Contents
- What is losartan?
- What is losartan molecular formula and weight?
- Losartan drug class
- How does losartan work in the body?
- Losartan brand names
- What is FDA approved indications for losartan?
- What is losartan used for?
- How to use losartan?
- Is losartan also a water pill?
- Is losartan potassium a blood thinner?
- Is losartan an ACE inhibitor?
- Losartan dosage for hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy
- Losartan dosage forms and strengths
- Losartan dosage
- Losartan side effects
- How to take losartan? Should I take losartan at morning or night? Can I take losartan after I eat?
- Can diabetics take losartan?
- Do I have to take potassium supplements while I am on losartan therapy?
- Is losartan addictive?
- Can I abrupt losartan therapy suddenly? Can losartan cause withdrawal effects?
- Precautions and warnings during losartan use
- How long does losartan take to work?
- Losartan during pregnancy
- Losartan during breastfeeding
- Does losartan cause a dry cough?
- Can patients with renal disease take losartan safely?
- Can patients with liver disease take losartan safely?
- How are losartan and Hyperkalemia related?
- Does Losartan cause Hypotension?
- Can Losartan Cause Weight Gain?
- Can I take losartan and Advil together?
- Can I take losartan and Tylenol together?
- Can geriatric patients use losartan safely?
- Losartan overdosage
- What happens if a dose is missed?
- What to do in case of an overdose of losartan?
- Losartan absorption, metabolism, and elimination
- Can I drink alcohol while taking losartan?
- Difference between losartan and ACEI drugs
- Difference between losartan and Amlodipine
- What is Losartan Potassium USP?
- What is losartan HCTZ?
- Can losartan cause dizziness?
- Can losartan cause dehydration?
- Can I take losartan and aspirin together?
- Can I take losartan and Viagra together?
- Can I take losartan and lisinopril together?
- Can I take losartan and atenolol together?
- Can I take losartan and amlodipine together?
- Can patients with angioedema take losartan?
- Can patients with congestive heart failure take losartan?
- Can I take losartan with grapefruit juice?
- Can I take losartan before surgery?
What is losartan?
Cozaar or losartan is a member of the drug family termed as the angiotensin II receptor antagonists. It prevents the narrowing of the blood vessels and lowers the pressure of blood, further improving the blood flow.
It is prescribed for the treatment of hypertension. Losartan is also used to lower stroke risk in individuals suffering from heart diseases. Additionally, it slows down the long – term kidney damage in type 2 diabetes patients who suffer from high BP as well. It may also be used for other purposes, which have not been mentioned in this guide, as per the prescription of a medical practitioner.
You must inform your doctor about any medicines that have been previously prescribed to you and you’re still using along with any medicinal drugs or combinations you might begin or terminate using during your losartan treatment, especially if:
- The medicine belongs to the category of ‘water pills’ or diuretics
- Contains lithium
- Is another medication for blood pressure
- Aspirin or any other non – steroidal anti – inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Motrin, Advil (ibuprofen); Aleve (naproxen), diclofenac, meloxicam, indomethacin, celecoxib, and others.
This is not an exhaustive list comprising of all drugs to be careful of. There may be others which can have drug interactions with losartan, including over the counter medicines and prescription drugs, vitamins or herbal products. We have made an attempt to cover important interactions.
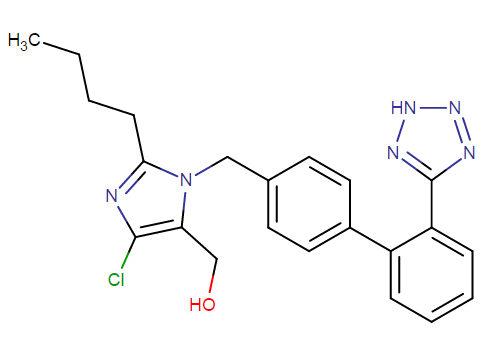
What is losartan molecular formula and weight?
Losartan potassium tablets USP has the molecular formula C22H22ClKN6O. It has the following structural formula
It is free flowing crystalline powder, with a white to off – white colour. The molecular weight of a single unit of the compound is 461.01 mass units. It possesses water as well as alcohol solubility. It is also soluble in certain organic solvents, which are commonly available, like methyl ethyl ketone and acetonitrile.
The formation of the active metabolite of losartan results from the oxidation of the 5–hydroxymethyl group on the imidazole ring.
The melting point lies between 183.5 – 184.5 degrees Celsius. It produces some hazardous products upon decomposition, like nitrogen oxides (NOx), potassium oxides, hydrogen chloride gas and carbon oxides.
