Contents
- What is Carvedilol
- Carvedilol brand and generic name
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)
- What is the drug carvedilol used for
- Carvedilol chemical structure
- Chemical information of the drug
- Carvedilol available strengths
- How carvedilol works
- What is the usual dose of Carvedilol
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Carvedilol
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Carvedilol
- How to use carvedilol
- Storage condition of carvedilol
- How to dispose the expired medicine
- Does Carvedilol has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies
- Other uses of the drug
- What special dietary precautions should I follow
- What special precautions should I follow? /What should I avoid while using Carvedilol?
- Carvedilol side effects
- Carvedilol overdose
- Carvedilol missed dose
- Carvedilol drug interactions
- Does Carvedilol have any interaction with Diseases
- Where can I get more information
- Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
What is Carvedilol
- Carvedilol is an antihypertensive drug that is used for the treatment of congestive heart failure and high blood pressure.
Carvedilol brand and generic name
- The drug is available under generic name Carvedilol and various brand names such as Coreg, Coreg CR, Carvil, Dilatrend, Kredex, Eucardic and
- Carvedilol was discovered by Fritz Wiedemann.
- Initially GlaxoSmithKline was responsible for the manufacturing of Carvedilol.
- Carvedilol is also manufactured and marketed by various pharmaceutical companies such as Cipla, Roche and Zydus Candila pharmaceuticals.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)
- Carvedilol is a synthetic (man-made) pharmaceutical antihypertensive/vasodialator agent.
What is the drug carvedilol used for
- Carvedilol plays a key role in the treatment of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF).
- Carvedilol is also used for the treatment of the hypertension and high blood pressure.
- Carvedilol is prescribed for the treatment of angina pectoris.
- It is also prescribed to treat the patients who have had a heart attack.
- Carvedilol is also used in combination with other drugs to treat other heart or blood pressure related problems.
- Carvedilol reduces cardiac output in normal subjects; exercise or isoproterenol induced tachycardia and also reduces reflex orthostatic tachycardia.
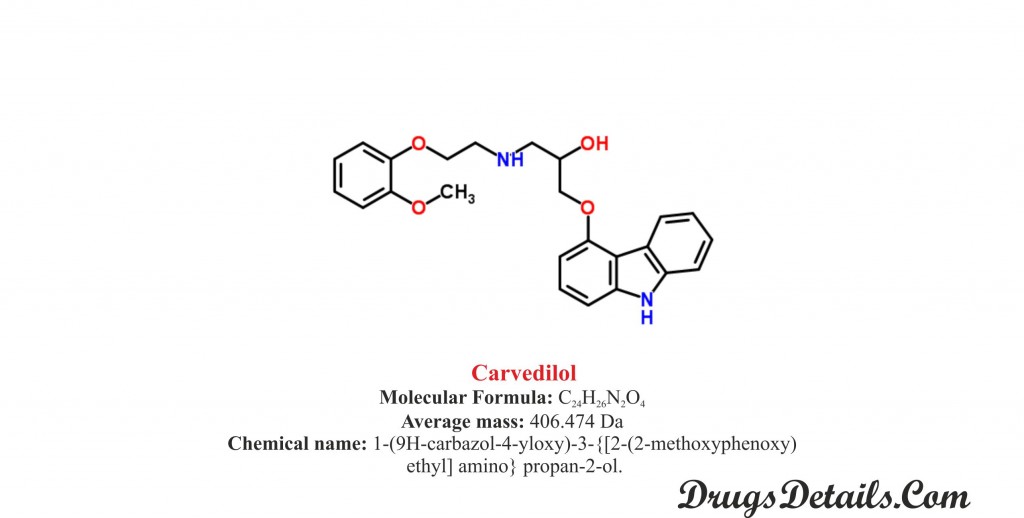
Carvedilol chemical structure
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug.
