Contents
- What is pericoronitis?
- What are the causes of pericoronitis?
- Is pericoronitis contagious?
- What bacteria cause pericoronitis?
- What are risk factors for pericoronitis?
- Is pericoronitis painful?
- Can pericoronitis cause headache?
- Can pericoronitis cause ear pain?
- Can pericoronitis cause bad breath?
- Difference between acute and chronic pericoronitis
- Difference between pericoronitis and Temporomandibular joint disorder
- What are the signs and symptoms of pericoronitis?
- Pericoronitis diagnosis
- How can I prevent pericoronitis?
- What should I do to maintain oral hygiene in pericoronitis?
- Natural remedies for pericoronitis
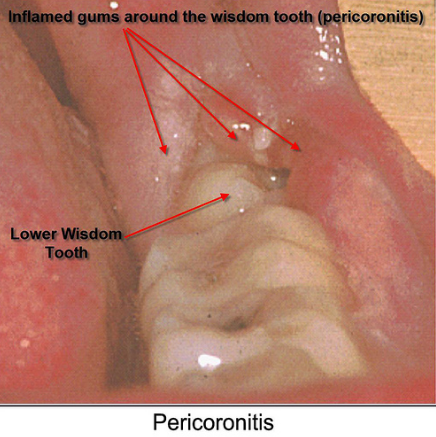
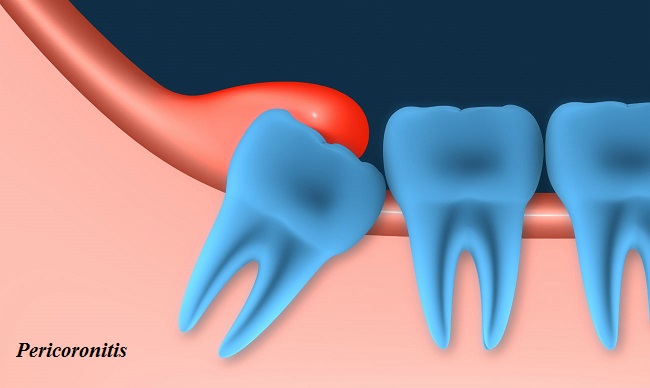
What is pericoronitis?
An inflammation in the gum tissue surrounding the crown portion of a tooth is called as pericoronitis. In this, the lower third molar (wisdom) tooth gets covered and chewing surface overlapped by gum tissue. Pericoronitis can be chronic or acute.
Chronic Pericoronitis: In this, the inflammation is mild but persistent.
Acute Pericoronitis: In this, infection starts spreading and cause fever, swelling and intense pain.
Pericoronitis is usually confused with peridontitis, and is differentiated by peridontitis in a way that peridontitis occurs specifically around a partially erupted tooth and gum cavity start covering the tooth before emerging from gum. Whereas the cause is same in both the conditions that is formation of gum abscess by entrapment of debris and bacteria under the gum tissue.
What are the causes of pericoronitis?
The primary cause of pericoronitis is accumulation of bacteria.
- It can develop when wisdom tooth is broken through the gum or erupted.
- The erupted space makes the opening for bacteria to enter the tooth and cause an infection.
- After having meals and after munching, a bacterial film left on the teeth and entered under the flap of gum around the tooth.
- The bacteria are trapped in between the tooth and overlapping gum that is also known as “operculum”.
- It starts accumulating under the gum fold and converted into the debris.
- After sometime, it starts irritating the gum and lead to pericoronitis.
- If left untreated, the infection may extend beyond the jaw to the cheeks and neck and results into the severe pericoronitis.
- Active infection is associated with an abscess that contains pus, which has the ability to spread if left unattended.
Is pericoronitis contagious?
Pericoronits is the condition in which the wisdom tooth gets affected only if it is partially erupted. Only then, it can give space to bacteria to enter into the gum cavity.
Just like viruses, you can also pass bacteria back and forth by means of kissing and sharing utensils. Only wisdom tooth can be affected by pericoronitis. The one who removed his/her wisdom tooth removed and their gums are intact, are less prone to catch this infection.
