Contents
- What is Tessalon Perles?
- Tessalon Perles active ingredient IUPAC name, molecular formula, weight, strucuture and drug class
- Tessalon Perles identification
- What is the mechanism of action of Tessalon Perles?
- What are the indications of Tessalon Perles?
- Tessalon Perles pharmacokinetics
- Use of Tessalon Perles in pregnancy and breastfeeding
- What are the possible side effects of using Tessalon Perles?
- What is the recommended dosage for Tessalon Perles?
- How should I take Tessalon Perles?
- What if I overdose Tessalon Perles?
- What is the treatment for overdosage of Tessalon Perles?
- What are precautions needed with Tessalon Perles?
- What drugs interact with Tessalon Perles?
- Can I take Tessalon Perles with tizanidine?
- How to store Tessalon Perles?
- What happens if I miss a dose of Tessalon Perles?
What is Tessalon Perles?
Tessalon Perles is the brand name for the drug benzonatate. This is a prescription only drug which was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1958.
Tessalon Perles is a non-narcotic medicine which is given orally for the purpose of suppressing and relieving cough.
It mainly works by numbing the respiratory tract including the throat and lungs decreasing the frequency of cough reflex. As this medicine is a non-narcotic, it has not been responsible for drug abuse.
Tessalon Perles is only available for oral route of administration and is manufactured as soft gelatin capsules.
Due to the potential harmful effects, this medicine is no longer available in the US but its manufacture is still continued in other areas of the world. Therapeutically this drug is classified as an anti-tussive.
Tessalon Perles active ingredient IUPAC name, molecular formula, weight, strucuture and drug class
Benzonatate description:
Benzonatate is a non-narcotic oral antitussive (cough suppressant) drug which works by anesthetizing the tissues of the lungs and pleura responsible for the cough reflex.
It is chemically related to other ester anesthetics such as procaine. It has an anesthetic (numbing) action similar to that of benzocaine and “numbs” the stretch sensors in the lungs.
It is the stretching of these sensors with breathing that causes the cough.
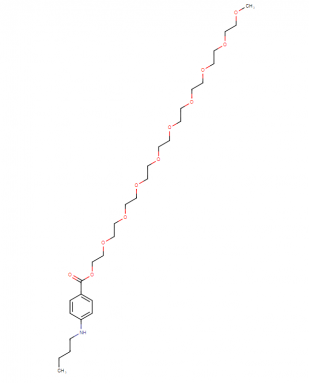
IUPAC name: 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23, 26-nonaoxaoctacosan-28-yl p-(butylamino) benzoate
Chemical Formula: C30H53NO11
Molecular weight: 603.7 g/mol
Molecular structure:
Tessalon Perles identification
Every single capsule of Tessalon Perles contains 100 mg or 200 mg of benzonatate. In addition to the active ingredient, it contains the following excipients: gelatin, glycerin, methylparaben, propylparaben, purified water and noncrystallating sorbitol solution.
The 200 mg capsule of Tessalon Perles is printed with a black pharmaceutical ink which consists of the following ingredients: purified water, propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, ferrosoferric oxide, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, polyvinyl acetate phthalate, ammonium hydroxide and ethanol.
What is the mechanism of action of Tessalon Perles?
Tessalon Perles, the generic for which is benzonatate, exerts its action by acting peripherally and numbing the stretch receptors of vagal afferent fibres which are present in the alveoli of the lungs, pleura, and the bronchi.
Benzonatate may also exert its action centrally by blocking the conduction of the cough reflex at the level of medulla at a point where the vagal afferent impulse is passed on to the nerve impulses.
In patients who are suffering from asthma, when Tessalon Perles is given to them intravenously, there is an increase minute ventilation, rate, and depth of the respiration.
On the other hand, it did not affect the overall lung volume and expiratory flow rate.
Orally, benzonatate at normal dosage had not inhibited the respiratory center but when benzonatate is given in overdose, clinical outcomes were observed which were similar to those that were obtained after using ester-type anesthetics.
Besides the effect on respiratory center, initially, stimulation of central nervous system was seen which was followed by CNS depression and compensatory respiration.
When benzonatate is applied topically, it works in a similar way like other local anesthetics. The local application of the drug is done in the oropharyngeal area mostly before intubation or endoscopy.
This drug block inhibits the generation and transmission of nerve impulses at the point of the cell membrane.
Usually, it binds directly to the intercellular part of the voltage-gated sodium channels. This, in turn, diminishes the rate of membrane depolarization ultimately increasing the threshold for electrical excitability.
The blockage influences all the nerve fibres in the following order: autonomic, sensory and motor. A rapid onset of action of about 1 – 2 minutes is observed as soon as the drug is directly applied on the oropharynx region.
What are the indications of Tessalon Perles?
This drug is recommended for the symptomatic treatment of relieving cough. This usually affects locally in the oral cavity in adults.
This topical application is done by the discharging the drug from liquid filled capsules and numbing the oropharyngeal region for conscious intubation.
