Contents
- What is phobia?
- Phobia classification
- Phobia prevalence
- Top 10 most prevalent phobias
- What are most typical signs and symptoms of phobias?
- How phobias develop?
- Who are at most high risks of phobias?
- Phobias treatment options
- Phobias from A-Z
- Most common animal phobias
- Racist, xenophobic, anti-cultural, anti-national, and anti-ethnic phobias
What is phobia?
Phobia (from Greek φόβος phobos, “fear”) is defined as a persistent, abnormal, irrational or in some cases disabling fear of activity, situation or specific object that leads to a definite desire of avoiding it. In medicine it is classified as a type of anxiety disorder characterized with rapid onset of fear and present for more than 6 months.
The phobic person will intensively go to great lengths and do abnormal things in order to avoid the potential cause of fear, typically to a level far greater than the actual danger posed. In cases where object or situation which are primary source of phobia cannot be avoided, the affected person will have important distress.
People who have phobias most commonly realize that their fear is irrational; however they are powerless to do anything about it. Such fears can interfere with their school, work and personal relationships. Sometimes phobia can be accompanies with panic attack or if it is specific phobia (e.g fear of blood) nausea, vomiting, trouble with breathing, fainting, loss of consciousness and other symptoms may also occur.
Phobia classification
According to Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-V) phobias are considered as a subtype of anxiety disorder and are divided into 3 groups:
- Agoraphobia with or without panic attacks – defined as irrational anxiety about being in places from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing. The word itself means “fear of open spaces” Patients with agoraphobia have a fear of being in large crowds or trapped outside the home. They often avoid all social situations and stay inside their homes. Many patients with agoraphobia fear that they will eventually get panic attack in a place where they can’t escape. Patients with chronic agoraphobia may have fear they will have a medical emergency in a public or where no help is available.
- Social phobia defined as irrational anxiety elicited by exposure to certain types of social or performance situations, also leading to avoidance behavior. A social phobia can be in some cases so severe that the simplest social interactions, such as answering the telephone or ordering at a restaurant can cause panic. Those with social phobia often avoid public situations in order not to get embarrassed.
- Specific phobia defined as persistent and irrational fear in the presence of some specific stimulus which commonly elicits avoidance of that stimulus, i.e., withdrawal.
There are 5 subtypes of specific phobias:
- Animal type – caused by animals or insects
- Natural environment type – cased by environmental stimuli, such as storms, heights, or water
- Blood-injection-injury type – caused by witnessing some invasive medical procedure
- Situational type – caused by a specific situation, such as elevators, tunnels, bridges, public transportation, flying, driving, or enclosed spaces
- Other type – caused from all different stimuli, such as of choking, vomiting, or contracting an illness, etc.

Phobia prevalence
According to NIMH, about 11.5 million adults worldwide which is about 8.0% adults suffer from some kind of phobia.
Phobias are shown to be common psychiatric disorders. Nearly 11 % of the U.S. population which is about 25 million people may suffer from a phobia at least once during their lifetime.
Just in the U.S. about 6.8 % of the population, (about 15 million adults) suffer from social phobia annually. It has been shown that social phobias typically start at about 13 years of age. Worldwide, annual prevalence of social phobia is estimated to be about 4.5 % while lifetime prevalence is approximately 3.6 %. However, rates are different from country to country.
For example, only 0.53 % of South Koreans suffer from social phobias compared to the the number of people in Russian region Udmurtia, where it has been estimated that almost 45% suffer from social phobias. Rates of social phobia appear to somewhat reduced from ages of 18 to 64, with a marked drop after the age of 65.
Agoraphobia may begin suddenly or gradually, usually between adolescence and mid-thirties. About 2/3 of patients with agoraphobia are women. Epidemiology studies found that rates of agoraphobia are not so much different between countries as those of other types of phobia.
In the U.S. and around the world the prevalence of agoraphobia without panic attacks is about 0.8 %. So it is about of 1.8 million U.S. adults with agoraphobia. But, 40 % of these cases are diagnosed as severe. The rates of agoraphobia accompanied with panic attack are a little bit higher and is about 1.1%. Rates of agoraphobia appear to be stable at ages of 18 to 64. Rates drop off in the elderly.