Losartan drug class
This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as biphenyls and derivatives. These are organic compounds containing to benzene rings linked together by a C-C bond.
From the pharmacological standpoint, Losartan belongs to Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists. These block the angiotensin II receptor, which acts on the AT 1 receptor subtype. Chemically described as 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[-p-(o-1 H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)-benzyl]-imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt, losartan potassium is a non – peptide molecule.
It may be utilized as a first line treatment agent for uncomplicated hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy and isolated systolic hypertension. It may also be utilized as a first line progression delay agent for diabetic nephropathy.
Losartan may be utilized as the second line treatment agent for systolic dysfunction, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, and myocardial infarction in individuals intolerant to ACE inhibitors. Losartan has also been associated with rare instances of acute liver injury and linked with lowering in rates of elevation of transient serum aminotransferase.
How does losartan work in the body?
Angiotensin II is formed after an angiotensin converting enzyme – catalyzed reaction (ACE, kinase II), from angiotensin I. It is a potent vasoconstrictor, the primary hormone with vasoactive properties of the rennin-angiotensin system. It is also a significant component in hypertension pathophysiology. It stimulates the secretion of aldosterone, by the adrenal cortex.
The vasoconstrictors as well as the aldosterone – secreting effects of angiotensin II, are blocked by losartan and its principal active metabolite. It selectively blocks the binding of angiotensin II to the AT 1 receptor. The AT 2 receptor is also found in some tissues but has not been proven to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis.
Any partial agonist activity is not exhibited at the AT 1 receptor by either the compound losartan or its principal active metabolite. Both is these have a higher affinity towards the AT 1 receptor, compared to the AT 2 receptor (about 100-fold).
Losartan is indicated to be a reversible, competitive inhibitor of the AT 1 receptor, as indicated by in vitro studies. Its active metabolite is about ten to forty times more potent by weight, compared to losartan and a reversible, non – competitive inhibitor of the AT 1 receptor.
ACE Kinase 2 is inhibited by neither losartan nor its active metabolite. They do not even bind to or block the ion channels or the hormone receptors which are important for cardiovascular regulation.
The pressor effect of angiotensin II and angiotensin I infusions is inhibited by losartan. A 100 mg dose of the drug inhibits up to 85% of the pressor effect at peak with 25 to 40% of the inhibition persisting for up to 24 hours. A doubling to tripling in the activity of plasma renin is caused by the removal of negative feedback of angiotensin II.
The resulting rise in angiotensin II concentration in plasma is also an effect in hypersensitive patients. The response to bradykinin is not affected by losartan. On the other hand, ACE inhibitors are known to increase the response to bradykinin. The plasma concentration of Aldosterone falls after administration of losartan. Despite this effect on the secretion of aldosterone, the only slight effect on serum potassium is observed.
Losartan brand names
Losartan Systemic
Brand Name: Cozaar
Used in treatment of –
- High Blood Pressure
- Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Alport Syndrome
Multi-ingredient Medication: Hydrochlorothiazide/ Losartan Systemic
Brand Name: Hyzaar
Used in treatment of –
- High Blood Pressure
What is FDA approved indications for losartan?
FDA approval for hypertension treatment has been obtained by Losartan. It can be used alone as well as with other antihypertensives, in combination, including diuretics. In patients suffering from hypertension as well as LVH (left ventricular hypertrophy), the risk of stroke is reduced by losartan.
The third indication of losartan is provided for the patients of diabetic nephropathy with type II diabetes, having an elevated serum proteinuria and creatinine. It reduces the occurrence of end – stage renal disease or doubling of serum creatinine. The benefit of the drug has additionally been tested in multiple other settings.
What is losartan used for?
Losartan has the following uses:
- Treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Protects from kidney damage caused by diabetes
- Decreases risk of stroke in patients with enlarged heart and high blood pressure
- Prevents heart attacks
- Relaxes blood vessels for easy flow of blood
How to use losartan?
If available with the pharmacist, you must read the patient information leaflet before losartan consumption. You must consult the pharmacist or the doctor, in the case of any queries.
Take the medicine by mouth (oral administration), as prescribed and directed by the doctor. While suing the liquid form, shake well before use. The dose must be measured carefully using a special spoon. Avoid use of the household spoon as that may not be the correct dose.
The medication must be used regularly to get the benefits. You must put reminders to consume at the same time every day. Even when feeling better or well, the medication must be continued. If the condition does not improve or worsens, consult the doctor immediately.
Is losartan also a water pill?