What bacteria cause pericoronitis?
A microscopic examination had been carried out in order to know the responsible bacteria for pericoronitis. We have seen the cultivation of facultative anaerobic microflora such as streptococcus Milleri group (78%), Stomatococcus mucilaginosus (71%) and Rothia dentocariosa (57%).
And we concluded that a well known, streptococci milleri group bacteria, which is known for its ability to cause superlative infections, and these microorganisms are involved in pathogenesis of acute severe pericoronitis of the lower third molar.
What are risk factors for pericoronitis?
Pericoronitis is a disease that mainly affects the young adults in their mid20sandinthepersonswho are experiencing poorly erupting wisdom teeth. Plaque formation is the main risk factor.
Other risk factors include the presence of excess opurculum (gum tissue) overlapping the wisdom tooth and difficult cleaning of wisdom tooth after overlapping of gum tissue.
Is pericoronitis painful?
When the infection exceeds in the jaw and cheeks area, the overlapping area of operculum starts swelling which cause intense pain.
The pain in the pericoronitis is severe and spontaneous. The pain more often aggravated by closing of mouth or unintentional chewing by wisdom tooth.
In some cases of swelling of operculum, opening and closing of the mouth during examination of the mouth, the pain is worsened.
Pain can be exceeds towards ear and cheeks.
Can pericoronitis cause headache?
This second approach can be a good one. Indistinct symptoms involving pain, pressure sensation or headaches are sometimes ultimately attributed to non-tooth conditions.
Can pericoronitis cause ear pain?
When pericoronitis left unseen, the infection in the tooth increases, which cause severe pain in lower jaw and wisdom tooth. This pain can spread to throat and ear.
Can pericoronitis cause bad breath?
The bacteria that is grown the gum cavity in the pericoronitis is responsible for causing bad breath. These bacteria release sulfur-containing compounds, which is called as “volatile sulfur compounds”, (or VSC’s for short).
When the volatile sulphur compounds are increased, they cause bad breath.
When tounge bacteria break down these bacteria, the bad breath gets worse.
Difference between acute and chronic pericoronitis
Acute pericoronitis:
Acute pericoronitis is caused due to trauma from the upper maxillary molar occlusion at the retromolar region. Symptoms of acute pericoronitis are inflammation of operculum, severe redness and soreness, continuous severe localized pain. Localized intra oral swelling occurs.
Pungent odour and halitosis is also most common in patients suffering from acute pericoronitis. Some other symptoms include tenderness and enlargement of lymph node locally, fever and malaise, leucocytosis, dysphagia, pyrexia associated with tachycardia can be seen if the condition left unseen or untreated.
Chronic pericoronitis:
Its presence shows the recurring inflammation and infection in the pericoronal region, and the dull pain in the pericoronal region. Its one of common symptom is halitosis and bad taste in oral cavity.
Difference between pericoronitis and Temporomandibular joint disorder
Pericoronitis is the gum disease in which the erupted wisdom tooth is overlapped by gum tissue that causes swelling in the overlapped tissues, which cause intense pain whereas tempo mandibular joint disorder is the disease, in which patient experience localized pain in the joint, which connect cheekbone and jaw bone. The pain occurs due to joint injury or tooth injury, misalignment of the teeth.
Cause:
Pericoronitis is the inflammation of the gum tissue surrounding the crown tissue of the wisdom tooth. It is caused by overlapping of the gum tissue on the erupted wisdom tooth. Whereas temporomandibular disorder is the pain in the cheekbone and jawbone. It is caused by jaw injury, tooth injury, misalignment of the tooth, teeth grinding, poor posture, gum chewing or arthritis.
Signs and symptoms:
In pericoronitis, there is Intense pain in tooth, oral swelling and bad breath, restricted mouth opening, Discharge from pericoronal space, pain in the jaw joint. Where as the symptoms of Temporomandibular joint disorder are Jaw clicking and popping, Ear pain, popping sounds in ears, headaches, sore jaw muscles, locking of jaw joint
What are the signs and symptoms of pericoronitis?
