Contents
- What is Alpha lipoic acid?
- What are different names for Alpha lipoic acid?
- What is Alpha lipoic acid used for?
- Alpha lipoic acid molecular formula, class and weight
- How alpha lipoic acid works in the body?
- Alpha lipoic acid side effects
- Precautions and warnings during alpha lipoic acid use
- Is alpha-lipoic acid powerful antioxidant? (High evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid for diabetic neuropathy (Very high evidence)
- What is the mechanism of action of alpha lipoic acid efficacy in diabetes neuropathy?
- Can Alpha lipoic acid improve insulin sensitivity in patients with diabetes? (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid for diabetic nephropathy (more evidence needed)
- Alpha lipoic acid for HbA1c reduction in patients with diabetes (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid for weight reduction (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid for cardiovascular complications prevention (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for hypertension (Very High)
- Alpha lipoic acid for dementia, Alzheimer disease and cognitive decline (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid for Parkinson disease (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Multiple sclerosis (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Glaucoma (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Cataracts (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Migraine prevention (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Pain relieve (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for heavy metal and toxic products poisoning (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Amanita mushroom poisoning (Low evidence)
- Is alpha lipoic acid good as a sport supplement? (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for high cholesterol (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for ulcers and inflammatory bowel disease (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Osteoarthritis (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Osteoporosis (Low evidence)
- Is alpha lipoic acid beneficial for the skin? (Low evidence)
- May alpha lipoic acid fight cancer? (Low evidence)
- May alpha lipoic acid increase life span? (Low evidence)
- May Alpha lipoic acid fight HIV-infection? (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for polycystic ovary syndrome (Low evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for Takotsubo syndorme (Low evidence)
- Can ALA reduce side effects of antipsychotics? (Low evidence)
- Can alpha lipoic acid be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
- Can alpha lipoic acid improve sense of smell? (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha lipoic acid use for burning mouth syndrome (Low evidence)
- How much alpha-lipoic acid should I take?
- Can patients with hypothyroidism take ALA safely?
- Can I take alpha lipoic acid with insulin or oral antidiabetics together?
- Can I take alpha lipoic acid and biotin together?
- Can I take alpha lipoic acid and Levothyroxine together?
- What are the best food sources of alpha lipoic acid?
- What should I know about alpha lipoic supplements?
- What is the difference between Racemic (R/S mixture) and R- ALA supplements?
- What are most common branded ALA supplements?
What is Alpha lipoic acid?
Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is an organosulfur compound which is well known to its anti-oxidative properties. It is derived from octanoic acid and normally produced in animals. This compound is essential for aerobic metabolism. As an antioxidant it helps fighting free radicals, which are the molecules that are able to cause cell damage.
ALA may also help the body be more sensitive to insulin thus it is recommendable in diabetes treatment. Naturally it can be found in many foods including: yeast, broccoli, spinach, potatoes, and organ meats such as kidney orliver. Alpha lipoic acid is also manufactured and is commonly available as a dietary supplement known for its antioxidant properties. Most common names for ALA are: Biletan, Lipoicin, Thioctan,
It should be known that alpha-lipoic acid benefits are not certain, and there is a need for bigger and relevant studies to prove its effectiveness in treating any medical condition. Medicinal use of this product has not been approved by the FDA. Thus Alpha lipoic acid should never be used in place of medication prescribed for you by your doctor.
What are different names for Alpha lipoic acid?
Alpha lipoic acid is also known as: α-lipoic acid, lipoic acid, thioctic acid, acetate replacing factor and thioctan.
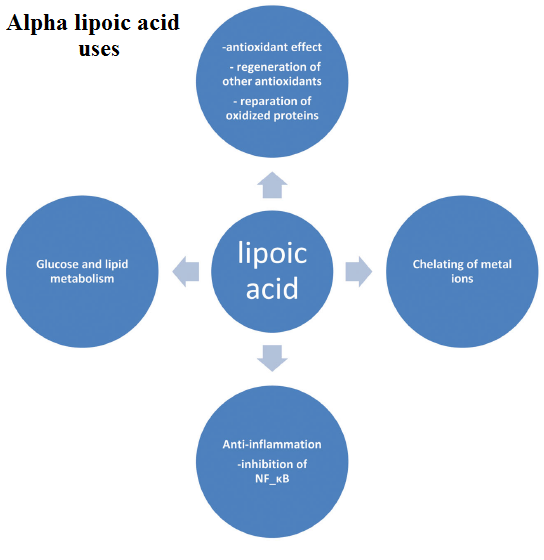
What is Alpha lipoic acid used for?
There are no FDA approved indications for alpha lipoic acid. However, there are reports about effectiveness for many different conditions, especially for diabetic nephropathy. Thus, alpha lipoic acid is used as an alternative medicine for different conditions such as:
- Diabetic nerve pain
- Lowering blood sugar
- Weight loss
- Vitiligo
- Complications after coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Alzheimer’s disease and dementia
- Alcoholic liver problems
- Altitude sickness,
- HIV-related brain problems
- Eye problems caused by diabetes
- Glaucoma
- Migraine
- Cardiovascular issues
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Anti-aging of the skin
- Leg pain caused by sciatic nerve damage or peripheral artery disease (PAD)
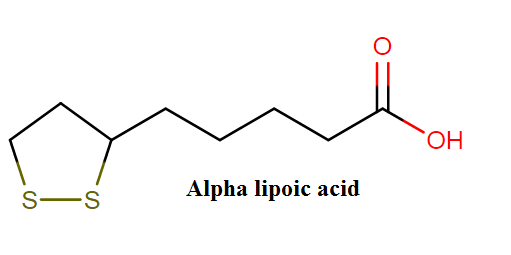
Alpha lipoic acid molecular formula, class and weight
Alpha lipoic acid belongs to the class of organic compounds known as lipoic acids and derivatives. These are molecules containing a lipoic acid moiety or octanoic acid derivatives which are made of a pentanoic acid or derivative attached to the C3 carbon atom of a 1,2-dithiolane ring.
