Contents
- What is Amoxicillin
- Amoxicillin generic and brand name
- What is Amoxicillin prescribed for
- Amoxicillin available strength and forms
- How does Amoxicillin work (mode of action)
- Recommended doses of Amoxicillin
- Adult dose
- Paediatric dose
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Amoxicillin
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Amoxicillin
- How to use Amoxicillin
- How to store the drug
- How to dispose the out of date Amoxicillin medicine
- Does Amoxicillin has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies
- Other uses of the drug
- What special dietary precautions should I follow
- What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Amoxicillin
- Amoxicillin side effects
- What should I do in case of overdose
- What should I do in case of missed a dose
- Amoxicillin drug interactions
- Does Amoxicillin have any interaction with diseases
- Where can I get more information
- Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
What is Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic that is used for the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections, skin and urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and strep throat.
Amoxicillin generic and brand name
- The drug is available under generic name Amoxicillin and commonly marketed under the brand name Amoxil.
- The drug Amoxicillin was developed by Beecham and initially manufactured and marketed by SmithKline Beecham.
- The drug became available in 1972 and was listed on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
- After the expiration of patent in 1998, many pharmaceutical companies started the manufacturing of Amoxicillin such as GlaxoSmithKline, Ranbaxy, Teva, and MiddleBrook Pharmas under various generic and trade names that include Amoxicilin, Amocla, Tycil, Trimox, Actimoxi, Trimox, Moxatag, Larotid and Alphamox.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Amoxicillin is a semi-synthetic, moderate spectrum, β-lactam class of
What is Amoxicillin prescribed for
- Amoxicillin plays a key role in the treatment of complications related to the bacterial infections such as bronchitis, pneumonia, gonorrhoea etc.
- The drug is also prescribed for treatments of skin infections, genitourinary tract infections, urinary tract infections and infections of ears, nose and throat .
- It is also recommended to treat the infections of Salmonella and Chlamydia, Lyme disease, Streptococcal pharyngitis and Tonsillitis.
- The drug is only indicated in the treatment of susceptible isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae,Streptococcus species, Staphylococcus , and Haemophilus influenzae. However, this drug does not provide any protection against flu, cold and other viral infections.
- Amoxicillin is also used in combination with Clarithromycin (Biaxin) to treat stomach ulcers caused by the infection of Helicobactor pylori.
- Amoxicillin is used as dual therapy in combination with Lansoprazole as delayed-release capsules in treatment of patients with pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease in patients who are allergic or intolerant to Clarithromycin or in whom resistance to Clarithromycin is known or suspected.
- Amoxicillin is also used as triple therapy forHelicobacter pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease in combination with Clarithromycin and Lansoprazole.
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
Amoxicillin chemically belongs to the class of organic compounds which are known as Penicillins containing penicillin core structure. Penicillin is characterized by penam ring bearing two methyl groups at position 2 and an amide group at position 6. The detailed chemical classification of Amoxicillin is described below:
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
| Class | Lactams |
| Sub Class | Beta lactams |
| Direct Parent | Penicillins |
Chemical information of the drug
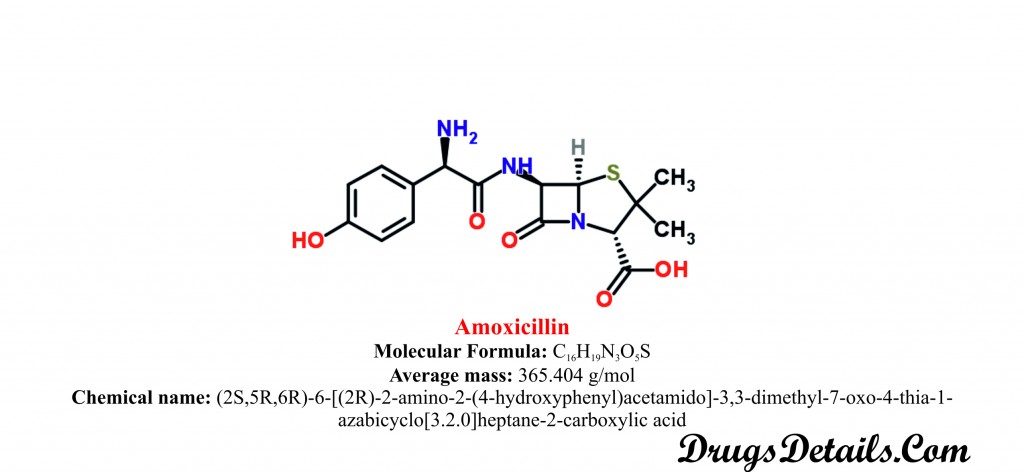
- Amoxicillin is a derivatives of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) and available as a trihydrate salt.
