Contents
- What is oxybutynin?
- What are oxybutynin molecular drug class, formula and weight?
- How oxybutynin works in the body?
- Oxybutynin brand names
- What is oxybutynin used for?
- Oxybutynin dosage for different indications
- Oxybutynin highest dose
- Oxybutynin side effects
- Oxybutynin overdose
- How to take oxybutynin?
- Can I abrupt oxybutynin therapy suddenly?
- Precautions and warnings during oxybutynin use
- How long does oxybutynin take to work?
- What happen if I miss oxybutynin dose?
- How long does oxybutynin stay in your system, urine, blood, saliva?
- Oxybutynin use during pregnancy
- Oxybutynin use during breastfeeding
- Can geriatric patients use oxybutynin safely?
- Oxybutynin absorption, metabolism and elimination
- Can I drink alcohol while taking oxybutynin?
- Can patients with liver disease take oxybutynin safely?
- Can patients with neuropathy take oxybutynin safely?
- Can patients with diarrhea take oxybutynin safely?
- Can patients with renal disease take oxybutynin safely?
- Can I take oxybutynin and potassium supplements together?
- Can I take oxybutynin and hydrocodone together?
- Can I take oxybutynin and amlodipine together?
- Can I take oxybutynin and topiramate together?
- Can I take oxybutynin and loperamide together?
- Can I take oxybutynin and oxycodone together?
- Can I take oxybutynin with antihistamines such as diphenhydramine?
- Can I take oxybutynin with beta blockers (metoprolol, propranolol, sotalol)?
- Can I take oxybutynin with codeine?
- Proper storage and disposal information of oxybutynin
What is oxybutynin?
Oxybutynin is a generic name for an anticholinergic medicine which is used to reduce muscle spasms of the bladder and urinary tract. Oxybutynin is used to relieve the symptoms of overactive bladder including: frequent or urgent urination, incontinence and increased night-time urination. This medication is also prescribed to treat symptoms associated with kidney stones.
Oxybutynin is most commonly available on the market under the brand names Ditropan XL or Urotrol. Doctors most commonly prescribed this drug to control bladder muscles in adults and children older than age 6 with spina bifida or other conditions related to the nervous system issues that affect the bladder muscles.
Oxybutynin comes as an immediate-release tablet, extended-release tablet, and oral syrup. It is available in doses of 1 mg, 2.5 mg, 10 mg and 15 mg. It is also available in the form of gel (100mg/g) and patch (3.9mg/24h) that should be applied on the skin. FDA first approved Oxybutynin in 1978 and is originally made made by Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
What are oxybutynin molecular drug class, formula and weight?
Chemically, oxybutinin belongs to the class of chemical compounds known as benzene and substituted derivatives. These are aromatic compounds containing one monocyclic ring system consisting of benzene.
Chemical name: 4-(diethylamino) but-2-ynyl 2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate
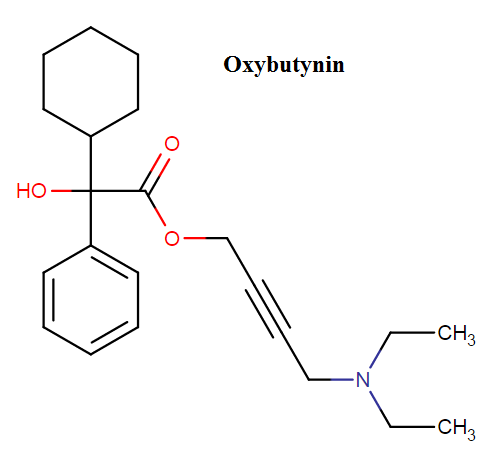
Molecular formula: C22H31NO3
Weight: 357.494 g/mol
(3D molecular formula of oxybutynin)
Pharmacologically, oxybutynin undergoes to a class of drug which is known as antispasmodics which is specially used to treat certain bladder and urinary conditions. It normally relaxes the bladder muscle and helps to lessen the problems of frequent and urgency urination.