Alpha lipoic acid molecule:
Alpha lipoic acid molecular formula: C8H14O2S2
Alpha lipoic acid 3D molecule:
Alpha lipoic acid molecule weight: 206.33 g/mol
How alpha lipoic acid works in the body?
Alpha lipoic acid is known as an anti-oxidant substance, mostly involved in reactions of keto-acid oxidative decarboxylations and is presented as a growth factor in some organisms. Alpha lipoic acid exists in enantiomer form of the R-enantiomer and the S-enantiomer.
For amino acid compounds, R-enantiomer is biologically active, but for alpha lipoic acid it has been showed that the S-enantiomer supports the reduction of the R-enantiomer when a racemic mixture is given. Some studies have been proposed that the S-enantiomer is actually an inhibitor of the R-enantiomer, and works by reducing biological activity and actually producing the oxidative stress rather than reducing it.
Additionally, the S-enantiomer has been noted to reduce the gene expression of GLUT-4s in cells which are responsible for glucose uptake and lowering insulin sensitivity. Alpha lipoic acid is able to pass the blood-brain barrier into brain and it can be used for mercury detoxification attached to the brain cells.
Alpha lipoic acid side effects
ALA is found in foods and is produced by the body in small quantities. Although not all side effects are described yet, because there are no relevant or controlled-randomized studies, alpha-lipoic acid is thought to be possibly safe when taken as directed. However ALA supplements are not free from side effects.
The most common, however very rare side effects of ALA are:
- abdominal pain
- diarrhea
- constipation
- nausea
- vomiting
- a skin rash
Stop taking alpha lipoic acid and call your doctor immediately if you experience:
- low blood sugar, hunger, headache, weakness, confusion, irritability, sweating, dizziness, fast heart rate, or feeling jittery; or
- a light-headed feeling, like you might pass out
Get emergency medical help if you experience symptoms of allergic reaction such as:
- hives
- difficult breathing
- swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat
Precautions and warnings during alpha lipoic acid use
Before using alpha lipoic acid supplements on your own, talk with your doctor or pharmacist if you have or ever had:
- liver disease
- diabetes
- thyroid disorder
- thiamine deficiency
- alcohol dependency
- It is not known whether alpha-lipoic acid is safe during pregnancy.Do not use this product without medical advice if you are pregnant
- It is not known whether alpha-lipoic acid passes into breast milk or if it could harm a nursing baby.Do not use this product without medical advice if you are breast-feeding a baby.
- Do not give ALA supplement to a child without the advice of a doctor
Is alpha-lipoic acid powerful antioxidant? (High evidence)
Alpha lipoic acid is able to neutralize free radicals which are associated with oxidative cellular damage. Both alpha lipoic acid (ALA) and its reduced form, dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA), work as extra and intracellular antioxidants and support vitamin C and E recycling. ALA and DHA are able to scavenge different free radical-reactive oxygen species.
Some of them are suspected to lead to endothelial dysfunction in patients with risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, lipoic acid stimulates the efficacy of other antioxidants such as coenzyme Q10 and glutathione, which are known as two essential anti-aging health-promoting compounds. Lipoic acid increases levels of GSH in tissues, which decline with age, by restoring glutathione peroxidase activity.
Alpha-lipoic acid also appears to be capable of chelating certain metals by forming stable complexes with Cu, Mn and Zn. Animal studies also showed that ALA may protect against arsenic and mercury poisoning. ALA may also reduce cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity. By preventing protein glycosylation and inhibition of the enzyme aldose reductase ALA may be also be beneficial for diabetes complications prevention.
Alpha lipoic acid for diabetic neuropathy (Very high evidence)
Alpha lipoic acid can be used as a possible alternative remedy to manage the pain related with diabetic polyneuropathy and there are good proofs for that.
Nerve damage or neuropathy is a common and potentially very serious complication of diabetes. Polyneuropathy involves the peripheral nerves of the body, and it is the most common form of neuropathy in patients with diabetes, that usually cause pain of the foot and leg. Polyneuropathy is also a major predisposed factor for diabetic foot ulcer, osteomyelitis, osteoarthopathy and lower limb amputation.
Diabetics may use alpha lipoic acid in supplemental form to help their neuropathy. This supplement is promising but you should always talk with your doctor first before using it. But, you should never discontinue any medicine for diabetes and start using ALA instead of it. ALA seems to be promise as a treatment for diabetic neuropathy, but it isn’t confirmed that it works. ALA’s effectiveness and safety can vary among patients with diabetes.
Here are some findings described below:
- One short-term study conducted on 24 diabetes mellitus type patients found improvement of the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy in those who use 1,800 mg per day of oral ALA during 3 weeks compared to patients who used a placebo.
- The other, double-blind-randomized, placebo-controlled study conducted on 181 patients with diabetic neuropathy found that oral supplementation with ALA in doses of 600 mg per day, 1,200 mg per day, or 1,800 mg perday of during 5 weeks considerably improved symptoms of neuropathy. 600 mg/day dose was as effective as the higher doses.