Hydrochlorothiazide (Hctz) is a water pill (or thiazide diuretic). It helps in preventing the body from excessive salt absorption, which can lead to retention of fluid.
Losartan potassium, on the other hand, is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. It prevents the narrowing of the blood vessels, further lowering the blood pressure and improving the flow of blood.
Hctz and losartan can also be used in combination for the treatment of hypertension (high BP). Stroke risk can be lowered in people suffering from heart disease.
Is losartan potassium a blood thinner?
No, losartan potassium is not a blood thinner. As per the classification which is given by FDA, losartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Its common use pertains to the treatment of high BP and some listed cardiac conditions.
Is losartan an ACE inhibitor?
Cozaar is not an ACE inhibitor, though it may display certain similar properties. Instead, it is an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). The working of ACE inhibitors and ARBs follows in the same pathway for controlling blood pressure. ARB, though, have a slightly specific mode of action.
Losartan dosage for hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy
Adult Hypertension
Usually, the initial dose of losartan potassium is 50mg, once a day. The same can be increased to a dose of 100mg once a day if needed for controlling blood pressure. Patients, who have possible intravascular depletion, may be recommended a dose of 25mg per day. (E.g. those patients, who are undergoing diuretic therapy)
Hypersensitive Patients with LVH (Left Ventricular Hypertrophy)
Usually, the initial dose of losartan potassium is 50mg, once a day. Hctz (Hydrochlorothiazide) shall be added at a dose of 12.5 mg once a day or the losartan dose must be increased to 100mg once a day followed by increase in Hctz dose to 25mg once a day, based on the response of blood pressure
Losartan dosage forms and strengths
- Losartan Potassium Tablets USP 25mg have ‘A’ engraved on one side of the oval tablet film coating and 25 on the other side
- Losartan Potassium Tablets USP 50mg have ‘A50’ engraved on one side of the oval tablet film coating, and a breakline on the other side
- Losartan Potassium Tablets USP 100mg have ‘A’ engraved on one side of the oval tablet film coating and are plain on the other side
Losartan dosage
Usual Adult Dosage for Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy or Hypertension
Initial Dose – oral administration, 50mg, once a day
Maintenance Dosage – oral administration, 25 to 100mg per day, divided into 1 or 2 doses
If the hypersensitive patient suffers from type II diabetic nephropathy or left ventricular hypertrophy, there is a requirement of titration for patients, from the initial dose. The dosage can be increased to 100mg once a day.
Usual Paediatric Dose for Hypertension
For children 6 years or older, the initial dose needs to be oral administration of 0.7mg per kg, once a day, not exceeding a total dose of 50 mg per day.
Patients suffering possible Intravascular Volume Depletion
Initial Dose – oral administration, 25mg once a day
Losartan side effects
Common Side Effects:
- Anxiety
- Stomach or abdominal pain
- Blurred vision
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Bladder pain
- Troubled breathing with exertion
- Slurred speech
- Shortness of breath
- Shakiness
- Seizures
- Pale skin
- Tingling or numbness in feet, hands or lips
- Nightmares
- Nausea or vomiting
- Side or lower back pain
- Irregular heartbeat
- Increased hunger
- Headache
- Frequent urge for urination
- Dizziness
- Burning, difficult or painful urination
- Difficulty in breathing
- Depression
- Cool skin
- Confusion
- Coma
- Cold sweat
- Chills
- Unusual bruising or bleeding
- Unusual weakness or tiredness
- Heaviness or weakness of legs
Rare side effects
- Weakness in feet, legs, hands and arms
- Sudden and severe weakness on one side of the body
- Awkwardness or unsteadiness
- Temporary blindness
- Puffiness or swelling of the face
- Sweating
- A sudden or severe headache
- Discomfort or pain in jaw, neck, back and arms
- Inability to speak
- Pounding, irregular, fast or racing pulse, or heartbeat
- Fainting
- Chest pain or discomfort
Side effects with incidence not known
- Light coloured stools
- Hive like, large swelling on sex organs, feet, legs, hands, throat, tongue, lips, eyelids, or face
- Itching
- Hive
- Difficulty with swallowing
- Dark urine
- Bleeding gums
- Black, tarry stools
- Yellow eyes and skin
- Stomach or upper right abdominal pain
- Skin rash
- Pinpoint red spots on skin
- Muscle stiffness or pain
- Muscle spasms or cramps
Certain side effects caused by losartan consumption might not call for medical attention. These side effects usually go away as the body adjusts to the medication. Medical practitioners and healthcare professionals might be able to suggest some methods and precautions for preventing or reducing some of these. Though, if they continue for a longer time period, consult the doctor.
