Contents
- What is atenolol/chlorthalidone?
- How long atenolol stays in your system?
- How long chlorthalidone stays in your system?
- What is the mechanism of action of atenolol/chlorthalidone?
- Pharmacokinetics of atenolol/chlorthalidone
- What are the indications and usage of atenolol/chlorthalidone?
- What are the contraindications of the atenolol and chlorthalidone?
- Is it safe to take atenolol and chlorthalidone in pregnancy?
- What are the side effects of atenolol/chlorthalidone?
- What are the precautions that one should take while using atenolol and chlorthalidone?
- What is the proper use of atenolol and chlorthalidone?
- What should I do if I miss a dose of atenolol/chlorthalidone?
- Electrolyte and fluid balance status during atenolol/chlortalidone use
- What should I do, if I overdose atenolol/chlorthalidone?
- What are some drugs that interact with atenolol/chlorthalidone?
- Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with aminophylline?
- Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with clonidine?
- Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together diltiazem and verapamil?
- Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with metformin?
- Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with NSAIDs (Ibuprofen or naproxen)?
- Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with alcohol?
- Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with furosemide?
What is atenolol/chlorthalidone?
Atenolol and chlorthalidone is a combination of medicine atenolol and chlorthalidone and is used for the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure). This medication is available in tablet form. Atenolol/chlorthalidone is a combination which is beneficial in lowering the risk of heart attack or stroke by lowering your blood pressure.
In this medication, atenolol is a beta blocker, which affects the heart and circulation (blood flow through arteries and veins) and chlorthalidone is a thiazide diuretic also called as “water pill” which is helpful in retaining the fluid by means of preventing the body from absorption of too much salt.
High blood pressure increases the workload of the arteries and heart and if it occurred for the longer periods, it may impair the function of heart and arteries. Also, it can lead to damage to blood vessels of various organs such as kidneys, heart, brain and which ultimately result in stroke, heart attack, or even kidney failure. The rate of heart attack is also increased due to hypertension. Therefore it becomes very necessary to control the blood pressure.
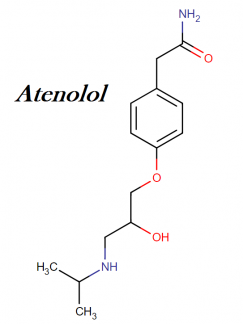
Atenolol IUPAC name, molecular weight, structure, and class
IUPAC name: 2-[4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl]acetamide
Molecular weight: 266.3361 g/mol
Molecular formula: C14H22N2O3
Molecular structure:
Drug class: This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenylacetamides. These are amide derivatives of phenylacetic acids.
How long atenolol stays in your system?
The atenolol can be out of your system after 36 hours, the elimination half-life of atenolol is 6 to 7 hours approximately that means the plasma levels of atenolol are reduced by half in every 6 to 7 hours. The drug needs at least 5 half lives to get out of our system; therefore it takes 7 x5 = 35 hours to get atenolol out of your system.
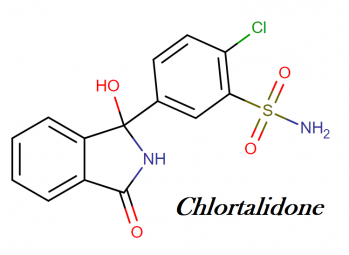
Chlorthalidone IUPAC name, molecular weight, structure, and class
IUPAC name: 2-chloro-5-(1-hydroxy-3-oxo-2H-isoindol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide
Molecular weight: 338.766 g/mol
Molecular formula: C14H11ClN2O4S
Molecular structure:
Drug class: This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as isoindolones. These are aromatic polycyclic compounds that an isoindole bearing a ketone.
How long chlorthalidone stays in your system?
The half life of the chlorthalidone is 40 to 60 hours (2-3 days) therefore it takes around five times of half life which is 12 to 13 days to get chlorthalidone from the body.
What is the mechanism of action of atenolol/chlorthalidone?