- It is a semi-synthetic aromatic heteropolycyclic antimicrobial agent with a molecular formula C16H19N3O5S.
- The molecular weight of the compound is 404 g/mol.
- Amoxicillin is available as a trihydrate salt and chemically known as (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
- Amoxicillin is white powder with sulphurous odour and has a water solubility of 958 mg/mL while Amoxicillin trihydrate is crystalline and off-white in color.
- Amoxicillin trihydrate is slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol and practically insoluble in fatty oils.
- The melting point of Amoxicillin is 194°C.
- Amoxicillin is available in capsule, tablet, chew able tablet and oral reconstituted suspension form for oral administration.
- Amoxicillin capsules are available in two different dosages of 250 mg and 500 mg.
- Body of capsule is pink in color while cap is royal blue in color.
- The capsule of 250 and 500 mg are imprinted with product name “AMOXIL” and “250” and “500” corresponding to different dosages of the drug respectively.
- Capsule contains Amoxicillin trihydrate as an active ingredient and gelatine, magnesium stearate, titanium dioxide, D&C Red no. 28, FD&C Blue No.1 and FD&C Red No. 40 as inactive ingredients.
- Amoxicillin tablets are available in two different dosages of 500 mg and 875 mg.
- Amoxicillin tablets are capsule shaped, pink in color, film coated debossed with “AMOXIL” centred over “500” and “875” corresponding to different dosages of the drug respectively.
- Amoxicillin tablets contain Amoxicillin trihydrate as an active ingredient and colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, sodium starch glycolate, magnesium stearate, titanium dioxide and FD&C Red no. 30 as inactive ingredients.
- Amoxicillin reconstituted suspensions are available in strength of 125, 200, 150 and 400 mg/ 5mL that contain 2.51mg, 3.39mg, 3.36mg and 4.33 mg sodium respectively.
- Amoxicillin reconstituted suspensions contains Amoxicillin trihydrate as an active ingredient and sodium citrate, sucrose, sodium benzoate, xanthan gum, silica gel, flavourings and FD&C Red No. 3 as inactive ingredients.
- Amoxicillin is also available in chewable tablet form in different strength of 125mg, 200mg, 250mg and 400 mg.
- 125 mg chewable tablet is round, mottled yellow in color, lemon-lime flavoured; biconvex that contains 125mg Amoxicillin and 31.25mg clavulanic acid.
- 200 mg chewable tablet is round, mottled pink in color, cherry-banana flavoured; biconvex that contains 200mg Amoxicillin and 28.50mg clavulanic acid.
- 250 mg chewable tablet is round, mottled yellow in color, lemon-lime flavoured; biconvex that contains 250 mg Amoxicillin and 62.50 mg clavulanic acid.
- 400 mg chewable tablet is round, mottled pink in color, cherry-banana flavoured; biconvex that contains 400 mg Amoxicillin and 57.0 mg clavulanic acid.
