Contents
- What is scabies and scabies rash ?
- What is Scabies mite? How scabies mite looks like?
- Is scabies rash contagious? How is scabies transmitted?
- Is scabies common condition?
- Scabies classification
- Classic Scabies rash signs and symptoms
- Crusted scabies rash signs and symptoms
- Nodular scabies rash signs and symptoms
- Scabies diagnosis
- Can you get scabies from a dog or cat?
- How long scabies rash lasts?
- What should I do prevent scabies?
- Bacterial infection caused by scabies
- What is postscabies pruritus? Will I feel itch even after scabies is eradicated?
- Scabies treatment
- Permethrin 5% cream (Elimite) for scabies
- Malathion 0.5% lotion (Ovide) for scabies
- Crotamiton 10% cream (Eurax, Crotan) for scabies
- Lindane 1% solution for scabies
- Benzyl benzoate for scabies
- Precipitated sulfur (5% or 10%) for scabies (Sulpho-Lac, Sulfo-Lo)
- Ivermectin (Stromectol) pills for scabies
- Antihistamines for scabies itching
- Mupirocin topical for scabies bacterial infection
- Hydrocortisone topical for scabies
- Cold showering for scabies itch relief
- Will soaking into colloidal oatmeal help itch relief from scabies?
- Epsom salt bath for scabies
- Caladryl lotion for scabies
- Should I need to drink a lot of water if I have scabies?
- Proper diet for scabies
- What material should I wear to reduce itching?
- Cayenne pepper for scabies itch
- Tiger Balm for scabies
- Tea Tree Oil for scabies
- Neem oil for scabies
- Rosemary oil for scabies
- Clove oil for scabies
- Anise oil for scabies
- St. John’s Wort extract for scabies
- Margosa oil for scabies
- Aloe vera for scabies
- Menthol for scabies
What is scabies and scabies rash ?
Scabies is a contagious condition of the skin caused by tiny-microscopic mites named Sarcoptes scabiei that burrow into the skin. “Seven-year itch” as it was previously called is predominately characterized with severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. The most common disease manifestations are facilitated through hypersensitivity and inflammatory and reactions to mites and their products.
Bacterial infection complication is a cause of significant morbidity. A patient with usual scabies might have on average about 12 but individuals with severe form of scabies with crusts may have thousands of them. The infestation can occur at all ages, but particularly in children.
It is a well-known public health issue in poor communities and is prevalent in the most of underdeveloped countries. The incidence of scabies is approximately 300 million cases each year worldwide.
Effective scabies management involves treatment of affected patients, their relatives and close contacts but also the environmental fomites. Control is sometimes tough to attain because of delayed or missed diagnosis, poor compliance, insufficient treatment and improper use of medicine. Treatmentwith most scabicidal agents start with treating with an initial dose and re-treating 7 days later.
What is Scabies mite? How scabies mite looks like?
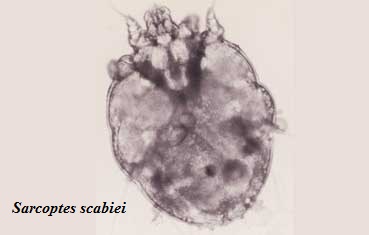
Scabies mite is medically known as Sarcoptes scabiei variety hominis. It is an arthropod of the order Acarina that causes Scabies, an ectoparasitic infestation in humans.
The name Sarcoptes comes from the Greek word “sarx”, which means flesh, and the word “koptein” which means to smite or to cut. Scabiei word origin comes from the Latin word “scabere” which means to scratch. Sarcoptes scabiei was first described more than 2,500 years ago, but it was originally first described in medical literature in 1687 identified by Bonomo and Cestoni using a light microscope.
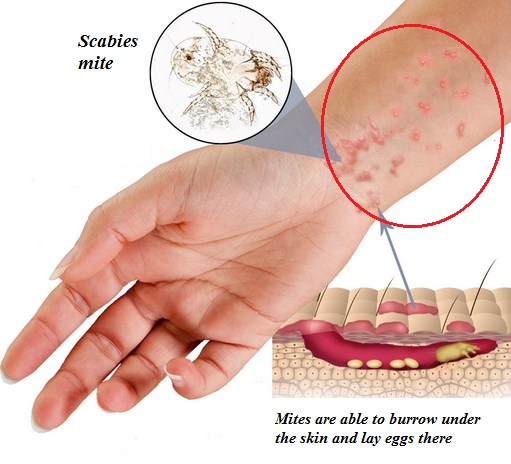
As an obligate parasite, the scabies mite burrows in the epidermis of human skin, approximately within 30 minutes after first contact. The adult mite is about 0.3 mm long and is difficult to see. The adult mite is able to burrow at 0.5 to 5.0 mm per day into the skin layer stratum corneum depositing feces in its path.
