Contents
- What is Pyuria?
- What is sterile Pyuria?
- What is Pyuria in teeth?
- Pyuria and appendicitis
- Is Pyuria rare disease? Pyuria epidemiology
- Pyuria symptoms and signs
- What causes Pyuria?
- Pyuria complications
- Pyuria diagnostic and tests
- What is the difference between Pyuria and Dysuria?
- What is the difference between pyuria and anuria?
- What is the difference between pyuria and oliguria?
- Pyuria treatment
What is Pyuria?
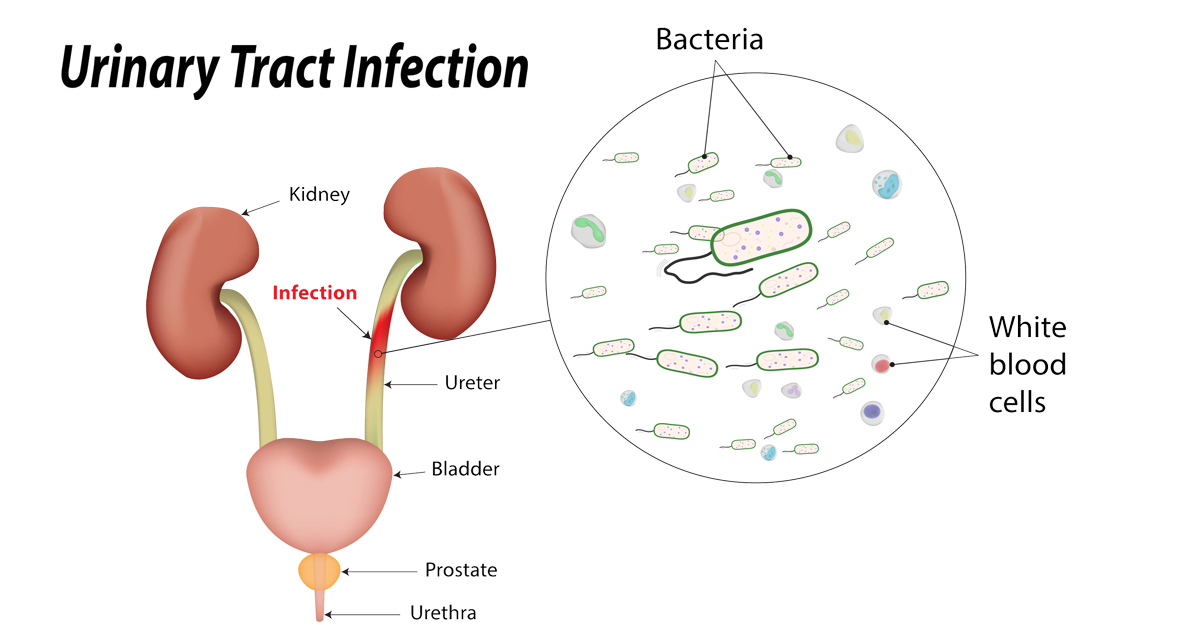
Pyuria is associated with Urinary tract infection (UTI). It is a condition in which excess of white blood cells or pus is present in the urine. It causes the cloudy and foul smelling urine indicating the presence of UTI infection. Pyuria is defined having the presence of ten or more WBSs per cubic mm in a sample of urine.
If the urine dipstick test is positive for leukocyte esterase or a positive result of unspun urine sample, then it is the indication of Pyuria. In older people, Pyuria can indicate the sepsis that is the life threatening bacterial infection and pneumonia. There are various reasons for Pyuria.
Bacterial infection is not the only cause of Pyuria. Without the bacteria, the Pyuria is asymptomatic. In this case the diagnosis and the treatment are very difficult. In that case other causes are cancer, kidney disease, tuberculosis and drugs. The older people are more prone to Asymptomatic Pyuria, as with age the muscular system tends to grow old. They use the catheter that can lead to the infection.
The infection accounts for 98 to 99% of pus cells in the urine. Our body responds to the irritation of the tissue in the form of inflammation. This response is manifested by an increase in the blood flow to that area. It results in swelling and the infiltration of white blood cells in the urine. The main cause of the inflammation is the bacterial infection, parasites, tumors and viral infection etc.