It is used in the treatment of a cough associated with common cold and other breathing problems such as pneumonia, emphysema, asthma, and bronchitis.
Tessalon Perles pharmacokinetics
Tessalon Perles is an orally administered drug which has an onset of action of about 20 to 25 minutes and its clinical effect of anti-tussive lasts for approximately 3 – 7 hours.
It is believed that benzonatate shows a metabolism that is similar to other ester-type local anesthetics. It is hydrolyzed by plasma esterases to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA).
However, the data for other pharmacokinetic parameters such as absorption, distribution, and excretion is still under consideration.
Use of Tessalon Perles in pregnancy and breastfeeding
Pregnancy:
This drug is classified under pregnancy category C. it is recommended that while prescribing Tessalon Perles, the benefits should prevail over the possible side effects for both the mother and fetus.
As the animal studies are still not conducted for the evaluation of carcinogenic or mutagenic so it should be prescribed to pregnant women when a clear indication is present and no other substitute can be administered.
The effects of this medicine in labor and obstetric delivery are still unknown. As benzonatate, the generic of Tessalon Perles is chemically related to the majority of anesthetic agents, it is assumed that it will also show similar absorption pattern.
These anesthetics can easily cross the placental barrier and has been responsible for causing fluctuating degree of toxicity to mother, fetus or even neonates when it has been used paracervically or via pudenal block at the time of labor and delivery.
Certain anesthetics, when administered at the time of labor, can cause the muscle strength and tone in newborns to weaken especially for the first two days after birth.
Breastfeeding:
Tessalon Perles should be used with great care in nursing mothers as it has yet not been fully demonstrated if the drug is excreted in breast milk.
It is advised to prefer another anti-tussive agent especially when the premature infant or newborn is being fed.
In case the breastfeeding infant suffers from an unwanted effect which is due to the drug that has been ingested by mother, healthcare providers are responsible for reporting it to the U.S. FDA.
What are the possible side effects of using Tessalon Perles?
Some of the most common side effects that take place on using this drug are as follows:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Drowsiness
- Nausea, vomiting, and constipation
- Skin rash
- Mild itching
More serious effects that can occur on the administration of this medicine are as follows. On the appearance of any of these symptoms, the patient should be immediately taken to the emergency and get a treatment.
- Numbness or pain in the chest
- A choking feeling
- Confusion
- Hallucination
- Feeling like you might pass out
- Allergic reaction: skin rashes, hives, and difficulty in breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat.
Some of the rarely occurring side effects are listed as below. These occur only in 0.1% of the population who uses this medicine.
- Burning sensation in the eyes
- Stuffy nose
- Narrowing of the airway tract
- Cardiovascular collapse
This is not a complete list of possible side effects and there is a chance that others may also occur which should be immediately reported to the nearby pharmacist or a doctor.
What is the recommended dosage for Tessalon Perles?
For each condition, the dosage of Tessalon Perles varies. It is as below:
- In the symptomatic treatment of cough
(For children above 10 years, adolescents, and adults) Recommended normal dosage is 100 mg, 150 mg or 200 mg PO 3 times in a day. Maximum dosage per day should not exceed 600 mg PO.
- In the treatment of intractable hiccups
(For children above 10 years, adolescents, and adults) a normal dosage of 100 mg PO should be given as a single dose. However, when needed it can be repeated after 4-hour interval but the maximum dosage should not be greater than 600 mg/day
(Tessalon Perles should only be prescribed when these intractable hiccups are unresponsive to standard therapies)
- For topical anesthesia
This is an off-label indication. A single dose of 200 mg can be topically applied on the oropharyngeal region along with 4% lidocaine translaryngeally.
(This route should only be applied by trained healthcare professionals)
How should I take Tessalon Perles?
Take exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Do not take in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended. Follow the directions on your prescription label.
Always ask a doctor before giving a cough medicine to a child. Death can occur from the misuse of cough and cold medicines in very young children.
Take each dose with a full glass of water.
Never suck or chew on a Tessalon Perles capsule. Swallow the pill whole. Sucking or chewing the capsule may cause your mouth and throat to feel numb or cause other serious side effects.
Store at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.
What if I overdose Tessalon Perles?
Drugs have been reported to cause death when unintentional or intentional intake in excess amounts is done. As Tessalon Perles is chemically related to tetracaine or other topical anesthetics, it shows a rapid absorption.
Signs and symptoms of benzonatate overdose appear within 15 – 20 minutes after ingestion.
In case the capsules are chewed or allowed to dissolve in the mouth, oropharyngeal numbness will quickly develop and leading to choking or airway conciliation.
Moreover, CNS stimulation occurs which involves restlessness and tremors and ultimately advances to clonic convulsions and intense CNS depression.
It has been reported that within 1 hour of ingestion of high dose of Tessalon Perles, cerebral edema, coma, convulsions and cardiac arrest occurs which leads to death.