Carvedilol chemically belongs to the class of organic compounds which are known as Carbazole characterized by three ring system which consist of a pyrrole ring fused on either side to a benzene ring. The detailed chemical classification of Carvedilol is described below:
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
| Class | Indoles and derivatives |
| Sub Class | Carbazoles |
| Direct Parent | Carbazoles |
Chemical information of the drug
- Carvedilol is available as a phosphate salt (in form of controlled release tablets) as well as in parental form (in form of immediate release tablets).
- It is a synthetic pharmaceutical aromatic heteropolycyclic compound with a molecular formula C24H26N2O
- The molecular weight of the compound is 4742 g/mol.
- Chemically, Carvedilol is 1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-{[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy) ethyl] amino} propan-2-ol.
- Carvedilol is white to off-white in color, powder and has a water solubility of 00444 mg/mL.
- Carvedilol is slightly soluble in ethyl ether, sparingly soluble in isopropanol and ethanol, soluble in methylene, chloride and methanol and freely soluble in dimethylsulfoxide.
- It is practically insoluble in water, gastric and intestinal fluid.
- The melting point of Carvedilol is 5°C.
Carvedilol available strengths
- Carvedilol is available in controlled-release capsules and immediate release tablets for oral administration.
- Carvedilol (COREG®) tablet is available in different dosage strength of 125 mg, 6.25 mg, 12.5 mg and 25 mg/tablet.
- The Carvedilol (COREG®) tablets are white, oval, and film-coated engraved with “SB” and “39”, “4140”, “4141”, or “4142” respectively.
- Carvedilol (COREG®) contain Carvedilol as active ingredient and lactose, hypromellose, sucrose, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, polysorbate 80, polyethylene glycol, povidone and titanium dioxide as inactive ingredients.
- Carvedilol controlled release (COREG CR®) capsule is available in different dosage strength of 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg and 80 mg/tablet.
- Carvedilol controlled release (COREG CR®) capsules are supplied as:
- 10 mg: capsule shell is white and green printed with “GSK COREG CR” and “10 mg”.
- 20 mg: capsule shell is white and yellow printed with “GSK COREG CR” and “20 mg”.
- 40 mg: capsule shell is yellow and green printed with “GSK COREG CR” and “40 mg”.
- 80 mg: capsule shell is white printed with “GSK COREG CR” and “80 mg”.
- Carvedilol controlled release (COREG CR®) hard gelatine capsule contains Carvedilol phosphate as an active ingredient and microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, magnesium stearate, hydrogenated castor oil and hydrogenated vegetable oil as inactive ingredients coated with methacrylic acid copolymer.
How carvedilol works
- Carvedilol is a non-selective blocker of beta-adrenoreceptors (β1 and β2) and alpha-adrenergic receptor.
- The beta-adrenoreceptor blocking activity is present in S(-) enantiomer and alpha-blocking activity is present in both R(+) and S(-) enantiomers at equal potency.
- Decrease in the heart rate, myocardial contractility and myocardial oxygen demand is due to the beta-adrenoreceptor blocking ability of Carvedilol while decrease in systemic vascular resistance is due to the alpha-adrenergic receptor blocking activity.
- Carvedilol and its metabolites have ability to restore the inotropic responsiveness to Ca2+ in OH– free radical treated myocardium.
- It also prevents the OH– radical-induced decrease in sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ -ATPase activity.
- Carvedilol is also a calcium channel antagonist which plays a prominent role in certain peripheral vascular beds such as cutaneous circulation and may be responsible for increasing the blood flow.
- As a result of these properties, Carvedilol may be advantageous in chronic heart failure by preventing free radical damage.
What is the usual dose of Carvedilol
The prescribed dose of Carvedilol varies depending upon the age and diseased state of the patient.
Adult dose
- Congestive heart failure
- Immediate release tablets
- Initial dose:125 mg twice a day orally or 14 days.
- Maintenance dose: increased up to 6.25 mg twice a day orally.
- Controlled release capsule
- Initial dose: 10 mg once a day orally for 14 days.
- Maintenance dose: increased gradually up to 80 mg once a day orally.
- Immediate release tablets
- Hypertension
-
- Immediate release tablets
- Initial dose:25 mg twice a day orally with food.