How to take losartan? Should I take losartan at morning or night? Can I take losartan after I eat?
Losartan dosage must be taken exactly as per the doctor’s prescription. All directions must be clearly followed. The dose may be occasionally changed by the doctor to achieve the best results. You must not take it for a longer time or in larger/ smaller amounts than the recommendation. Losartan can be taken after eating food or empty stomach.
If you observe ongoing symptoms of nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea, or in case you are sweating more than the usual, you must immediately contact the doctor. Dehydration is common during the treatment period. This can further lead to serious electrolyte imbalance or severely low blood pressure.
Visit the doctor regularly, to keep a check on the blood pressure. The medicine needs to be stored at room temperature, away from light, heat, and moisture.
Can diabetics take losartan?
In case you are diabetic, losartan must not be taken along with any other medication containing aliskiren (Valturna, Tekamlo, Tekturna, and Amturnide).
In some rare, special case, a condition resulting in the breakdown of skeletal muscle tissue may be caused by losartan. This further leads to kidney failure.
Do I have to take potassium supplements while I am on losartan therapy?
Salt substitutes or potassium supplements must not be used while taking losartan unless prescribed by the doctor.
Is losartan addictive?
Instances of drug addiction have been noticed among individuals taking losartan, especially, in males. A study indicated the following results:
Gender of People having Drug Addiction by Losartan
- Females – 50%
- Males – 50%
Age of People having Drug Addiction by Losartan
- 0-1: 0.0%
- 2-9: 0.0%
- 10-19: 0.0%
- 20-29: 0.0%
- 30-39: 42.86%
- 40-49: 14.29%
- 50-59: 28.57%
- 60+: 14.29%
Top conditions involved in these individuals
- Bipolar disorder (15.38%)
- High Blood Cholesterol (15.38%)
- Schizophrenia (15.38%)
- Type II diabetes (15.38%)
- High blood pressure (30.77%)
Top drugs co-used by these individuals
- Amlopidine (15.38%)
- Invega Sustenna (15.38%)
- Lantus (15.38%)
- Lovaza (15.38%)
- Lisinopril (23.08%)
Top side effects for these individuals
- Slowed or stopped breathing (15.38%)
- Lactic acidosis (15.38%)
- Overdose (15.38%)
- Pain in limbs (15.38%)
- Cardiac arrest (30.77%)
Can I abrupt losartan therapy suddenly? Can losartan cause withdrawal effects?
Without consulting the doctor, so not stop taking your losartan medication. Sudden stopping can cause a quick increase in the blood pressure. This highly increases the risk of occurrence of a stroke or heart attack. You must ask the doctor before stopping. The doctor will slowly taper the dosage such that the drug use can be safely stopped.
The effect of the drug shows within a week but according to some studies, the maximal or peak effect has been observed between 3-6 weeks of treatment therapy. The effect of losartan has been shown to be maintained up to a year in long term, follow-up studies. Rebound effects seem to be non-apparent after abrupt withdrawal. In controlled trials, no change in the average heart rate was observed in losartan-treated patients.
Precautions and warnings during losartan use
- Losartan must not be consumed if you are allergic to the drug
- In case you’re suffering from diabetes, losartan must not be combined with medications consisting of aliskiren.
- Taking losartan with aliskiren must also be avoided in case you are a patient of any kidney disease.
- So ensure safety, inform the doctor about any liver disease, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance (like low potassium levels in the blood), congestive heart failure or kidney disease that you may have suffered or are suffering from.
- Dosage must be strictly followed as per the doctor’s instructions.
How long does losartan take to work?
The maximal or peak blood pressure lowering effect is usually observed within 3 to 6 weeks after the treatment therapy has begun.
Losartan during pregnancy
Losartan must not be used during pregnancy. Stop using and immediately inform the doctor about the pregnancy. Losartan acts directly on the RAS – renin-angiotensin system and can potentially cause injury or death to the unborn baby in the womb (developing foetus) if the medication is administered especially during the second and the third trimester of pregnancy. If you are on losartan treatment, use effective birth control.
Animal studies have revealed evidence of fetal and neonatal toxicity and mortality. In humans, use of drugs that act on the renin angiotensin system (RAS) during the second and third trimesters increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. There are no controlled data in human pregnancy
US FDA pregnancy category D: There is positive evidence of human fetal risk based on adverse reaction data from investigational or marketing experience or studies in humans, but potential benefits may warrant use of the drug in pregnant women despite potential risks.