Female mites lay eggs on their way. Larvae start to develop within 2 to 3 days after the egg is laid, which then leave the burrow to the skin surface. After about 10-11 days, females develop into egg-laying adults. The total life span of the adult female is about 5 weeks. Adult mites have 8 legs, compared to larval forms, which have 6 legs.
During their growth on the skin surface, larvae of the mites are also capable of burrowing into the epidermis of the skin or moving to a different host. Scabies mites crawl they are not able to jump or fly. Mites can crawl as fast as 2.5 cm/minute on warm skin.
At room temperature mites can survive off the human host and stay capable of infestation for about 24 to 36 hours and up to 19 days in a cool, humid environment. Using odor and thermotaxis adult scabies mites can identify a new host.
Is scabies rash contagious? How is scabies transmitted?
Scabies is most commonly spread via prolonged periods of skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, or through sexual contact. Rarely scabies can pass from person to person by sharing towels, clothing and bedding with someone who’s infected.
Transmission is most likely to occur in cases with crusted scabies, in which a high parasite load resides are easy to be spread. Theoretically scabies can be transferred by eggs, larvae to the skin of the new host. But, mature mites are the most likely transmitters.
Transmission of scabies mites between family members is most common and proved by the studies that showed that the genotype of scabies mites from household members is more homogeneous compared to the genotypes of mites from separate households within a community. Transmission can also occur from parents to children, mostly from mother-to-infant. Scabies is also very common in school children.

It can take up from 4 to 6 weeks for the scabies symptoms to appear after the initial infection. This is known as the incubation or clinically latent period. This delay is responsible for unknown transmission and is suggested to be the cause of delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction against mites and their products.
If patient is reinfested, symptoms can appear after just few days. Scabies can initiate humoral immune response, which has been described by high peripheral levels of IgG and IgE and dermal IgE deposits, found on biopsy of infected patients.
Scabies can be seen worldwide in people of all: ethnicities, ages, sexes and socioeconomic statuses. The infestation is not caused only by lack of personal hygiene but it is more commonly seen in people who live in crowded, urban conditions. People at particular risk are those who are in crowded living situations, such as schools, hospitals, nursing homes, and prisons.
Even though scabies is very contagious, it typically needs prolonged direct skin-to-skin contact with an invested patient. Limited contact, such as a handshake or hug should not normally spread the infection. It should be known that even if individual doesn’t have manifestation, he or she can pass the infestation on to other people.
Is scabies common condition?
The incidence of scabies is approximately 300 million cases per year. The most affected are children living in poor and overcrowded tropical areas because of the chance to be exposure and their lack of immunity.
Poor hygiene and nutritional status, poverty, homelessness, dementias are among the leading risk factors for scabies. Scabies is mostly widespread in populated areas with high-density and limited access to medical care. It is the most common in the following tropical and subtropical areas:
- Africa
- Central and South America
- Northern and central Australia
- Caribbean Islands
- India
- Southeast Asia
However, scabies is also able to occur in developed, probably because expensive medical healthcare.
The prevalence of scabies in many populations rises and falls cyclically, peaking every 15-25 years, yet unknown reasons. According to data reports a lower prevalence of Scabies has been observed in African-Americans than in other ethnic groups in the United States.
Scabies classification
Scabies can be divided into following 3 groups:
- Classic Scabies – most common form
- Crusted Scabies (Norwegian Scabies) – rare form
- Nodular Scabies – very rare form
Classic Scabies rash signs and symptoms
Classic scabies, the most common form, produces symptoms of severe pruritus (worse in the evening),
The signs and symptoms of scabies rash are burrows, erythematous papules, and generalized itching with nocturnal predominance. Itching can also be present in unaffected skin. Scabies rash most commonly appears on the body at sites such as: wrists, elbows, armpits, the skin between the toes and fingers, around the nails, and at the parts of the skin that is usually covered by clothing such as the buttocks, nipples, belt line and penis.
Infants and children may have scabies rash developed on their head, neck, face, palms and soles. If untreated, scabies rash may become crusted. Patients with weaken immune system are more likely to develop crusted scabies rash. Fatigue, irritability and in some patients fever caused secondary impetigo or cellulitis may be also present. Progression from classic scabies is uncommon.
The most noticeable signs of scabies are pink to red bumps that look like bug bites or pimples, sometimes accompanied with scab or scale on them. However, the source of scabies is the mite’s burrows on the skin, which are very small and often non-observable to the naked eye.