What is sterile Pyuria?
Sterile Pyuria is the presence of white blood cells in the urine with the absence of bacteria. It is more prevalent in women as compared to men. The study shows that 13.9% of women and 2.6% of men suffer from sterile Pyuria.
The causes of sterile Pyuria are sexually transmitted infection, fungal infections, viral infection, Genito- tuberculosis infection, parasitic infections and other Urologic conditions.
In men the sexually transmitted infections cause symptomatic urethritis. In case of women, the sexually transmitted infections can be asymptomatic initially. The most common fungal infection is caused by Candida species that are the main source of UTI infections. Trichomonas vaginalis is the most widely spread source of infection.
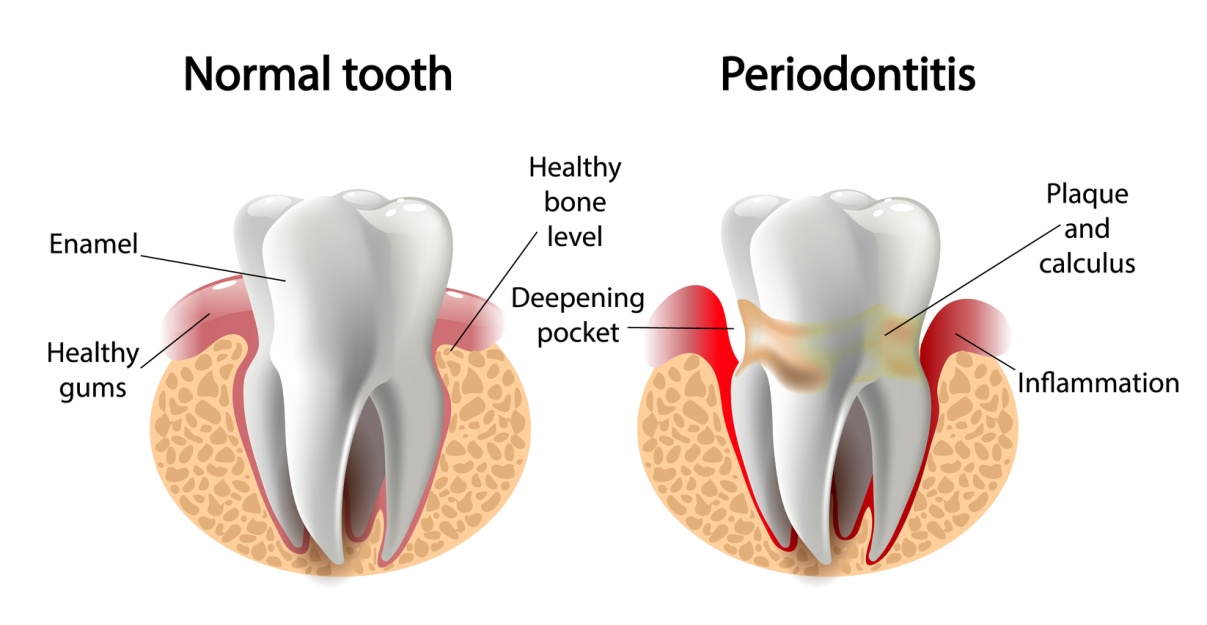
What is Pyuria in teeth?
Pyuria in teeth is also known as Periodontitis. It is a serious infection in the gum, damaging the soft tissue. It also damages the bones that support the teeth. It can result in tooth loss and increased risk of stroke and heart attack with other serious health problems.
Chronic Periodontitis is more common in adults. Aggressive Periodontitis starts from childhood or early adolescents and affects a small number of people. It occurs due to poor oral hygiene. Brushing twice the day can reduce the chances of Pyuria in teeth.
The signs and symptoms of Periodontitis are:
- Loose teeth
- Swollen gums
- Space between the teeth
- Bad breath
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Tender gums
Causes: It happens due to the formation of plaque and tartar for a longer period of time. Plaque is formed due to interaction between sugar in food and bacteria in the mouth.
