Contents
- What is uvula? What does uvula do in our body?
- Swollen uvula (uvulitis)
- What causes swollen uvula (uvulitis)?
- Swollen uvula symptoms
- Swollen uvula diagnosis
- Swollen uvula treatment
- Treatment of viral/bacterial caused uvulitis
- Treatment of allergy caused uvulitis
- Treatment of hereditary angioedema caused uvulitis
- Tips for swollen uvula relief
- When to seek medical attention in the case of swollen uvula?
- Uvula surgical removal
- Honey and garlic for swollen uvula
- Turmeric and ginger for swollen uvula
- Basil tea for swollen uvula
- Belladonna and wormwood homeopathy for swollen uvula
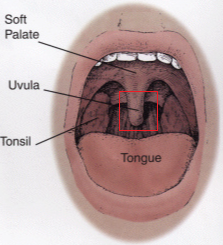
What is uvula? What does uvula do in our body?
Uvula or the palatine uvula is muscle part of tissue that hangs down over the tongue toward the back of the mouth. It is anatomical part of soft palate that helps in pushing food towards throat. It is made of muscle and glandular tissue (racemose glands and serous glands) but also with canals that excrete saliva.
During swallowing, uvula move together with soft palate to close the nasopharynx, preventing food from getting into the nasal cavity. Additionally uvula produces large amounts of thin saliva that serves as a throat lubricant. It has also important function in speech. In different languages, the uvula is used for articulating a series of consonant sounds, called uvular consonants.
The voiced uvular trill is one example that is commonly used in French, Arabic and Hebrew languages. Moreover, only in mammals uvula produces such amounts saliva indicating that it may serve as an accessory speech organ.
Uvula and emesis
Uvula stimulation may activate the reflex of gag. This is often a problem for people with uvula piercings. It is also known as a common technique for inducing vomiting.
Uvula relations with snoring and sleep apnea
The uvula may be responsible for snoring by causing vibrations or for having problems with breathing during sleep. In some cases uvula defects may lead to sleep apnea, which can be managed by the uvula or its part removal by a surgery known as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP, or UP3).
In some cases this surgery may also lead to reoccurrence of sleep apnea if scar tissue is formed and the velopharynx airspace is shrank. The success of this procedure for sleep apnea is approximately considered to be 40–60% effective in reducing symptoms.
Uvula and Velopharyngeal insufficiency
In not so common cases, the uvula can’t be closed appropriately against the back of the throat, which may lead to the condition known as velopharyngeal insufficiency -VPI. This may predispose “nasal” speech, where additional air comes down the nose, and the speaker is unable to say certain voices, such as pronouncing ‘b’ like ‘m’.
Uvula and nasal regurgitation
When we are swallowing food/drink, the uvula and soft palate work together and move to close off the nasopharynx, thus preventing the food from entering the nasal cavity. If this process fails, nasal regurgitation may occur.
This can be commonly seen in patients with velopharyngeal insufficiency or in the cases of myositides, and neuromuscular disease. This may also happen during intensive coughing or during accidental inhalation of water because coughing may prevent the uvula from blocking the nasopharynx, thus liquid may be expelled through the nose.
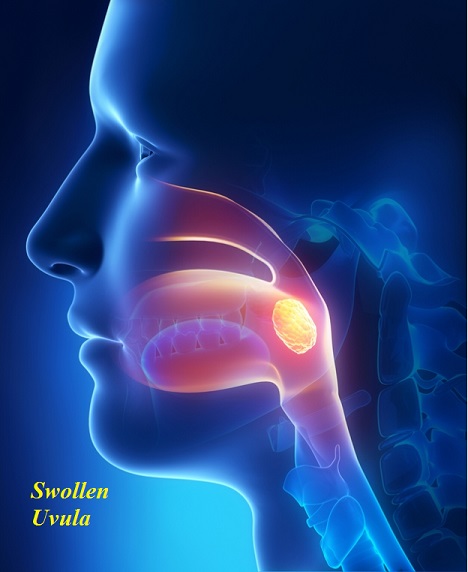
Swollen uvula (uvulitis)
If the inflammation of uvula occurs, it will become swollen, red, painful, itching, burned, with swallowing difficulties. In that case, uvula can expand 3–5 times its normal size which may cause issues with breathing, eating and talking. Although, uvulitis is not considered as a serious or life-threatening condition it can be very uncomfortable.