Early stage of pericoronitis is often confused with normal teething. Symptoms of acute pericorornitis are :
- Severe throbbing pain.
- Extra oral swelling
- Restricted mouth opening.
- Purulent discharge from pericoronal space.
- Halitosis, leucocytosis and malaise are also common in some cases of pericoronitis.
- In addition patient may also notice sloughing or ulceration around the operculum.
When left untreated, the infection spread in sublingual and para-pharyngeal spaces, which is followed by dysphagia. In this, the patient has difficulty in swelling food.
Pericoronitis diagnosis
Pericoronitis can be diagnosed by symptoms and appearance during a clinical evaluation with a dentist or a oral surgeon. A dental x-ray can be used to check out the other possible causes of the pain or dental decay. It can be diagnosed by the means of:
- X-ray Examination
- Oral examination
- Clinical evaluation by a dentist
Difference between pericoronitis and Temporomandibular joint disorder
Pericoronitits is the gum disease in which the erupted wisdom tooth is overlapped by gum tissue that cause swelling in the overlapped tissues, which cause intense pain.
Whereas tempomandibular joint disorder is the disease, in which patient experience localized pain in the joint, which connect cheekbone and jaw bone. The pain occurs due to joint injury or tooth injury, misalignment of the teeth.
Cause:
Pericoronitits is the inflammation of the gum tissue surrounding the crown tissue of the wisdom tooth. It is caused by overlapping of the gum tissue on the erupted wisdom tooth.
Temporomandibular disorder is the pain in the cheekbone and jawbone. It is caused by jaw injury, tooth injury, misalignment of the tooth, teeth grinding, poor posture, gum chewing or arthritis.
Signs and symptoms:
Signs and symptoms of pericoronitis are:
- Intense pain in tooth
- Oral swelling and bad breath
- Restricted mouth opening
- Discharge from pericoronal space
Whereas signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorder are:
- Pain in the jaw joint,
- Jaw clicking and popping
- Ear pain
- Popping sounds in ears
- Headaches
- Sore jaw muscles
- Locking of jaw joint
How can I prevent pericoronitis?
The prevention of pericoronitis can be carried out by preemptive care and regular visit to dentist. The dentist keep a track on the problem spots, keep them clean and diagnose the need for extraction of the overlapping gum.
Pericoronitis treatment
Pericoronitis is the diseases, which require immediate attention due to intense pain and disturbed quality of life.
Depending upon the severity of the condition, pericoronitis can be treated by three methods:
- Pain management and infection resolution
- Dental surgery
- Tooth Extraction
Pain management of pericoronitis
The pain can be reduced by OTC (Over the counter) medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Painkillers can help with any dental pain from pericoronitis. If the infection is severe, the pain will be intense. If there is no spread of infection, the pain will be localized and less severe.
A course of antibiotics may be recommended by the dentist to treat infection. If there is swelling or fever, oral antibiotics such as amoxicillin or erythromycin can be prescribed.
Dental surgery for pericoronitis
In case of pericoronitis, a minor surgery can be performed, depending upon need and use of tooth. In this, operculum is removed. The operculum is removed in order to easy access and proper cleaning of the infected area. This prevents the accumulation f the bacteria and food debris. Sometimes, gum tissues grow again and cause the same problem again.
It may be recommended to refer a oral surgeon or maxillofacial surgeon if wisdom tooth cause problems, the removal of wisdom tooth.
Removal of tooth in case of pericoronitis
When the wisdom tooth does not erupt completely and poorly impositioned, the removal of tooth is necessary and is most common treatment known. The removal of tooth prevents any kind of future consequences.
In rare cases, the symptoms become so severe that an individual needs to go the hospital emergency room to seek care due to the rapid spread of infection. After treatment of pericoronitis, and removal of tooth, oral hygiene measures may be advised.
Are antibiotics helpful for pericoronitis? What antibiotics should I use?
Drainage of abscess and empirical antibiotic therapy is recommended for severe infections such as pericoronitits and cellulitis. Metronidazole in 250mg dose every 8 hours is recommended for infections in which anaerobic bacteria are implicated, such as pericoronitis, periodontal abscess and ulcerative gingivitis. It is given due to its best pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics properties.
