Contents
- What is Glucocorticoids
- How does fluocinonide work
- Chemical structure
- USES
- Precautions
- Side Effects
- Contradictions
- Adverse Reaction
- Dosage and Route of Administration
- Fluocinonide Overdose
- Interaction
- Expired Fluocinonide
- Fluocinonide ointment and poison ivy
- Fluocinonide spray
- Fluocinonide Shampoo
- Fluocinonide Topical Ear Drops
- Fluocinonide Natural Alternatives
Fluocinonide is a potent glucocorticoid used topically as an anti inflammatory agent for treatment of various dermatological conditions such as eczema and seborrhoeic dermatitis (dandruff , cradel cap).
It also provides relieves from itching, redness, dryness, crusting, scaling, inflammation and discomfort. Fluocinonide ranks as a high potency topical corticosteroid.
The amount used be used in minimal amounts and that for minimal lenght of period to avoid the occurrence of adverse effects. It is majorly sold under the brand name of Lidex, Vanos, dermacin, and Fluex (fluocinonide topical preparations ).
What is Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids something are thought to be typical steroids but they are not they are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones, these are not the addiction causing steroids.
The name (glucose + cortex + steroid ) derives from its role in the regulation of the metabolism of glucose, they are synthesized in the adrenal cortex. They bind to the glucocorticoid receptor(GR) that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. GCs are part of the immune feedback mechanism.
How does fluocinonide work
The mechanism of action by which pathways it works as an anti-inflammatory drug is not clear . However as corticosteroids play a role in cellular signaling, immune function, inflammation, and protein regulation.
It binds to the cyctosolic glucocorticoid receptor, the complex translocates itself into the cell nucleus where it binds to many glucocorticoid response elements (GRE) in the promoter region of the target genes.
The DNA interacts and causing the increase in expression of specific target genes, it suppresses the formation of inflammation causing chemicals like prostaglandins , cyclooxygenase expression is also suppressed, potentiating the effect.
Additionally the immune system is suppressed by corticosteroids due to decrese in the function of the lymphatic system, a reduction in immunoglobin and complement concentrations. Additionally it promotes the breakdown of lipids (lipolysis).
Pharmacodynamics(what drug does to body)
As it is known is a potent glucocorticoid steroid used topically as anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of skin disorders such as eczema. It relieves itching, redness, ddryness, crusting, scaling, inflammation, and discomfort.
Pharmacokinetics(what body does to drug)
ADME is a standard what body does to the drug .Abbreviation A means Absorption, D for distribution, M for metabolism and E for excretion.
Absorption: It permeates through the skin layers, about 1% of the drug get absorbed from thick stratum corneum, 36% from thin stratum corneum. Area of absorption increases with the increase in the area of damage or inflammation.
Distribution: It is distributed from muscles, liver, skin, intestine & kidney.
Metabolism: The metabolism mostly occurs in the liver where the drug is metabolized into their metabolites, primary metabolized in skin ( layers are not specified), small amount is absorbed via systemic circulation and then metabolized in liver into inactive compounds.
Excretion: Route of elimination: The inactive metabolites are excreted in the feces and in the urine from kidneys with process called glomerular filteration . The major metabolites are glucuronides and sulphate. Some of it is excreted in feces but majorly in urine..
Toxicity: Side effects may include acne-like eruptions, burning, dryness, excessive hair growth, infection of the skin, irritation, itching, lack of skin color, prickly heat, skin inflammation, skin loss or softening, stretch marks.
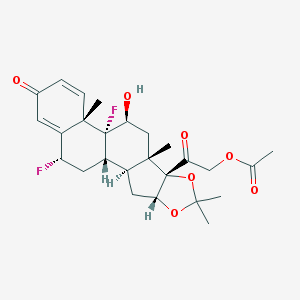
Chemical structure
IUPAC: 6α,9-difluoro-11β,16α,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, cyclic 16,17-acetal with acetone,21-acetate
Pronunciation: floo-oh-SIN-oh-nide
Physical and Chemical Properties:
Molecular Formula: C26H32F2O7
Molecular weight: 494.524889 g/mol
Hydrogen bond donor count: 1
Hydrogen bond acceptor count: 9
Rotatable Bond Count: 4
Exact Mass; 494.21161 g/mol
Heavy Atom Count: 35
Isotope atom Count: 0
Melting Point: 309 °C
Solubility: Water soluble 4.74 mg/L
USES
Anti-inflammatory: As it is a potent glucocorticoid and acts by binding glucocorticoid receptor and suppresses the chemical mediator and provides anti-inflammatory action.