- Maintenance dose: 25-25 mg twice a day orally with food (maximum 50 mg/day).
- Controlled release capsule
- Initial dose: 20 mg once a day orally for 7-14 days.
- Maintenance dose: increased gradually up to 80 mg once a day orally after 7-14 days.
- Immediate release tablets
- Left ventricular dysfunction
- Immediate release tablets
- Initial dose:25 mg twice a day orally for 3-10 days.
- Maintenance dose: increase dose to 12.5 mg and then after 3-10 days, 25 mg twice a day orally.
- Controlled release capsule
- Initial dose: 20 mg once a day orally for 3-10 days.
- Maintenance dose: increase dose to 40 mg and then after 3-10 days, 80 mg once a day orally.
- Immediate release tablets
- Angina pectoris
- Initial dose: 25 mg twice a day orally with food.
- Maintenance dose: increased up to 25mg twice a day orally with food (maximum up to 50 mg).
- Hepatic patients: not recommended for the patients with liver failure or cirrhosis.
- Initial dose: 25 mg twice a day orally with food.
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Carvedilol
- The usual dosing of the drug may vary depending upon the efficiency and side effects of the drug in a particular individual.
- Do not use the medicine if you are allergic to Carvedilol or any of the ingredients present in the Carvedilol product.
- Carvedilol is contraindicated in patients with bronchial asthma, second or third degree AV block, severe bradycardia or patients with cardiogenic shock.
- It may not be used in patients with severe hepatic impairment, hyperthyroidism, low blood pressure and prinzmental’s angina (chest pain during rest with no understandable cause)
- Carvedilol is contraindicated with the use of other drugs such as Cimetidine, Clonidine (Catapres, Kapvay), Cyclosporins (Sandimmune, Neoral), Digoxin (Lanoxin), Diltiazem (Cartia, Cardizem, Taztia), Fluoxetine (Sarafem, Prozac), Insulin, Paroxentine, Propafenone, Quinidine, Reserpine, Rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane) and Verapamil (Calan).
- Carvedilol is also contraindicated with medication of diabetes and monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors such as Isocarboxazid (Marplan), Phenelzine (Nardil) and Selegiline (Zelapar, Eldepryl).
- Consult with your doctor if you are having surgery as well as dental surgery.
- Carvedilol is not used for the patients under 18 year age (not recommended for paediatric patients).
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggested that after oral administration, Carvedilol is rapidly and extensively absorbed and has a bio-availability of 25%-35% due to first pass metabolism.
- It has been observed that following a single dose of maximum (or peak) plasma concentration (476 ng/mL) is achieved in ~90 minutes in the fasted state.
- Following absorption the majority (98%) of the drug is bound to plasma proteins primarily with albumin.
- The drug is mainly metabolized by the hepatic enzyme CYP450 2D6 and CYP450 2C9 through aromatic ring oxidation and glucuronidation. Some other enzymes are also involved in the metabolism such as CYP450 1A2, CYP450 2A19, CYP450 3A4, and CYP450
- These oxidative metabolites are additionally metabolised by conjugation through glucuronidation and sulfation.
- After the hydroxylation and demethylation at the phenol ring, three active metabolites with beta-receptor blocking activity are produced.
- The average median half-life of Carvedilol is 7-10
- Carvedilol is primarily excreted in the feces (60%) and urine (16%) in the form of metabolites and less than 2% dose is excreted as uncharged drug in the urine.
- The average steady state volume of distribution of the drug is 115
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Carvedilol
- The Carvedilol is classified by US FDA pregnancy category:
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies the use of Carvedilol in pregnant women is contraindicated and recommended only when benefit justifies the risk.
- Laboratory animal studies have shown fetotoxicity and teratogenicity but there is no evidence in human pregnancy.
Studies support the excretion of the beta-blockers (including Carvedilol and its metabolites) into animal (rat) milk. However, no studies are available for its excretion in human breast milk. Despite these facts caution should be exercised when taking Carvedilol.