The short course antibiotic therapy requires the antibiotics with certain characteristics:
- Rapid onset of activity
- Bactericidal activity
- Easy permeability into tissues
- Activity against non-dividing bacteria
- Administration of optimal dose
- Optimal dosing regimen
Other common used antibiotic in dental practice are amoxicillin which is followed be penicillin. Among the group of penicillin, amoxicillin, amoxicillin and clavulanate combination is used most commonly because penicillin is still the gold standard therapy. A combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid has many advantages that includes increased inconvenience, improved compliance and improved tolerability, in a dose over three times daily.
What should I do to maintain oral hygiene in pericoronitis?
- Erupted wisdom tooth with overlapping gum tissues is very had to clean and non cleaning can result into tooth decay. The erupted wisdom tooth can be treated after checking the reason of infection.
- After a difficult surgical extraction of lower wisdom tooth, the extraction socket get inflamed, swelled and infectious, which is called as alveolitis. And it is caused by poor oral hygiene.
- Proper oral hygiene is the key to prevent symptoms. Its proper cleaning should be carried out by using soft electrical or manual toothbrush.
- One can try small or kids toothbrush for cleaning of wisdom tooth and they should use mouthwash, which contains fluoride. The cleaning with mouthwash is necessary to prevent the spread of infection.
- When toothache caused by pericoronitis, one should be treated with normal painkillers and mouthwash containing chlorhexidine.
Antiseptics for pericoronitis
The antiseptic gels should be used topically after gentle lifting of gum covering the erupted wisdom tooth.
A mouth rinse containing essential oils (e.g., Listerine Antiseptic) is as effective as chlorhexidine in the treatment of pericoronitis and may result in less calculus accumulation and tooth staining.
What analgesics are best for pericoronitis?
Analgesics are the other name for painkillers. Analgesics are of two types:
- Opioid
- Non-opioid
Opioid prescription analgesic:
These are referred as narcotics such as morphine derived from opium and are very powerful. They give additional pain relief in high doses but there are other potentially dangerous side effects. These opioids should not be used in dentistry. If needed, It should be used for very short period and for very short time periods due to its potential side effects.
Non-Opioid prescription or OTC analgesics:
Non-opioid analgesics are generally used to control dental pain until definitive treatment can be instigated. These are given pre and post operatively as an adjunct to dental treatment.
Ibuprofen is also considered as best painkiller and should be given before dental procedure as it can help in reducing post operative pain. It acts by blocking the production of pain causing chemicals inside the body. An analgesic should be taken as a recommended dose.
Analgesics acts by two ways i.e. reducing the inflammation or by diminishing the brain’s perception of pain through nervous system. They are considered best painkillers because they increase the pain relieving effect as well as minimal side effects.
The non-opioids analgesic are divided in to two types:
- Salicylates
- NSAIDs (Non-steriodal Anti Inflammatory Agents)
- Acetaminophen
Salicylates:
Best known and most commonly used salicylate is Aspirin. It is helpful in reducing pain and fever. Dentists or surgeon interests this medication as it cause thinning of blood and diminished blood clotting. After a dental surgery or tooth extraction, aspirin is not advised.
NSAIDs:
These painkillers are similar to aspirin due to same mode of action, pharmacological effects and adverse reactions.
It possesses anti-inflammatory properties and has a powerful pain relieving effect as well as action. They are superior over opioids due to better safety profile and it is most useful in density due to its sontrol on mild to moderate pain.
Ibuprofen is an important NSAID which is used in combination of paracetamol for pain relief in toothache. NSAIDs are available in varying strengths, sometimes used without prescription. The effective dose of ibuprofen is 400-800 mg and higher doses do not have a benefit as far as dental pain relief is concerned. Higher doses are prescribed when there is swelling apparent, as well as pain and the anti-inflammatory effect is important.