- The available findings also suggests that therapy with 600 mg per day of intravenous alpha lipoic acid for 3 weeks significantly releves the symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
- The benefit of long-term oral ALA supplementation is less known, there are some proofs suggesting that oral ALA may be helpful in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy when taken in doses 600-1,800 mg/day.
- Studies also showed that ALA can be also beneficial when taken in doses of 800 mg/day for the treatment of another neuropathic complication of diabetes called cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy which occurs in approximately 25% of diabetic patients when taken in doses of 800 mg/day.
In Germany, intravenous ALA is approved for use in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy.
What is the mechanism of action of alpha lipoic acid efficacy in diabetes neuropathy?
Alpha lipoic acid may increase reduced glutathione (GSH) levels which is an important antioxidant in the body. GSH and ALA seem to play important role in redox-dependent mechanisms of different cellular targets. Alpha lipoic acid is a potent free radical scavenger of peripheral nerve. This action can be very helpful in case of diabetes, as this condition is related with increased production and decreased clearance of free radicals.
Oxidative stress has been proposed to lead to oxidative nerve damage. Through the process of auto-oxidative glycosylation high blood glucose is considered as the main cause of increased free radicals production among diabetic patients.
The increased blood-glucose causes glycation of antioxidant enzymes and inactivation of the same. Except positive antioxidant effects, alpha-lipoic acid has extra actions such as promoting fiber regeneration and stimulating nerve growth factor.
Can Alpha lipoic acid improve insulin sensitivity in patients with diabetes? (Moderate evidence)
There is limited data that high doses of alpha lipoic acid supplementation may improve glucose utilization in patients with type 2 diabetes melitus. But there are some positive findings including:
- Studies showed that ALA can enhance glucose uptake by improving insulin sensitivity and may also prevent the destruction of beta cells in pancreas. When ALA was administered in rats, there have been shown increased insulin stimulated whole body glucose disposal and also in skeletal muscle. ALA also increased fatty acid oxidation and stimulated AMPK in skeletal muscles. Treatment with ALA in dose of 600 mg twice daily for 4 weeks increased sensitivity to insulin and prevented serum lactate/pyruvate-induced hyperglycemia
- A small study conducted on 13 patients with type 2 DM found that intravascular infusion of 1,000 mg of ALA improved insulin sensitivity by 50% compared to a placebo infusion. Another study which was placebo-controlled with 72 participants with type 2 DM found that ALA oral talbets used in doses of 600 mg/day, 1,200 mg/day or 1,800 mg/day improved insulin sensitivity by 25% after 4 of therapy. There were also no significant differences among the 3 doses of ALA, suggesting that 600 mg/day should be maximum effective dose.
- It has been also described that R-isomer of ALA may have better efficacy in improving insulin sensitivity than the S-isomer. In an animal studies, R-ALA given for 10 days increased uptake of glucose by skeletal muscle of obese rats by 65 %, compared to 29 % with S-ALA. Furthermore, R-ALA considerably reduced insulin levels in plasma by 17 %; whereas, S-ALA increased insulin levels by 15 %. According to this S-ALA produces insulin resistance. So, overall effect on ALA boosting insulin sensitivity may be the mixture of beneficial and no-beneficial of R-ALA and S-ALA.
However, the effect of oral alpha lipoic acid supplementation for chronic use has not been well studied. At present, it is not yet clear if oral or intravenous ALA treatment improves long-term glycemic control in individuals with type 2 of diabetes mellitus.
Alpha lipoic acid for diabetic nephropathy (more evidence needed)
One animal study proposed that alpha lipoic acid may be effective in the prevention of early glomerular kidney damage in patients with diabetes and may provide better protection than high doses of vitamin E or vitamin C.
Study conducted on diabetic rats either prevented or significantly increases clearance of albumin, and fractional albumin glomerular volume, and glomerular content of immunoreactive proteins. Moreover, it was found that ALA significantly increased renal-cortical glutathione levels.
Alpha lipoic acid for HbA1c reduction in patients with diabetes (Moderate evidence)
HbA1c or glycosylated hemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin that is measured primarily to identify the 3 month average plasma glucose levels. In patients with diabetes mellitus, higher levels of HbA1c may prognoses poorer control therapy control of glucose which may lead to serious complications with cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy and retinopathy.
Some studies have been shown that ALA supplementation may be beneficial for diabetic patients with increased levels of HbA1c:
- One study proved that hemoglobin glycation was reduced after ALA supplementation at doses of 90 mg when taken together with vitamin C at 250 mg and vitamin E at 200IU. However, the reduction in hemoglobin glycation was rejected 4 weeks after discontinuation of this therapy.
- Another study showed that ALA in doses of 300 mg, 600 mg, 900 mg or 1,200mg was effective in reducing HbA1c % and blood glucose during a period of 6 months in patients with diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- One study showed inefficacy of ALA when it was used 4 years in dose of 600 mg at daily basis. There were no important efficacy and prevention of diabetes showed compared to placebo. However, it was used as a racemic mixture of R-ALA and S-ALA. It is not known whether R-ALA may be more beneficial.
Alpha lipoic acid for weight reduction (Moderate evidence)
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid has been showed to inhibit AMPK (adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase) in the hypothalamus. AMPK is an enzyme that plays important role in cellular energy regulation. ALA is shown to work by mimicking a caloric surplus that may lead to the suppression of appetite. These properties may be secondary to increasing uptake of glucose into the hypothalamus, and are reversed upon AMPK activation in the hypothalamus.