Atenolol/chlorthalidone is a combination of beta-adrenergic receptor blocker and a thiazide diuretic and available in the form of a tablet. Atenolol acts by affecting the response from some nerve impulses to the heart, which results in a lower heartbeat and reduced blood pressure. When blood pressure is lowered, the amount of blood and oxygen is increased to the heart.
Chlorthalidone inhibits sodium ion transport across the renal tubular epithelium in the cortical diluting segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. By increasing the delivery of sodium to the distal renal tubule, Chlorthalidone indirectly increases potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange mechanism.
Pharmacokinetics of atenolol/chlorthalidone
Atenolol:
Atenolol shows its peak effect after 2 to 4 hours of administration. It has the protein binding of 6 to 16%, and it is mainly metabolized by the liver. It stays in your system for 12 to 24 hours as per normal renal function.
The half-life of atenolol which means the half of the medicine is absorbed in 6-7 hr (normal renal function); 15-35 hr (end stage renal disease); >5 hr (children >10 years of age); < 5 hr (children 5-10 year of age), and lastly 50% of the drug is excreted in feces whereas 40% excreted in urine.
Chlorthalidone:
Chlorthalidone is a diuretic which stays in your system for almost 24 to 72 hours. The onset of action of this medication is occurring in almost 2 to 6 hours. It is also metabolized by the liver. Around 60 to 65% of the drug is bioavailable after administration.
It is mainly excreted in urine i.e. 50-65%. Chlorthalidone has a half-life of 40 to 60 hours in normal renal function and prolonged in renal impairment i.e. 81 hours in anuria.
What are the indications and usage of atenolol/chlorthalidone?
Atenolol/chlorthalidone tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension in order to lower blood pressure. High blood pressure may give rise to many diseases such as fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions which can be reduced by lowering the blood pressure with the help of medications.
There should be a proper comprehensive cardiovascular risk management and control of high blood pressure should be an important aspect including lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, limited sodium intake, and exercise. In order to achieve the blood pressure goals, many patients may require more than one drug.
The reduction in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality can be achieved by numerous antihypertensive drugs that may be from different pharmacological classes with a variety of mechanism, as reported by randomized controlled trials.
The conclusion that occurred from various clinical trials shows that the only high blood pressure is responsible for almost all cardiovascular diseases and reduction in high blood pressure is responsible for the benefits such as cardiovascular morbidity reduction.
The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. The cardiovascular risk is increased by elevated systolic or diastolic pressure; the risk is so high that even the modest reduction of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit.
Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, Therefore in a patient who is at higher risk independent of their hypertension, the absolute benefit is greater (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and more aggressive and well-framed treatment towards a lower blood pressure goal can benefit such patients.
This fixed dose combination drug is not indicated for initial therapy of hypertension. If the fixed-dose combination represents the dose appropriate to the individual patient’s needs, it may be more convenient than the separate components.
What are the contraindications of the atenolol and chlorthalidone?
This combination of atenolol and chlorthalidone is contraindicated in patients who have sinus bradycardia, more than first degree heart block, cardiogenic shock, and overt cardiac failure, anuria, hypersensitive to this product or to sulfonamide-derived drugs.
Is it safe to take atenolol and chlorthalidone in pregnancy?
A pregnant woman should take this medication only after proper consultation with her doctor and after knowing the risks and benefits of this drug. Extreme precautions should be taken when you administer atenolol and chlorthalidone tablets during pregnancy or lactation.
Atenolol:
Administration of atenolol, starting in the second trimester of pregnancy, has been associated with the birth of infants that are small for gestational age. Atenolol appears in the cord blood as it crosses the placental barrier. Therefore it can harm the fetus when administered during pregnancy. The women are at risk of hypoglycemia, of receiving atenolol at parturition or breastfeeding.
Chlorthalidone:
Chlorthalidone also appears in cord blood as it also crosses the placental barrier. The use of chlorthalidone and related drugs in pregnant women requires that the anticipated benefits of the drug be weighed against possible hazards to the fetus. Fetal or neonatal jaundice and thrombocytopenia are such hazards that can occur in the fetus.