How to use carvedilol
- Carvedilol is available in controlled release capsule and immediate release tablet forms for oral administration with food.
- Controlled release capsule should be taken once a day in morning time with food.
- Immediate release tablet should be taken twice a day with food.
- Controlled release capsule should not be chewed, split or crushed, but to be swallowed as a whole.
- It is also recommended to take the drug at almost the same time every day.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor as the dosage is prescribed depending upon adverse side effects or medication response.
- If you have any queries about the drug immediately consult your doctor to clarify any part you do not understand.
Storage condition of carvedilol
- Carvedilol is stored at room temperature 25°C (77°F).
- Brief excursion period is permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
- Store the medicine away from direct sunlight, excess heat and moisture.
- The drug should be kept away from children and pets.
How to dispose the expired medicine
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used medication.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company for proper disposal.
- Carvedilol has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September, 1995 for the treatment of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF).
- Carvedilol controlled release formulation was also approved by US Food and Drug Administration in October 2006.
Other uses of the drug
- Carvedilol is also used in the treatment of left ventricular dysfunction.
- Carvedilol may also be used for other uses not listed here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more detailed information regarding its use.
What special dietary precautions should I follow
- Take diet as prescribed by your doctor otherwise follow usual diet.
What special precautions should I follow? /What should I avoid while using Carvedilol?
- Consult with your doctor and pharmacist about all prescription and non-prescription medications, vitamins, and nutritional supplements you are taking or plan to take.
- Before taking Carvedilol, tell your doctor about your medical history preferentially if you have any kind of lung disease, asthma or other breathing problems, liver disease.
- Consult to your doctor if you have thyroid problem, diabetes and pheochromocytoma (rare, catecholamine-secreting tumor of adrenal gland).
- Carvedilol medication should not be stopped suddenly and avoid to skip the dose.
- Alcohol consumption is avoided for 2 hour before and 2 hour after you take Carvedilol.
- It may cause dizziness, fainting or light-headedness during quickly getting up from lying position. Therefore, it is advisable to get up slowly to avoid this problem.
- Avoid using machinery requiring alertness or clear vision as well as driving because the use of Carvedilol may make you feel tired and dizzy.
Carvedilol side effects
In addition to the associated benefits, Carvedilol also is accompanied with the side effects some of which are more common, others less common whereas some that fade away with time while you take the drug. It is always recommended to consult a doctor if you encounter any of the side effects.
Most common side effects caused by Carvedilol are as follows:
- Allergy
- Tightness and pain in chest, discomfort, or heaviness
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting
- Generalized swelling or swelling of the feet, ankles, or lower legs
- Shortness of breath
- Slow heartbeat
- Weight gain
There are some adverse effects that fade away while consuming the drug with time. These symptoms do not require any medical attention, but if these symptoms persist immediately contact to your doctor.
- Burning, numbness or tingling in the arms or legs
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Dizziness
- Dry eyes
- Headache
- Joint pain
- Light-headedness
- Nausea
- Tiredness
- Vision changes
- Vomiting
- Weakness
Carvedilol may cause some serious side effects that require immediate medical help:
- Fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Weight gain
- Swelling of the arms, hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs
- Chest pain
- Slow or irregular heartbeat
- Rash
- Hives
- Itching
- Difficulty in breathing and swallowing
Besides these, Carvedilol may also be associated with some other side effects. These include:
- Cardiovascular effects: hypotension, myocardial ischemia, bradycardia, syncope, edema, postural hypotension, tachycardia, hypertension, bundle branch block, peripheral ischemia, hypovolemia.
- Dermatologic effects: pruritus, rashes, photosensitivity, exfoliative dermatitis and alopecia.
- Endocrine effects: hypoglycaemia including extreme thirst, frequent urination, extreme hunger, blurred vision.
- Gastrointestinal effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastro-intestinal pain, periodontitis and melena.