AU TGA pregnancy category D: Drugs which have caused, are suspected to have caused or may be expected to cause, an increased incidence of human fetal malformations or irreversible damage. These drugs may also have adverse pharmacological effects.
Losartan during breastfeeding
It is yet, unknown whether losartan is passed in the human breast milk. Additionally, it isn’t known whether it will effect or harm the nursing baby in any way. Hence, breastfeeding while using losartan is not recommended.
Significant levels of losartan, as well as its active metabolite, have been shown to be passed into rat milk. Due to the lack of knowledge and potential adverse effects on the nursing infant, either nursing or the administration of the drug needs to be discontinued. The decision depends on how important the drug treatment therapy is for the mother.
Does losartan cause a dry cough?
With an incidence of a few percent in a study, persistent dry cough has been shown to be associated with the use of ACE inhibitors. The incidence of a cough is shown in the table below.
| STUDY 1* | HCTZ | LOSARTAN | LISINOPRIL |
| Cough | 25% | 17% | 69% |
| STUDY 2† | PLACEBO | LOSARTAN | LISINOPRIL |
| Cough | 35% | 29% | 62% |
| * Demographics = (89% Caucasian, 64% female) † Demographics = (90% Caucasian, 51% female) |
|||
The study also demonstrates the association of a cough with losartan treatment therapy. In post-marketing experiences and reports, cases of a cough have also been reported with the use of losartan, including positive re-challenges.
Can patients with renal disease take losartan safely?
After oral administration, AUCs and plasma concentration of losartan plus its active metabolite witness an increase of 50-90% in the individuals having mild (50 to 74 mL/ min creatinine clearance) or moderate (30 to 49 mL/ min creatinine clearance) renal insufficiency.
In a study, reduction in renal clearance for both losartan and its active metabolite was observed up to 55 to 85%, in individuals with moderate to mild renal insufficiency. Neither the active metabolite nor losartan can be removed by hemodialysis.
RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS
Patients of bilateral or single kidney renal artery stenosis may experience renal perfusion reduced to critically low levels, due to angiotensin II receptor antagonists. There has been reported increase in blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine due to ACE inhibitors. This class of drugs is also known to have an inhibiting effect on renin – angiotensin – aldosterone system.
There is lack of supportive data for long term use of AR antagonists in patients with renal artery stenosis, the anticipated effect is on similar lines. At least for the first few weeks of the treatment therapy, there is a need to monitor renal function closely.
RENAL IMPAIRMENT
Drugs that have an inhibiting effect on renin – angiotensin system and diuretics can cause certain changes in the renal function, which also include renal failure. Patients suffering from volume depletion, severe congestive heart failure, chronic kidney disease or renal artery sclerosis have a renal function depending partly on the activity of renin – angiotensin system.
They are hence at high risk of development of acute renal failure. If a clinically significant disease develops in the renal function, with these agents, either the therapy should be withheld or discontinued.
Can patients with liver disease take losartan safely?
Post oral administration of losartan in individuals suffering from moderate or mild alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, losartan, and active metabolite plasma concentration were 1.7 and 5 times respectively in young males. A 50% decrease in the total plasma clearance of the drug has been observed in patients with hepatic insufficiency. Oral bioavailability was shown to be doubled.
In the liver, conversion of losartan to an active carboxylic acid metabolite occurs, apart from the various inactive metabolites. The kidney eliminates 35% the parent drug as well as metabolites, whereas, biliary excretion is responsible for 60% elimination. In patients suffering from renal impairment, unless there is volume depletion, the dosage need not be adjusted.
In the later case, the therapy is monitored under strict medical supervision. Though, patients of cirrhosis have been reported to have significant increase in concentration of drug and metabolites in the plasma. Hence, losartan therapy must have a cautious initiation in these patients with about 50% reduced dosage if the liver function is impaired.
Drugs like losartan, classified as ARBs can be a causative agent for hyperkalemia. Parallel use of these drugs can lead to increased potassium levels which further heighten the risk of hyperkalemia. Serum potassium hence must be periodically monitored.
Does Losartan cause Hypotension?
Symptomatic hypotension can be caused due to AR antagonists in patients having an activated renin – angiotensin system. These include sodium as well as volume depleted patients. Administration of therapy with AR antagonists in these patients must be highly cautious.
Also, careful administration procedures need to be followed for individuals predisposed to hyponatremic or hypovolemic states (for example, patients on diuretic therapy and especially if recently instituted or used doses have been high; renal dialysis patients; individuals on dietary salt restrictions). Sodium and/ or volume depletion need to undergo correction before the therapy initiation with AR antagonists.