Typically, a burrow looks like a small, scaly line (3–10 mm long), occasionally occurring with a tiny black fleck at one end. Scabies is extremely itchy, especially at night. Excessive scratching may cause the wounds on the skin, which then may become infected with bacteria.
According to reports, a burrow is observed in most classic scabies rash cases diagnosed in nontropical climates. Hypersensitivity of both immediate and delayed types has been implicated in the development of lesions other than burrows. It should be known that the degree of rash does not correlate with the number of mites present
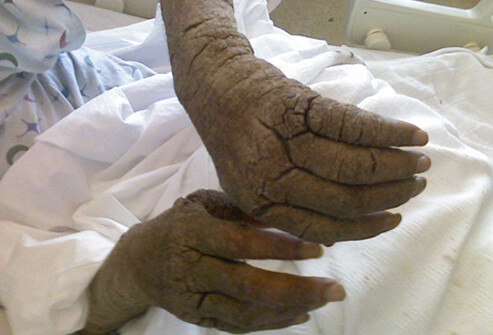
Crusted scabies rash signs and symptoms
The most severe form of scabies rash is crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies (term comes from affected Norwegian patients with leprosy). Individuals with highest risk for this type of scabies are:
- Elderly
- Individuals with weakened immune systems including organ transplant recipients or patients with HIV/AIDS
- Patients on a long-term immunosuppressive therapy
- Malnourished people
- Patients who are physically and/or mentally impaired or disabled
Crusted/Norwegian scabies is medically also known as psoriasiform dermatitis, frequently related with hyperkeratotic skin crusts, peripheral eosinophilia, and high levels immunoglobulin IgE and IgG levels. The lesions are mostly widespread and may appear on the scalp, face, knees, elbows, palms, and soles of the feet.
Although it might not be itchy in about 50% of cases, the lesions may contain up to 2 000 000 mites. This difference in mite’s number between classic and crusted scabies indicates that crusted scabies is considerably more infectious than classic scabies. The development of fissures and secondary bacterial infections are common and are partially responsible for the high mortality rates linked with this type of scabies.
According to the data, most cases of this scabies variant have been developed in patients with HIV or HTLV-1 infection or in patients on immunosuppressive therapy, after chemotherapy or organ transplantation.
Other vulnerable groups are patients with mental disorders or physically handicapped patients including those with paralyzed limbs, sensory neuropathy, or leprosy, because they may be unable to feel the itch or to scratch. Nearly 40 % of cases with crusted scabies don’t have a definitive risk factor, proposing an inherited predisposition to this variant of scabies rash.
Crusted scabies carries a high mortality risk due to secondary sepsis caused by bacteria infection. Data showed that 5-year mortality rate is up to 50 % in patients with crusted scabies.
Nodular scabies rash signs and symptoms
Nodular scabies is another clinical variant of scabies occurring in about 7 % of documented cases. Scabies rash is characterized with extremely pruritic nodules 2–20 mm mostly present on the buttocks, genitalia, groin, and axillary area.
The color of the nodules is reddish to brown. Nodules do not contain mites, thus they are thought to be secondary caused by hypersensitivity reactions to mite products. The exact treatment of the nodular scabies rash can be uncertain since nodules can persist for weeks after treatment, so corticosteroid injections may be needed. Often, patients will require repeated scabicides treatment and aggressive anti-inflammatory therapy.
Scabies diagnosis
In practice, scabies diagnosis is often confirmed or excluded empirically from correlation between history of a contact with a person who has or had scabies and clinical symptoms such as easy observable skin lesions and nocturnal itching, however using such correlation may lead to both overdiagnose and underdiagnose actual cases.
Scabies may be easily mistaken for other pruritic skin conditions thus differential diagnosis may be necessary in order to exclude atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, contact dermatitis and papular urticaria, among others.
In addition to the clinical manifstations, sscabies can be confirmed by some of the following methods:
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) scraping of a burrow
- Serologic testing (ELISA)
- Dermoscopy
- Magnification of digital photography
- Skin biopsy
- Burrow Ink test
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) scraping of a burrow test
The gold standard involves all techniques that can directly visualize the mite, eggs or mite’s feces. Direct visualization can be done with potassium hydroxide preparation – KOH method of a scraping or biopsy taken from a burrow. KOH testing provides excellent specificity because false-positives results are very rare, however it does have low sensitivity because of many false-negatives results, since in most typical/classic scabies variants, there is a small number of mites.
Fecal remains or scybala in isolation can be most commonly found during visualization. Since they may also be debris of nonscabies origin, the presence of scybala alone can’t confirm the diagnosis.