Specific phobia usually begins in childhood, around the age of seven. According to data, in the U.S. a fear of animals is the most common specific phobia, with dogs, snakes, and bugs at the top of the list.
In the U.S., it is considered that 9 % of adults have specific phobia, with 22 % of diagnosed cases labeled as severe. 15% of children between the ages of 13-18 have specific phobia, however only 0.6 % are considered as severe cases. But the rates are different from country to country and may vary from the bravest 0.2 % in Northern Ireland to approximately 9% of most frightened in the United States.
Women are known to be 2-4 times more likely compared to men in specific phobia development. Rates appear to be increased somewhat from ages 18-64. In elderly the prevalence of specific phobias appears to drop dramatically.
Top 10 most prevalent phobias
Most common phobias by prevalence in the U.S. are:
- Glossophobia – The fear of public speaking affecting approximately 74% of population
- Necrophobia – The fear of death affecting approximately 68% of population
- Arachnophobia – The Fear of spiders affecting approximately 30.5% of population
- Achluophobia, Scotophobia or Myctophobia – The fear of darkness affecting approximately 11% of population
- Acrophobia – The fear of heights affecting approximately 10% of population
- Sociophobia, social phobia – Fear of people or social situations affecting approximately 7.9% of population
- Aerophobia – The fear of flying affecting approximately 6.5% of population
- Claustrophobia – The fear of small spaces affecting approximately 2.5% of population
- Agoraphobia – The fear of open spaces affecting approximately 2.2% of population
- Brontophobia – The Fear of thunder and lightning affecting approximately 2% of population
What are most typical signs and symptoms of phobias?
The most common symptom accompanied with phobia is a panic attack. Features of a panic attack include:
- shortness of breath
- pounding or racing heart
- rapid speech or inability to speak
- upset stomach or nausea
- dry mouth
- elevated blood pressure
- chest pain or tightness
- trembling or shaking
- choking sensation
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- profuse sweating
- sense of impending doom
A person with a phobia may or may not have panic attacks for accurate diagnosis.
How phobias develop?
The certain cause and mechanism of phobias development is not yet known. There are various theories, but they can be all classified into following 3 categories:
- psychoanalytic
- learning-based
- biological
Psychoanalytic theory of phobia development
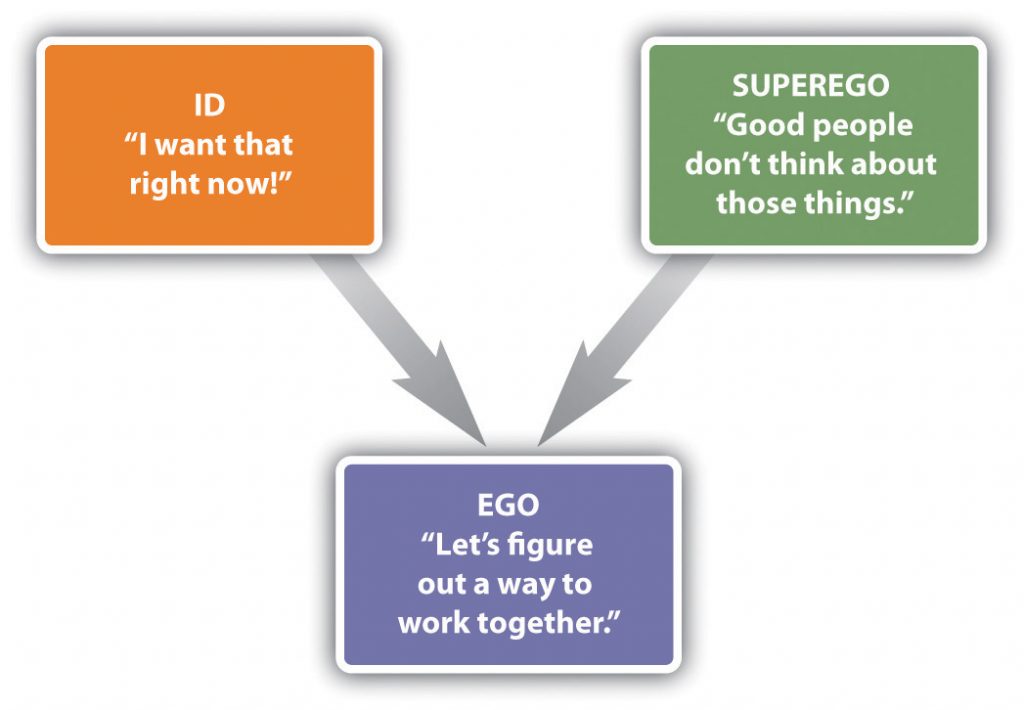
According to Sigmund Freud pioneering structural theory, phobias may be related with three stages of conscience:
- id
- ego
- superego
The id is the most primitive and instinctive part of the mind and may be behind primitive emotions such as fear and anxiety. The superego is the selfless higher state of conscience, with value of judgments and the concept of guilt. The ego is known to be rational moderator between the two. A significant part of the ego is to control the impulses of the id.