How does Amoxicillin work (mode of action)
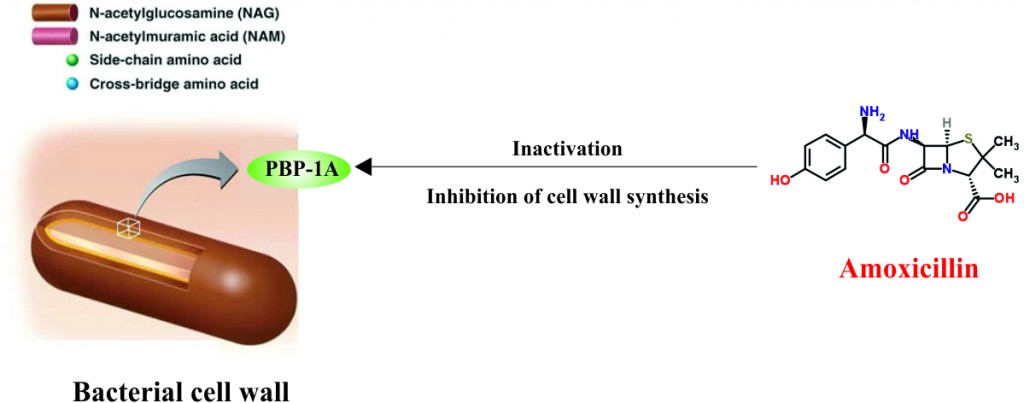
- Amoxicillin is bacteriolytic antibiotic (antibiotic that acts by dissolution or destruction of bacteria) that works against susceptible gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- Amoxicillin acts by inhibiting the biosynthesis of cell wall mucopeptide (protein polysaccharide component of bacterial cell wall) during bacterial cell multiplication.
- This results in inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis and ultimately death due to lysis of bacteria. In this view, amoxicillin is useful only for actively growing and cell wall synthesizing bacteria.
- In bacteria, Amoxicillin interacts and binds with penicillin-binding protein 1A (PBP-1A), which is positioned inside the bacterial cell wall.
- After binding Amoxicillin acylates (process of adding an acyl group) the penicillin sensitive transpeptidase C-terminal domain of PBP-1A by opening the lactam ring.
- Inactivation of PBP-1A enzyme prevents the development of a crosslink of two linear peptidoglycan strands.
- Cross-link formation is the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis which is necessary for the cell shape and cell division.
- Besides this, studies also suggest that Amoxicillin may interfere with autolysin inhibitors. Autolysin is bacterial cell wall autolytic enzyme that causes the lysis of bacterial cell.
- Amoxicillin is more effective against gram positive bacteria than gram negative bacteria.
Recommended doses of Amoxicillin
The recommended dose of the drug for adult is usually 500 mg thrice a day or 875 mg twice a day.Beside these, the dose of Amoxicillin varies depending upon the age and diseased state of the patient.
-
Adult dose
- Actinomycosis
- 500 mg thrice or 875 mg twice a day orally for six months.
- Anthrax prophylaxis
- 500 mg thrice a day orally.
- Bacterial endocarditis prophylaxis
- 2000 mg one hour prior to procedure orally.
- Bronchitis
- 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 7-10 days or 500-875 mg twice a day orally.
- Chlamydial infection
- 500 mg thrice a day orally for 7 days.
- Cutaneous Bacillus anthracis
- 500 mg thrice or 875 mg twice a day orally.
- Cystitis
- 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 3 to 7 days or 500-875 mg twice a day.
- Helicobactor pylori infection
- 1000 mg twice or thrice a day orally.
- Lymph disease
- Arthritis: 500 mg trice a day orally for 14-30 days.
- Carditis: 500 mg trice a day orally for 14-30 days.
- Erythema chronicum migrans: 500 mg trice a day orally for 14-30 days.
- Neurological: 500 mg trice a day orally for 14-30 days.
- Otitis media
- 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 10-14 days.
- Pneumonia
- 500 mg thrice a day or 875 mg twice a day orally for 7-10 days.
- Sinusitis
- 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 10-14 days or 500-875 mg twice a day orally.
- Skin infection
- 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 7-10 days or 500-875 mg twice a day orally.
- Tonsillitis
- 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 7-10 days or 500-875 mg twice a day orally.
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 7-10 days or 500-875 mg twice a day orally.
- Urinary tract infection
- 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 3 to 7 days or 500-875 mg twice a day.
- Actinomycosis
-
Paediatric dose
- Anthrax prophylaxis
- 80 mg/kg in divided dose orally in a day at every 8 hours.
- Bacterial endocarditis prophylaxis
- 50 mg/kg one hour prior to procedure.
- Cutaneous Bacillus anthracis
- 80 mg/kg in divided dose orally in a day at every 8 hours for only confirmed cases of cutaneous Bacillus anthracis.
- Otitis media
- 4 weeks to 3 months: 20-30 mg/kg in divided doses orally in a day (twice in every 12 hour).
- 4 months to 12 years: 20-50 mg/kg in divided doses orally in a day (twice or thrice in every 12 or 8 hour respectively).