It must be noted that the patient needs to be thermodynamically stable. Preferably, AR antagonist therapy must be initiated by patients at high risk for excessive hypotension, only under close medical supervision. The dose must be low. Close follow up for the initial two weeks of the therapy as well as whenever the diuretic or the losartan dosage is increased, is required.
Can Losartan Cause Weight Gain?
Weight gain is a side effect of losartan treatment, which is rare and varies from individual to individual.
Can I take losartan and Advil together?
A decrease in the effect of losartan can result from the combined administration of losartan with Advil. You must consult the doctor about the same.
Can I take losartan and Tylenol together?
Moderate interaction has been traced between Tylenol and losartan. Considering another combination is hence, a wise idea. Before taking these medications together, consider consulting a medical practitioner.
Can geriatric patients use losartan safely?
In clinical studies for hypertension, of the total number of patients administered with losartan potassium, 391 patients (about 19%) were either 65 in age or older. 37 patients of the total (around 2%) were 75 years or older. Though any overall differences in either safety or the effectiveness of the drug were not observed, greater sensitivity in older individuals cannot be completely ruled out.
Losartan overdosage
Significant lethality has been observed in studies on rat and mice after oral administration of 2000 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg of losartan, respectively. These are about 170 and 44 times the maximum recommended dosage for humans on mg/mass basis.
As far as an overdose in humans is concerned, only limited data is available. The potential manifestations of human losartan overdosage can be tachycardia and hypotension; bradycardia occurring from vagal (parasympathetic) stimulation. In cases of occurrence of symptomatic hypotension, there is a need for an institution of supportive treatment.
What happens if a dose is missed?
The missed dose must be taken as soon as the individual remembers. If the time is almost for the next scheduled dose, the missed dose can be skipped. Extra medicine must not be taken to compensate for the missed dose.
What to do in case of an overdose of losartan?
Immediately seek medical attention in case of overdose.
Losartan absorption, metabolism, and elimination
ABSORPTION
Post oral administration, sufficient absorption of losartan is observed and it undergoes substantial first-pass metabolism. There is approximately 33% systemic bioavailability of the drug. Within 1 hour and 3-4 hours respectively, mean peak concentrations of losartan, as well as its active metabolite, are reached.
While the maximum concentrations of the two, in the plasma, are almost equal, the area under the curve (AUC) of the metabolite is four times greater than that of losartan. Meals slow down losartan absorption, and also reduce the Cmax; only minor effects on the AUC of losartan and the active metabolite are observed (approximately 10% decrease).
METABOLISM
Losartan is considered to be an agent, which is orally active and undergoes considerable first-pass metabolism by enzymes cytochrome P450. In part, it undergoes conversion, into an active carboxylic acid metabolite. The active metabolite is mostly responsible for the angiotensin II receptor antagonism which follows the treatment therapy of losartan.
Around 14% of the dose of losartan, which is administered orally, undergoes conversion into an active metabolite. Apart from the active metabolite, a number of inactive metabolites are also formed. It has been indicated by in vitro studies that cytochrome P450 C29 and 3A4 have involvement in the biotransformation of losartan to the active/ inactive metabolites.
ELIMINATION
The total clearance of losartan and its active metabolite from the plasma is approximately 600 mL/min and 50 mL/min, respectively. Renal clearance of the two has been observed to be 75 mL/min and 25 mL/ min respectively. 2 hours is the approximate terminal half-life of losartan, while that of the metabolite is about six to nine hours.
Following single doses of losartan oral administration, around 4% of the dose is excreted without any changes or interactions via the urine. Almost 6% excretion in the urine is the active metabolite. Elimination of losartan, as well as the metabolites, is contributed by the biliary excretion. Following the oral administration of 14C labeled losartan, about 35% recovery of the radioactivity is in the urine and 60% is faecal.
After an intravenous dosage administration of 14C labeled losartan, about 45% recovery of radioactivity is in the urine and 50% is faecal. Neither of the two, losartan or the metabolite exhibit plasma accumulation on repetition of single daily dose.
Can I drink alcohol while taking losartan?
Alcohol consumption can further reduce the blood pressure and hence cause and increase in the occurrence of side effects of losartan.
Difference between losartan and ACEI drugs
Two of the various different types of blood pressure pills are ACEIs and ARBs.
- Both these classes of pills lower the blood pressure effectively
- There are rare instances of occurrence of serious problems. A major difference is the higher chance of occurrence of a dry cough due to ACEIs, compared to ARBs.