In accordance to this theory, phobias are caused by anxiety reactions of the id that have been repressed by the ego. So, it can be said that the feared object is not the original subject of the fear.
Learning theory of phobia development
The learning theory contains a set of theories based on doctrines of behaviorism and cognitive theory. Ivan Pavlov who developed the learning theory showed that dogs could be trained to salivate when a bell rung. Since then, numerous theories of human behavior have been developed.
According to this theory, phobias will develop when fear reactions are punished or reinforced. Both punishment and reinforcement can be positive or negative. Positive reinforcement can be exhibition of something which is positive, including a parent rewarding his child for staying away from a snake.
Positive punishment is the presentation of something negative or unfavorable to prevent that behavior from happening again, such as a child being bitten by a snake.
Biological theory of phobia development
This theory is based on neuropsychology, which is a part of psychology that is dedicated to studying the structure and function of the brain.
Neuropsychologists have been researched and identified specific genes that may play an important role in the development of phobias. Although more researches are needed it is known that certain drugs may affect the chemistry of the brain and be helpful in treating phobias. Most of these therapies are proposed to help anxiety relief by increasing the level of a neurotransmitter serotonin.
Who are at most high risks of phobias?
Patients who have a genetic predisposition to anxiety are at higher risk for developing phobias. Age, gender and socioeconomic may be risk factors for certain phobias. E.g. women are at more high risk to have animal phobias. Those with a low socioeconomic status are at higher risk to have social phobias. Men make up the majority of those with dentist and doctor phobias.
Phobias treatment options
Treatment for phobias may include therapeutic techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy, medications, or a combination of these two.
Cognitive-Behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy or shortly CBT is the most commonly used therapeutic option for phobias. CBT includes exposure to the primary source of the fear in a controlled setting. This treatment can decondition people and reduce anxiety.
The treatment is based on identifying and changing negative thoughts, wrong beliefs, and negative reactions to fear. New CBT techniques use virtual reality technology to safely expose people to the sources of their phobias.
Medication
Anti-anxiety drugs and antidepressants can help calm both emotional and physical reactions to fear. Often, the combination of medication and professional therapy makes the biggest difference. If you have a phobia, it’s critical that you seek treatment. Overcoming phobias can be difficult, but there’s hope. With the right treatment, you can learn to manage your fears and lead a productive, fulfilling life.