Pyuria and appendicitis
If a patient is suffering from pain in the right side of the lower abdomen with nausea, vomiting, fever and leukocytosis, then the diagnosis will be acute appendicitis. In case the patient’s urine contains pus, the diagnosis will be Pyuria.
In the case where there is appendicitis with the associated Pyuria then the decision about the surgical treatment must be taken after careful examination of all the clinical aspects as well as the condition of the patient.
The surgical procedure is required to prevent the patient from the dangerous outcomes because of Pyuria. It is very difficult to do the proper diagnoses of the condition. So, all the aspects and reports must be carefully studied while taking any decision regarding the mode of treatment.
Is Pyuria rare disease? Pyuria epidemiology
The prevalence of Urinary Tract infection occurs in 30 to 50% of individuals with ADPKD (Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease). The evidences of the clinical relevance of asymptomatic Pyuria in ADPKD patient is not much.
However the Pyuria is not a rare disease but it remains misdiagnosed. The diagnosis is often missed. The diagnosis of the Pyuria must be done on the basis of sterile Pyuria, alkaline urine ph and calcifications of the urinary tract through the CT scan. It must be confirmed by the prolonged culture on the appropriate medium.
Because of not getting appropriate treatment of Pyuria, there are serious complications like heart diseases and stroke that is life threatening.
Pyuria is the infection of the urinary tract common in the people of all the age groups. It is more prevalent in females as compared to males. Overall the prevalence of this infection is 3.5%. Risk factors include UTI history, diabetes and lower socioeconomic status. Pregnant women are more susceptible to Pyuria. The percentage varies from 4 to 10%.
Pyuria symptoms and signs
There are not any particular symptoms (Asymptomatic) of Pyuria. In case of any reported symptoms, they are linked to the underlying health condition that is causing Pyuria.
When it is present with bacteria then the cause of Pyuria is not clear. The conditions like kidney infection, kidney stones, tuberculosis and cancer can be the reason of it.
Symptoms and sign if occurred, must consult with the physician are-
- Foul smelling urine
- Fever
- Cloudy urine
- Discomfort in urinating
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Abdominal pain
- Chills
- Nausea & Vomiting
What causes Pyuria?
- There are many causes of the Pyuria. The most common is the increase in white blood cells in urine without infection.
- In case if a person is suffering from any sexually transmitted disease, then the excess of white blood cells can be found in urine. Certain types of viral, bacterial and fungal infection can give rise to this problem.
- Men who are suffering from prostate gland infection will have a foul smell and pus in the urine. The intake of medicines like gluco-corticoid can cause this condition. Kidney stone, tumor and kidney infection can cause excess white cells in the urine.
- Pregnant women can have cloudy discharge in urine that indicates the presence of white blood cells. Inflammation and urinary tract infection can cause Pyuria.
- White cells in the urine can indicate the inflammatory conditions in the urinary system like the problem in the kidney.
There are some of the health problems that results in Pyuria. They are-
- Diabetes
- Renal Stone
- Cancer
- Infection
- Kidney disease
- Tuberculosis
- Papillary necrosis
- Kawasaki disease
Pyuria complications
The complication depends on the underlying condition that causes Pyuria.
- In the bladder infection, possible complications are the progression of upper urinary tract infection of the ureter and kidney.
- In kidney infection, generalized infection that is sepsis or kidney damage can occur as a result of the infection.
Pyuria diagnostic and tests
Pyuria is a laboratory finding that helps in the diagnosis of other conditions like urinary tract infection. The presence of pus in the urine can be detected by the analysis of the urine sample. Through microscopic examination and chemical analysis in the lab, the analysis of the urine sample is done.
When there are greater than six neutrophils per high power of unspun, mid stream urine, then Pyuria is confirmed. We have to take special care that other secretions might not contaminate the urine sample. This is specifically in case of women as the vaginal secretions can contaminate the urine sample. Vaginal secretions contain bacteria that can confound the result of urine analysis.
