Contents
- What is Atorvastatin (Lipitor)?
- What is the generic and brand name of Drug?
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Why is this medication prescribed?
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug?
- Chemical information of the drug
- What is the available strength of the drug?
- How the medicine works (mode of action)?
- What are the recommended doses of Atorvastatin?
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Atorvastatin?
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug?
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Atorvastatin?
- How to use the drugs?
- How to store the drug?
- How to dispose the medicine?
- Does Atorvastatin has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies?
- Other uses of the drug.
- What special dietary precautions should I follow?
- What special precautions should I follow? / What should I avoid while using Atorvastatin?
- What are the possible side effects of this drug?
- What should I do in case of overdose?
- What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- Does Atorvastatin have any interaction with drugs?
- Does Atorvastatin have any interaction with Diseases?
- Where can I get more information?
What is Atorvastatin (Lipitor)?
Atorvastatin is an anticholesteremic pharmaceutical compound, which aids to reduce blood cholesterol and triglycerides (fatty acids) levels.
What is the generic and brand name of Drug?
- The drug is available under generic name Atorvastatin and brand name Lipitor.
- The drug was originally discovered by Bruce Roth and coworkers at Parke-Davis.
- Pfizer is responsible for the manufacture and distribution of Atorvastatin. During 1996-2012, Atorvastatin (Liptor) became the world’s best-selling drug and acquired more than US $125 billion.
- Pfizer’s patent expired in 2011 and then two other pharmaceuticals companies, Watson Pharmaceuticals and Ranbaxy Laboratories have started manufacturing of the Atorvastatin.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Atorvastatin is a synthetic (man-made) pharmaceutical anti-hyperlipidemic/ anticholesteremic drug commonly known as Statins.
Why is this medication prescribed?
- Atorvastatin is an anti-hyperlipidemic (lipid lowering) class of drug which reduces the amount of fatty or lipid substances such as cholesterol and triglycerides from the body.
- Usually, Atorvastatin is used in combination of low fat diet or exercise or other drugs as adjunctive therapy to reduce elevated total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood and to increase the amount of HDL (high-density lipoprotein; a type of fatty substance that decreases the risk of heart disease) in the blood.
- Atorvastatin is used in primary prevention in individuals with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) and as secondary prevention in individuals with CHD to decrease the risk of heart attack, stroke, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, and revascularization.
- The drug is usually prescribed for adult patients with primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb) and hypertriglyceridemia (Fredrickson Types IV).
- Atorvastatin is also prescribed for the treatment of dysbetalipoproteiemia (Fredrickson Types III) and combined hyperlipidemia.
- It is also used in prophylaxis of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with type II diabetes.
- Unique structure, hepatic selectivity and long half-life provide greater LDL-lowering potency to Atorvastatin in comparison with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. By decreasing LDL-C and TG and increasing HDL-C, Atorvastatin significantly lowers the risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug?
Atorvastatin chemically belongs to the class of organic compounds known as Diphenylpyrroles, a heterocyclic aromatic molecule which contains pyrrole ring attached to two phenyl groups. The detailed chemical classification of Atorvastatin is as follows.
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
| Class | Pyrroles |
| Sub Class | Substituted Pyrroles |
| Direct Parent | Diphenylpyrroles |
Chemical information of the drug
- Atorvastatin selectively brings about the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase.