Skin diseases: It is used in psoriasis, eczema, dermatitis, allergies, rash.
Hair Fall: Fluocinonide is used to treat hair fall as it is applied on the skin and it targets the root cause for hair fall and solves the problem.
One of the side effect while treating skin problem with this drug is hair growth which can be used as a treatment for falling hair, but not to forget other mild and serious side effects of the drug.
Precautions
- The safety and efficacy of the drug is not established in patients less than 12years of age.
- It should not be used on face, groin or axillae.
- Drug applied to the affected area should not be covered, wrappled or bandaged.
- Childrens may absorb excessive amount of corticosteroid and may be susceptible to toxicity.
- Skin Atropy: This is the major precaution that should be taken care off. Prolonged use may cause atropy of skin.
- In Pregnant women: It should be used only when the benefits justify the potential risk to foetus. Dosage should not be large and time shoould not be prolonged.
- Nursing mother: proper care should be taken because corticosteroids have systemic absorption and this might also be detectable in breast milk.
- Pediatric: There is adrenal suppression which include growth retardation, delayed weight gain, no response to ACTH stimulaation.
Side Effects
- Burning, stinging, itching, dryness, or redness may occur when this medication is first applied to the skin. this should disappear in a few days as your body adjust to medication.
- Blister, crust, dryness & flakes of the skin.
- Irritation
- Thinning of skin.
- Fever, headache, muscle ache, sore throat, running nose, tiredness and weakness.
Contradictions
It is contraindicated in people with hypersensitivity. Hypersensitivity is a set of undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity.
Adverse Reaction
- Burning
- Folliculitis: Is a skin disorder that appears as pinpoint red bumps, each one involving hair follicle.
- Perioral dermatitis
- Itching
- Hypertrichosis; It is a excessive hair growth over and above the normal for the age, sex and race of an individual.
- Skin atropy
- Irritation
- Striae
- Dryness
- Hypopigmentation
- Miliaria: It is marked by small and itchy rashes.
Dosage and Route of Administration
It is freely available in the dosage forms that are topical forms i.e gel, creams and ointments.
Usual adult dose for dermatitis
- 0.05% gel, cream and ointment: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for two to four times a day.
- 0.1% cream: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for once to twice a day.
Usual adult does for Eczema
- 0.05% cream, gel and ointment: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for two to four times a day.
- 0.1% cream: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for once to twice a day
Usual adult dose for atopic dermatitis
- 0.1% cream: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for once a day
Usual adult dose for Psoriasis
- 0.1% cream: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for once a day.
Pediatric Dose
12 years or older for Eczema
- 0.05% gel, cream and ointment: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for two to four times a day.
- 0.1% cream: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for once to twice a day.
12 years or older for psoriasis
- 0.1% cream: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for once to twice a day.
12 years or more fpr Atopic dermatitis
- 0.1% cream: Apply a thin layer to the affected area for once to twice a day.
Fluocinonide Overdose
As mentioned above, fluocinonide is a potent steroid and this is the reason why it is not available as over the counter drug. The drug is generally prescribed as anti-inflammatory.
Before using this drug, the patient must be aware that the drug is supposed to be used only in the amount prescribed by the doctor. It is important to keep in mind that each patient might have a different dose as each patient has a different condition.
The reason why drug should be used in the dose prescribed, is to get full effectiveness and to avoid/minimize unwanted side effects due to overdose. Overdose should taken care off as it may affect health condition.
Less serious side effect include itching, burning, dryness and peeling of skin, headache, stuffy nose, sore throat, thinning of skin, swollen hair follicles, changed color of the skin that is being treated and stretch marks.
Serious side effects include severe irritation of skin being treated, mood changes, blurred vision, weight gain, muscle weakness and tiredness. In case of severe side effects the drug must be discontinued and doctor must be contacted.