How oxybutynin works in the body?
When you take oxybutynin drug its antispasmodic effect always slows down the action of acethycholine which occur no blocking effects at the junction of the skeletal neuromuscular. By inhibiting M1, M2 receptors of the bladder, detrusor activity is clearly decreased. In this way this medication works in human body and helps to lessen the problems of urgency and frequent urination.
Oxybutynin brand names
Oxybutynin is available under different brand names on the market including: Ditropan, Ditropan XL, Oxytrol and Gelnique.
What is oxybutynin used for?
Oxybutynin is a special type of anticholinergic medicine which normally used to reduce bladder and urinary difficulties. It also decreases the muscle spasms of the bladder and helps to control frequent urination. This medication also used for symptoms associated with kidney stones, overactive bladder, incontinence, increase night time urination and urgent urination. FDA approved indications for oxybutynin are:
- Detrusor Hyperreflexia
- Neurogenic Bladder
- Over Active Bladder
Oxybutynin dosage for different indications
Usual adult dose for urinary incontinence:
Initial:In this stage you need to take immediate release tablet or syrups 5mg two to three times in a day on regular basis. If you are using extended release tablets then take 5mg once regularly. For transdermal system, the dose is 3.9mg/day, applied twice in a week.
Oxybutynin 3% transdermal gel: 3 pumps around 84mg/day applied once daily to clean, dry, intact skin on the abdomen, or upper shoulders/arm, or thighs. Apply immediately after actuating the dose.
Oxybutynin 10% transdermal gel: You need to use one gram of dose which is around 1.14 ml or 100mg/g oxybutynin chloride gel once on regular basis to dry, intact skin on the abdomen, upper arms, shoulders, or thighs.
Usual adult dose for urinary frequency:
Initial: In this stage you need to take immediate release tablet or syrups 5mg two to three times regularly. If you are using extended release tablets then you need to take 5mg once regularly. For transdermal system, the dose is 3.9mg/day, applied twice weekly.
Oxybutynin 3% transdermal gel:
3 pumps around 84mg/day applied once daily to clean, dry, intact skin on the abdomen, or upper shoulders/arm, or thighs. Apply immediately after actuating the dose.
Oxybutynin 10% transdermal gel:
You need to use one gram of dose which is around 1.14 ml or 100mg/g oxybutynin chloride gel once on regular basis to dry, intact skin on the abdomen, upper arms, shoulders, or thighs.
Usual Pediatric dose for urinary incontinence:
Immediate release: For greater than 1 to 5 years old you need to take 0.2mg/kg per dose and you have to give it around 2 to 4 times on regular basis. For greater than 5 years old you need to give 5 mg two times regularly, up to 5 mg three times daily.
Extended release: For greater than or equal to 6 years you have to give 5mg once regularly. These are the whole dose information so you can follow these as per your requirement but it’s always better to follow your doctor’s prescription for the better result.
Oxybutynin highest dose
20 mg per day is the highest dose of oxybutynin but it’s always better to consult your doctor for the best dose because it totally depends on your health condition. Never take any extra dose for better effects. If you exhibit any side effects then immediately consult your doctor because sometimes you may need medicine dose adjustment for the best result.
Oxybutynin side effects
Oxybutinin may cause following side effects with following incidence:
- Dry mouth (21-71%)
- Constipation (7-15%)
- Somnolence (2-14%)
- Nausea (2-12%)
- Asthenia (6-10%)
- Dizziness (6-10%)
- Headache (6-10%)
- Blurred vision (6-10%)
- Dry eyes (6-10%)
- Diarrhea (6-10%)
- Nausea (6-10%)
- Pain (6-10%)
- Rhinitis (6-10%)
- Anorexia (<1%)
- Fluid retention (<1%)
- Hot flush (<1%)
- Dysphonia (<1%)
- Dysphagia (<1%)
- Frequent bowel movements (<1%)
- Chest discomfort (<1%)
- Thirst (<1%)
Potentially life-threatening allergic reaction called angioedema may be caused after oxybutynin use, which requires immediate medical attention.