- Another research found that alpha lipoic acid is able to inhibit the production of chemerin, a molecule that is related with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- Even without dieting, ALA can significantly improve fat and glucose metabolism. As a result, more of the sugars and fats in foods will be metabolized and used for energy instead of being stored as fat. This will also cause the consumer to feel the need to eat less.
- In obese patients with diagnosed type 2 diabetes, patients who were treated with ALA lost considerably more weight and had lower blood- triglyceride levels.
- When ALA was given to the rats during 14 weeks it was able to reduce body weight compared to placebo rats.
- One study conducted on obese or overweight patients accompanied with metabolic abnormalities such as metabolic syndrome investigated ALA use for obesity. ALA was given in doses of 1,200mg or 1,800mg in three daily doses before meals for 20 weeks. Studies showed significant decrease in weight in the patients receiving 1,800 mg when all groups were subject to a 600 kcal deficit.
- The other study on ALA use of 600mg for appetite reduction was conducted in schizophrenic patients and confirmed suppression of appetite with increased energy but had a very low sample size.
- Study on 24 obese individuals pre-diabetes who were receiving 1 g of ALA during 12 weeks found that those who used ALA without exercise had negative effects on ‘’bad’’ LDL-cholesterol levels despite increased anti-oxidant potential. However, those who also did exercise eliminated this effect.
- In several different studies conducted on overweight or obese individuals, lipoic acid showed mild but significant weight loss with a reduction in waist circumference
Alpha lipoic acid for cardiovascular complications prevention (Moderate evidence)
Endothelium is the inner lining of blood vessels that plays an important role in vascular disease. If endothelial function is impaired it may increase the risk for vascular disease. There are some findings that alpha lipoic acid can improve endothelial function by reducing oxygen-derived free radicals.
- One study showed that in adolescents with type 1 diabetes, alpha lipoic acid improved endothelial function
- Different studies propose the possible role of alpha lipoic acid in prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular disease. ALA can decrease atherosclerotic plaque formation and prevent LDL oxidation.
- ALA also promotes anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic activity and increases nitric oxide-mediated blood vessels vasodilatation in mild-moderate fashion. It has been also showed that alpha lipoic acid increases vasodilatation in response to acetyl holine.
- One study showed that ALA can reduce inflammatory markers in bloodstream, such as CRP and leukocyte count in healthy obese or overweight women independently of weight loss. It has been also showed that it can reduce NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses.
- Lipoic acid scavenges ROS, such as superoxide anions, may also regulate activity of NADPH oxidase activity and can prevent angiotensin II-induced monocyte, macrophages, and T cell infiltration
- It has been also found in adolescents and children with asymptomatic type 1 diabetes, ALA improved left ventricular function, proposing that it may be also helpful for prevention cardiomyopathy.
- Another study revealed that in aged type 2 diabetes patients complicated with acute brain infarction, ALA considerably reduced the patient’s oxidative stress, cholesterol and blood glucose levels
- Clinical studies have been also confirmed that alpha lipoic acid can reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides levels, but increases HDL (good) cholesterol
- In patients with diabetes type 2, ALA reduces concentrations of amino acid derivative ADMA – dimethylarginine. Elevated ADMA concetrations are known as predictor of cardiovascular events in diabetes 2 patients.
Alpha lipoic acid use for hypertension (Very High)
Many studies have showed that ALA may have useful effects in prevention of the hypertension development by lowering the amounts of the inflammatory cytokines in the blood, therefore preventing blood vessels pathological changes and normalizing changes in blood pressure.
Numerous clinical trials have been described that alpha lipoic acid can inhibit the overproduction one of the major vasoconstrictor endothelin. Additionally, ALA may significantly increase the synthesis of NO, the most potent vasodilator in the body.
- One Italian large cohort study investigated use of ALA in daily doses of 800mg in obese and pre-obese patients. Decreases in weight and blood pressure were noted.
- The other study found that when ALA was used in combination with Vitamin C and Vitamin E, ALA had no acute effect on reducing blood pressure, without exercise-induced beneficial changes in blood pressure.
- ISLAND study described that ALA at 300 mg per day was able to reduce serum pro-inflammatory markers after 4 weeks. Study also revealed vasodilation of the brachial artery although it was used with Irbesartan
- McMackin et al study showed that a combination of lipoic acid and acetyl-L-carnitine lowered blood pressure and improved the function of arteries.
However, clinical studies demonstrated that alpha lipoic acid is not so effective in lowering blood pressure when it is used as a monotherapy. However, it can more effectively reduce blood pressure when used in together with other drugs, antioxidants, and L-carnitine
Alpha lipoic acid for dementia, Alzheimer disease and cognitive decline (Low evidence)
Because alpha lipoic acid contains lipophilic structure, it is able to pass easily into the brain, and due to its antioxidant effects it may protect nerve tissue. Among various mechanisms, ALA may improve brain function by increasing the levels of glutathione.
Researchers are currently investigating it as a potential treatment brain conditions involving free radical damage, such as dementia and Alzheimer disease which are associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, and increased cholesterol levels. So far, there’s no relevant evidence to say whether or not it works, but here are some findings:
- Hager et al study from 2007 published in Journal of neural transmission showed that when lipoic acid was given in daily dose of 600 mg, during 1 year to patients with Alzheimer disease who were also receiving a standard treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors, it has been confirmed that the treatment led to a stabilization of cognitive functions and might delay the onset or slow down the progression of the disease. Since the study was not double-blinded, randomized, and placebo-controlled, it has been only suggested that treatment with ALA might be a successful ‘neuroprotective’ option for AD.