- Haematological effects: thrombocytopenic and non-thrombocytopenic purpura, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis, decline of platelet adhesiveness, anemia, decreased prothrombin, hypovolemia, pancytopenia, leucopenia and atypical lymphocytes.
- Hypersensitivity effects: allergy, anaphylactoid reaction, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, and hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions, angioedema, and urticaria.
- Hepatic effects: increased hepatic enzymes, elevation in serum transaminases.
- Nervous system effects: dizziness, headache, hyperthesia, paresthesia, neuralgia, hypokinesia and sweating increased.
- Ocular effects: blurred vision, abnormal vision.
- Renal effects: renal insufficiency (low systemic blood pressure) and albuminuria.
- Respiratory effects: cough, dyspnea, asthma, lung edema, bronchospasm, dyspnea.
Carvedilol overdose
What should I do in case of overdose?
- If you overdose the drug contact with your doctor or pharmacist for symptomatic and supportive measures.
- Symptoms of Carvedilol overdose may include:
- Slow heart beat
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Difficulty in breathing
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
Carvedilol missed dose
What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule.
- Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose.
- Keep in mind to not use a double dose to make up a missed dose.
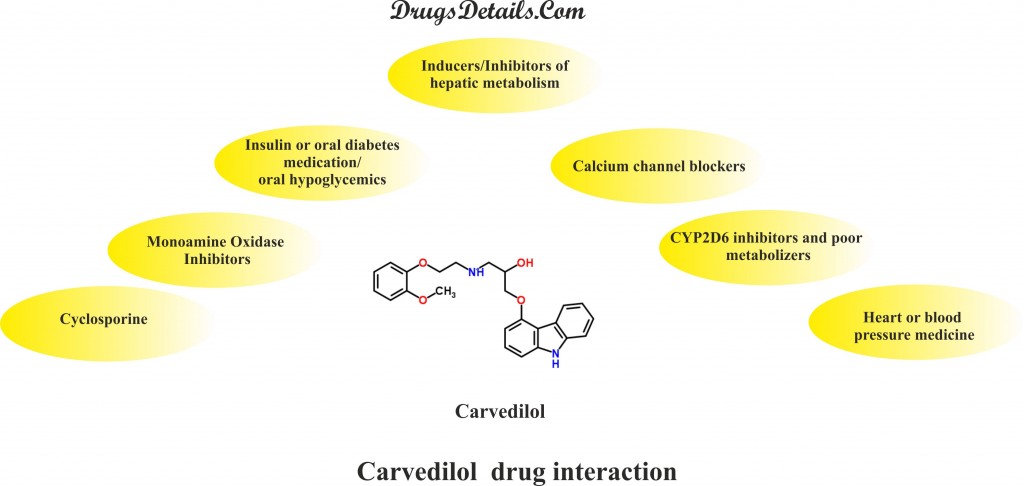
Carvedilol drug interactions
A number of drugs are known to interact with Carvedilol that affects the working of the drug, its effectiveness and poses the risk for serious side effects.
It is always advisable to discuss about all the prescription, non-prescription drugs, vitamins and herbal supplements you are taking before you go on Carvedilol medication therapy.
Also inform your doctor if you are undergoing any type of allergy skin testing or allergy treatments. A list of few medications that interact with Carvedilol include:
- Cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune, and Gengraf): Carvedilol brings about a modest increase in the Cyclosporine concentrations and its exposure. It is therefore recommended to closely monitor the concentration of Cyclosporine for its therapeutic effect and required dose adjustments be made accordingly during Carvedilol therapy.
- Insulin or oral diabetes medication/ oral hypoglycemics: Carvedilol may bring about an increase in the blood-sugar-lowering effect of Insulin and oral diabetes medication/ hypoglycemics and therefore, requires a regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): MAOIs such as Tranylcypromine (Parnate), Isocarboxazid (Marplan), Selegiline (Zelapar, Emsam, Eldepryl), Rasagiline (Azilect), Phenelzine (Nardil), or Furazolidone (Furoxone) are known to interact with Carvedilol.