Also, biopsy showing only inflammatory perivascular cell infiltrates with edema, eosinophils and epidermal spongiosis are also not specific enough to confirm diagnosis. New visualization techniques focused on so called “pink pigtail” structures connected to the stratum corneum that represents empty mite egg casings may suggest scabies.
Dermoscopy and magnification
Dermoscopy and magnification of digital high-resolution images are also respectable diagnostic methods, although less definitive compared to KOH or biopsy visualization.
The keypoint of these methods is a selection of a suitable lesion for testing since excoriated or inflamed lesions are less likely to harbor the mite or mite products. Areas such as wrists and finger webs proved to be best sites for sampling; however, any place containing a red papule with central burrow usually has a mite.
Burrow ink test
Burrow ink test has been showed as a good alternative method for scabies diagnostic. In this method doubtful papules are marked with ink and then wiped off with an alcohol in order to remove the surface ink from the lesion.
A positive results of this test can be confirmed when the ink tracks forms typical dark, zigzagged line that is readily obvious to the naked eye. This test is useful in cases when camera, microscope, dermatoscope skin biopsy are missed
New diagnostic methods
Epiluminescence microscopy and HD videodermatoscopy are newer, noninvasive methods that allow investigation of the skin in vivo from the skin surface to the superficial papillary dermis.
A new approach and good way for diagnosis of scabies is serologic testing. Polymerase chain reaction followed by ELISA may detect S. scabiei DNA from cutaneous places of infected patients. This test can be also used to monitor the efficacy of therapy.
In Rama et al. study specific IgE antibody against a recombinant scabies antigen has been developed. In this study, the sensitivity was 100% and specificity for diagnosing scabies was 93.75 %.
Can you get scabies from a dog or cat?
Pets and other animals can’t spread the same types of mites that cause human scabies, thus it is not possible to get scabies from a cat or dog. Mites that can infest pets and cause scabies are called “mange.” People get mange mites, but they will not cause any scabies. However, minor itching and redness can be manifested.
This is because mange can’t survive and reproduce on human skin therefore they’ll die out on their own without having a time to produce significant symptoms on humans. People do not need to be treated if they come into contact with mange, but cats and dogs must be treated because they can spread and cause itchy and scaly skin and fur loss.
How long scabies rash lasts?
Many different factors may have an impact on how long will scabies last. These factors may include: the severity of infestation, immunity and health status, adequate and on-time treatment, hygiene and prevention etc.
Scabies mites can only live about 72 hours without host contact, but once they got on a person, they can live up to 2 months. Mites will survive longer in colder conditions and higher humidity. Once person get mites they will burrow into the skin, and symptoms usually begin three to six weeks after infestation.
What should I do prevent scabies?
Scabies requires therapy in order to stop the infestation and further complications. Once you got a proper therapy follow next steps in order to prevent scabies from coming back:
- Wash all: clothes, towels and bedding which are used by you or the infested person living with you in the past 72 hours in hot water dry them in a hot dryer.
- Vacuum all rugs and furniture, and then discard the vacuum bags.
- Anything that can’t be laundered should be put into plastic bags for at least 72 hours.
- You don’t need to treat your pets because the mite only lives on humans.
You can return to work or school the day after treatment is started.
Bacterial infection caused by scabies
Patients who have scabies may become secondarily infected if bacteria enter into excoriated skin and wounds caused by intense itching. Mites may also transmit bacteria itself, since it has been shown that Staphylococcus aureus and nephritogenic strains of Streptococcus group A have been isolated from mites and their fecal pellets.
Bacterial infection may further lead to: impetigo, cellulitis or furuncles that if not treated may progress to rheumatic heart disease and acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Such complications are the greatest concern in tropical areas and are seen less often in locations with dry climates. When bacterial superinfection is suspected, treatment with topical and/or systemic antibiotics should be started as soon as possible.
What is postscabies pruritus? Will I feel itch even after scabies is eradicated?
Pruritic condition that can last for days or even weeks after the primary infestations of scabies are eradicated is called postscabies pruritus. Such itching is most probably the result of hypersensitivity reaction to mites and mite products.
So, practitioners should not confuse this complication with treatment failure and should not prescribe more drugs or higher doses of existed scabicidal medications. Postscabies pruritus can be successfully controlled with oral antihistamines or corticosteroids, trial of phototherapy may be acceptable in resistant cases.
Scabies treatment
The choice for scabies management is based on efficacy and potential toxicity, type of scabies, and the patient’s age. Since there are no adequate randomized-controlled and comparable studies that will prove the most safest and efficient topical and oral anti-scabies treatment choice, many findings suggest: malathion 0.5% lotion, permethrin 5% cream and oral ivermectin in dose of 200 mg/kg as a good and proved treatment options.