- Another study by Shinto et al published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s disease conducted on patients with Alzheimer disease and dementia, found that alpha lipoic acid slowed down the progression of the diseases. Also, a combination of omega-3 fatty acids and ALA cognitive and functional decline in patients with Alzheimer disease.
- Animal studies conducted on rats noted that ALA raises the level of acetylcholine and choline acetyltransferase and decreases the activity of acetycholinesterase (AchE) in the brain. All these actions are beneficial for both dementia and Alzheimer disease.
- Another animal study showed that ALA monotherapy or ALA combination with other antioxidants or L-carnitine, may improve memory in aged animals with age-related cognitive decline, including rats, mice and dogs. However, it is not clear whether oral ALA supplementation can slow cognitive decline in humans.
Alpha lipoic acid for Parkinson disease (Low evidence)
Parkinson’s disease in neurodegenerative and progressive disease characterized with the loss of dopaminergic neurons and reduced dopamine levels in the brain due to misfolded proteins, increased oxidative stress and inflammation, mitochondria dysfunction and poor autophagy.
As described above, ALA is able to pass into the brain and exhibit its neuroprotective properties. There are some studies describing benefits of ALA for eventual Parkinson disease treatment:
- Animal models on mice with Parkinson’s disease, described that ALA may protect dopaminergic neurons loss and thus improve motor dysfunction, but also it able to decrease accumulation of α-synuclein proteins in the substantia nigra of the brain. Furthermore, ALA is able to inhibit nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and reduce molecules related with inflammation.
- Zhang et al study described that concomitant use of R-alpha-lipoic acid and acetyl-L-carnitine utilizes efficient preventative effects in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease.
- Another study also found that lipoic acid is able to reduce neuronal death in laboratory models of Parkinson’s disease.
Alpha lipoic acid use for Multiple sclerosis (Moderate evidence)
Multiple sclerosis is a progressive demyelinating condition in which cover shields of nerve cells in the CNS are damaged. This damage may result in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, motor and sometimes psychiatric issues.
Due to its ability to pass into CNS, ALA has been showed as an effective anti-inflammatory agent. ALA therapy has been shown to inhibit the migration of leukocytes possibly by inhibiting enzymes called matrix metalloproteinases (MMP), and reducing the permeability of the blood-brain barrier.
- Lipoic acid was shown to have anti-inflammatory effect in patients with multiple sclerosis. This study described that ALA is able to reduce inflammation through the cAMP and Protein Kinase A signaling.
- Yadav et al pilot study proved that ALA can be useful in treating patients with multiple sclerosis by interfering with T-cell migration into the CNS, by inhibiting MMP-9 activity, and reducing both Th1 and Th2 cytokines.
- Animal models also showed that ALA is very effective at suppressing and treating multiple sclerosis in mice
- Another study, conducted by Russian scientsist found the ALA is able to reduce frequency of relapses in multiple sclerosis patients and as a result of this it may decrease corticosteroid use. Results were even better when other antioxidants were added.
- However, larger and long-term clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of LA in the treatment of Mltiple sclerosis
Alpha lipoic acid use for Glaucoma (Moderate evidence)
Alpha lipoic acid can be very effective for fighting oxidative stress in the eyes. There are some studies with positive results:
- In one study lipoic acid was administered to in patients with open-angle glaucoma at daily dosages of 75 mg for two months or 150 mg for one month. The best improvements of glaucoma and visual function were observed in the group receiving 150 mg of alpha lipoic acid.
- Animal studies showed that ALA inhibits cataract formation especially diabetes-associated cataracts
- Another study conducted by Tao et al described that ALA treatment improved vision-related quality of life in patients with dry age-related macular degeneration perhaps by enhancing antioxidant activity. Thus, ALA can be considered as a promising agent for the treatment of macular degeneration.
- ALA is also able to reduce retinal cell death in mice with retinis pigmentosa
Alpha lipoic acid use for Cataracts (Low evidence)
Animal studies discovered that ALA was able to inhibit the enzyme called aldose reductase in the rat lenses. This enzyme is known to have an important role in the development of cataracts in diabetes patients.
ALA was also able to inhibit cataract formation phamracologically induced by buthionine sulfoximine, which is an inhibitor of glutathione synthesis. ALA use maintained levels of glutathione, ascorbic acid, and alpha-tocopherol in the lens. It has been also found that R-ALA is more effective than S-ALA as a protection of cataracts developing.
Alpha lipoic acid use for Migraine prevention (Low evidence)
There are a lot of proposed mechanisms for migraine cause. One of various is that migraines are related with mitochondrial disorders and oxidative stress. Lipoic acid has both abilities
- Ahmed et al study showed that ALA improved the effectiveness and safety of migraine prophylactic drug topiramate. This combination has better frequency and duration of migraines reduction than the drug alone. In addition, lipoic acid helped topiramate-related side effects to be reduced.
- Another, randomized, double-blinded study conducted on patients with migraine, described that alpha lipoic acid has the ability to reduce the frequency, duration, and intensity of migraines.
Alpha lipoic acid use for Pain relieve (Low evidence)
Due to its antioxidant and potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties there are some studies showing ALA benefits for pain relieving.
- ALA seems to improve the quality of life in patients with neuropathic pain. Reduction of pain intensity, burning sensations, unpleasantness and superficial pain has been observed in patients with neuropathic conditions.