- Pneumonia
- 40-50 mg/kg in a day in divided doses orally (thrice daily in every 8 hour).
- Skin infection
- 4 weeks to 3 months: 20-30 mg/kg in divided doses orally in a day (twice in every 12 hour).
- 4 months to 12 years: 20-50 mg/kg in divided doses orally in a day (twice or thrice in every 12 or 8 hour respectively).
- Tonsillitis
- 4 weeks to 3 months: 20-30 mg/kg in divided doses orally in a day (twice in every 12 hour).
- 4 months to 12 years: 20-50 mg/kg in divided doses orally in a day (twice or thrice in every 12 or 8 hour respectively).
- 12 years or older: 250-500 mg thrice a day orally for 7-10 days.
- Urinary tract infection
- 4 weeks to 3 months: 20-30 mg/kg in divided doses orally in a day (twice in every 12 hour).
- 4 months to 12 years: 20-50 mg/kg in divided doses orally in a day (twice or thrice in every 12 or 8 hour respectively).
- Anthrax prophylaxis
- Doses in patients with renal impairment
- CrCl 10-30 mL/min: 250-500 mg twice a day orally.
- CrCl >10 mL/min: 250-500 mg once a day orally
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Amoxicillin
- The usual dosing of the drug may vary depending upon the efficiency and side effects of the drug in a particular individual.
- Do not use the medicine if you are hypersensitive or allergic (e.g., anaphylaxis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome) to Amoxicillin or any other penicillin antibiotic such as Ampicillin, Dicloxacillin and Oxacillin.
- Amoxicillin is contraindicated with Chloramphenicol or other antibiotics and Probenecid (Benemid).
- Amoxicillin is also contraindicated with the use of birth control pills because Amoxicillin make birth control pills less effective.
- Consult to your doctor if you are allergic to the Cephalosporins such as Cefzil, Ceftin, Keflex and Omnicef.
- In case of patients with renal impairment specific recommendations and dosing of Amoxicillin should be adjusted accordingly, since the drug is primarily eliminated through the kidney
- Consult with your doctor and pharmacist if you are taking any prescription and non-prescription medications or herbal products.
- In paediatric population (neonates and young infants) dosing of Amoxicillin should be modified.
- Clinical studies with Amoxicillin were unable to identify any significant differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. However, higher sensitivity to Amoxicilline cannot be ruled out in older individuals.
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggested that after oral administration, Amoxicillin is rapidly absorbed in gastro-intestinal tract and has a bio-availability of approximately 95%.
- Following absorption, approximately 20% of the drug is bound to plasma proteins.
- It has been observed that following a 500 mg dose of the drug, maximum (or peak) plasma concentration (approximately 6 mg/L) is achieved with in 1-2 hours.
- The drug is metabolized in liver. Approximately 20-30% of the drug is metabolised into the penicilloic
- The average median half-life of Amoxicillin is 3 minutes.
- Approximately 80% of dose of Amoxicillin is mainly excreted in the urine of which 50-70% is uncharged (of administered dose) drug.
- The average steady state volume of distribution of the drug is 26-0.31 L/kg.
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Amoxicillin
- The Amoxicillin is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: B
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies the use of Amoxicillin in pregnant women is contraindicated and recommended only when benefit justifies the risk.
- Laboratory animal studies have revealed that the penicillin class antibiotics can penetrate through placenta but there is no evidence of adverse effect to fetus due to Amoxicillin.
- Following Amoxicillin administration in pregnant women, a temporary decrease in plasma concentration of total estriol-glucuronide, conjugated estriol, conjugated estrone, and estradiol has been noted.
- Studies support the excretion of the Amoxicillin into animal milk as well as in human milk. Therefore, breast-feeding is not recommended. It may lead to sensitization of infants.
- Despite these facts caution should be exercised when taking Amoxicillin.
How to use Amoxicillin
- Amoxicillin is available in capsule, tablets, chewable tablets and oral solution form for oral administration.
- Amoxicillin is also available in the paediatric drop form for oral use.
- The time duration between the drug uses should be 12 hours (twice daily use) to 8 hours (thrice daily use).
- Liquid and paediatric dose should be shaken well before every use.
