Contents
- What is Maca?
- Maca family, other names, origin, and botanical drug used
- Maca’s chemical composition and main compounds
- Maca indications and uses
- Maca evidence of efficacy and mechanism of action
- Maca side effects
- Maca’s interactions
- Maca contraindications
- Maca dosage
- Maca use for fertility improvement
- Maca as an aphrodisiac
- Maca postmenopausal and osteoporosis benefits
- Maca and growth rate improvement
- Maca antiproliferative effects
- Maca top 5 selling products
What is Maca?
Maca (lat. Lepidium meyenii) is a biennial herbaceous plant that belongs to the family of Brassicae. It is cultivated in the Andes mountains, mainly in the regions of Peru.
It has been traditionally used for more than 2000 years as food and medicine. It has been most commonly used as a general tonic, but also for treating anemia, female hormone disbalance and infertility.
There are different types of maca (8 or more different) with various colours, from white to black, but the yellow one is the most common cultivar in the Andes.
Nowadays, it has also been introduced to Western countries, but there is significant concern about itsthe quality and appropriate composition of its products as different maca ecotypes appear to differ in their biological effects.
It has been showed that the planting site is probably the most important factor affecting chemical variation.
Maca family, other names, origin, and botanical drug used
Family: Brassicaceae (Cruciferae)
Other names: Chilque; macaia; Peruvian ginseng
Origin: Maca is mainly domesticated in the central Andes of Peru at elevations of 3500–4500 m above sea level, a zone characterized by areas of barren, rocky terrain, intense sunlight, fierce winds, and freezing temperatures.
In this inaccessible and intensely cold habitat, few other crops survive with the exception of some highland grasses, and a few hardy members of the Solanaceae.
Domesticated maca has been grown in Peru for at least 2000 years ago, but little is known about its origin.
There are eight or more different ecotypes in the cultivation area, distinguished according to the color of their roots, such as, yellow, purple, white, grey, black, yellow/purple and white. The yellow ecotype is the commonest cultivar in this region.
Botanical drug used: Dried powdered ‘root’ (hypocotyl)
Maca’s chemical composition and main compounds
Main compunds of Maca plant are: unsaturated fatty acids, mainly macaene and macamide, as well as linoleic and oleic acids, the glucosinolates glucotropaeolin and m-methoxyglucotropaeolin, alkaloids including lepidiline A, lepidiline B and macaridine, and sterols such as β-sitosterol, campesterol and stigmasterol. The root is rich in minerals and trace elements.
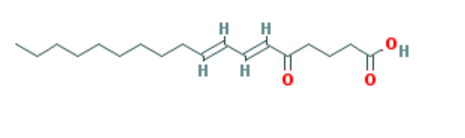
Macaene and macamide: Different secondary metabolites have been found in maca root. The typical compounds that can be found in maca are macaene and macamide.
These novel polyunsaturated fatty acids and their amides are unique and are not found in other plants.
It has been suggested that macaene and macamide be the group of biologically active components in maca involved in improving sexual performance.
The contents of these specific compounds may vary widely in different maca samples. In dried maca, macaene may range from around 0.09–0.45%, and macamide ranges from 0.06% to 0.52%. One macaene and sixteen types of macamide have been found up to now.
Glucosinolates and their derivatives
Glucosinolates of maca, and their derived products, have received important scientific attention because of their biological activities, particularly their ability to combat pathogens and cancer.
They are widely distributed in cruciferous crops, and are considered largely responsible for the distinctive, pungent flavor of maca.
There are nine kinds of glucosinolates found in maca and most of them are aromatic glucosinolates. The amount of glucosinolates that can be found in fresh maca is about 1% which is about 100 times more that can be found in cruciferous crops such as cabbage, cauli- flower and broccoli.
The type and content of glucosinolates in maca differ in various organs of the plant, including sprouts, seeds but also differ according to plant age.
In maca, the highest amount of glucosinolates is in fresh hypocotyls. They can be also found in sprouts, seeds, then fresh leaves and dried hypocotyls.
Glucosinolate are compounds that can be easily hydrolyzed into a series of different molecules, including thiocyanate, iosthiocyanate and nitriles. Endogenous enzyme called myrosinase is responsible for that.
In the intact cells, glucosinolates are separated from myrosinase. But, when the cells are damaged, glucosinolates can be easily broken down by this enzyme.
This is the main reason why dried maca roots or processed products have much lower glucosinolates content than fresh tissue and seeds.
Alkaloids: Alkaloids are mainly found in nature amongst the members of the plant kingdom, though some fungi also naturally secrete these compounds.
They are generally classified into about 60 different kinds according to their basic structures. Most alkaloids show some form of biological activities.
For now 3 different alkaloids have been isolated from the toots of maca: lepidiline A and lepidiline B and 1,2-dihydro-N-hydroxypyridine (macaridine).
Sterols: Many types of phytosterols have been isolated from maca. Phytosterols are bioactive compounds found in all vegetable foods. In exhibit anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidatant properties.
Maca indications and uses
- Popularly, it is used as a tonic and as an aphrodisiac to enhance sexual drive and female fertility.
- Managing menopausal symptoms.
Maca evidence of efficacy and mechanism of action
The evidence from clinical studies to support its use as an aphrodisiac is very limited, although there is some evidence for its use in managing menopausal symptoms. Further studies are needed before any recommendation can be made.
A systematic review on the use of maca for treatment of menopausal symptoms, which included four double-blind randomised placebo-controlled clinical trials in healthy peri-menopausal, early post-menopausal and late post-menopausal women, showed that there is limited evidence to support its use, and that further studies are needed.