What are the side effects of atenolol/chlorthalidone?
This combination can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea, and diarrhea. You should let your doctor know immediately if you see these side effects.
- You should get up slowly when getting up from sitting or lying position in order to reduce the risk of dizziness
- You may feel your hands and feet go cold as the blood flow reduced in that area. You should avoid smoking as it can worsen this situation. Try to keep yourself warm.
- There are many people who use this medication without any side effects but it does not mean that it does not have any side effects on you too. Your doctor may prescribe you this medication only if he/she thinks that the benefit outweighs the risk of this medication.
- You should keep an eye on your body fluid loss because chlorthalidone may cause severe fluid loss from the body along with the loss of essential minerals and even can cause dehydration. Therefore tell your doctor right away about the symptoms such as extreme thirst, very dry mouth, muscle cramps, weakness, fast/irregular heartbeats or confusion.
- Some side effects that need immediate attention are a very slow heartbeat, fainting, trouble breathing, signs of kidney problems, joint pain, mood swings, depression, extreme fatigue, blue fingers and nails, shortness of breath, or sudden weight gain.
- Very rare and extreme side effects of this medication include a reduction in vision or eye pain. So, get the medical help immediately in such cases.
- Get the medical help right away, if you see the allergic reactions such as rashes, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, trouble breathing. However, these side effects are very rare.
Apart from these side effects, you may also experience some unusual side effects that may not be mentioned in this list, you are advised to not to take any side effect lightly and seek medical help in case of any unusual side effects.
What are the precautions that one should take while using atenolol and chlorthalidone?
If you are allergic to atenolol or chlorthalidone, you should let your doctor know about this, because there may be any ingredients present in this medication which can cause allergy or other problems. You can simply ask your pharmacist in case of any confusion or more details.
Before using this medication, check if you have any of these, liver disease, kidney disease, heart-beat problems, gout, lupus, breathing issues, blood circulation problems, untreated mineral imbalance, serious allergic reactions including those needing treatment with epinephrine, a certain muscle/nerve disease (myasthenia gravis) and let your doctor know about such conditions.
- You should not drive, work on heavy machinery or do any activity that need alertness as it causes dizziness and you can increase the risk of certain misshapen while on this medication. Therefore make sure to get proper alertness before performing such activities, you should also limit your alcoholic beverages.
- Report any case of prolonged diarrhea or vomiting to your doctor as too much sweating, diarrhea can cause dehydration and increase dizziness or even can cause lightheadedness. Along with taking proper precaution, make sure to keep yourself hydrated to prevent dehydration.
- Let your doctor know about all the prescribed and non-prescribed (including herbal medications) that you are taking, before undergoing any surgery.
- You can ask your doctor about increasing potassium in your diet as this medication can reduce the level of potassium in your blood. A potassium supplement may be prescribed to you.
- If you have diabetes, this product may mask the fast/pounding heartbeat you would usually feel when your blood sugar falls too low (hypoglycemia).
- This medication does not affect other symptoms of low blood sugar level (dizziness and sweating), and also it makes difficult to control your blood sugar. Therefore if you have symptoms of high blood sugar (increased thirst and urination), let your doctor know about such symptoms. You may be advised to add exercise and special diet along with diabetes medication while you are on this medication with symptoms of diabetes.
- You should avoid going to the sun, tanning at a booth or under sunlamps as this medication already enhance your sensitivity to the sun. You can try wearing sunscreens, or protective clothing. It may even cause sunburns or skin blisters, therefore, let your doctor know about such conditions that you are suffering from.
- Sometimes dizziness can be more prominent in older adults as a side effect of this medication.
- If you are about to use this medication and you are pregnant or going to be pregnant, let you doctor know this thing, because atenolol and chlorthalidone combination can prove harmful to your baby. You should discuss all the risk and benefits of this medication with a pharmacist or your doctor.
The combination of atenolol and chlorthalidone can also harm nursing infant as it can pass in breast milk therefore consult your doctor before breastfeeding your baby while you are on this medication. In pregnancy, this medication should be used with extreme caution.