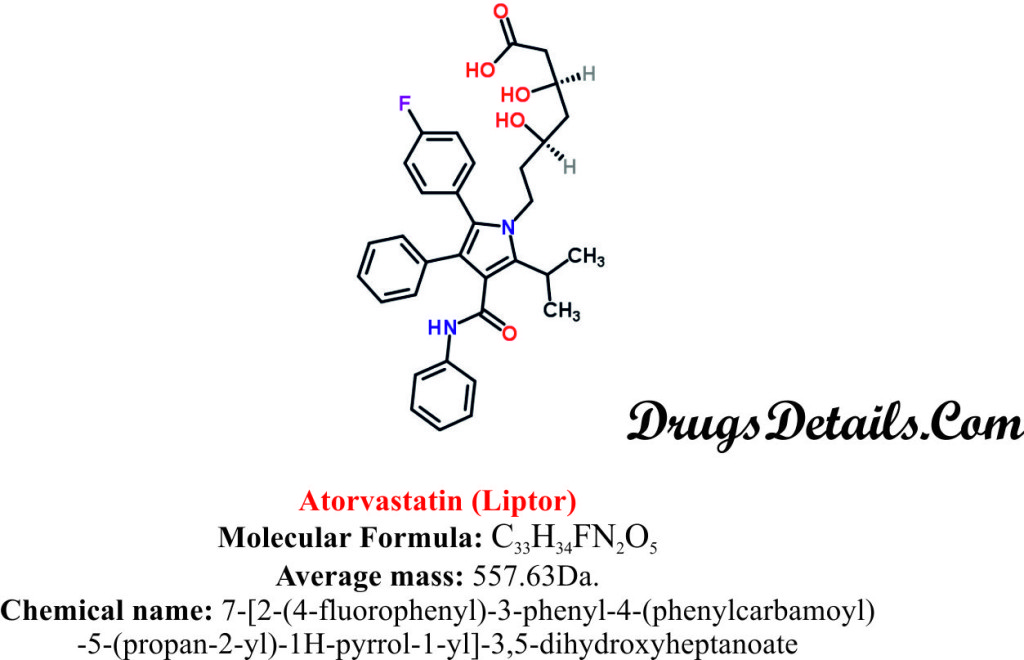
- Atorvastatin is a synthetic aromatic heteromonocyclic compound with a molecular formula C33H34FN2O5 and molecular weight of 63Da.
- Chemically, Atorvastatin is known as 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate.
- Atorvastatin is available as a calcium trihydrate salt known as Atorvastatin calcium.
- Atorvastatin calcium is chemically known as 7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate, calcium salt (2:1) trihydrate.
- Chemically Atorvastatin calcium is represented by the empirical formula of (C33H34FN2O5)2Ca•3H2O and molecular weight of 42 Da.
- Atorvastatin calcium is a white to off-white, crystalline powder and has a water solubility of 000495 mg/mL.
- Atorvastatin calcium is very slightly soluble in acetonitrile and distilled water, slightly soluble in ethanol while freely soluble in methanol.
- The melting point of Atorvastatin is 2-160.7°C.
What is the available strength of the drug?
- Atorvastatin is available for oral administration in tablet form.
- It is available in different dosage strength of 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg and 80 mg/tablet.
- The tablet is white in colour, film coated and elliptical in shape.
- Atorvastatin tablets of 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg and 80 mg are coded with “10”, “20”, “40” and “80” on one side responding to the dose of the drug and “PD 155”, “PD 156”, “PD 157” and “PD 158” on another side respectively.
- Each tablet contains Atorvastatin calcium as an active component and inactive ingredients such as calcium carbonate, USP; croscarmellose sodium, NF; candelilla wax, FCC; microcrystalline cellulose, NF; magnesium stearate, NF; hydroxypropyl cellulose, NF; lactose monohydrate, NF; Opadry White YS-1-7040 ((hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide); polysorbate 80, NF; simethicone emulsion.
How the medicine works (mode of action)?