Therapy should be done concomitantly with treating the source, avoiding contacts and sanitizing fomites and domicile. If used alone, topical antiscabies preparations should be applied to the entire skin surface with particular attention to the face including eyelids, back, groin, and back, under the nails, and in and behind the external ears.
If hands are washed before the typically recommended 8-hour application time, the topical agent should be reapplied to the hands. If bacterial infection occurs, topical or systemic antibiotics should be started as soon as possible and continued in addition to the scabies treatment.
In some cases pruritus can persist for up to 4 weeks after successful treatment thus antihistamines and/or anti-inflammatory (e.g. medium-potency topical corticosteroids) should be introduced. In the case of crusted scabies, keratolytics should be given with existing treatment regimen until the hyperkeratosis has resolved. Cases of crusted scabies need more cycles of treatment compared to the classic scabies.
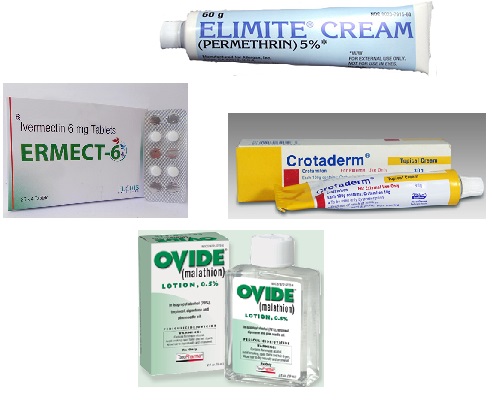
Permethrin 5% cream (Elimite) for scabies
Permethrin is a pyrethroid antiparasitic agent that acts on the neuron membrane disrupting sodium channel current and thus the polarization of the cell membrane. Delayed repolarizations that may provoke paralysis of the pests are the consequences of this disturbance. Permethrin 5% cream is accepted as the current gold standard for scabies treatment. Different Studies showed efficacy of about 90 %.
Most studies also proved its safety. According to a 2007 Cochrane review, permethrin showed to be most effective topical scabicide, considerably more efficacious than crotamiton and linden. Compared with lindane, permethrin 5% cream is less toxic and has lower percutaneous absorption, thus there is a lower risk of drug’s blood and brain concentrations.
It is safe even for children, infants, pregnant and breastfeeding women. Although there are no reports of in vivo resistance, in vitro resistance of scabies mites to permethrin has been well demonstrated. Recently in a number of Aboriginal people in northern Australia, resistance to the permethrin 5% has been desribed.
Permethrin can be applied to the entire body 8 to 12 hours, for best results best before bedtime and repeat in 7 days to kill eventual hatched larvae. On the market, it is most commonly known under the brand name Elimite.
Malathion 0.5% lotion (Ovide) for scabies
Malathion 0.5% lotion is an organophosphate anti-parasite agent. This drug works by nhibitng acetylcholinesterase activity of most eukaryotes. Malathion is very toxic to aquatic organisms, but has a relatively low toxicity for mammals and birds. It works on scabies as a neurotoxin, causing muscle spasms and ultimately death.
It is in the U.S. approved for the treatment of head lice but it is not yet approved for the treatment of scabies. However, in the United Kingdom, malathion 0.5% lotion is approved for scabies and is available as OTC product. Malathion requires two applications 7 days apart. Different small studies proved malathion’s efficacy in scabies, with efficacy rates ranging from 83% to 100%.
The safety profile has been also showed to be excellent. Since malathion is formulated as a lotion, it may be more suitable than creams for treatment of hairy parts of the body, such as the scalp. Side effects of malathion may include occasional skin irritation and conjunctivitis with eye contact.
Crotamiton 10% cream (Eurax, Crotan) for scabies
Crotamiton is a scabicidal and antipruritic agent available as a cream for topical use only. Although its mechanism of action is unknown, it does have high antiscabies efficacy. It is labeled for topical use from the chin down, with repeat application after 24 hours. Although crotamiton cream is only labeled for use during 1 to 2 days, daily application during 5 days has produced better cure rates.
It is not known whether crotamiton is safe for use in newborns, infants and children younger than 18 years of age. Pregnant and breastfeeding woman should also avoid this medicine, since there are no adequate studies that will confirm its safety. One comparable double-blind randomized study has been showed that crotamiton cream is significantly less efficacious than permethrin.
Potential side effects after crotamiton cream use may include erythema and conjunctivitis. Moreover, high mite resistance has been reported after a single use of 8 to 12 hours, thus many health providers will recommend its use for 5 days, although it is considered as off-labeled.