Oxybutinin should be discontinued and medical attention should be sought right away if you or your child has any of the following symptoms:
- Frequent, urgent, or painful urination
- Fast, irregular, or pounding heartbeat
- Hives or a severe rash
- Swelling of the eyes, face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Hoarseness
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Fever
- Flushing or redness of the face
- Hallucinations (seeing, hearing, or feeling things that are not there)
- Unusual excitement, nervousness, restlessness, or irritability
Tell your doctor immediately if any of these rare but very serious side effects occur:
- Seizures
- Stomach/intestinal blockage
Oxybutynin overdose
Oxybutynin overdose has been related with serious anticholinergic effects. Central nervous system excitation usually appears as a result of oxybutynin overdose with symptoms such as: irritability, convulsions, delirium, restlessness, tremor, hallucinations, flushing, fever, dehydration, vomiting, cardiac arrhythmia and urinary retention. Other symptoms may include hypotension or hypertension, respiratory failure, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Activated charcoal as well as a cathartic may be given.
How to take oxybutynin?
Always take oxybutynin medication exactly according to your health provider prescription. Never take this medication in smaller or larger amounts or during the longer period than prescribed. Always take this medication with a full glass of water and try to take this medicine at the same time every day for the best result. You can take this drug with or without food.
Never chew, break or crush an extended-release table. Always try to swallow it whole. If you are using syrup or liquid medicine then measure it with a special dose-measuring spoon or medicine cup if you haven’t such measuring device then never hesitate to ask your pharmacist for one.
When the things come to storage always keep this medication at room temperature and away from heat and moisture. Try to keep this medication away from children and pet.
Can I abrupt oxybutynin therapy suddenly?
No, you can’t abrupt oxybutynin therapy suddenly on your own without the permission of your doctor because it can very harmful to you. If your doctor suggest you to stop this medication then you can stop it and it’s totally depends on your present health condition. So consult your healthcare provider and take advice never abrupt this medication as per you own choice.
Precautions and warnings during oxybutynin use
If you have untreated narrow-angle glaucoma or you are unable to urinate then never take oxybutynin medication. Always ask your doctor before using oxybutynin if you have liver, kidney disease or glaucoma, ulcerative colitis, myasthenia gravis, stomach disorder or blockage in your stomach. Avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated during exercise or in hot weather while you are taking oxybutynin.
Oxybutynin can decrease the perspiration which can cause a heat stroke so be careful. Oxybutynin medication may cause blurred vision and may impair your reactions or thinking so always be careful if you are driving or doing any hazardous works.
According to the medical science report and research there are various medications which are interact with oxybutynin so always tell your doctor about your previous medications when your doctor suggest you to take oxybutynin.
If in the case, you have any serious side effects just stop the medication and immediately consult your doctor for the best treatment and accurate dose according to your present health condition. If you are pregnant consult your healthcare provider for clear instructions.
Never take this medication according to your own choice during your pregnancy because it can be dangerous. There is no such clear-cut statement regarding use of oxybutynin during breastfeeding but the decision should be made by your doctor and totally depends on your health condition. Never give this medicine to a child on your own.
How long does oxybutynin take to work?
If you are taking this medication then you can mark some improvement in your symptoms within first 2 weeks of your medication but it may take around 6 to 7 weeks to experience the full benefit of this medication. If you do not see any improvement in your health condition even after 8 weeks then immediately consult your doctor may be you need any other therapy or dose adjustment.
What happen if I miss oxybutynin dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as possible or when you remember. If it is almost the time for the next dose then just skip the dose and take care that never happen in future. Remember one thing never takes double dose or any extra dose for the drug adjustment because it can cause serious health problems to you.
How long does oxybutynin stay in your system, urine, blood, saliva?