- Amoxicillin tablets/capsules should not be chewed, split or crushed. Whole tablet/capsules should be swallowed.
- Chewable tablets must be crushed or chewed prior to swallowing.
- It is also recommended to take drug at almost the same time every day.
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet and take Amoxicillin exactly as directed.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor since the dosage is based on patient medical condition, treatment responses and usage with other drugs.
- Do not take more or less amount of the drug or during shorter or longer time then prescribed. Stopping Amoxicillin before time or too early may cause bacteria to become resistant to antibiotics
- Some of the brands of Amoxicillin may be taken with or without food. Care should be taken and check your medicine leaflet for proper instruction.
- During the course of drug, blood tests are always prescribed in order to check the kidney and liver function.
- If you have any queries about the drug immediately consult to your doctor to get information regarding any part you do not understand.
- It is advisable to inform your doctor if you are taking Amoxicillin. Amoxicillin sometimes may cause some unusual changes in certain medical tests.
- Do not share Amoxicillin with any other person, even if they have the same symptoms as you have.
How to store the drug
- Amoxicillin is stored at 25°C (77°F) and excursion permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
- Amoxicillin oral solution may be stored in refrigerator but should not be freezed.
- The drug should be kept away from children and pets.
- Medicine should not be stored in the bathroom.
- Store the medicine at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.
How to dispose the out of date Amoxicillin medicine
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used container.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- Parental drug products containing visible particulates should not be used and it is for single-use only, therefore, discard the unused portion.
- The drug Amoxicillin was approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 1974 to treat many types of bacterial infections such as pneumonia bronchitis, gonorrhoea and infections of ears, nose, throat, skin and urinary tract.
- In January 2008, FDA approved Moxatag – Amoxicillin PULSYS – for treatment of Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis in young people and adults.
Other uses of the drug
- Amoxicillin is also used for the prevention of Anthrax after exposure and treatment of Anthrax infection of the skin.
- Amoxicillin may also be used for other uses not listed here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special dietary precautions should I follow
- Take diet as prescribed by your doctor otherwise follow usual diet.
What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Amoxicillin
- Before taking Amoxicillin, tell your doctor about your medical history if you have kidney disease, liver disease, asthma, liver disease, mononucleosis (also called “mono”), a bleeding or blood clotting disorder, or any type of allergy, hay fever or hives.
- Take medical advice if you take medication of gonorrhoea.
- Antibiotic agent occasionally can cause diarrhea, sometimes it may be a sign of a new infection. In case if you develop diarrhea (watery or bloody), do not take anti-diarrhea medicine and immediately stop taking Amoxicillin and call your doctor.
- Amoxicillin therapy can reduce the effect/efficacy of birth control pills. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with your physician about alternate non-hormone method of birth control (i.e. diaphragm, condom, spermicide) to prevent pregnancy.
- Consult with your doctor if you have phenylketonuria (inherited disorder of impaired metabolism of phenylalanine).
- It is recommended to complete the entire course of the drug (full prescribed length of time) even if the symptoms improve before the infection is completely cleared.
- Do not stop taking Amoxicillin until you do not finish the prescription. If you do not follow the prescription or stop taking amoxicillin too early, it may lead to the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
- Consult with your doctor and pharmacist if you are taking any prescription and non-prescription medications or herbal products.
- Amoxicillin is an antibacterial agent therefore not effective against viral infection such as the flu or common cold.
- The drug is not recommended to be used in person who is allergic to penicillin and other beta lactam class of antibiotics.
- Amoxicillin use during pregnancy and breastfeeding does not show any harmful effect. However, it is recommended to consult with your physician while taking Amoxicillin during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Amoxicillin side effects
In addition to the associated benefits, Amoxicillin also is accompanied with the side effects some of which are more common, others less common whereas some that fade away with time while you take the drug. It is always recommended to consult a doctor if you encounter any of the side effects.
Some of the commonly occurring side effects but requiring medical attention is outlined as:
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
Sometime, it may cause serious side effects. Upon appearing of these symptoms stop taking the medicine and immediately talk to your doctor:
- Excessive tiredness
- Hives
- Lack of energy
- Pale skin
- Seizures
- Severe skin rash
- Unusual bleeding or bruising
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
Besides these, Amoxicillin may also be associated with some other side effects. These include:
- Nervous system effects: confusion, insomnia, dizziness, headache, reversible hyperactivity, agitation, anxiety, behavioral changes and aseptic meningitis.