What is the proper use of atenolol and chlorthalidone?
You should follow the directions that are given by your doctor along with the prescription. In order to get the best results, your doctor may change your doses. You should take proper dosage as per advised, don’t take exceeded or reduced dosages than a recommendation. You must have a proper check on your blood pressure while using atenolol and chlorthalidone and also you may need frequent blood tests.
You can also become dehydrated due to excessive sweating, diarrhea or vomiting. This can lead to very low blood pressure, electrolyte disorders, or kidney failure while you are taking atenolol and chlorthalidone. Drink plenty of water each day while you are taking this medicine.
You should not leave this medication without proper consent of the doctor, therefore, you should keep taking this medication even if you are feeling well. This medication is given for the treatment of high blood pressure which has no symptoms. You may need to take this medication or any medicine for hypertension for rest of your life.
You may need to stop taking this medication if you are undergoing any surgery soon, also let your surgeon or doctor about the administration of such medication. You should not stop this medication abruptly as it may worsen the condition. If you do stop taking this medicine, limit your physical activity to prevent heart problems. You should store this medication at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.
What should I do if I miss a dose of atenolol/chlorthalidone?
You should take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If you remember it at the time of next dose, in that case, skip the next scheduled dose. In order to make the missed dose, never take an additional dose.
Electrolyte and fluid balance status during atenolol/chlortalidone use
Periodic determination of serum electrolytes to detect possible electrolyte imbalance should be performed at appropriate intervals.
Patients should be observed for clinical signs of fluid or electrolyte imbalance; i.e., hyponatremia, hypochloremic alkalosis, and hypokalemia. Serum and urine electrolyte determinations are particularly important when the patient is vomiting excessively or receiving parenteral fluids. Warning signs or symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalance include dryness of the mouth, thirst, weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, restlessness, muscle pains or cramps, muscular fatigue, hypotension, oliguria, tachycardia, and gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting.
Measurement of potassium levels is appropriate especially in elderly patients, those receiving digitalis preparations for cardiac failure, patients whose dietary intake of potassium is abnormally low, or those suffering from gastrointestinal complaints.
Hypokalemia may develop especially with brisk diuresis, when severe cirrhosis is present, or during concomitant use of corticosteroids or ACTH.
Interference with adequate oral electrolyte intake will also contribute to hypokalemia. Hypokalemia can sensitize or exaggerate the response of the heart to the toxic effects of digitalis (e.g., increased ventricular irritability). Hypokalemia may be avoided or treated by use of potassium supplements or foods with a high potassium content.
Any chloride deficit during thiazide therapy is generally mild and usually does not require specific treatment except under extraordinary circumstances (as in liver disease or renal disease).
Dilutional hyponatremia may occur in edematous patients in hot weather; appropriate therapy is water restriction rather than administration of salt except in rare instances when the hyponatremia is life-threatening. In actual salt depletion, appropriate replacement is the therapy of choice.
What should I do, if I overdose atenolol/chlorthalidone?
If you overdose this medication, you may suffer from the symptoms such as nausea, extreme weakness, wheezing, chest tightness, trouble breathing, slow heartbeats, swelling, rapid weight gain, feeling light-headed, or fainting.
Therefore proper treatment should be adopted and it should be symptomatic and supportive and directed to the removal of any unabsorbed drug by induced emesis or by the means of administration of activated charcoal. General circulation and hemodialysis can remove the atenolol (If administered in overdoses). Dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and hypotension should be considered further.
What are some drugs that interact with atenolol/chlorthalidone?
You should follow your doctor’s instructions about the quantity of liquids that you need to administer in order to keep you dehydrated and prevent dehydration. You should avoid becoming overheated or dehydrated while doing exercise and also in hot weather. Another considerable factor is that sometimes drinking too much liquid can be unfit just like not drinking enough.
Tell your doctor about all medicines you use, and those you start or stop using during your treatment with atenolol and chlorthalidone, especially:
- Any other diuretics or blood pressure medicines
- Lithium
- Heart rhythm medicine–amiodarone, disopyramide.