Phobias from A-Z
Following list include majority of phobias:
A
- Ablutophobia – The fear of bathing, washing, or cleaning
- Acousticophobia – The fear of loud noise – a type of phonophobia
- Acrophobia – The fear of heights
- Aerophobia – The fear of flying
- Agoraphobia – The fear of open places
- Agyrophobia – The fear of crossing streets
- Aichmophobia – The fear of needles, knifes and other sharp or pointed objects
- Ailurophobia – The fear of cats
- Algophobia – The fear of physical pain
- Amychophobia – The fear of being scratched
- Androphobia – The fear of adult men
- Anthropophobia – The fear of people or the group of people, a type of social phobia
- Aquaphobia – The fear of water. Not the same as hydrophobia. Averse to scientific chemical reactions with water
- Arachnophobia – The fear of spiders
- Astraphobia – The fear of weather storms, specifically thunder and lightning
- Autophobia – The fear of isolation
- Aviophobia, aviatophobia – The fear of flying
B
- Basophobia – The fear related with astasia-abasia (fear of walking/standing erect) and a fear of falling
- Blood-injection-injury type phobia – a subtype of specific phobias
C
- Chemophobia – The fear of chemicals
- Chiroptophobia – The fear of bats
- Chromophobia, chromatophobia – The fear of colors
- Chronophobia – The fear of time and time moving forward
- Cibophobia, sitophobia – The neurological aversion to food, similar to anorexia nervosa
- Claustrophobia – The fear of having no escape and being closed in
- Coimetrophobia – The fear of cemeteries
- Colorphobia – Th fear or a very strong aversion towards a particular color
- Coprophobia – The fear of feces or action of defecation
- Coulrophobia – The fear of clowns
- Cyberphobia – The fear of computers and of learning new technologies
- Cynophobia – The fear of dogs
D
- Decidophobia – The fear of making decisions
- Demonophobia, daemonophobia – The fear of demons
- Dentophobia, odontophobia – The fear of dentists and dental procedures
- Dromophobia – The fear of crossing streets
- Dysmorphophobia – A phobic obsession with a real or imaginary body defect
E
- Eurotophobia – Aversion to female genitals
- Emetophobia – The fear of vomiting
- Enochlophobia – The fear of crowds
- Ephebiphobia – The fear of youth people
- Ergophobia, ergasiophobia – The fear of working, doing activities, or a surgeon’s fear of operating
- Erotophobia – The fear of sexual love or sexual abuse
- Erythrophobia – The fear of the color red, or fear of blushing
F
- Frigophobia – The fear of becoming too cold
G
- Gamophobia – The fear of cohabitation, marriage or nuptials
- Gelotophobia – The fear of being laughed at
- Gephyrophobia – The fear of bridges
- Genophobia, coitophobia – The fear of sexual intercourse
- Gerascophobia – The fear of growing old or aging
- Gerontophobia – The fear of the elderly
- Globophobia – The fear of balloons
- Glossophobia – The fear of speaking in public or of trying to speak, probably most common type of phobia
- Gynophobia – The fear of women
H
- Halitophobia – The fear of bad breath
- Haphephobia – The fear of being touched
- Hedonophobia – The fear of obtaining pleasure
- Heliophobia – The fear of the sun or sunlight
- Hemophobia, haemophobia – The fear of blood
- Hexakosioihexekontahexaphobia – The typical irational fear of the number 666
- Hoplophobia – The fear of firearms
- Hypnophobia, somniphobia – The fear of falling sleep or sleep
I
- Ichthyophobia – The fear of fish, also including fear of eating fish, or fear of dead fish
K
- Koumpounophobia – The fear of buttons
L
- Lilapsophobia – The fear of hurricanes or tornadoes
M
- Mageirocophobia – The fear of cooking
- Melanophobia – The fear of black color
- Melissophobia, apiphobia – The fear of bees
- Monophobia – The fear of being isolated or alone
- Musophobia/murophobia/suriphobia – The fear of mice or rats
- Myrmecophobia – The fear of ants
- Mysophobia – The fear of germs, dirt or being contaminated
N
- Necrophobia – The fear of death
- Neophobia/cainophobia/cainotophobia/centophobia/kainolophobia/kainophobia, metathesiophobia or prosophobia – The fear of newness, changes, progress and novelty
- Nomophobia – The fear of being out of mobile phone contact
- Nosocomephobia – The fear of hospitals
- Nosophobia – The fear of contracting a disease
- Nostophobia, ecophobia – The fear of returning home
- Numerophobia – Fear of numbers, or certain number
- Nyctophobia/achluophobia/lygophobia/scotophobia – Fear of the dark
O
- Oikophobia – The fear of home surroundings and household appliances
- Oneirophobia – The fear of dreams or to dream