Overdose can be avoided by following the below tips:
- For dermatitis, an adult should apply a thin layer to the affected area 2-4 times a day.
- If the concentration is 0.1% then it should be applied only once a day.
- For psoriasis, a thin layer should be applied 2-4 times a day for an adult.
- Pediatric dose for dermatitis is the same as adult, 2-4 times a day and a thin layer.
- Treatment should not be carried out for more than 2 consecutive weeks and should not be applied on a wide area.
- The drug should be used only in the dose prescribed by the doctor and the dose should not be changed as it may cause overdose.
Patients think that if they take the drug in excess, they will get quick results which is not true. If the drug is taken in excess it will cause overdose which will lead to side effects that are mentioned above.
Symptoms like increased acne or facial hair, menstrual problems and impotence may occur due to overdose. Although overdose does not produce life threatening symptoms, even then immediate medical help is needed. Hence, to avoid unwanted side effects the patient should use the drug as described by the doctor.
Interaction
Fluocinonide has interaction with a few disease condition which include diabetes, infections, diaper rash, ocular toxicities and hyperadrenocorticism.
Expired Fluocinonide
It is important to know the shelf life of fluocinonide. Fluocinonide is available as gel, ointment, cream and solution. Two brands of cream are available, Lidex and Vanos. Lidex contains 0.05% and Vanos contains 0.1% fluocinonide.
Doctor decides the form and dosage of drug that is needed for treating a symptom. The width and severity of the disease helps the doctor to decide the dose of drug to be given to the patient.
Shelf life of the drug is the amount of time that a properly packaged and stored standard will last without undergoing physical and chemical changes.
Shelf life should be provided on items such as food items, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs and chemicals. Shelf life is different from expiration date.
The expiration date depends on chemical stability of the standard, transfer losses of standard and human factors while using the standard.
Expiration date is used to estimate the time when the drug has full potency and safety. If there is full potency and safety, the drug will be able to perform the function that it is supposed to.
The expiration date will tell us how long we can use the drug. Although fluocinonide has passed the expiration date, it can still be used but it will no longer have maximum effectiveness.
It is advised not to use this drug after the expiration date. In order to get full benefit, the drug should be applied to the affected skin and expired fluocinonide should not be used.
Fluocinonide ointment and poison ivy
Exposure to parts of ivy i.e poiosn ivy, poison oak and poison sumac can produce rash .It is caused by sensitivity to Urushiol, an oily resin that is commonly found in the leaves, stem, flowers and roots of these three plants.
Even though the plant dies the active ingredients remains potent. The rash can develop through direct and indirect contact with these plants.
Treatment: some common poison ivy treatments include cold, wet compresses that are applied on the itching skin, anti itch creams, oral antihistamine, topical steroids and oral steroids.
For topical steroids you can use fluocinonide ointment as it is an corticosteroid.The combination of fluocinonide ointment and poison ivy is great because fluocinonide ointment works effectively in eliminating the inflammation and itching too as its primary mode of action is anti inflammatory.
As it is known it is potent steroid therefore it should not be used excessively so it should be prior recommended by the doctor.
Fluocinonide spray
When it comes to complaince for the pateints constantly the scientist are thinking for the easiest way to use medication for fastest relief . When using fluocinonide ointment ,cream, gel and emollient and it must be only applied to the affected area as it might me dangerous for areas like underarms, face and groin.
So, here fluocinonide spray the usual instruction in applying medication is quite standard. Wash clean the affected areas before ares before applying it. Doctor will only instruct pateint to apply very thin film application of fluocinonide unto the skin.
Leave it dry naturally. Bandage or any wrapping is not required. In fact, it can make things getting worst. Clinically, fluocinonide is only meant for adult and not for children. For such cases, it takes special case as the diaper must be kept lose to prevent serious rash.
Fluocinonide Shampoo
Itching on the scalp is really disturbing and embarrassing and can occur to anyone, anytime and anywhere. It may be really embarrassing in your business meetings.These anti itching products are available in the market.