However, based on these studies, maca was considered to be more effective than a placebo. Its effect on improving sexual function was also assessed in a systematic review.
Again, the evidence available to support its effects on the treatment of sexual function in healthy volunteers (men and women) and men with sexual dysfunction was limited.
The mechanisms of maca action are unknown. It has been proposed that the polyunsaturated fatty acids (macaene and macamide), the glucosinolates, and the alkaloid macaridine are the compounds responsible for its biological activity.
Pre-clinical studies suggest that maca may improve sperm count and motility and enhance fertility, and it improved sexual performance in rats, although the mechanism is not clear.
Maca has antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects and a high nutritional content, which might help to promote vitality. The phytosterols may have an effect on menopause symptoms, as shown in ovariectomised rats studies.
Maca side effects
Overall, considered to be safe, as the root is also used as a vegetable, but further studies are needed to confirm its safety.
Despite the limited clinical studies on its efficacy and safety, it is widely marketed over the Internet for its purported beneficial effects on sexual function and menopausal symptoms.
Maca’s interactions
There are no-known interactions between maca prodcuts and other drugs. Although, further studies are needed.
Maca contraindications
Not recommended during pregnancy and lactation due to lack of safety data.
Maca dosage
For products, as recommended by the manufacturer. The optimum dose of maca is unknown
but doses up to 3500 mg/day have been used.
Maca use for fertility improvement
Incas used maca to improve fertilities of both humans and their livestock. This was considered as very important because fertility rates are generally weakened at high altitude.
Effects of maca are examined on rats and administration was found that is able to prevent the reduction in epididymal sperm count affected by high altitude, but also to lessen the deleterious effect of the compounds such as lead acetate or malathion on that impact spermatogenesis in rats.
Examinations on male rats treated with maca extracts showed increased epididymal sperm counts and spermatids, and higher testicular and epididymis weights. All of these effects were dose-dependent.
Maca has also been shown to have the same effects in humans. It was found that oral administration of maca tablets to normal adult men over a period of 4 months, led to seminal volume increasing, sperm count per ejaculum increasing and motile sperm count increase.
These semen variables following the oral administration of maca for the period of 4 months were significantly different from those on the test group prior to administration. Maca has also been shown to improve the fertility in females.
When maca was given per os to mice, it increased litter size and pregnancy rates in adult female mice. The mechanism of improving fertility is not yet fully elucidated.
Some studies pointed out that maca extracts can exhibit estrogenic activity, which then led MCF-7 cells, to proliferate in vitro. Moreover, it also increased uterine weight in rats.
Estrogenic activity of maca can be explained partly due to the phytosterols content in the extracts. This estrogenic activity of maca may help explain the means by which it improves female fertility.
Maca as an aphrodisiac
Within the Andean region maca is widely held in high repute as an aphrodisiac for both men and women.
Animal models have been used to examine the validity of this claimed effect. It has been found that oral usage of maca extracts may improve the copulatory performance male mice or rats that are sexually inexperienced.
Moreover, the use of maca extracts may improve the erectile function and decreased the latent period of an erection of testes-removed rats.
RCT studies carried out on men have been shown an increase in the sexual desire of maca extracts. One study found that the 40.0% and 42.2% of man experienced increased sexual desire after 8 and 12 weeks, respectively of maca treatment, which was importantly different from the placebo groups.
On the other hand, maca extracts did not affect penile blood flow in men with moderate and mild erectile dysfunction. Larger studies are needed to confirm these effects.
The mechanisms of maca’s proposed improvement of sexual performance have been studied, but have not been fully clarified so far.
Test results have shown that maca’s effect on fertility and sexual desire may not act by modulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary axis to regulate hormone secretion and was also independent of changes in scores for depression and anxiety.
Meanwhile, during oral administration of maca to mice, the apparent absence of correlation between effect on spontaneous motility and sexual behavior, seemed to support the hypothesis that maca had a pharmacological action independent of its nutritional value.
Maca was also found not to activate the human androgen receptors and thus not to influence genes regulated by androgens.
Maca postmenopausal and osteoporosis benefits
The onset of the menopause symptoms is generally linked with reduced concentrations of the female sex hormones. One of the consequences of this is reduction of bone mineral density.
Maca is said to regulate incretion, and has been used to treat women with menopausal symptoms. Studies in ovariectomized rats have shown that maca significantly increased calcium content in the femur of the rats.
Phytosterols and other secondary metabolites in maca may contribute to this function.
Maca and growth rate improvement
Maca supplementation increased food intake, growth and feed utilization along with improving survival in rainbow trout juveniles.
The improvement in survival might be explained via maca stimulating growth hormone and imparting increased resistance to diseases or stresses.
First, it has been widely shown that maca contains many kinds of sterol, which have estrogenic effects and previous studies have shown that estrogen promoted the growth of yellow perch and production of growth hormone in goldfish.
Secondly, maca improves immunity by increasing leucocyte number. Thirdly, anti-oxidant activity in maca meal may be partly responsible for the increased immunity and resistance to pathological antigens in the rainbow trout alevins and juveniles. Fourthly, maca is a good nurture which is abundant in protein, unsaturated fatty acid, vitamins and minerals.
Maca antiproliferative effects
Maca has anti-proliferative functions, and may mitigate the prostate weight increase induced by testosterone treatment.
Maca top 5 selling products
According to the amazon.com, following five Maca products are listed as top selling:
- Mighty Maca Plus
- Black Maca Liquid Extract
- Earth Circle Organics Raw Organic Maca Powder
- Whole World Botanicals – Organic Royal Maca
- Sunfood Red Maca Powder