The more diagnostic testing is required to confirm the Pyuria. This includes IVP (Intravenous pyelogram), MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), CT (Computed tomography) and ultrasound imaging of the abdominal area.
What is the difference between Pyuria and Dysuria?
Many clinicians suspect the diagnosis of bacterial cystitis that has Dysuria with frequent urination without any clinical evidence of UTI. Cystitis is a common syndrome of Dysuria, frequent urine and urgency of urination that is sometimes associated with suprapubic pain and often found in the presence of Pyuria. These symptoms indicate the presence of bacterial cystitis, may be associated with other infections of vagina and urethra.
The most common bacterial infection that occurs in women is Bacterial Cystitis. At least thirty percent of women will suffer from Bacterial cystitis once in their lifetime. One third of patients having the symptoms of cystitis suffer from upper urinary tract infection.
The symptoms of chronic cystitis with sterile urine without Pyuria may represent intestinal cystitis. Dysuria can be the compliant of women with vaginitis and urethritis. Thus the analytical approach is essential to diagnose the exact cause of Dysuria.
What is the difference between pyuria and anuria?
Anuria is the condition where there is almost complete absence of urine production or the output of urine is less than 100 ml per day. Anuria is the advanced stage of oliguria.
Causes of Anuria
- Prerenal– It refers to the problems of the structures, before the kidneys i.e. blood vessels supplying the kidneys. It includes sepsis, cardiogenic shock, hypoxia and hypovolemia. Hypovolemia may result due to inadequate fluid intake or excessive loss of fluid from the body. Blood loss due to injury can also result in Hypovolemia. Cardiogenic shock due to MI can result in poorly oxygenated blood and low cardiac output.
- Renal– It occurs due the problem in the kidney. A low output of urine is due to the glomerulus and renal tubules.
- Postrenal– It is the problem that arises due to obstruction of urine flow. Calculus disease is the most common reason of this.
Pyuria is the presence of leucocytes or white blood cells or pus in the urine. It is associated with UTI (Urinary tract infection) due to bacteria.
What is the difference between pyuria and oliguria?
Oliguria– When the output of urine is less than 500 mm in a day; the condition is termed as Oilguria. The symptoms are sepsis, diarrhea, enlarged prostate, fever, dizziness and problems of the heart. The causes are Cholera, bacterial infection that is characterized by dehydration. Acute Glomerulonephritis, Hypovolemia, chronic renal failure and acute polynephritis are the other causes of Oliguria.
Pyuria is the condition of excess of white blood cells in the urine. The urine becomes cloudy and foul smelling due to infection. The Pyuria can be without symptoms if there is no infection. If it is infected with bacteria and virus, the symptoms are foul smelling urine, discomfort or irritation in passing the urine and cloudy urine. The person can also suffer from fever and nausea. It is just a laboratory finding and not a disease.
Pyuria treatment
After the diagnostic tests and other tests of urine analysis, your doctor will decide the course of treatment. Antibiotics are the main source of treating bacterial and viral infection in the urinary tract. Medicines that are given for treatment are –
- Ampicillin
- Norflaxacin,
- Ciprofloxacin,
- Minocycline,
- Amoxicillin
- Doxycycline
- Livofloaxacin
- Erythromycin
If the person is having Pyuria due to sexually transmitted disease like gonorrhea or Chlamydia, then antibiotics are prescribed according to it. For tuberculosis bacterial infection, recommended dose of antibiotic are very important. The method of treating Pyuria varies according to the root cause of the disease. There will be the separate course of treatment for kidney stones and UTI that causes Pyuria.
Which antibiotic is the best for pyuria treatment?
Pyuria is a clinical manifestation. The treatment with antibiotic will depend on the underlying cause of Pyuria. The physical examination and the medical history of the patient are necessary to study before choosing any treatment schedule. Asymptomatic Pyuria does not require the treatment.
Treatment of UTI due to Enterococci- Amoxicillin or Ampicillin is the best antibiotic for the treatment.
Treatment of UTI due to extended spectrum betalactamase producing organisms- Meropenem and ertapenem can be widely used to treat most of the infections caused by the organism.