss of appetite
- Pain in your back or side
- Pain or burning with urination
- Vision changes
- Vomiting
- Yellowing of skin or eyes (especially in newborn infants)
Stop taking the Atazanavir if following side-effects are observed:
- Development of severe rashes with other symptoms like fever, blisters or peeling skin, mouth sores, red or swollen eyes, muscle or joint aches, swelling of your face or neck.
- ‘Flu-like’ symptoms, painful, warm, or red lump under your skin.
- Symptoms of kidney stone like blood in urine or pain in your side.
- Symptoms of Lactic acidosis such as unusual muscle pain, stomach pain with vomiting and nausea, irregular heartbeats or unusual weakness.
- Symptoms of overdose of Atazanavir include yellowing of eyes or skin.
- Overdose usually occurs when someone by mistake or deliberately takes more than the prescribed limit of this medication.
- If you overdose the drug contact immediately with your doctor or pharmacist for symptomatic and supportive measures.
- Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule. Keep in mind to take the missed dose only on an empty stomach.
- Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind to not use a double dose to make up a missed dose
It has been observed that Atazanavir may interact with or increase or decrease the effect of following drugs. Caution should be taken when co administrating Atazanavir with one of the following drugs.
- Insulin or oral diabetes medication
- Drugs that weaken the immune system, such as Tacrolimus (Prograf), Sirolimus (Rapamune), or Cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune, Gengraf)
- Telaprevir (Incivek)
- Antifungal or antibiotic medication
- Antidepressant
- Buprenorphine (Suboxone, Subutex, Buprenex)
- Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
- Other HIV/AIDS medicine such as Saquinavir (Invirase), Tenofovir (Viread), or Efavirenz (Sustiva)
- Salmeterol (Advair, Serevent)
- Medicines for treatment of erectile dysfunction, such as Vardenafil (Levitra), Tadalafil (Cialis, Adcirca), or Sildenafil (Viagra)
- A blood thinner such as warfarin (Jantoven, Coumadin)
- Heart rhythm or blood pressure medication
- Stomach acid reducers such as Famotidine (Pepcid),Omeprazole (Prilosec), Lansoprazole (Prevacid), Cimetidine (Tagamet), Esomeprazole (Nexium), Ranitidine (Zantac), and others.
Atazanavir should not be concomitantly used with Ritonavir (Norvir) in case you are also taking a steroid medicine called Fluticasone (Flovent, Flonase, Advair). Consult your doctor for a different HIV drug, or using another treatment for allergic reaction.
This list is not complete and there can be many more drugs that can interact with Atazanavir.
It has been observed that following medical conditions (disease) may interact with Atazanavir:
- Heart block:
- Use of Atazanavir should be done very cautiously in such patients (HIV patients or heart patients) suffering with conduction abnormalities.
- Atazanavir extends the PR interval (atrioventricular (AV) conduction time or interval from where the P wave begins until the beginning of the QRS complex in the electrocardiogram) in some patients and causes conduction abnormalities.
- Nephrolithiasis (kidney stones in urinary tract):
- Some cases of nephrolithiasis may result in acute interstitial nephritis, renal failure, and/or hospitalization upon receiving Atazanavir therapy.
- Atazanavir should be used very cautiously in patients with renal and/or hepatic insufficiency or past history of nephrolithiasis.
- Therapy should be withheld or discontinued temporary under such situations.
- Haemophilia:
- Types A and B hemophiliac patients show an increased bleeding including spontaneous skin hematomas (collection of blood under the skin) and hemarthrosis (bleeding into joints spaces) on treatment with Atazanavir.
- Atazanavir therapy is interrupted and then reintroduced in hemophiliac patients.
- Patients of haemophilia and with other coagulation defects should be monitored closely for bleeding during Atazanavir therapy.
- Liver Disease:
- Patients who are suffering with hepatitis B or C viral infections or have noticeable increase in transaminases before Atazanavir treatment are more prone to further transaminase elevations or hepatic decompensation during use of Atazanavir.
- Besides, Atazanavir may get accumulated in patients with moderate or severe hepatic insufficiency as it is primarily metabolized by the liver.
- Hyperglycemia (high glucose levels):
- HIV patients treated with Atazanavir show an onset or increased severity of already existing glucose intolerance, hyperglycemia, and diabetes mellitus.
- Insulin resistance may be accompanied with HIV-associated lipodystrophy syndrome characterized by fat redistribution and serum lipid elevations.
- Adjustments in dose for insulin or oral hypoglycemic drugs may be necessary in patients with diabetes.
- Hyperlipidemia (high lipid levels):
- Patients treated with Atazanavir are associated with hyperlipidemia.
- Severe hyperlipidemia can occasionally lead to pancreatitis.
- Some patients receiving Atazanavir therapy may develop symptomatic atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
It is usually recommended to discuss any medical condition or allergies you have before you start taking Atazanavir.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- An open-label, multicenter clinical studies indicated the safety profile of Atazanavir in pediatric patients comparable to that in adults.
- The clinical studies with Atazanavir indicated that pharmacokinetic of Atazanavir did not showed any differences due to age or gender.
- Clinical studies prescribed the concomitant use of Atazanavir and Lopinavir (HIV protease inhibitors) during pregnancy.
- Pharmacokinetic study with Atazanavir (400 mg once a day) and diltiazem (180 mg once a day) indicated a 2-fold increase in the diltiazem plasma concentration and an additive effect on the PR interval.
- No additive effect of Atazanavir and atenolol on the PR interval is observed in clinical study between Atazanavir (400 mg once a day) and atenolol (50 mg once a day).
- In vivo studies indicated that Atazanavir neither induce its own metabolism nor increase the bio-transformation of substrates of CYP3A.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
- Wikipedia Information. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atazanavir.
- Pubchem Information. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Atazanavir
- Medline Plus Information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a603019.html.
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18389089.
- DrugBank: Atazanavir (DB01072). drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01072.
- Atazanavir | C38H52N6O7 | ChemSpider. chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.130642.html.
- Clinical pharmacokinetics and summary of efficacy and tolerability of atazanavir. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16176117
- Treatment of advanced HIV disease in antiretroviral-naïve HIV-1-infected patients receiving once-daily atazanavir/ritonavir or twice-daily lopinavir/ritonavir, each in combination with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21732894.
- Atazanavir (By mouth). Pubmed Health. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0009133/.
- Atazanavir/ritonavir: a review of its use in HIV therapy.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18389089.
Where can I get more information
Your pharmacist or health care provider can provide more information about Atazanavir.
Read about,
“Clopidogrel“