The half-life of oxybutynin is only about two to three hours. So for the full clearance from system, blood and saliva would be take around 10 to 18 hours but to wear off the full clearance it may take few days.
Oxybutynin use during pregnancy
Oxybutinin is classified in FDA pregnancy category B which means: Animal reproduction studies have failed to show a risk to the fetus and there are no acceptable and well-controlled studies in humans.
Minor reproductive toxicity has been showed in animal studies, but it is detected only in the occurrence of maternal toxicity. In the absence of understanding the relationship between maternal toxicity and development, the relevance to human safety cannot be addressed.
Oxybutynin use during breastfeeding
Oxybutynin use should be avoided during breastfeeding. It is excreted into human milk probably in small amounts. Anticholinergics can inhibit lactation by inhibiting growth hormone and secretion of oxytocin.
Long-term use of oxybutynin during lactation may reduce milk production or letdown, but single dose will probably not interupt breastfeeding. Anticholinergic drugs can lower serum prolactin levels in nonnursing women. However, the prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed.
Can geriatric patients use oxybutynin safely?
No, geriatric patients can’t use oxybutynin medication safely. There is no such risk found till now but that doesn’t mean that there is no risk in real so it’s always better to consult your doctor for the best medication and dose. Medication always depends on your present health condition so it’s never safe to take any medication according to your own choice.
Oxybutynin absorption, metabolism and elimination
Absorption:
Oxybutynin is quickly absorbed achieving Cmax within an hour. As a result plasma concentration decreases with an effectively half-life which is around two to three hours. The absoulately bioavailability of oxybutynin is found about 6% for the tablets.
Metabolism:
Oxybutynin is metabolized mainly by the cytochrome P450 enzyme systems, mostly CYP3A4 found in the gut wall and the liver. Its metabolic products include desethyloxybutynin, which is pharmacologically active and phenylcyclohexylglycolic acid, which is pharmacologically inactive.
Elimination:
The half-life of oxybutynin is only about two to three hours. So for the full clearance from system, blood and saliva would be take around 10 to 18 hours but to wear off the full clearance it may take few days.
Can I drink alcohol while taking oxybutynin?
No, you can’t drink alcohol while taking oxybutynin because there may be serious interactions happen between these two. Alcohol may increase the risk of dizziness and drowsiness while you are taking oxybutynin.
Can patients with liver disease take oxybutynin safely?
No, you can’t take oxybutynin if you have liver problems. Always take permission from your doctor before taking this medication for the best result. Never take medicines according to your own choice because it can be dangerous for you.
Can patients with neuropathy take oxybutynin safely?
Oxybutinin can exacerbate symptoms of autonomic neuropathy, including tachycardia, bladder atony, anhidrosis, obstipation, dry mouth and eyes, vision issues, and sexual impotence in males. Therapy with high doses of antimuscarinic agents should be administered carefully in patients with autonomic neuropathy.
Can patients with diarrhea take oxybutynin safely?
Oxybutynin use is contraindicated in patients with infectious diarrhea caused by pseudomembranous enterocolitis or enterotoxin-producing bacteria. This drug may prolong or worsen diarrhea related with bacteria that invade the intestines, such as Salmonella, E. coli and Shigella, and pseudomembranous colitis caused by broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Other symptoms such as fever, shedding of organisms and extraintestinal illness may also be prolonged. Because oxybutynin decrease gastrointestinal motility, it may delay excretion of infective gastroenteric bacteria or toxins and should be used with caution in patients who have infectious diarrhea, particularly if it is accompanied with high fever, pus or blood in the stool.
Can patients with renal disease take oxybutynin safely?
Patients with renal disease should avoid oxybutynin use, because this drug has dominant renal excretion. Dose adjustments may be necessary in order to obtain proper safety during oxybutynin use.
Can I take oxybutynin and potassium supplements together?