What is the treatment for overdosage of Tessalon Perles?
For the treatment of benzonatate overdose, it is recommended to evacuate gastric contents and give an abundant amount of activated charcoal slurry.
Even in those patients who are conscious, the coughing reflex is so low that it is necessary to give protection against aspiration of gastric contents and other orally administered materials.
For the symptomatic treatment of convulsions, short-acting barbiturates are given to the patient via intravenous route and then gradually reduced to the lowest effective dosage.
For treating respiratory or cardiovascular depression, intense support should be a vital feature of the treatment. It is important to know that in such a situation CNS stimulants should never be administered.
What are precautions needed with Tessalon Perles?
Tessalon Perles is a prescription drug which was approved by FDA but still, sufficient data on safety and efficacy profile is still to be established. Certain precautionary measures are taken while using this medicine, which is listed as below.
- Neonates, infants, and children
According to FDA, Tessalon Perles can be given to children who are 10 years old or above but with great caution and close monitoring. For those who are below 10 years, safety profile isn’t yet recognized.
Unintentional ingestion of Tessalon Perles liquid capsule posses a considerable potential for overdose or poisoning and is due to the possible candy-like appearance.
Death has been reported in pediatric patients within 1 hour of ingestion of these capsules. In addition, the benzonatate capsule could represent a choking danger to young children.
In infants and children who are below 10 years of age, overdosage occurs from the unintentional ingestion of one or more than one capsules.
- Geriatric patients
Elderly patients taking Tessalon Perles are usually able to swallow the capsules as prescribed by the doctor. An unintended release of the capsule contents in the mouth can produce a temporary local anesthesia in the oral mucosa and cause choking.
Along with this, other serious side effects can also occur. As geriatric patients usually have weakened muscles so they usually suffer from dysphagia.
Thus, those who are suffering from dysphagia, they should not use Tessalon Perles. This medicine should not be used for more than 14 consecutive days.
- Ester local-anesthetic hypersensitivity
Benzonatate is chemically similar to tetracaine and other ester-type local anesthetics. Tessalon Perles is contraindicated in patients who have a previous hypersensitivity history with benzonatate or have shown hypersensitivity to any of the local anesthetic agents.
Severe allergic reactions have been reported on the administration of this drug in some patients. This is mostly due to the sucking or chewing of Tessalon Perles capsule which has caused bronchospasm or laryngospasm.
What drugs interact with Tessalon Perles?
Tessalon Perles has shown drug interactions with the following agents:
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors:
It has been observed that majority of the local anesthetics have been antagonizing the effects of cholinesterase inhibitors by blocking the neuronal conduction in skeletal muscles especially when local anesthetics are given in high doses.
It has also been reported that local anesthetics also have the ability to interfere with the release of acetylcholine.
This decreases the efficacy of cholinesterase inhibitors making it necessary to adjust the dose accordingly if it has to be given to patients concomitantly.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs):
A major drug interaction is reported when MAOIs and Tessalon Perles are coadministered to a patient. It is suggested to avoid using of Tessalon Perles to those patients who are already taking the MAOIs as these patients are at a greater risk of developing hypotension and CNS related effects.
Such a patient should be closely monitored for additive effects including low blood pressure, dizziness, sedation, mental confusion and other unwanted effects.
If a high dose of MAOIs is being used, the patient is at a high risk of developing cerebral edema and ultimately coma.
Can I take Tessalon Perles with tizanidine?
The sedative effect of tizanidine may be potentiated by concomitant use of other agents with central nervous system (CNS) depressant effects.
In addition, tizanidine and many of these agents (e.g., alcohol, anxiolytics, sedatives, hypnotics, antidepressants, antipsychotics, opioids, muscle relaxants) also can exhibit hypotensive effects, which may be additive during coadministration and may increase the risk of symptomatic hypotension and orthostasis, particularly during initiation of therapy or dose escalation.
Tizanidine itself is a central alpha-2 adrenergic agonist. Pharmacologic studies have found tizanidine to possess between 1/10 to 1/50 of the potency of clonidine, a structurally similar agent, in lowering blood pressure.
In a single-dose study where blood pressure was monitored closely after dosing, two-thirds of patients treated with an 8 mg dose had a 20% reduction in either the diastolic or systolic blood pressure.
The reduction was seen within 1 hour after dosing, peaked 2 to 3 hours after dosing, and was associated at times with bradycardia, orthostatic hypotension, lightheadedness, dizziness, and rarely, syncope.
The hypotensive effect of tizanidine is dose-related and has been measured following single doses of 2 mg or more.
How to store Tessalon Perles?
Tessalon Perles are liquid-filled soft gelatin capsules which are light yellow in color. They have special storage conditions allowing the drug to remain stable for the specified shelf life.
- It should be dispensed in a tight, light-resistant container reducing its exposure to sunlight and humidity.
- The temperature at which it is stored should be in between 20°C to 25°C.
What happens if I miss a dose of Tessalon Perles?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.