Lindane 1% solution for scabies
Lindane is organochlorine insecticide that has been used as a pediculicide and a scabicide. It exhibits its anti-parasitical action by being directly absorbed in the exoskeleton of parasite and their ova. Inhibition of GABA-ergic activity reduces neuronal inhibition, which leads to hyperexcitation in the CNS provoking paralysis, convulsions, and death. However, lindane has very low ovicidal activity.
Efficacy of lindane was confirmed by early studies and it is in the range between 49-96% after 4 weeks of a single topical application. Treatment failure can be caused due the fact of mite resistance. As an organochlorine insecticide it may cause a range of serious side effects including: irritability, seizures, vomiting, vertigo, diarrhea, and syncope.
Thus its use is greatly limited by safety concerns regarding its potential neurotoxicity. Lindane has been banned in California, Australia, United Kingdom and many western countries (about 50) due to concerns about neurotoxicity and because of toxic effects on environment. In Canada, Lindane is not prescribed as a first-line therapy due to reports of mites’ resistance, neurotoxicity, and bone marrow suppression.
However, lindane 1% solution is approved by the FDA as a second-line topical treatment. Safety studies revealed that only 1 bottle of lindane can contaminate 6 million gallons of water, costing $4000 of wastewater clean-up per treatment. Since its low safety, mild efficacy and risk for environment, it is expected that this drug will be banned for both pharmaceutical and insecticidal use.
Benzyl benzoate for scabies
Benzyl benzoate is one of the older agents used to treat scabies. Benzyl benzoate has toxic effects on parasite CNS resulting in its death. It is also toxic to the ova of the mite; however the exact mechanism of action is still unknown. In vitro studies have been found that benzyl benzoate is able to kill the Sarcoptes mite within 5 minutes.
Although it is effective it is not the treatment of choice due to its irritant properties. It can be used alone or in combination with topical sulfiram. It is labeled for use in adults and in diluted concentrations for children, infants, and breastfeeding mothers. In the US benzyl benzoate is not approved.
Comparable studies showed lower cure rates of benzyl benzoate than with oral ivermectin while in vitro testing has been shown that benzyl benzoate is able to eradicate scabies mites more rapidly than permethrin and may be a useful as an effective alternative to permethrin in severe crusted scabies. After administration, benzyl benzoate should be washed off during 24 hours because of its irritant side effects.
In some cases, analgesics and antihistamines can be used as pretreatment to diminish discomforts caused by this agent. If ingested benzyl benzoate may provoke difficulty urinating, jerking movements and consciousness loss. Efficacy can be even better if it is used together with sulfiram, in that case alcohol should not be taken at least 48 hours after treatment because serious side effects may happen.
Precipitated sulfur (5% or 10%) for scabies (Sulpho-Lac, Sulfo-Lo)
Precipitated sulfur (5% or 10%) is prepared with petroleum jelly and should be applied nightly for 3 consecutive nights. Because of its safety, it is often the therapy of choice for children younger than 2 years and for pregnant and breast-feeding women. Unfortunately, it is oily, has an odor, and will stain clothing.
Ivermectin (Stromectol) pills for scabies
Ivermectin is a broad-spectrum anti-parasite agent. It was first marketed under the name Stromectol and used against worms. This drug works by selectively binding to glutamate-gated chloride ion channels in muscle and nerve cells of parasites. This binding causes hyperpolarization of the cell, leading to paralysis and death of the parasite.
Ivermectin is sometimes used off label as an oral pill for severe cases of scabies. It can be used alone or in combination with topical antiscabicidal agents. Different large studies have been proved that 1-2 doses of ivermectin 200 mg/kg that should be taken 3–9 days apart produced cure rates at the same rate as conventional topical preparations with benzyl benzoate, lindane, permethrin.
Studies showed efficacy rates ranging from 76-100%. After initial dose of ivermectin cure rates were 70% which increased to 95% with a second dose during 2 weeks. According to this, it looks like ivermectin may lack ovicidal properties and thus may not be effective during all stages of the mite life cycle.
Since the therapy with a pill is relatively quick, easy, efficient and virtually guarantees whole-body exposure, ivermectin may have advantage over topical preparations. The best results have been showed when it was used together with topical permethrin.
Ivermectin should be taken once and then repeat after 1–2 weeks later. It should not be given to a children and pregnant or breastfeeding woman.
Potential side effects of ivermectin may include: hepatotoxicity, tachycardia and hypotension. Ivermectin is also inhibitor of P-glycoprotein. This inhibition may lead to serious side effects if ivermectin is used together with other P-glycoprotein substrates, such as methotrexate, digoxin, cyclosporin and some anticancer treatments.