- Sciatic pain is a condition characterized by burning leg pain that most commonly comes from a herniated disc in the spine. Memeo and Loiero study showed that ALAdecreased sciatic pain caused by a herniated disc and also need for additional analgesia.
- Another study found that ALA reduced the incidence of postoperative pain in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Coadministration of ALA and gamma-linolenic acid – GLA reduced symptoms and functional impairment in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome
- Combination of ALA and superoxide dismutase improved pain control and the efficacy of physiotherapy in patients with chronic neck pain.
Alpha lipoic acid use for heavy metal and toxic products poisoning (Moderate evidence)
Due to its possibility to pass into the brain and chelate heavy metals, it has been discovered, however only in animal studies that ALA might have potential benefits for preventing heavy metal and other toxic materials poisoning.
- In vitro and animal studies have been proposed that alpha lipoic acid supplementation may have positive effects in the treatment of heavy metal toxicity, including toxicity involving mercury, lead, cadmium, or copper.
- Study on rats showed that ALA intraperitoneal injection of 25 mg/kg ALA given during a week able to considerably alter the oxidative stress induced by lead toxicity.
- Another study on rats demonstrated that ALA was able to protect hepatocytes from cadmium toxic doses by preventing loss in total glutathione levels and lipid peroxidation. Nevertheless, injection of ALA was able to prevent nerve damage caused by mercury poisoning by inhibiting lipid peroxidation.
- ALA has been shown to protect rats from developing hepatitis caused by copper poisoning.
- ALA has been also shown to be able to increase the effects of chelating compunds such as dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA)
- Lipoic acid protects againstPCB-induced testicular toxicity in male rats
- Dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) is known as a waste product from factories. Lipoic acid reduced kidney damage caused by DMN in male mice.
- Another study showed that ALA was able to reduce nicotine-induced lung and liver damage in rats
- There are also opinions that ALA is able to stimulate excretion of toxic metals
Alpha lipoic acid use for Amanita mushroom poisoning (Low evidence)
According to the reports, ALA intravascular infusions were used in the treatment of amanita mushroom poisoning in 75 patients between 1974 and 1978. Normally, up to 50 % of patients recover without intervention. However, 89 %, or 67 of 75 patients recovered after lipoic acid infusion. More studies are needed to prove that.
Is alpha lipoic acid good as a sport supplement? (Moderate evidence)
ALA may promote muscle regeneration after exercise. Short-term ALA supplementation may protect DNA and cells against oxidative stress induced by exercise, and therefore increase muscle regeneration. It has been also showed that:
- ALA supplementation reduced oxidative damagein the muscles of the men who perform muscle-damaging exercises, no matter whether they are trained or untrained.
- ALA protects DNA and fatty acids from oxidative stress due to exercise due to its antioxidant properties
- Lipoic acid helps shift chemicals inside the cells and cytokines towards favoring the regeneration of injured muscles.
- In physically active males, ALA was able to increase H2O2 and reduce NO production before or after exercise. 20 minutes after exercises, lipoic acid increases interleukins levels including IL-6and IL-10 levels and decreases IL-1β and TNF-α levels before and after exercise.
- Concomitant use of ALA and creatine improves muscle total creatine amount therefore those who want to gain muscle mass with creatine supplements may do it more efficiently with concomitant use with ALA
Alpha lipoic acid use for high cholesterol (Low evidence)
Alpha lipoic acid supplementation showed its efficacy in decreasing total cholesterol, free fatty acids, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol. ALA is also able to decrease proinflammatory markers and increased adiponectin, the protein involved in regulating fatty acids metabolism. Different studies showed that ALA significantly reduced free radicals and improve HDL cholesterol in men with metabolic syndrome.
Alpha lipoic acid use for ulcers and inflammatory bowel disease (Low evidence)
Due to its anti-inflammatory effects it has been proposed that ALA may be beneficial for ulcers and IBD treatment.
- As a supplement or a as medicine approved in some countries, ALA can be used to treat the ethanol – induced gastric ulcers.
- Animal study on mice with IBD showed that ALA suppresses following symptoms of diarrhea and inflammation, and may reduce colon lining injuries.
- Different studies also showed that ALA effectively lessens ulcerative colitis in mice, but, in one study in mice with mild ulcerative colitis, ALA actually increased oxidative damage to the colon.
Alpha lipoic acid use for Osteoarthritis (Low evidence)
Animal studies found that ALA decreased inflammation and ameliorated cartilage degeneration in rats with osteoarthritis.
Alpha lipoic acid use for Osteoporosis (Low evidence)
By impacting oxidative stress in age-related degenerative processes, such as postmenopausal bone loss, ALA may be used as an antioxidant defense in elderly osteoporotic women.
- In postmenopausal women with osteopenia, ALA slightly increased bone mineral density.
- Different laboratory studies showed that ALA inhibits inflammation induced bone loss
- In female rats with osteopenia, ALA not only stopped the bone loss, but it also stimulated its formation
Is alpha lipoic acid beneficial for the skin? (Low evidence)
El-Komy et al study described that 5% cubosomal ALA is an effective and safe modality for improving aging face. It has been also proposed that ALA may increase the thickness and decreased the roughness and photoaging of skin in older women. Yildirim Bas et al study found that ALA can reverse smoking-induced skin damage.
May alpha lipoic acid fight cancer? (Low evidence)
Studies in both in vitro cells and in vivo animal models have noted that ALA may inhibit the initiation and promotion stages of carcinogenesis, suggesting that ALA has considerable attention as a chemoprotective agent.