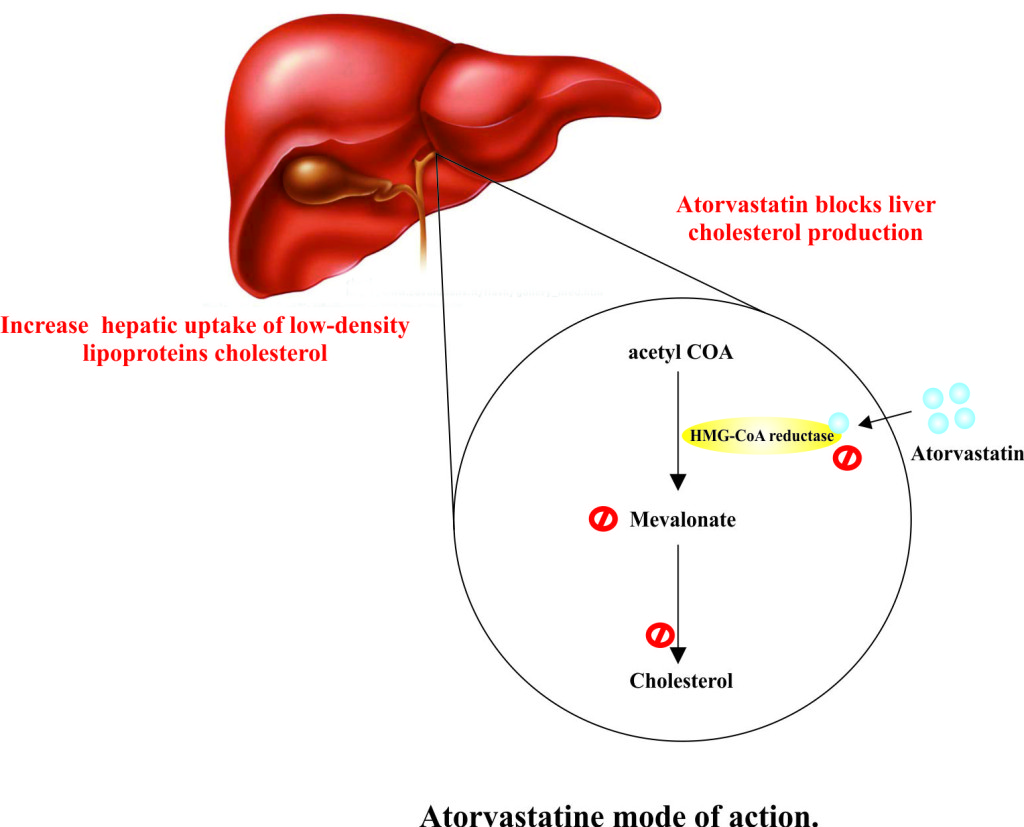
- Atorvastatin primarily acts in the liver, where it increases the hepatic uptake of dietary cholesterol and reduces the hepatic cholesterol levels and plasma cholesterol levels.
- Atorvastatin is a selective, competitive inhibitor of the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme of cholesterol biosynthesis pathway.
- HMG-CoA reductase is involved in the conversion of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A to mevalonate. It is the key rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis via the mevalonate pathway.
- Due to the inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, hepatic cholesterol level decreases which stimulate the upregulation of hepatic low-density lipoproteins cholesterol (LDL-C) receptors on cell surface.
- As a result hepatic uptake of low-density lipoproteins cholesterol increases and serum LDL cholesterol concentration decreases. Atorvastatin also decreases the level of very low density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C) and triglycerides (TG) and produce variable increase in high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and apolipoprotein A-1.
What are the recommended doses of Atorvastatin?
Atorvastatin is available in tablet form and the dosage varies depending upon the diseases status.
Adult dose:
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases:
- 10 mg-80 mg once a day orally.
- Primary hypercholesterolemia (heterozygous familial and non-familial):
- Initial dose: 10 mg-20 mg once a daily or 40 mg once daily for those patients who require large reduction in LDL-C.
- Maintenance dose: 10 mg-80 mg once a day depending on the condition of the disease.
- Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia:
- 10 mg-80 mg once a daily.
- Dyslipidemia (Fredrickson type IIa and IIb):
- Initial dose: 10 mg-20 mg once a daily.
- Maintenance dose: 10 mg-80 mg once a day depending on the condition of disease.
- Hypertriglyceridemia (Fredrickson type IV):
- Initial dose: 10 mg once a day.
- Maintenance dose: 10 mg-80 mg once a day.
- Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia (Fredrickson type III):
- 10 mg-80 mg once a day orally.
Paediatric dose:
- Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia:
- <10 years: Not recommended.
- ≥10 years: 10 mg once a day orally (maximum 20 mg).
- Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia:
- <10 years: Not recommended.
- ≥10 years: 10 mg-40 mg once a day orally.
However, the represented dose schedule can vary according to patient response and can change on the basis of repeated lipid determinations at 4 to 8 weeks interval. Treatment should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Atorvastatin?
- Do not use the medicine if you are allergic to Atorvastatin or any of the ingredients present in the Atorvastatin product.
- The use of Atorvastatin is contraindicated or temporarily withheld in case of severe renal impairment.
- The drug is also not recommended in patients with hepatic encephalopathy, hepatitis, cholestasis and jaundice.