This list is not complete. Other drugs may interact with atenolol and chlorthalidone, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Not all possible interactions are listed in this medication guide.
Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with aminophylline?
No, aminophylline cannot be taken together with atenolol and chlorthalidone because the pharmacologic effects of theophyllines (aminophylline) and beta-blockers (atenolol) are exactly opposite. Theophyllines cause bronchodilation and nonselective beta blockers can oppose this effect which can result in severe and fatal bronchospasm.
Ophthalmic beta-blockers undergo significant systemic absorption and may also interact. The hepatic metabolism of theophylline can also be reduced by propanolol and other beta blockers, which can increase in theophylline levels.
Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with clonidine?
The concurrent administration of these drugs needs to monitor very closely. Clonidine and beta-blockers have synergistic effects which collectively can result in bradycardia (slower heartbeat), and hypotension. However, few cases of antagonism of hypotension are also reported, which occur due to an unknown mechanism.
In addition, potentiation of the hypertensive rebound associated with abrupt withdrawal of clonidine or both clonidine and the beta blocker may occur. After the withdrawal of Clonidine, few cases have also been reported which includes increased blood pressure, hypertensive crisis, hypertensive encephalopathy, strokes, and other fatalities.
This may be caused by increased catecholamine release after clonidine withdrawal; also vasoconstriction can also occur due to unopposed alpha-adrenergic effects of the catecholamine caused by concurrent administration of beta-blockers. Patients are at higher risk of developing rebound hypertension when they discontinue Clonidine along with noncardiac selective beta blockers.
Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together diltiazem and verapamil?
The concurrent administration of atenolol and calcium channel blockers (diltiazem and verapamil) should be monitored very closely as additive reductions in heart rate, cardiac conduction, and cardiac contractility may occur.
Potential serious cardiovascular adverse effects such as CHF (congestive heart failure), severe hypotension, or exacerbation of angina may occur when atenolol is taken with verapamil or diltiazem. Although this combination is usually considered as useful and effective.
However, Ventricular asystole, sinus arrest, and heart block have also been reported. High doses, IV administration can increase the risk of left ventricular dysfunction or AV conduction abnormalities.
As beta-blockers are systemically absorbed, they may also interact and can produce significant systemic effects even at low levels or undetectable plasma levels. Verapamil and diltiazem may also decrease the clearance of some beta blockers.
Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with metformin?
The patients who take metformin concurrently with metformin can increase the risk of lactic acidosis due to diuretic-induced renal impairment and dehydration. Also, it can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new onset diabetes mellitus, and exacerbation of preexisting diabetes due to interference in glucose control due to thiazides and diuretics combination.
Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with NSAIDs (Ibuprofen or naproxen)?
The antihypertensive effects of beta blockers can be reduced by NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). The mechanism behind this is induced inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis, which results in unopposed pressor activity producing hypertension.
In addition, blood pressure also affected by the fluid retention caused by NSAIDs. As compared to other NSAIDs, indomethacin and piroxicam have the most attenuating effects. In patients with eclampsia, indomethacin shows the most significant effect.
Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with alcohol?
Many psychotherapeutic and CNS-active agents (e.g., anxiolytics, sedatives, hypnotics, antidepressants, antipsychotics, opioids, alcohol, muscle relaxants) exhibit hypotensive effects, especially during initiation of therapy and dose escalation. Addictive effects on blood pressure and orthostasis can occur due to coadministration with hypotensive agents, in particular vasodilators and alpha-blockers and other antihypertensive.
Can atenolol/chlorthalidone be taken together with furosemide?
The combination of thiazide and loop diuretic must be monitored when taken together, as it may produce synergistic effects on diuresis and excretion of electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium, and chloride).
When a single agent is not enough to produce the effect, these medications can be combined therapeutically in some patients, but some symptoms such as increased risk of dehydration, hypotension, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hyponatremia should be monitored. The exact mechanism of interaction is pharmacodynamic rather than pharmacokinetic, however, it is unclear.
“Is Naltrexone a controlled substance? What are the uses of naltrexone?“