- ALA might be useful chemotherapeutic agent in the management or prevntion of obesity-related cancers according to Moon HS study.
- Recent study discovered that ALA might be beneficial in lung cancers, due to its suggested ability to affect ROS, O2·- and H2O2 in integrin regulation, anoikis and chemotherapeutic sensitizations. Another study also found that ALA may increase the susceptibility of lung cancer cells to cisplatin, etoposide and paclitaxel-induced cell death
- Li BJ, Hao XY, Ren GH and Gong Y discovered that ALA may promote paclitaxel inhibition of breast cancer cells proliferation
May alpha lipoic acid increase life span? (Low evidence)
Lipoic acid may improve lifespan by:
- Fighting free radicals. Aging and reduced longevity may be provoked by the action of free radicals.
- Rejuvenating function of mitochondria. Feeding old rats with L-carnitine and ALA for a few weeks showed beneficial result by restoring mitochondrial function and lowered oxidants to the level of young rats.
- Increasing telomerase. As we aged telomere becomes shorter. ALA may increase enzyme telomerase thus increasing telomere length and reversing the aging process.
In vivo and in vitro animal studies also found following:
- ALA extends the life span of flies and worms
- Lipoic acid may decrease or increase lifespan of mice, there are no good studies to confirm that
- A study showed that while lower doses of ALA increased the total life span in mice, high doses decreased it
May Alpha lipoic acid fight HIV-infection? (Low evidence)
ALA increased glutathione levels and improved or stabilized lymphocyte proliferation in patients infected with HIV with a history of unresponsiveness to highly active antiretroviral treatment.
Alpha lipoic acid use for polycystic ovary syndrome (Low evidence)
When ALA was used in combination with d-chiro-inositol, it does show some improvements in clinical and metabolic health in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Supplementation with myoinositol and lipoic acid improved reproductive outcome and metabolic profiles in women with polycisitc ovary syndrome undergoing in vitro fertilization
Alpha lipoic acid use for Takotsubo syndorme (Low evidence)
Takotsubo syndrome is a form of stress-induced heart muscle damage. There are some findings reporting that ALA treatment improves the innervation of adrenergic nerve cells in the hearts of patients with Takotsubo syndrome.
Can ALA reduce side effects of antipsychotics? (Low evidence)
It is known that weight gain and various metabolic issues are very problematic and common side effects of atypical antipsychotic drugs.
- Kim et al study showed that ALA can reduce BMI and total cholesterol levels in patients with schizophrenia patients using atypical antipsychotics.
- ALA also improved metabolic risk factors in schizophrenia patients. A study showed that lipoic acid increased adiponectin and decreased fasting glucose and AST levels.
Can alpha lipoic acid be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
It is not known if ALA use is safe during pregnancy, despite studies proving its benefits during pregnancy. So, always consult your doctor first before do anything on your own.
- In pregnancies with high risk, studies have been showed that ALA can speed up the return to normal pregnancy conditions and improve the conditions of both the mother and the fetus. Also, smaller number of miscarriages was recorded with ALA supplementation.
- ALA also decreased inflammation in women with gestational diabetes
- ALA also showed reduced cervical inflammation after a preterm labor episode
It is not known whether alpha lipoic acid passes into breast milk or if it could harm a nursing baby. Do not use this product without medical advice if you are breast-feeding a baby.
Can alpha lipoic acid improve sense of smell? (Moderate evidence)
Many patients found significant improvement in their ability to detect and differentiate odors during ALA supplementation. One study showed that 26% of participants used to have “moderate improvement” over the study period, 35% showed “remarkable improvement.” However in 30% olfactory function remained unchanged while 9% exhibited a further decline in function.
Overall improvement was better in the younger individuals than in elderly (60+) patients. This study was placebo-uncontrolled thus further studies are needed to confirm such effects, especially when it is known that spontaneous recovery may occur in some individuals. Results also indicate that alpha lipoic acid may be helpful in patients with olfactory loss caused by post upper respiratory tract infection.
Alpha lipoic acid use for burning mouth syndrome (Low evidence)
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a condition characterized by chronic stinging or burning sensation in the mouth which can be very painful. The true cause of BMS is still unknown, but according to some health professionals it is believed that it may be a peripheral neuropathy similar to those that are often seen in advanced cases of diabetes. Since lipoic acid is known to be effective in the treatment of nerve-cell damage, especially in diabetic neuropathy, it has been also proposed that it may be beneficial for threating BMS.
How much alpha-lipoic acid should I take?
Recommended oral therapeutic dosages ALA supplementation is from 600-1800 mg daily. Studies show that increased doses of ALA are also followed by increased side effects. One study determined that the evidence is convincing for the administration of 600 mg of ALA a day for 3 weeks on symptoms of diabetic neuropathy.
Can patients with hypothyroidism take ALA safely?
Patients with diagnosed thyroid diseases need to be careful while taking supplemental lipoic acid. Thyroid dysfunction can affect entire body, as the hormones secreted by it are used by all cells and organs. Alpha lipoic acid supplements taken in conjunction with supplemental thyroid hormones require a fair quantity of extra care.
The effect of ALA on peripheral conversion of the relatively inactive thyroxine or T4 to the active form triiodothyronine or T3 thyroid hormone in relation with serum lipid-protein-glucose levels has been inspected. ALA, when given in combination with thyroxine, suppresses the conversion.