- Atorvastatin is contraindicated with the use of drugs that decrease the level of endogenous steroid hormone such as Ketoconazole, Cimetidine and Spironolactone.
- Atorvastatin also contraindicated with HIV protease inhibitor drugs (Darunavir, Lopinavir, Ritonavir, Nelfinavir, Fosamprenavir, Saquinavir and Tiiprenevir), oral contraceptives and cholesterol lowering medications (Fenofibrate, Gemfibrozil and Niacin).
- Dose of Atorvastatin should be adjusted in medications that suppress immune system such as Cyclosporine, Rifampin, Telaprevir and Spironolactone.
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug?
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggested that after oral administration, Atorvastatin is rapidly absorbed and has a bio-availability of approximately 14% and systemic availability of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity is 30%.
- It has been observed that following a single dose of maximum (or peak) plasma concentration is achieved in 60-120 minutes in the fasted state.
- Following absorption the majority (>98%) of the drug is bound to plasma proteins.
- The drug is extensively metabolized to parahydroxylate and ortho derivatives and various beta–oxidation Atorvastatin metabolism is also facilitated by the hepatic enzyme CYP3A4.
- The average median half-life of Atorvastatin is 14 hours while on the other hand, due to the longer lived active metabolites, half-life of HMG-CoA inhibitory activity is 20-30 hours.
- Atorvastatin is primarily eliminated in the hepatic biliary excretion after hepatic or extra-hepatic metabolism and very little amount in the urine (<2%).
- The average steady state volume of distribution of the drug is 381
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Atorvastatin?
- The Atorvastatin is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: X
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies the use and safety of Atorvastatin in pregnant women is contraindicated and recommended only when benefit justifies the risk.
- Laboratory animal studies have revealed fetal abnormalities and positive evidence of fetus damage.
- No adequate data is available on excretion of Atorvastatin into human breast milk. However, the use of drug is not recommended in nursing mothers.
- Despite these facts caution should be exercised when taking Atorvastatin.
How to use the drugs?
- Atorvastatin is available in tablet form for oral administration by mouth with or without food.
- Atorvastatin tablets are not chewed, split or crushed. Whole tablet should be swallowed.
- It is advisable not to take more than one tablet daily.
- It is also recommended to take drug at almost the same time every day.
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet and take Atorvastatin exactly as directed by your health care professional.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor as your doctor may decrease the dose of Atorvastatin depending upon adverse side effects or medication response.
- If you have any queries about the drug immediately consult to your doctor to get explained any part you do not understand.
How to store the drug?
- Atorvastatin is stored at room temperature at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
- The container should be tightly closed and kept away from excess heat, direct sun light and reach of children.
How to dispose the medicine?
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used container.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
- Atorvastatin has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December, 1996.
- Atorvastatin is approved to treat medical complications such as primary hypercholesterolemia, mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb) and hypertriglyceridemia.
Other uses of the drug.
- Atorvastatin is also used in the patients with acute coronary syndrome and thrombotic stroke.
- Atorvastatin may also be used for other uses not listed here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more detailed information regarding its use.
What special dietary precautions should I follow?
- It is generally recommended to avoid high fat/cholesterol diet and follow a routinely exercise regimen.
- Follow a routine diet as prescribed by your dietician and avoid spicy foods.
- For more detailed information about the dietary plan please visit the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) website for additional dietary information at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/public/heart/chol/chol_tlc.pdf.
- Avoid grapefruit juice and drinking in large amounts while taking Atorvastatin.
What special precautions should I follow? / What should I avoid while using Atorvastatin?
- Consult with your doctor and pharmacist about what prescription and non-prescription medications, vitamins, and nutritional supplements you are taking or plan to take.
- Avoid the use of alcohol; it may increase the risk of serious side effects.
- Use of high fat and high cholesterol diet should be avoided.
- Inform your doctor if you are breastfeeding or pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- Grapefruit juice is also avoided because its components are known inhibitors of intestinal CYP3A4.
- Use of vitamin D supplements should also be avoided. These supplements reduce the concentration of Atorvastatin and active metabolites.
- Inform your doctor if you are alcoholic and have diabetes or hypothyroidism.
What are the possible side effects of this drug?