- Immunological effect: vulvovaginal mycotic infection, mucocutaneous candidiasis.
- Dermatologic effects: erythematous maculopapular rashes, fixed drug eruption.
- Gastrointestinal effects: nausea, hemorrhagic colitis, pseudomembranous colitis, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhoea.
- Hematologic effect: anaemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, eosinophilia and granulocytopenia.
- Hepatic effect: jaundice, hepatic cholestatic, acute cytolytic hepatitis.
- Renal effect: crystalluria, acute interstitial nephritis.
- Respiratory effects: cough and rhinorrhea.
What should I do in case of overdose
- Try to avoid taking the overdose of the drug. If you overdose the drug contact with your doctor or pharmacist for symptomatic and supportive measures.
- In case you or some other person has taken overdose of this medication contact your local poison control center at 1-800-222-12×22 or emergency room immediately.
- Call local emergency services at 911 in case a patient collapses or faces difficulty in breathing.
What should I do in case of missed a dose
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule.
- Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind to not use a double dose to make up a missed dose.
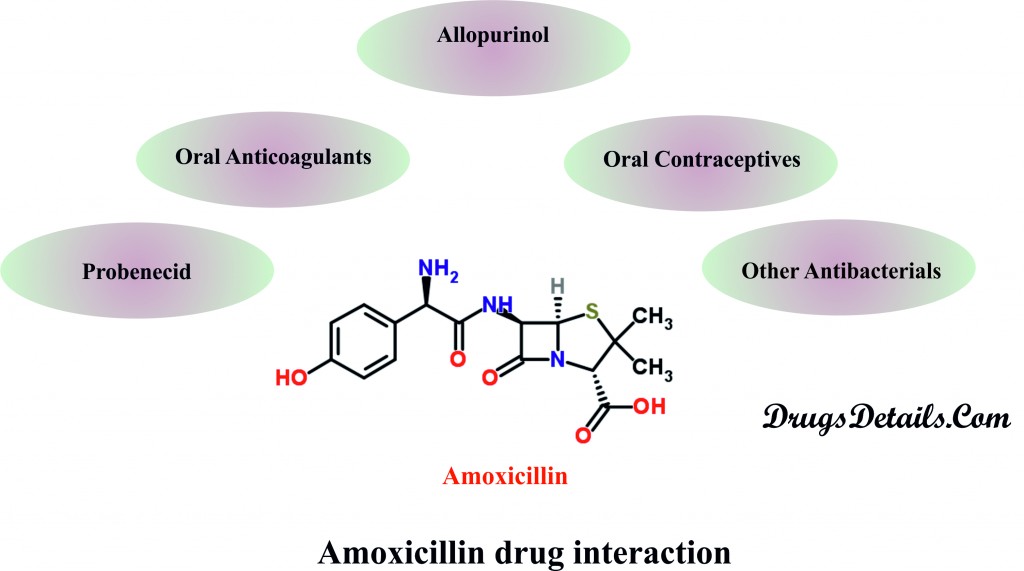
Amoxicillin drug interactions
The Amoxicillin may interact with one of the following drugs. Care should be taken when you are taking these medications together. It is advisable that you do not start, stop or change the medication by your own and without professional consult.
- Probenecid: Probenecid also known as Probalan, is a uricosurics medication that increases uric acid excretion in the urine. The drug effect decreases the renal tubular secretion of Amoxicillin and therefore maintains prolonged increased blood levels of Amoxicillin.
- Oral Anticoagulants: Oral anticoagulants are group of medicines that are used orally to prevent blood clot formations. It has been observed that patients receiving oral anticoagulants and Amoxicillin showed unusual long or prolonged prothrombin time (test that is used to check for bleeding problems. It measures how long it takes blood to clot.)
- Allopurinol: Clinical studies have suggested that simultaneous administration of Amoxicillin and Allopurinol cause rashes. Comparative studies using Amoxicillin alone or in combination with Alopurinol showed that incidence of rashes is higher in patients receiving both drugs as compared to patients receiving Amoxicillin alone. However, the potentiation of rashes by Amoxicillin is due to Allopurinol or the hyperuricemia present in these patients is not known.