- Inducers/Inhibitors of hepatic metabolism: Rifampin that upregulates hepatic metabolism brings about a decrease (about 70%) in the plasma concentrations of Carvedilol whereas the inhibitor of hepatic metabolism such as Cimetidine increases the levels of Carvedilol by about 30% and hence the exposure of the drug and its effect.
- Calcium channel blockers: Concomitant use of Carvedilol with calcium channel blockers such as Verapamil or Diltiazem causes disturbance in conduction. It is always suggested to monitor the ECG and blood pressure during coadministration of beta blockers such as Carvedilol and calcium channel blockers.
- CYP2D6 inhibitors and poor metabolizers: Although no studies have been performed in relation to the interaction of Carvedilol with inhibitors of CYP2D6 including Propafenone, Quinidine, Paroxetine, and Fluoxetine, but these drugs are expected to increase the concentration of Carvedilol.
- Heart or blood pressure medicine: Hypotension and/or severe bradycardia may result in patients who are on medications with β-blocking properties such as Carvedilol and a drug with catecholamines depletion effects. Medications belonging to this category include Reserpine, Diltiazem (Cardizem, Cartia), Nifedipine (Procardia, Nifedical), Clonidine (Catapres), Verapamil (Covera, Calan, Verelan, Isoptin), Amlodipine (Caduet, Exforge, Lotrel, Norvasc, Twynsta Tekamlo, Tribenzor) and others. Coadministration of Clonidine with Carvedilol (drug with β-blocking properties) may increase blood pressure and heart rate lowering effects.
- Heart rhythm medications/ Digitalis glycosides: Heart rhythm medications such as Propafenone (Rythmol), Flecainide (Tambocor), Amiodarone (Pacerone, Cordarone), Digoxin (Lanoxin, Digitalis), or Quinidine (Quin-G) interact with Carvedilol and bring about a change in its concentration. Amiodarone, and its metabolite namely, Desethyl amiodarone; inhibitors of CYP2C9 such as Fluconazole and P-glycoprotein result in increased concentrations of Carvedilol and increase its β-blocking properties resulting in further slowing of the heart rate or cardiac conduction.
Concomitant use of digitalis glycosides such as Digoxin and β-blockers including Carvedilol results in slowing down of atrioventricular conduction, decreases heart rate and increases the risk of bradycardia.
Besides, the concentration of Digoxin increases by about 15% in presence of Carvedilol. Some other drugs that are known to interact with Carvedilol are as follows:
- Antidepressants: These include Sertraline (Zoloft), Duloxetine (Cymbalta), Bupropion (Zyban, Wellbutrin), Paroxetine (Paxil), Fluoxetine (Prozac, Sarafem), Desipramine (Norpramin), Amitriptyline (Limbitrol, Elavil, Vanatrip), Clomipramine (Anafranil), or Imipramine (Tofranil).
- HIV or AIDS medicine: The medicines belonging to this category include Ritonavir (Norvir or Kaletra) and Delavirdine (Rescriptor).
- Narcotics: These include Propoxyphene (Darvocet, Daron) and Methadone (Dolophine, Diskets, Methadose).
- Nausea and vomiting medications: Drugs such as or Metoclopramide (Reglan) Promethazine (Antinaus, Phenergan, Anergan, Pentazine) belong to this category.
- Medicines for psychiatric disorders: These are Chlorpromazine (Thorazine), Haloperidol (Haldol), Perphenazine (Trilafon), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Thioridazine (Mellaril) or Fluphenazine (Permitil, Prolixin).
This is not a complete list of drugs that interact with Carvedilol and there exists many more drugs that can interact with Carvedilol. Always inform your doctor about all medications you take and never start a new medication without consulting your doctor.