Antihistamines for scabies itching
Since the itch of scabies is caused by sensitive allergic reaction to the mites and their eggs, larves or fecal debris taking an antihistamine will temporarily relieve unbearable itch. Since the itch is the most intensive at night and during sleep, taking antihistamines with sedative actions before bed is the best way to relief an itch and have a good nap.
Pruritus can be effectively treated with an oral antihistamine drugs, such as hydroxyzine (Atarax), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), or cyproheptadine hydrochloride (Periactin). More severe symptoms may require a short course of topical or oral steroids.
Mupirocin topical for scabies bacterial infection
Mupirocin topical can be effectively used to treat secondary infected lesions. This agent is used to treat infection caused by Staphylococcus species, beta-hemolytic streptococci, or Streptococcus pyogenes. It works by inhibiting protein and RNA synthesis by inactivating transfer-RNA synthetase.
Hydrocortisone topical for scabies
In cases of intense pruritus caused by scabies, hydrocortisone topical can be used to relieve the symptoms. This corticosteroid is safe and suitable for application to skin or external mucous membranes. Because of its anti-inflammatory effects it is able to relieve severe itching, redness, and swelling caused by mites. Hydrocortisone is considered the lowest-potency topical steroid and thus it is the safest one.
Cold showering for scabies itch relief
Never take hot showers if you have scabies because it will make your itch worse since excessively hot water quickly dries out and irritates the skin. Instead, take a bathe in cold water. It will soothe your skin as well as keeping the natural balance of sebum intact. If you are not able to handle cold water showers then you can start with mild-warm water and slowly decrease the temperature until it is just enough that you can bear it.
Will soaking into colloidal oatmeal help itch relief from scabies?
Colloidal oatmeal is oats ground into an extremely fine powder. Its properties may relieve itch very well. When added to the water in bath it creates a milky cloud and sets into the skin, nourishing it and keeping the itch away.
While your tub is filling with lukewarm water, add a packet (two to three cups) of colloidal oatmeal to help disperse the oatmeal. Some of helpful ingredients that can be also added to your oatmeal bath are baking soda and coconut oil. Feel free to take up to 3 baths a day. After a long soak, it is good to wash off a bit in cold water to keep your skin nice and cool.
Epsom salt bath for scabies
Epsom salt bath can be very useful for itch relief produced by scabies.
Epsom salts contain magnesium-sulphate that is able to reduce inflammation of the skin and help keep your mineral contents. If you like to take a hot bath that is okay in the case of Epsom salt bath, as the heat will help the salts to absorb easily into your skin, but it could also leave your skin a bit dryer. You can also add more ingredients into bath water including: baking soda or essential oils like jojoba oil, neem oil and tee trea oil.
Caladryl lotion for scabies
Caladryl lotion is very effective itch reducer. It has been used for generations to treat all kinds of itchiness. It contains pramoxine, camphor, zinc and calamine as active ingredients. Pramoxine is local anesthetic that works by numbing the skin to block the feelings of pain and itching. Zinc and calamine are used as skin protectants while camphor gives cooling and drying effects that additionally helps for itch relief.
Should I need to drink a lot of water if I have scabies?
Yes, water is very important. We are made of water we need to keep taking it so our body will stay healthy. This is especially important for the health and adequate hydration of your skin. It’s pretty much guaranteed that if you don’t drink enough amounts of water your skin will dry out and you will be itchier.
Proper diet for scabies
Some foods are also known to make people more prone to dry and itchy skin. Problems including dermatitis and psoriasis are often food related. In general, patients with scabies should avoid foods rich with histamine and tyramine and foods that may cause allergy to you. Your body is already producing too much histamine while you have an allergy, thus extra intake may complicate symptoms even more.
During your scabies infestation avoid following tyramine and histamine rich food:
- Red wine
- Citrus fruits
- Fermented foods (sauerkraut, kombucha, yogurt)
- Bacon (and other cured meats)
- Aged cheese
- Seafood
- Spices
- Eggs
- Artificial food colors and preservatives
- Alcohol
- Vinegar
Other foods that may trigger allergic reactions include:
- Tree Nuts
- Milk
- Soy
- Wheat
- colorings, additives
What material should I wear to reduce itching?
Avoid wearing following clothing materials:
- New clothes, regardless of materials. They often have additives such as formaldehyde on them to avoid creasing
- Latex
- Wool
- overly tight clothes
Materials to wear:
- Cotton
- Dye free / perfume free
- Silk
- Linen
- Loose clothing
Cayenne pepper for scabies itch
Capsaicin from Cayenne pepper is a substance that is able to reduce pain sensations when it is applied on the skin. Capsaicin may also relieve itching sensations by desensitizing skin neurons. There are even some theories that when applied to the skin, cayenne pepper can kill scabies mites.