- Oral Contraceptives: It has been observed that Amoxicillin treatment significantly affects the gut microbial flora. The gut microbial flora is involved in the hydrolysis of estrogen conjugates and thereby reduces the estrogen reabsorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Due to this, Amoxicillin also reduces the efficacy of combined oral estrogen/progesterone contraceptives.
- Other Antibacterials: In vitro studies suggested that some antibacterial drugs such as Sulfonamides, Macrolides, Chloramphenicol and Tetracyclines may interfere with bactericidal effects of penicillin. However, this observation is not clinically well documented.
Before starting the medication, it is recommended to inform your doctor or pharmacist about your medical history, all prescription and non-prescription and herbal products you may use.
Does Amoxicillin have any interaction with diseases
Chemically Amoxicillin is glucocorticoid steroid therefore it may interact with one or more than one of the following disease conditions.
- Renal Dysfunction: Amoxicillin is a beta-lactam class of antibiotics that are eliminated by kidney as sole drug or their metabolites. Therefore, in patients with impaired renal dysfunction the total serum concentration of beta-lactam antibiotics and their metabolites is comparatively higher with prolonged half lives. In some cases nephrotoxicity and alterations in renal function have been associated with the use of Amoxicillin and other beta lactam class of drugs. In this view, caution should be taken when prescribing Amoxicillin or any other beta-lactam class of drug to patients with renal impairment. Dosage adjustments and modifications are usually suggested and are typically based on severity of infection and the degree of renal impairment. Besides this, kidney function tests are recommended periodically during prolonged and/or high-dose Amoxicillin therapy.
- Mononucleosis: It has been observed that when patients with mononucleosis (diseased condition associated with abnormally high content of monocytes in the blood) are treated with Amoxicillin or any other Aminopenicillin antibiotic (particularly Ampicillin), they develop skin rashes (known as pruritic erythematous maculopapular). These rashes are possibly developed due to an immune-mediated process or drug metabolism and not by hypersensitive reactions. The rashes usually develop within 5-10 days following drug therapy and resolved (self limiting) within few days once therapy is discontinued. In this view, Amoxicillin and other penicillin derivatives (Aminopenicillin antibiotics) are usually avoided in patients with mononucleosis.
- Collitis: Colitis is a medical condition caused by inflammation of large intestine and associated with growth of unusal harmful bacteria (microbial infection) and range in severity from mild to life-threatening. The disease is associated with severe, persistent diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and passage of blood and mucus. It has been observed that colitis is occasionally caused by taking antibiotics and thus named as antibiotic associated colitis. Antibiotic therapy usually associated with reduced gut microbial flora, permits overgrowth of some of the harmful bacteria over normal gut flora. Clostridium difficile is one of such bacterial species that flourish well under antibiotic therapy. Its toxin is supposed to be a primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. The most common antibiotics that cause colitis are Lincomycin, Amoxicillin, Ampicillin (Aminopenicillins), Clindamycin, and Cephalosporins. Besides Clostridium, Pseudomembranous colitis has also been reported with broad spectrum antibacterial agents. Thus, antibiotic therapy with Amoxicillin and other broad-spectrum antibiotics agents should be managed cautiously in patients with a history of gastrointestinal diseases, particularly colitis. In such patients, antibiotic therapy should be discontinued immediately if significant diarrhea occurs and stool assay and large bowel endoscopy recommended to establish a definitive diagnosis.
- Anaphylactic Reactions: In some clinical observations abnormal fatal hypersensitivite (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported during Amoxicillin and other Penicillin antibiotics therapy. The anaphylactic reactions are more frequent in patients with a previous history of Penicillin hypersensitivity or sensitivity to multiple allergens. Most of cases of anaphylactic reaction are observed following parenteral therapy (dosage forms that are intended for administration as an injection or infusion). Therefore, careful examination and enquiries are necessary regarding patients history about hypersensitivity reactions to Penicillins, Cephalosporins, or other allergens. In case of allergic or hypersensitive reaction drug administration should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
- Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria: Antibiotic therapy of Amoxicillin in the absence of suspected bacterial infection and discontinuation of therapy before time or too early increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Where can I get more information
Your pharmacist or health care provider can provide more information about Amoxicillin.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- Studies indicate the effectiveness of Amoxicillin and Clavulanic acid taken orally over classical parenteral then oral sequence for treating acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in children.