In addition to the associated benefits, Atorvastatin also is accompanied with the side effects some of which are more common, others less common whereas some that fade away with time while you take the drug. It is always recommended to consult a doctor if you encounter any of the side effects.
There are some adverse effects that disappear while consuming the drug with time. But, if any of them keep on persisting, consult your doctor.
Less commonly occurring side effects include:
- Back pain
- Constipation
- Excessive gas or belching
- Feeling of discomfort or illness
- Indigestion
- Lack or loss of strength and appetite
- Nausea
- Pain in abdomen or stomach
- Shivering
- Sleeplessness
- Stomach discomfort
- Sweating
- Vomiting
More common side effects include:
- Difficult or painful urination
- Headache
- Hoarseness
- Pain in lower back or side
- Runny nose
- Tenderness around the eyes and cheekbones
Some of the commonly occurring side effects that require medical attention is outlined as:
- Chest tightness
- Difficulty with swallowing
- Fast heartbeat
- Fever and cough
- Light-headedness
- Muscle cramps, stiffness, pain, swelling, or weakness
- Puffiness or swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes, face, lips, or tongue
- Skin rash and itching
- Unusual tiredness or weakness
Besides these, Atorvastatin may also be associated with some other side effects. These include:
- Cardiovascular effects: chest pain, angioneurotic edema, peripheral edema, haemorrhagic stroke.
- Dermatologic effects: rashes, dermatomyositis.
- Endocrine effect: gynecomastia, thyroid dysfunction, hypospermia, acid maltase deficiency.
- Gastrointestinal effects: constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
- Genitourinary effects: hematuria, erectile dysfunction, impotence and testicular pain.
- Haematological effect: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, haemolytic anemia.
- Hepatic effect: choestatic jaundice, fatty changes in the liver, cirrhosis, fulminant hepatic necrosis.
- Hypersensitivity effects: allergic reactions, chills, angioedema, anaphylaxis, flushing, dyspnea, epidermal necrolysis.
- Musculoskeletal effects: severe myopathy.
- Nervous system effects: headache, dizziness, fatigue, memory loss, vertigo, paresthesias, peripheral neuropathy, cranial nerve dysfunction, drowsiness, decline in cognitive function, peripheral nerve palsy.
- Ocular effects: ocular myasthenia, reversible ophthalmoplegia, blurred vision.
- Renal effects: rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure.
- Respiratory effects: pharyngitis, rhinitis, bronchitis, sinusitis.
What should I do in case of overdose?
- Overdose usually occurs when someone by mistake or deliberately takes more than the prescribed limit of this medication.
- If you overdose the drug contact with your doctor or pharmacist for symptomatic and supportive measures.
- Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule.
- Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind to not use a double dose to make up a missed dose.
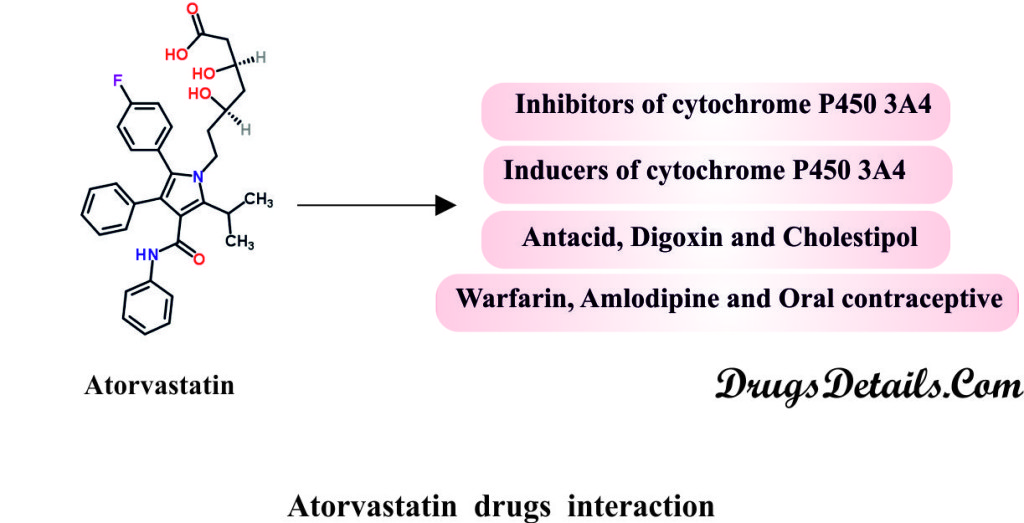
Does Atorvastatin have any interaction with drugs?