Coadministration of oxybutynin and potassium chloride may potentiate the risk of upper gastrointestinal damage related with oral formulations of potassium chloride. The suggested mechanism is increased gastrointestinal transit time because of the decrease of stomach and intestinal motility caused by oxybutynin.
Because of that there is localized high concentration of potassium ions in the region of a where capsule or tablet is dissolving, thus there is increased contact time with gastrointestinal mucosa. Solid formulations of potassium chloride have been associated with upper GI bleeding, bowel ulceration, stenosis, perforation, and obstruction. Deaths have been reported rarely.
Can I take oxybutynin and hydrocodone together?
Coadministration of narcotic analgesics such as hydrocodone with anticholinergic drug such as oxybutynin may result in additive CNS and gastrointestinal side effects, and increase the risk of CNS depression and severe constipation or paralytic ileus. Therefore, these two drugs should not be used together.
Can I take oxybutynin and amlodipine together?
According to the medical report there are no such interactions between oxybutynin and amlodipine but however there may be an interaction still exist so it’s always good to consult your physician before using these two medications if still you mark any side effects then tell your doctor because you may need any dose adjustment.
Can I take oxybutynin and topiramate together?
These two drugs should not be taken together especially in children. Oxybutynin may potentiate the risk of hyperthermia and oligohidrosis associated with the use of topiramate, particularly in children. Oxybutynin may enhance electrolyte and fluid and inhibit peripheral sweating mechanisms due to anticholinergic effect.
It may also interfere with temperature regulation in the hypothalamus resulting in the inability to regulate to temperature changes, especially in hot weather. Oxybutynin may also cause drowsiness and other CNS depressant effects, which may work additively or synergistically with topiramate.
Can I take oxybutynin and loperamide together?
These drugs should not be used together since both of them possess significant anticholinergic activity and may potentiate the antimotility effect of loperamide increasing the risk of side effects to happen such as: intensive obstipation and paralytic ileus.
Can I take oxybutynin and oxycodone together?
Coadministration of narcotic analgesics such as oxycodone with anticholinergic drug such as oxybutynin may result in additive CNS and gastrointestinal side effects, and increase the risk of CNS depression and severe constipation or paralytic ileus. Therefore, these two drugs should not be used together.
Can I take oxybutynin with antihistamines such as diphenhydramine?
Oxybutinin and antihistamine drugs such as diphenhydramine may have additive effects when used in combination. Excessive anticholinergic effects may cause serious side effects such as paralytic ileus, heat stroke, hyperthermia, and the anticholinergic intoxication syndrome.
Peripheral symptoms of as a result of interaction may include mydriasis, blurred vision, fever, flushed face, tachycardia, dry skin and mucous membranes, urinary retention, and constipation.
CNS symptoms can be also caused and may include memory loss, incoherence, disorientation, hallucinations, psychosis and delirium, hyperactivity, twitching movements, stereotypy, and seizures. CNS depressant effects are especially recognized in elderly or debilitated patients when these two drugs are used together.
Can I take oxybutynin with beta blockers (metoprolol, propranolol, sotalol)?
Theoretically, Oxybutynin may increase heart rate and counteract the bradycardic effects of beta blockers. Oxybutinin may also delay the gastrointestinal absorption of beta blockers. The suggested mechanism involves increased gastrointestinal transit time due to reduction of stomach and intestinal motility caused by oxybutinin
Can I take oxybutynin with codeine?
Concomitant useon of narcotic analgesics such as codeine with anticholinergic agents such as oxybutynin may result in additive CNS) and gastrointestinal adverse effects, and increase the risk of CNS depression and severe constipation or paralytic ileus.
Proper storage and disposal information of oxybutynin
Always keep oxybutynin at room temperature which is around 59 and 86F within a tight container. Always store this medication away from moisture, heat and light. Never keep it in your bathroom. Keep this medication out of the pets and children. As per the disposal concern it’s always better to ask your physician about it and one more thing never keep the expired medication in your home.
“Fexofenadine oral : Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings“