But, there are no studies that will confirm such claims, and in almost 30% percent of patients burning sensations have been described making scabies status even worse. Probably the best way to use cayenne pepper is to add one cup into hot bathwater, sit in the bath until the water gets cold and then rinse your body.
Always make sure cayenne not to get into your eyes, as it may irritate them. Another way is to make a cayenne paste and apply it to visible burrows beneath the surface of the skin. If after first application cayenne paper makes your symptoms worse, never use it anymore, as you are probably too sensitive to its effects. Also don’t use cayenne pepper if you have crusted scabies.
Tiger Balm for scabies
Tiger balm contains camphor that will cool off your skin and relieve itch for some period of time. This topical cream will also reduce inflammation and provide relief from muscle aches and pain. Tiger Balm contains also analgesic effects that come from camphor and clove oil. Tiger balm will not kill the itch mites or cure the scabies infestation, but it will provide good relief during the waiting period after conventional treatment.
Tea Tree Oil for scabies
When applied topically, Tea tree oil is able to fight scabies mites and parasite. Its antiparasitic and insecticide activity comes from terpenoids, which are natural microbial-killer ompounds that may heal scabies on the top and beneath the skin.
One study by Walton SF et al. found that tea tree oil’s active ingredient – oxygenated terpenoids, has a potential role as a new topical therapy for scabies. When tested on a 20-year-old woman with crusted scabies the tea tree oil topical treatment was highly effective in reducing survival times of mites.
Scabies mites were placed in continuous and direct contact with the tea tree oil product, and they began to die within five minutes. This study was published in Archives of Dermatology in 2004.
Newer study from Mounsey KE et al published in Future Microbiology, suggests that tea tree oil topical products may serve as an appropriate alternative therapeutic option to oral ivermectin and permethrin because of resistance, in severe cases and or in endemic areas where first-line treatment options are not approved or are too much expensive.
Neem oil for scabies
Neem oil is able to kill scabies mites, and it prevents their ability to grow and breed. Neem oil may also numbs pain and alleviate itching, making it perfect to treat scabies symptoms as well.
One large study conducted in India on patients with scabies used Neem oil and turmeric for treatment. After 3 to 15 days in 97 % scabies was cured. Additionally no toxic or side effects were observed. This is a safe and effective alternative that is also cheap and easily available, which can be especially significant when treating patients or communities in developing countries.
Rosemary oil for scabies
The potential power to stop the infestation of scabies can be exhibited after Rosemary administration. Rosemary oil may also decrease pain and prevent the development of secondary infections. A study conducted at in China found that when combined, rosemary and clove oil significant antimicrobial activity have been showed.
Clove oil for scabies
Clove oil contains analgesic, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. It can be used to dry up scabies rashes and blisters.
Animal study conducted on pigs and rabbits in 2010 showed that clove oil was highly effective against scabies mites, killing mites within an hour of direct contact. It has been suggested that the major component of clove oil, called eugenol, contains higher of scabies toxicity than benzyl benzoate.
The general recommendation for clove oil use for scabies is:
Combine 10 drops of clove oil with one teaspoon of honey and one teaspoon of coconut oil for skin relief. Rub it onto the area of concern twice daily.
Anise oil for scabies
Studies showed that oil extracted from anise seeds display insecticidal activity. It can be used topically to treat scabies as well as head lice. Anise oil should not be used in pregnant and breastfeeding woman.
St. John’s Wort extract for scabies
St. John’s Wort is known as a very valuable cure for scabies. Extract the juice of the fresh herb and apply directly on the affected areas. This method should be conducted at least four times in a day to attain benefit in a period of seven days.
Margosa oil for scabies
Margosa is another herb of Indian origin that has been proven to be very effective against scabies. Oil of margosa should be applied on the affected area and then massaged gently till the oil seeps into the skin. Margosa oil also removes bacteria and fungus trapped in the skin.
Aloe vera for scabies
Aloe vera is another herbal remedy for scabies. Aloe vera lotions, gels and creams are easily available in supermarkets and pharmacies and should be used according to the instructions provided.
Menthol for scabies
Menthol gives a cooling effects, relieving itching and helps curing scabies at much quicker pace. Menthol is an active ingredient found in mint. The different types of mint which you can apply are peppermint, ginger mint, mountain mint and many more.
“Pilar cyst – Causes, Symptoms, Removal Treatment and Pictures“