- They do not seem to affect blood sugar levels or the cholesterol levels
- There are certain ACEIs available as generic drugs, which reduces the costs
- Brand name ARBs and ACEIs have a similar price label
- Both can cause side effects like dizziness, cough, headache
- Due to more occurrence of a cough by ACEI, about 8% people stop taking the drug and change to other drugs
- 3% people quit ARB due to side effects
- If we compare serious risks, people rarely get the drug reaction angioedema. About 0.1% people only suffer from angioedema due to ARBs and ACEIs. It causes swelling in lips and tongue.
Difference between losartan and Amlodipine
Cozaar or losartan is an ARB (angiotensin receptor blocker). It causes the blocking of the chemical causing the tightening of blood vessels. Hence, it results in the relaxing of blood vessels and leads to lowering of the blood pressure. This also allows greater and easier passage of blood as well as oxygen to the heart and other body organs. On the other hand, Amlodipine (Norvasc) is a calcium channel blocker.
What is Losartan Potassium USP?
Losartan potassium is commercially available as oral administration tablets, which contain 25mg, 50 mg or 100mg of losartan potassium USP drug. The active ingredients in the same are pre-gelatinized starch, microcrystalline cellulose, opadry white (titanium dioxide, hypromellose, hydroxypropyl cellulose), magnesium stearate and lactose monohydrate.
Potassium is present in the following amounts, in 25mg, 50mg and 100mg losartan potassium USP, respectively – 2.12 mg (or 0.054 mEq), 4.24 mg (or 0.108 mEq) or 8.48 mg (or 0.216 mEq).
What is losartan HCTZ?
Losartan Potassium-Hydrochlorothiazide is also known as Hyzaar or HCTZ. It is a combination of a water pill (thiazide diuretic) and angiotensin II receptor antagonist, which is used for the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure). Hyzaar is also advised for lowering the risk of stroke in some people who are suffering from a heart disease.
Can losartan cause dizziness?
Dizziness is a side effect of losartan. To avoid feeling dizzy, avoid getting up too fast from a lying or sitting position. Make sure you prevent a fall by getting up slow and steady.
Can losartan cause dehydration?
Losartan doses can be consumed with or without food. If you are suffering from ongoing diarrhoea or vomiting, or experience sweating more than the usual, consult the doctor immediately. While taking the medication, becoming dehydrated is quite easy and this can cause a serious electrolyte imbalance or severely low blood pressure.
Can I take losartan and aspirin together?
Before you take losartan with aspirin, make sure that you talk to your doctor. Combining the two medications can cause a reduction in the effectiveness of losartan in lowering blood pressure. The combination can also have an adverse effect on the function of the kidneys, especially when the combined use is too frequent or chronic.
Can I take losartan and Viagra together?
Addition to the blood pressure lowering effect of losartan can be done by Sildenafil. The doctor must be contacted if any signs and symptoms of low blood pressure, like rapid pulse or heart rate, headache, flushing, fainting, light-headedness, and dizziness are experienced.
Can I take losartan and lisinopril together?
The two medications losartan and lisinopril have a few side effects if taken together, by the same person; hence, consulting the doctor is a must. Only if advised by the same doctor, the two medications should be taken together.
Lisinopril is an ACEI (angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor) drug. It generally causes a dry cough as a side effect and generally, people are then shifted to ARB (angiotensin receptor blockers) like losartan.
Can I take losartan and atenolol together?
Yes, taking losartan and atenolol together is safe. There mechanisms of action for lowering blood pressure are different.
Can I take losartan and amlodipine together?
Combined hypersensitive agents help control blood pressure better and also cause a reduction in the number as well as the severity of side effects, compared to a monotherapy. Since both ARBs, as well as CCBs (calcium channel blockers), serve as effective antihypertensive drugs, they can be taken together.
Can patients with angioedema take losartan?
Angioedema is a condition which is potentially life threatening. Administrations of drugs which inhibit angiotensin converting enzymes have since long, been associated with angioedema. The increase in the levels of bradykinin in the body which is caused due to the inhibition of the enzyme which converts angiotensin is considered to be responsible for this infection or side effect.
AT2 blockers like Cozaar Losartan Potassium (Merk & Co.) are a relatively new class of anti-hypertensive drugs which have been developed to partly eliminate angioedema and dry cough, which are associated with ACEI drugs. The action of the agents is by selective binding of angiotensin II receptor sites, which eliminates the angiotensin hypertensive effects without any effect on the systemic or the local bradykinin levels.