The concurrent use of Statin such as Atorvastatin with acid derivatives, lipid modifying doses of niacin, cyclosporine, or strong CYP 3A4 inhibitors (e.g. itraconazole, HIV protease inhibitors, and clarithromycin) is contraindicated.
- Strong Inhibitors of CYP 3A4: Cytochrome P450 3A4 brings about the metabolization of Atorvastatin. In presence of strong inhibitors of CYP 3A4, Atorvastatin plasma concentration is increased.
- Clarithromycin: Atorvastatin exposure is significantly increased when given concomitantly with Clarithromycin as compared to that of Atorvastatin alone.
- Itraconazole: Atorvastatin AUC gets significantly enhanced with concomitant administration of LIPITOR 40 mg and Itraconazole 200 mg. Therefore, in patients taking Itraconazole, caution should be used when the LIPITOR dose exceeds 20 mg.
- Combination of Protease Inhibitors: Co-administration of the drug with a variety of combinations of HIV protease inhibitors and also hepatitis C protease inhibitor Telaprevir causes an increase in the Atorvastatin AUC. It is, therefore, recommended to avoid the use of Atorvastatin in patients consuming HIV protease inhibitor Tipranavir and Ritonavir, or the hepatitis C protease inhibitor Telaprevir. Caution is required while taking HIV protease inhibitors Saquinavir plus Ritonavir; Darunavir plus Ritonavir; Lopinavir plus Ritonavir; Fosamprenavir, or Fosamprenavir plus Ritonavir.
- Cyclosporine: Atorvastatin and Atorvastatin-metabolites are substrates of the OATP1B1 transporter. Inhibitors of the OATP1B1 (e.g., Cyclosporine) can increase the bioavailability of Atorvastatin. In cases where co-administration of LIPITOR with cyclosporine is necessary, the dose of LIPITOR should not exceed 10 mg.
- Rifampin or other Inducers of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Co-administration of Atorvastatin with inducers of cytochrome P450 3A4 such as Efavirenz, or Rifampin may bring about variable reductions in Atorvastatin plasma concentrations. It is usually recommended to co-administer Atorvastatin and Rifampin simultaneously to avid reduction in the plasma levels of Atorvastatin.
- Oral Contraceptives: Concomitant use of Atorvastatin and an oral contraceptive causes a rise in AUC values for Norethindrone and Ethinyl estradiol. Hence, careful selection of the oral contraceptive is required for the women who are taking Atorvastatin.
- Colchicine: Co-administration of Atorvastatin with Colchicine results in increased cases of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis and caution should be exercised when prescribing these drugs together.
- Digoxin: The steady state plasma concentration of Digoxin gets increased by 20 % in cases of multiple co-administration doses of Atorvastatin and Digoxin. Hence, patients taking Digoxin should be monitored appropriately.
- Grapefruit Juice: The grape juice contains one or more components that inhibit CYP 3A4 and can increase plasma concentrations of Atorvastatin, especially with excessive grapefruit juice consumption (>1.2 liters per day).
- Warfarin: Atorvastatin shows no clinically significant effect on prothrombin time when given to patients who are receiving warfarin treatment.
- Niacin: Dose adjustment is required in case of concomitant use of Atorvastatin and Niacin due to the enhanced risk of skeletal muscle effects.
- Gemfibrozil: Atorvastatin may result in an increased risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis when co-administered with Gemfibrozil. It is therefore recommended to avoid the use Atorvastatin when the patient is taking Gemfibrozil.
- Other Fibrates: Atorvastatin use should be done very cautiously in case of co-administration with Gemfibrozil or other fibrates as the risk of myopathyis greatly enhanced.
Does Atorvastatin have any interaction with Diseases?
Before you begin to take Atorvastatin, it is necessary to discuss any medical condition or allergies you have or any other significant medical fact. It has been observed that following conditions may interact with Atorvastatin:
- Geriatric population: Older people have higher levels of Atorvastatin in plasma as compared to young ones. Hence, the chances of lowering of LDL at any dose are greater in older ones in comparison to young population.