- Pregnant women who are not able to tolerate erythromycin are generally recommended to take Amoxicillin for treating chlamydia infections.
- Amoxicillin in combination with Penicillin V are used for the treatment of early Lyme disease (an infectious disease that is caused by bacteria of the Borrelia type).
- Amoxicillin is advised in combination with Probenecid, and Penicillin G (parenteral) to treat the advanced stages of Lyme disease, (including arthritis, cardiac manifestations, and mild neurological manifestations) and also to treat gonorrhea (a sexually transmitted disease characterized by inflammatory discharge from the urethra or vagina) caused by Neisseria gonorrhoea.
- Amoxicillin has been recommended in combination with bismuth subsalicylate and metronidazole, in the treatment of peptic ulcer and gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori.
- Amoxicillin is used to treat bacterial pneumonia and urinary tract infections caused by susceptible organisms.
- Amoxicillin is currently also used for the treatment of typhoid fever caused by Salmonella typhi.
- Clinical studies in pregnant women do not demonstrate any risk to the fetus during first trimester or any risk in later trimesters.
- Studies indicate the attenuation of the effectiveness of oral contraceptive in women who take Ampicillin, Penicillin V and, Amoxicillin that results in unplanned pregnancy.
- In vitro studies indicate the mutual inactivation in case of simultaneous use of Penicillins (including Amoxicillin) with Aminoglycosides. Hence, concurrent use of these drugs requires their administration at different sites at interval of atleast 1 hour.
- Penicillins and Probenecid are most commonly used in combination for the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases or other infections requiring high and prolonged antibiotic serum and tissue concentrations.
- Both in vitro and in vivo studies suggest the combination of Amoxicillin or Ampicillin with Clavulanic acid or the combination of Amoxicillin or Ampicillin with Sulbactam resulting in enhanced activity against many strains of beta-lactamase-producing bacteria.
- Studies indicate the development of rashes in 1.4-10% of patients who receive Amoxicillin or Ampicillin treatment.
- The frequency of occurrence of adverse dermatologic effects, including rash, urticaria (a kind of skin rash characterized by pale red, raised, itchy bumps), erythema multiforme (an inflammatory skin eruption), and pruritus (severe itching of the skin) upon the administration of Aminopenicillin is substantially higher (about 10-fold) in patients suffering from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections as compared to other patients.
- Cases of acute interstitial nephritis have been associated rarely with the consumption of Ampicillin and Amoxicillin.
- Clinical studies indicate a significant (p < 0.0001) enhancement in the prevalence of low-birth-weight (< 2.5 kg) babies among users (9.6%) of the drug Amoxicillin in comparison to the nonusers (6.6%).
- Amoxicillin has also been recommended for the treatment of bronchitis, sinusitis and in prophylaxis of bacterial endocarditis caused by susceptible organisms.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
- DrugBank: Amoxicillin. http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01060
- Amoxicillin: MedlinePlus Drug Information. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a685001.html
- amoxicillin|C16H19N3O5S–PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/amoxicillin
- amoxicillin | C16H19N3O5S – Chemspider. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.31006.html
- Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amoxicillin
- Effect of amoxicillin use on oral microbiota in young children. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15273096
- Pubmed health.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0008968/
- Amoxicillin and amoxicillin plus clavulanate: a safety review. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19236222
- Common harms from amoxicillin: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials for any indication. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4284189/
- Adverse drug reactions related to amoxicillin alone and in association with clavulanic acid: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17449881
- Documenting Penicillin Allergy: The Impact of Inconsistency. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26981866
- Is amoxicillin-cotrimoxazole the most appropriate antibiotic regimen for listeria meningoencephalitis? Review of 22 cases and the literature. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8889993
- Amoxycillin: A review of its antibacterial and pharmacokinietic properties and therapeutic use. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1126306
- Antibiotics for acute maxillary sinusitis in adults. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24515610
- Antibiotic prescribing practices by dentists: a review. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2909496/
“Is it OK to take expired amoxicillin for a strep infection?“
“What does Fluocinonide treat?”
“Flonase and Sudafed interaction“