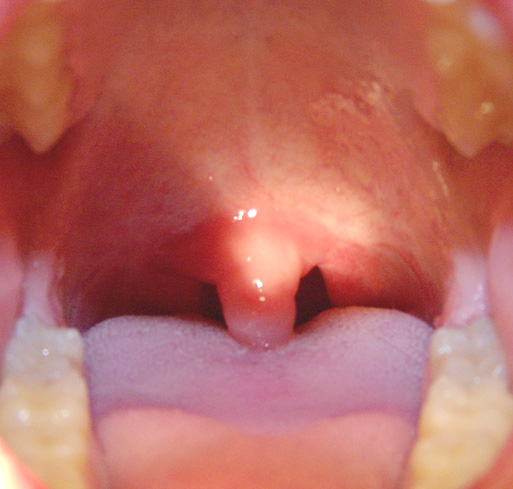
What causes swollen uvula (uvulitis)?
A swollen uvula may also be caused by following conditions:
- Infections
Throat infections may cause uvulitis. These infections can be both bacterial and viral, and may include:
- strep throat
- tonsillitis, and tonsillitis causing disorders such as mononucleosis
- epiglottitis
Common viral infections that may cause uvulitis are:
- the common cold
- mononucleosis
- chickenpox
- the flu
- measles
- croup
The most common bacterial infection that may cause swollen uvula is strep throat, which occurs due to Streptococcus pyogenes infection which is a type of group A Streptococcus.
Swollen uvula is also common in patients with tonsillitis.
Epiglottitis is uncommon but very dangerous condition that may occur in children. It is caused by an infection that causes an inflammation of epiglottis and surrounding structures, and can progressively lead to severe breathing problems.
- Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions may cause swelling of the mouth and throat, including uvula. This usually occurs in the case of severe allergic reactions such as anaphylactic reaction that can be fatal if not treated on time. Patients who experience fast and intense swelling of the mouth and throat should go to the nearest emergency room. Epinephrine shot will relieve the allergy.
- Acid reflux disorder
Acid reflux may also cause uvulitis. Different GIT conditions such as chronic gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or Zoolinger-Ellison diseases may cause the stomach acid being thrown back into the esophagus reaching the mouth and uvula and provoking irritation and swelling.
- Hereditary Angioneurotic Edema – HANE
HANE is uncommon genetic disorder caused by a gene mutation. The condition is represent with swelling attacks that may also involve the uvula. Most people with this disorder experience their first attack during childhood.
- Trauma
Injured uvula may become swollen however uvula injuries are not very common. Though, it is possible to burn the uvula with hot food, and the uvula can also be injured as the result of some medical procedures, such as intubation. However, complications from intubation are rare.
- Genetic Conditions
Certain genetic conditions may cause uvula abnormalities. Congenital condition called Cleft lip/palate may cause absent of the uvula or other abnormalities. Some people can be born with elongated uvula. If symptoms are troublesome, the uvula may have to be surgically removed.
Other causes may include:
- Excessive smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Oral dehydration
- Common colds
- Exposure to extremes in weather condition and environment
- Aphthous ulcers or canker sores
Can swollen uvula be caused by medication treatment?
According to the reports drugs such as: NSAIDs or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ketorolac, diclofenac, nimesulid, etc), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (enalapril, quinapril,etc) and angiotensin II receptor antagonists (valsartan, irbesartan,valsartan, etc) can cause uvulitis as a side effects. Uvulitis has also been related with the abuse of cannabis and cocaine and the topical administration of Ecballium elaterium herbal remedies used in the treatment of sinusitis and rhinitis.
Swollen uvula symptoms
Uvulitis signs and symptoms may include:
- Inflammation and redness of the throat
- Choking or gagging sensation because swollen uvula is enlarged and may touch the tongue. This can sometimes result in vomiting
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain in the throat, similar to that of a sore throat.
- Burning sensations in the throat
- Difficulties with swallowing drinks and foods, sometimes accompanied with pain
- Hoarseness or a voice sound changes
- Excessive drooling
- Snoring
- Fever
- Headache
- Breathing issues
- Tickling or itching sensation that may result with coughing
- Spots on your throat
Swollen uvula diagnosis
Clinical features and physical examination are very important in diagnosing uvulitis. Swollen uvula is most commonly presented with: sore throat, difficulty in swallowing and with sensations of feeling that something is in the throat. Different causes may provoke different symptoms, so the patient might or might not have a fever or tendency to gag, spit or choke because of severe discomfort while engulfing saliva.
Blood test is always recommendable in order to confirm infection. Increase counts of white blood cells are a good indicator of the present infection.
The throat or uvula culture is also recommended in order to find the exact cause of infection and will be helpful to decide which microorganism is responsible for uvulitis. A cotton swab is wiped onto the uvula and sample is examined in the lab to identity the bacteria.