- Gender: Although the plasma concentration of Atorvastatin varies between men and women but the LDL-C lowering effect of the drug do not show clinically significant difference.
- Pediatric population: The effect of the drug has not been evaluated in the pediatric population.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Atorvastatin brings about inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase and thereby decreases the synthesis of cholesterol and other biologically active components obtained from cholesterol which are essential for fetal development. The drug is therefore contraindicated in pregnant women and nursing women as it may harm the fetus.
- Hemodialysis: Hemodialysis in patients of advanced renal dysfunction does not significantly enhance the clearance of the drug Atorvastatin due to its extensive binding to the plasma proteins.
- Renal Insufficiency: No dose adjustment is required in patients suffering from renal dysfunction as the condition neither influences the plasma concentration nor the LDL-C lowering effect of Atorvastatin.
- Hepatic Insufficiency: Plasma concentration of Atorvastatin and its exposure time is greatly enhanced in the patients with hepatic dysfunction.
- Liver Dysfunction: Atorvastatin causes biochemical abnormalities of liver function by bringing about an increase in serum transaminases and hence should be used with caution in patients with liver disease.
- Endocrine Function: Atorvastatin interferes with cholesterol synthesis and decreases adrenal and/or gonadal steroid production. The drug does not lower basal plasma cortisol concentration or impair adrenal reserve. No adequate data is available on the effects of Atorvastatin on male fertility. Atorvastatin should be administered cautiously in case of concomitant use with drugs that decreases the levels or activity of endogenous steroid hormones including cimetidine, spironolactone, and ketoconazole.
- CNS Toxicity: Brain hemorrhage and optic nerve vacuolation have been observed in animal studies. However, no CNS lesions were seen in mice and rats after chronic treatment for a period of 2 years at doses of 400 mg/kg/day or 100 mg/kg/day respectively. Other members of this class of drug or a chemically similar drug have been associated with CNS vascular lesions and optic nerve degeneration respectively in dogs.
- Skeletal Muscle: Atorvastatin has been associated with rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of muscle tissue leading to the release of muscle fiber in the blood stream), myalgia (muscle pain) and myoglobinuria (presence of myoglobin in the urine). Atorvastatin therapy should be stopped promptly in case of elevation of CPK (creatine phosphokinase) levels or myopathy.
- Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility: In vivo studies in rats represent 2 rare types of muscle tumors namely, rhabdomyosarcoma and, fibrosarcoma. Similar studies in mice have shown cases of liver adenomas and liver carcinomas. However, in vitro studies do not show any mutagenic or clastogenic effect.
Where can I get more information?
Your pharmacist can provide more information about Atorvastatin.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug.
- Clinical studies indicate the effectiveness of Atorvastatin in bringing about reductions in cardiovascular events in patients with and without Coronary heart diseases (CHD).
- Studies indicate the use of high-dose of Atorvastatin in arresting and reversing the progression of atherosclerosis.
- Clinical studies in diabetic patients showed the decrease in the occurrence of stroke, acute CHD events, and coronary revascularizations via Atorvastatin.
- Atorvastatin has also been found to be effective in decreasing nonfatal myocardial infarctions and fatal CHD in hypertensive patients.
- Clinical trials indicate the effectiveness of high doses of Atorvastatin in reducing risk of stroke in patients with prior cerebrovascular events, benefiting patients suffering from recent acute coronary syndrome, and in slowing cognitive decline in preliminary studies of Alzheimer’s patients.
- Studies indicate the association of Atorvastatin with decreased progression of mild chronic kidney dysfunction and no significant benefit in patients on hemodialysis with advanced renal dysfunction.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases.
- Drug Bank information. http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01076
- Wikipedia information. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atorvastatin
- Atorvastatin | C33H35FN2O5 | ChemSpider. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.54810.html
- Atorvastatin: MedlinePlus Drug Information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a600045.html
- atorvastatin | C33H35FN2O5 – PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/atorvastatin
- Clinical pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14531725
- Lipid lowering efficacy of atorvastatin. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23235655
- An overview of the clinical safety profile of atorvastatin (lipitor), a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9521221
- Atorvastatin efficacy in the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular events. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17910519.