Does Carvedilol have any interaction with Diseases
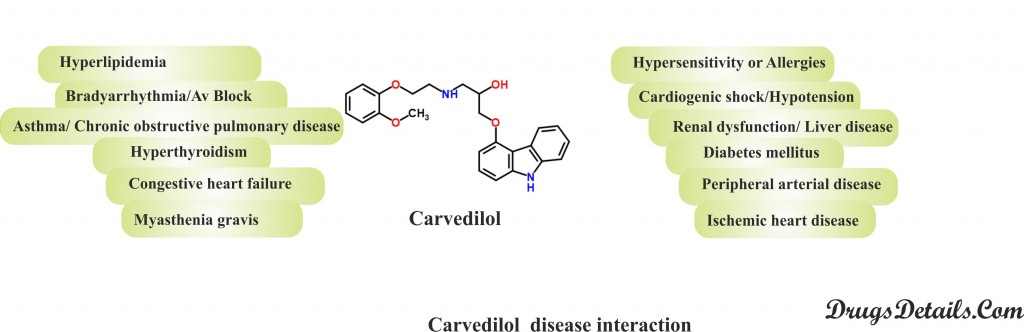
Before you begin to take Carvedilol, it is necessary to discuss any medical condition or allergies you have or any other significant medical fact. It has been observed that following medical conditions (diseases) may interact with Carvedilol:
- Hypersensitivity or Allergies: Beta blockers such as Carvedilol may increase the risk, frequency and severity of attacks of an allergic reaction or anaphylaxis. Besides, these patients may require a beta-agonist (isoproterenol) along with epinephrine to treat acute hypersensitivity reactions.
- Hemodialysis: Beta-blockers (Carvedilol) should be administered cautiously in patients requiring hemodialysis. It may bring about a marked fall in blood pressure if administered without establishing the hemodynamic stability after dialysis.
- Diabetes mellitus: Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents such as Carvedilol may mask symptoms of hypoglycemia, inhibit catecholamine-mediated glycogenolysis, potentiate insulin-induced hypoglycemia and defer the recovery of blood glucose levels to normal levels. Carvedilol therapy should be administered cautiously in diabetic patients or in patients predisposed to spontaneous hypoglycemia.
- Cardiogenic shock/Hypotension: Administration of Carvedilol, a beta blocker is contraindicated in patients with cardiogenic shock or hypotension owing to their negative inotropic (agent that changes the force of muscular contraction) and chronotropic (that changes the heart rate) effects on the heart. Besides, the drug can also result in further reducing the level of strength of cardiac output and blood pressure that can even cause death.
- Renal dysfunction/ Liver disease: Although the use of Carvedilol rarely affects renal function in patients with congestive heart failure but poses greater risks in patients with ischemic heart disease, low blood pressure, and/or underlying renal impairment. Close monitoring of renal function and dosage adjustment is recommended in such patients.
The use of Carvedilol is contraindicated in patients with hepatic dysfunction due to an increase in plasma concentration of approximately 4-7 fold owing to reduced metabolization by the liver.
- Intraocular hypertension/Glaucoma: Administration of Carvedilol may cause decrease in intraocular pressure. Therefore, dose adjustments are required during ophthalmic treatment in case of patients with glaucoma or intraocular hypertension following a change in dose or discontinuation of Carvedilol.
- Hyperlipidemia: Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents such as Carvedilol may bring about a change in serum lipid profiles by increasing serum VLDL and LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, and decreasing HDL cholesterol. Close monitoring and dosage adjustments (lipid-lowering drugs) is required in patients with preexisting hyperlipidemia.
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF): Carvedilol is not recommended in patients with NYHA (New York Heart Association) class IV decompensated heart failure (i.e., advanced disease requiring hospital-based support, a heart transplant) as it may worsen the situation due to imbalance in the hemodynamic function in these patients. However, the drug can be used in the treatment of mild to moderate (NYHA class II or III) heart failure of ischemic or cardiomyopathic origin in patients.
- Asthma/ Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): The use of beta blockers such as Carvedilol is contraindicated in patients with bronchospastic diseases. Carvedilol may counteract the bronchodilation effect of the catecholamine and worsen the pulmonary function. An agent with beta-1 selectivity can be an alternative approach for beta blocker (Carvedilol) therapy in these patients.