In some cases, X-ray scans may be good alternative especially in the case of severe scenarios when the patient is having severe issues with swallowing and sensations of chokeing. In such cases X-ray of neck is effective diagnostic method.
How long does swollen uvula last?
If treated on time or if it is not caused by serious underlying problem it is possible to stop the pain within 1-2 weeks after seeing a doctor and getting diagnosed.
Swollen uvula treatment
If swollen uvula is caused by mild condition for example common cold, swelling can be usually healed without any treatment. On the other hand, treatment will depend on the severity of symptoms, and inflammation causes.
In most cases uvulitis caused by viral infections don’t require any specific treatment. However, if swollen uvula is caused by Influenza viral infection, then antiviral medication can be prescribed. In the case of bacterial infections, antibiotics may be prescribed. The best results will be achieved if antibiotic is prescribed according to antibiogram laboratory results.
Patients should always take all the medications as prescribed, and should not stop taking them on their own even after infection is healed.
Treatment of allergy caused uvulitis
Antihistamines (loratadine, desloratadine, cetirizine, etc) or corticosteroids (prednisolone, dexamethasone, etc) can be prescribed if uvulitis is caused by allergy. In cases of severe allergy such as anaphylaxis, epinephrine shot should be given in emergency cases.
Treatment of hereditary angioedema caused uvulitis
Following medicines can be prescribed in order to treat angioedema:
- Anabolic steroids, or androgens
- Antifibrinolytics drugs
- C1 esterase inhibitor (Berinert) or C1 esterase inhibitor (recombinant) (Ruconest)
- Plasma kallikrein inhibitor, such as ecallantide (Kalbitor)
- Bradykinin receptor antagonist, such as icatibant injection (Firazyr)
Tips for swollen uvula relief
If you have swollen uvula follow next steps for better relief:
- Intake enough amount of fluids. If your throat hurts after drink, try drinking small quantities during the day. Drinking water will ease dry mouth and it will also prevent the spread of infection. Water will wash away bacteria during the process of swallowing. You should drink at least 2 liters of water a day. Urine should be light in color if you intake enough fluids. If it’s dark yellow or brown then you’re not drinking enough and may be dehydrated.
- If uvula is not caused by infection and if you don’t have a fever, cool your throat by sucking on ice chips. Ice cream and cold not sour juice may also be helpful;
- Gargle warm salt water to ease your dry, scratchy throat.
- Try to have full night’s sleep, or short nap during the day if you can
When to seek medical attention in the case of swollen uvula?
Seek medical attention if:
- The symptoms are worsening despite treatment or if you develop new symptoms
- You have trouble opening your mouth or turning your head
- Your voice becomes muffled or you become unable to speak
- You have trouble with breathing
Uvula surgical removal
Surgical removal of uvula or uvulopalatopharyngoplasty can be done in extreme cases such as cancer. If uvula is removed partly, there are chances of it reoccurrence.
Honey and garlic for swollen uvula
Honey is a good remedy for swollen uvula. A teaspoon of honey licked twice a day is considered good for uvulitis. Many herbalists recommend honey because it helps in neutralizing toxicity.
Garlic contains allicin which is a powerful antimicrobial agent that can be beneficial for swollen uvula treatment. The best way is to take raw garlic. Take a few garlics, crush them and leave to stand for 15 minutes to allow the allicin to form. Mix crushed garlic with some honey for best effects.
Turmeric and ginger for swollen uvula
Turmeric spicy contains curcumin which is well-known anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agent. Ginger is also known for its anti-inflammatory benefits especially for respiratory infections. By combining turmeric and ginger anti-inflammatory properties will be added and may reduce swelling in the uvula.
Follow next steps for best results:
- Use 1 teaspoon of fresh ginger root and fresh turmeric root for every cup of water. You can also use 1/3 teaspoon of ground dried powder.
- Bring the water to boil and then add the ginger and turmeric. Let it gently to simmer for 10 minutes. If powder is used then boil it for 5 minutes
- You can also add a teaspoon of coconut oil as it promotes curcumin absorption
- Allow to cool. You can also add a few ice cubes to reduce swelling
- Gargle the mixture and let it stay in your mouth for about 15 seconds.
Basil tea for swollen uvula
For many years, the benefits of drinking basil tea have been proven. Simply place the basil in the hot water and try and drink 2-3 cups daily. It will reduce soreness and inflammation.
Belladonna and wormwood homeopathy for swollen uvula
Belladonna and wormwood are homeopathic remedies that can be helpful in the case of uvulitis. However, there are risks of consuming this remedy, so it’s absolutely essential to speak with a herbalist before consuming.
“Ecchymosis – Definition, Types, Symptoms, Causes, Diet and Treatments, Pictures“