Patients who have a medical history of angioedema have an increased risk of developing it again, when receiving the treatment therapy of AR antagonists. Any symptoms or signs that suggest angioedema, like difficulty in breathing or swallowing, swelling in tongue, lips, eyes, extremities, or face, must be immediately reported to the medical practitioner.
Until otherwise directed by the doctor, medication should be stopped. Measures to prevent the obstruction of the airway, and/ or emergency therapy are required for angioedema involving larynx, glottis or tongue. Permanent discontinuation of treatment with AR antagonists is advised if the development of angioedema is associated to the therapy.
Can patients with congestive heart failure take losartan?
Renal impairment can result from the administration of AR antagonists, in patients who have a renal function dependent on the renin – angiotensin – aldosterone system activity. Additionally, susceptible individuals may also suffer from symptomatic hypotension which can compromise the myocardial and renal perfusion.
Patients of severe CHF, i.e. the congestive heart failure can exhibit association of AR antagonist treatment with oliguria and/ or progressive azotemia as well as rare instances of myocardial ischemia, renal failure and death. AR antagonist treatment therapy should undergo a careful initiation in individuals suffering from severe CHF, especially when sodium and/ or volume depletion are its companions.
If the individual undergoing treatment experiences decline in the renal function, usually, there is no requirement for the AR antagonist therapy to be discontinued, provided symptomatic improvement in the heart failure is displayed along with tolerance for renal deterioration.
Improved survival and hospitalizations in patients with heart failure have been shown due to blockade of the RAS system, by treatment with ACE inhibitors and ARBs. These beneficial effects of treatment with losartan have also been thoroughly evaluated. The ELITE (Evaluation of Losartan in the Elderly) was the first trial, for comparing the treatment of NYHA class II-IV patients of heart failure (age group 65 and above).
The treatment comparison was between captopril (around 50mg, thrice a day) and losartan (50mg once per day), for 47 weeks. Worsening renal function was the primary end point. No significant changes in renal function were observed. Yet, it is important to take note of the fact that the event rate was lower than what had been anticipated.
Therefore, the study was not powerful enough to show a significant difference. 46% decrease in mortality was the second end point, as observed in patients treated with losartan. A second trial was also run to prove the superiority of losartan with NYHA class II-IV heart failure. Losartan also exhibited better tolerance compared to captopril with a few patients who discontinued prematurely due to the adverse effects.
Both these studies were conducted for the administration of 50mg of losartan in a day. Further decrease in blood pressure can be caused due to higher doses of the drug. With an increase up to 150 mg of the drug, there is observed an increase in levels of renin.
The effects on clinical outcomes, for the high versus the lower doses of losartan in heart failure patients, were a randomized, double-blind trial of losartan dose 50mg compared to 150mg dosage. The individuals who displayed intolerance towards ACE inhibitors had a median follow-up of 4.7 years. Admission for heart failure or death were marked the primary end points.
There was hardly any difference in deaths but hospitalizations for heart failure witnessed a significant decrease in higher dose losartan administration. Hypotension, renal impairment, and hyperkalemia were greater in the group which had undergone higher dose administration. Yet, increase in the rate of discontinuation was not observed in the same group.
Can I take losartan with grapefruit juice?
The grapefruit juice is known to reduce the ability of the body to activate the drug when consumed with losartan. The reduction in the amount of activated losartan can be insufficient for the controlling the blood pressure.
During oral administration of losartan, drinking grapefruit juice or eating grapefruit must be avoided. Alternative citrus beverages like the juice of oranges can be chosen, instead. In certain case, the doctors or medical practitioners instruct or advise eating grapefruits or drinking grapefruit juice with the drug. In any such case, you must clearly discuss the effect of grapefruit on the blood levels of active losartan.
The lowering effects can be observed even when the consumption is not at the same time as of the drug or medicine administration but is instead a few hours before or after the same. Usually, the healthcare professionals are clearly aware of the effects and interactions between the two and might already be monitoring the same for you. You must not stop, start or even change your dosage of the drug without consulting with them beforehand.
Can I take losartan before surgery?
Before a surgery, angiotensin II receptor antagonists like losartan and candesartan must be avoided, because –
- During an anesthetic, both these drugs increase the chances of drop in blood pressure
- Administration of these drugs may be requested by anesthetists before a surgery, but this request depends on individuals. Until requested or recommended, withhold administration of the drug.
“Cephalexin- Brand name, Dosage, Use, Side effects”
“Should you eat yogurt while you’re on antibiotics such as azithromycin?