The use of ALA and T4 separately does not affect cholesterol levels, but given together, they tend to reduce the conversion that is otherwise required. Total protein and albumin levels also decrease when both ALA and the thyroid supplement are given together.
As standalone supplements, both tend to increase blood glucose, but the same is not observed when given together. The net result is that although ALA may have a positive effect on metabolism, but when taken with thyroid supplements, it requires constant monitoring of hormone levels in the blood to avoid adverse effects.
The dual dosage of ALA along with thyroid supplements may also give an impression that the body is not reacting to the thyroid treatment being administered.
Can I take alpha lipoic acid with insulin or oral antidiabetics together?
There are evidences that ALA supplementation might improve insulin-mediated glucose utilization thus it is possible that ALA could increase the risk of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients who are using insulin or oral antidiabetic agents such as metformin, glyburide, glimepiride etc… Therefore, blood glucose levels should be closely monitored when ALA supplementation is taken with antidiabetic drugs.
Can I take alpha lipoic acid and biotin together?
Because of similar chemical structures between biotin and ALA, there is some evidence that high concentrations of intravascular given ALA can compete with biotin for transport across cell membranes. ALA injection given to the rats decreased the activity of two biotin-dependent enzymes by about 30%-35%. However, it is not known whether oral or intravenous ALA decreases biotin levels in human.
Can I take alpha lipoic acid and Levothyroxine together?
ALA supplements should not be taken together with Levothyroxine. Alpha lipoic acid may reduce the levels of thyroid hormone levothyroxine. Blood hormone levels and thyroid function tests need to be closely monitored in patients taking thyroid hormones who are also using alpha lipoic acid.
What are the best food sources of alpha lipoic acid?
R-lipoic acid occurs usually in foods where it is covalently bound to amino acid lysine in proteins making the chemical structure known as lipoyllysine. Although ALA is found in a various types of foods, precise quantitative data on of the LA or lipoyllysine content of food is is not well established.
Animal tissues such as kidney, liver, and heart are rich in lipoyllysine (~1-3 μg/g dry wt) while vegetables that are rich in lipoyllysine include spinach and broccoli. Tomatoes and peas are also good sources of lipoyllysine (~0.5 μg/g dry wt).
What should I know about alpha lipoic supplements?
In supplements ALA is in free form, it is not bound to proteins like in food. Additionally, the doses of ALA in supplements are in range of 200-600 mg and are about 1,000 times greater than the doses that can be found in food.
ALA is available as an oral dietary supplement and OTC product without a prescription in the US and most countries. In Germany, ALA injections are approved for the treatment of diabetic neuropathies and are available only by prescription.
Most ALA supplements are racemic (50/50) mixture of R-ALA and S-ALA. As described above, many studies claimed that R-ALA is effective and safer than S-ALA.
Therefore, supplements that claim to contain only R-LA are usually more expensive, which will be justifiably if the information regarding their purity is available. Since taking ALA with a food decreases its absorption, the recommendation is that ALA should be taken on an empty stomach of about one or two hours before or after meal.
What is the difference between Racemic (R/S mixture) and R- ALA supplements?
Racemic ALA supplements are mixture of R-ALA and S-ALA compounds in 1:1 ratio. So, the natural form of ALA is R-ALA isomer which is produced by animals and plants and works as a cofactor for mitochondrial enzymes in its protein-bound form with lysine. There is no study which directly compares R-ALA with S-ALA, but is has been noted that for some conditions R-ALA is more effective and safer than S-ALA form.
Also, after oral dosing with LA, peak plasma concentrations of R-ALA were found to be 40%-50% higher than S-ALA, suggesting R-ALA is better absorbed than S-ALA, but both isomers are rapidly metabolized and excreted.
As described, in rats, S-ALA was less effective than R-ALA in enhancing insulin-stimulated glucose transport skeletal muscle metabolism, and R-ALA shown to be more effective than ALA racemic mixture and S-ALA in preventing cataracts.
Since almost all of the published studies of ALA supplementation in humans have used racemic ALA, there is a need for a well-controlled study that will directly compare R-ALA and S-ALA. For now, it is not clear whether R-ALA supplements are more effective than ALA racemic or S-ALA supplements in humans.
What are most common branded ALA supplements?
There are a number of different ALA supplements worldwide. Some of the commonly used Brand names are:
- Alpha betic Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Nature’s Sunshine Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Solgar Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Bronson Laboratories Alpha Lipoic Acid
- NOW Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Spring Valley [Walmart] Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Country Life R-Lipoic Acid
- Olympian Labs Inc. Alpha Lipoic Acid Naturopathic
- Sundown Naturals Alpha Lipoic Acid
- GNC Alpha Lipoic Acid 600 mg
- Ortho Molecular Products Lipoic Acid
- Vitacost Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Jarrow Formulas Alpha Lipoic Sustain 300 with Biotin
- Pure Encapsulations Metabolic Xtra
- Vitamin World Alpha Lipoic Acid 200 mg
- Natrol Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Puritan’s Pride Alpha Lipoic Acid 300 mg
- Vitamin World Extra Strength Alpha Lipoic Acic
- Nature’s Bounty Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Radiance Platinum [CVS] Alpha Lipoic Acid
- Vitamin World Triple Strength Alpha Lipoic Acid
Some of the more expensive products were made with R-isomer-only alpha lipoic acid.
“how much vitamin B12 is too much? Can you overdose on vitamin B supplements?”
“Are prenatal vitamins really safe? Can you take prenatal vitamins if you re not pregnant?“