These conditions gives you many more options to choose from. Eczema and seborrhea affect the scalp, and may cause an itchy feeling. Scalp with eczema produces unpleasant smell which might cause uneasiness when in crowd.
Eczema and Seborrheic scalp dermatitis is a complex skin problem and should be treated with prescription medication. Doctor prescribes fluocinonide for this condition.
The drug is a strong steroid and when topical applied reduces itching of skin. The use of this drug on the scalp should be done with care because of the unwanted side effects of the drug.
Common side effects related to the application on scalp include burning, itching, irritation, dryness,redness and headache. Serious side effects for the drug include severe allergic reaction, rash, fainting, tiredness, weakness, atrophy (thinning of shin) and loss of appetite.
Fluocinonide is available as gel, cream, ointment and solution. The drug is applied as a thin layer on the scalp and this might thinning of the skin. This is also a reason why fluocinonide is not available as shampoo. If itching is persistent or gets worse, you should consult a doctor and take fluocinonide.
Fluocinonide Topical Ear Drops
Discussions, rumors and claims are going on for the use of fluocinonide for treating ear blockage. Some news are spreading that tell us the how this drug relieves itching and blockage of ear.
Scientific evidence for the use of fluocinonide as ear drop is still a new thing. The doctor takes care while prescribing this medication. This is because it is available as gel, cream, emollient and ointment.
This makes it difficult to administer into the ears. Doctor’s recommend that the patient must wash their hands after using the drug.
If the drug comes in contact with eyes, it may cause glaucoma and this proves the risk associated with administering the drug into the ears. With the progress in technology, it might be possible to use this drug into the ears without any side effects.
Fluocinonide Natural Alternatives
People in general do not pay attention to their skin as they think it might affect their appearance. Some people feel uncomfortable because of the itching sensation they might get due to skin problem.
This might ruin their confidence level as skin problems mainly itching comes with redness on skin followed by scalping of that portion of skin. Clothing limitation may also be caused as exposed diseased skin may not look good.
Fluocinonide is used in patients having skin problems and to treat disease conditions like eczema, psoriasis etc. There are many reasons that people are finding alternatives for fluocinonide.
Many side effects are minor which may not be harmful but some are serious side effects like thinning of skin, tiredness etc which may be disturb daily routine. The continuous use of this product may cause side effects and this is the reason that doctors recommend for not using this drug once symptoms are relieved.
The chemical ingredients present in this product is not a good option to be used in babies and children with skin problems. This is because the skin of children is very sensitive. Children with skin problems should be treated with alternatives of fluocinonide which may not have side effects as the drug itself.
Alternate method for treating eczema is aromatherapy. Oil of geranium, eucalyptus, lavender, chamomile, bergamot and juniper are proved helpful in relieving the symptoms of eczema.
When these oils are applied topically to the affected area, they are proved to heal faster. To enhance the healing process, patient should eat whole food and wholesome organic diet.
Some foods like wheat, dairy, product and sugar should be usually avoided. This is because they might trigger allergic reaction which may worsen the disease condition.
Some fruits that have sour and citrus content can be consumed but in smaller amount as it may aggravate the symptoms. Itching may also be increased if the affected area comes in contact with cold or lukewarm infusion of chickweed.
Calendula flowers and St. John’s wort leaves made salve can be used to solve skin problem like dryness, cracked and painful skin. Primrose oil when applied to affected area is also proved useful.
Patient Education:
Following instruction may be useful for patient
- The patient should be taught how to apply the drug with the help of sterile applicator, gloves or careful hand washing. Proper education on how to apply the drug can help prevent potent adverse reaction that might occur due to poor handling of the drug.
- In case of occlusive dressing the patient must be advised not to leave the dressing for more than 12 hours each day and not to use it on the infected or exudative lesions. Leaving the dressing for a longer time may cause drug to be absorbed into systemic circulation which may in turn cause an adverse reaction.
- The strength and direction of the drug must be used as prescribed by the doctor and overuse should be avoided.
- If adverse reactions like systemic absorption, skin irritation or ulceration, hypersensitivity or infection persist, the patient should stop using the medication and visit a doctor immediately.
Read about,
“Side effects of Levothyroxine“
“Flonase and Sudafed interaction“