- Myasthenia gravis (a neuromuscular disease characterised by muscle weakness and fatigue): Carvedilol, a beta blocker may increase the likelihood of muscle weakness in patients with preexisting myasthenia gravis or myasthenic symptoms such as diplopia (double vision), ptosis (drooping of the upper eyelid), and generalized weakness.
- Bradyarrhythmia/Av Block: Administration of a beta blocker like Carvedilol is not recommended in patients with sinus bradyarrhythmia (slow heart rate) or heart block (except in case of functioning pacemaker). It may result in worsening of the conditions of slow heart rate or heart block due to the associated negative inotropic and chronotropic effects on the heart.
- Hyperthyroidism: Sudden withdrawal of beta blockers such as Carvedilol in patients of hyperthyroidism can result in intensifying the thyrotoxicosis (condition caused by an excessive amount of thyroid hormones in the blood) or result in a thyroid storm (rare, life-threatening condition characterized by severe clinical manifestations of thyrotoxicosis). It is therefore recommended to gradually decrease the dose of Carvedilol and avoid the discontinuation of the drug without consulting the doctor.
- Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD): Carvedilol, a beta blocker may cause or worsen the symptoms of arterial insufficiency and reduce the effect of catecholamine-mediated vasodilation in peripheral blood vessels during physical exercise in patients suffering from peripheral vascular disease. The use of Carvedilol should be done very cautiously and regular monitoring of progression of arterial obstruction is recommended in patients with peripheral vascular disease.
- Ischemic heart disease: Long term use of the beta blockers including Carvedilol may confer increased sensitivity to catecholamines. Besides, sudden withdrawal of the drug may increase the severity of the diseases such as angina, myocardial infarction and ventricular arrhythmias in patients with coronary artery disease.
Where can I get more information
Your pharmacist can provide more information about Carvedilol.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- Carvedilol is being evaluated for its role in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Studies indicate no adverse effect of Carvedilol on glycemic control in a population with mild-to-moderate hypertension and well-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Clinical studies suggest the use of Carvedilol in the reduction of the risk of death and hospitalization for cardiovascular causes in patients with heart failure and on therapy with an angiotensin-converting–enzyme inhibitor, digoxin, and diuretics.
- Studies have been conducted for the safety evaluation of Carvedilol in patients with heart failure (mild, moderate, and severe), left ventricular dysfunction following myocardial infarction and in hypertension.
- No studies have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of Carvedilol in pediatric patients younger than 18 years.
- Clinical studies indicate the use of Carvedilol in the management of hypertension either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents especially thiazide-type diuretics.
- Treatment with Carvedilol results in reversible elevations in serum transaminases (ALT or AST).
- Studies indicate the effectiveness and safety of Carvedilol in the treatment of group I pulmonary arterial hypertension.
- Clinical studies suggest the superiority of Carvedilol (a beta-blocker with a moderate anti-alpha-1 activity) over propranolol in reducing the portal pressure and risk of variceal bleeding.
- Studies indicate the effectiveness of Carvedilol in reduction of cardiovascular mortality in patients who have survived the acute phase of a myocardial infarction and have a left ventricular ejection fraction of ≤40%.
- Carvedilol therapy may also be used for hypertension in patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH).
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
- Carvedilol: MedlinePlus Drug Information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a697042.html
- DrugBank: Carvedilol (DB01136). drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01136
- Carvedilol | C24H26N2O4 | ChemSpider. chemspider.com/ChemicalStructure.2487.html
- Use of carvedilol in hypertension: an update. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22661898
- A critical review of the use of carvedilol in ischemic heart disease. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23061698
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23668404
- Carvedilol: a third-generation β-blocker should be a first-choice β-blocker. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22149523
- Carvedilol in hypertension treatment. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2464772/
- A reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in cardiovascular disorders. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9211087
- Tolerability of carvedilol in patients with heart failure and concomitant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12490274
- Differential effects of carvedilol and metoprolol succinate on plasma norepinephrine release and peak exercise heart rate in subjects with chronic heart failure. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18287590