- Ophthalmophobia – The fear of being stared at
- Osmophobia, olfactophobia – The fear of odors
P
- Panphobia – Fear of everything and constant fear of an unknown cause
- Pedophobia – The fear of children
- Phagophobia – The fear of swallowing
- Phallophobia – The fear of erections
- Pharmacophobia – The fear of drugs or medication
- Phasmophobia – The fear of ghosts or phantoms
- Philophobia – The fear of love
- Phobophobia – The fear of fear itself or fear of having some phobia
- Phonophobia – The fear of loud sounds or voices
- Pogonophobia – The fear of beards
- Pornophobia – The fear or averse of pornography
- Pyrophobia – The fear of fire
R
- Radiophobia – The fear of radioactivity or X-rays
S
- Scopophobia – The fear of being looked by somoene
- Sexophobia – The fear of sexual organs or sexual activities
- Siderodromophobia – The fear of trains or railroads
- Sociophobia – The fear of people or social situations, type of social phobia
- Spectrophobia – The fear of mirrors
- Stasiphobia – The fear of standing or walking
T
- Taphophobia, taphephobia – The fear of the grave, or fear of eventually being graved while still alive
- Technophobia – The fear of advanced technology
- Telephone phobia – The fear of making or taking telephone calls
- Teratophobia – The fear of disfigured people
- Tetraphobia – The fear of the number 4
- Thalassophobia – The fear of the sea, or ocean
- Thanatophobia – The fear of dying
- Thermophobia – The fear of high temperatures
- Tokophobia – The fear of childbirth or pregnancy
- Toxiphobia – The fear of being poisoned
- Traumatophobia – The fear of having an injury
- Trichophobia – The fear of hair loss
- Triskaidekaphobia, terdekaphobia – The fear of the number 13
- Trypanophobia, belonephobia, enetophobia – The fear of needles or injections
- Trypophobia – The fear of holes or textures with a pattern of holes e.g fear of sponges
W
- Workplace phobia – The fear of the workplace
X
- Xanthophobia – The fear of yellow color
- Xenophobia – Fear of strangers, foreigners, or aliens
Most common animal phobias
Animal phobias belong to the group of specific phobias, and some of the most common are following:
- Ailurophobia – The fear or aversion to cats
- Apiphobia – The fear or aversion to bees (also called as melissophobia)
- Arachnophobia – The fear or aversion to arachnids
- Batrachophobia – The fear or aversion to amphibians
- Chiroptophobia – The fear or aversion to bats
- Cynophobia – The fear or aversion to dogs
- Entomophobia – The fear or aversion to insects
- Equinophobia, hippophobia – The fear or aversion to horses
- Herpetophobia – The fear or aversion to reptiles or amphibians
- Ichthyophobia – The fear or aversion to fish
- Murophobia – The fear or aversion to mice or rats
- Ophidiophobia – The fear or aversion to snakes
- Ornithophobia – The fear or aversion to birds
- Ranidaphobia – The fear or aversion to frogs
- Scoleciphobia – The fear or aversion to worms
- Zoophobia – The fear or aversion to animals
Racist, xenophobic, anti-cultural, anti-national, and anti-ethnic phobias
Most common anti-ethnic or anti-demographic phobias are:
- Americanophobia – The fear of Americans
- Europhobia – The fear of Europeans
- Francophobia – The fear of French
- Hispanophobia – The fear of Spanish or hispanic populations
- Christianophobia – The fear of Christians and Christianity
- Islamophobia – The fear of Islamic religion or islamists
Similar types of these phobias are:
- Albanophobia – The fear of Albanians
- Anglophobia – The fear of England or English culture
- Germanophobia – The fear of Germans
- Hinduphobia – The fear of Hindus
- Indophobia – The fear of India or Indian culture
- Judeophobia – The fear of Jews
- Nipponophobia – The fear of the Japanese
- Koryophobia – The fear of Koreans
- Polonophobia – The fear of Polish
- Russophobia – The fear of Russians
- Shiaphobia – The fear of Shiites
- Sinophobia – The fear of Chinese people
- Sunniphobia – The fear of Sunnis
- Turcophobia – The fear of Turks
- Xenophobia – The fear of foreigners
Phobias against different categories of people may include:
- Biphobia – The fear of bisexuality or bisexuals
- Ephebiphobia – The fear of youth
- Gerontophobia, gerascophobia – The fear of aging or the elderly
- Heterophobia – The fear of heterosexuals
- Homophobia – The fear of homosexuality and homosexuals
- Lesbophobia – The fear of lesbians
- Pedophobia – The fear of children
- Psychophobia – The fear of mental illness or the mentally ill patients
- Transphobia – The fear of transgender people
“What is the medical term of Odynophagia? What are causes of Odynophagia?“