Ibuprofen is generally well tolerated and produces some gastro-intestinal in some patients. Ibuprofen can reduce the blood thinning effect of aspirin so patients taking aspirin for cardiovascular protection should avoid it.
Diclofenac is another potent NSAID, as is also aceclofenac which may cause less gastrointestinal side effects.
Acetaminophen/paracetamol for pericoronitis pain relief
Acetaminophen/paracetamol acts more centrally, to block the pain messages in the brain and has little effect in reducing inflammation but is an effective medicine for toothache. It is useful for those who can’t take aspirin or it can be combined with aspirin or a NSAID to greater effect.
A dose of 4-500 mg is commonly used and adequate, although the maximum effective dose for toothache relief is about 1000 mg. An excessive amount of acetaminophen can potentially cause liver damage so this needs to be taken into account, especially when analgesic products combining two or three types are used.
Only when the dose of NSAID and/or paracetamol is at optimum levels, is it usually necessary to consider adding an opioid, and this is fairly rare in most dental problem circumstances.
Operculectomy for pericoronitis
Operculectomy is the surgical procedure of removing the operculum, the flap of gum that partially covers a tooth in pericoronitis. Pericoronitis typically occurs in patients whose wisdom tooth starts to erupt and is most common among young adults.
Operculum is the extending part of the gum tissues that overlap the erupted wisdom tooth. It is a mass of soft tissue and is most commonly associated with lower wisdom tooth.
Sometimes it also covers the permanent molars and some baby teeth. In normal teething, the gum tissue moves back as the tooth continue to erupt and takes its accurate position. Whereas in pericoronitis these gum tissue exceeds and cover the tooth instead to recede. A normal tooth should not be covered with any gum tissue on it chewing surface.
In the case of pericoronitis, the lower wisdom tooth is not able to erupt fully and come out of the gum line. Also the operculum do not recede fully and cover the wisdom tooth completely and permanently. The upper molar start putting pressure on lower counterparts which cause intense pain and disturbs the quality of life of patient. Therefore, there is a need for operculectomy in case of pericoronitis.
Tooth extraction and pericoronitis
In pericoronitis, the primary aim to get relief from pain associated. An inflammation in the gum tissue surrounding the crown area of tooth occurred due to overlapping of erupted wisdom tooth with operculum. A dental surgery known as operculctomy is done to remove operculum.
But if there is swelling, infection, difficulty in swallowing, fever or intense pain, the wisdom tooth be extracted as soon as possible. After extraction of tooth, proper antibiotics should be taken as prescribed. Warm saltwater rinse and OTC painkillers are also advised in order to get relief from toothache.
Natural remedies for pericoronitis
Swelling in the gum area cause severe toothache. One should seek medical attention immediately in case of excessive pain. But meanwhile you can try some natural painkillers and remedies to avoid pain at home.
Salt and Pepper:
One should make a paste from salt and pepper in equal quantities and place it on the infected area. Salt and pepper contains anti-inflammatory and painkilling properties. Apply the mixture and rest it for sometime.
Garlic:
Apart from its great antibiotic and other medical properties, garlic is a great painkiller for toothache. One can crush the garlic, clove and add in the black pepper and salt, and apply the mixture on the affected area.
Cloves:
Clove is considered as one of the best natural remedy for toothache. It contains anesthetic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties due to which clove is known to relieve toothache and combat infections. One can mix clove oil with water to make a mouthwash and then rinse the infected area thoroughly with this mouthwash. You can also soak a cotton ball in clove oil and rub this on infected tooth in order to get relief.
Onion:
One of the best natural remedy for treating toothache is onion. It contains antimicrobial and antiseptic properties. It is beneficial in killing the bacteria and germs and provides relief from pain. Chew an onion in case of excessive pain, and if chewing is not possible then place an onion slice on the infected tooth.
Salt water:
Gargling with warm salty water is highly advised to get relief from toothache. For this mixture, one can mix warm water with half spoon salt. Rinse your mouth with the mixture and any inflammation or swelling will reduce. Gargling with this solution is beneficial in killing of germs that may be associated with tooth infection.
“What is the cause of excessive sweating? How do you stop sweating?“