Contents
- What is Darunavir (Darunavir)?
- What is the generic and brand name of the drug?
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Why is this medication prescribed?
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug.
- Chemical information of the drug.
- What is the available strength of the drug?
- How the medicine works (mode of action)?
- What are the recommended doses of Darunavir?
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Darunavir?
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug?
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Darunavir?
- How to use the drug?
- How to store the drug?
- How to dispose the medicine?
- Does Darunavir has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies?
- Other uses of the drug.
- What special dietary precautions should I follow?
- What should I do in case of overdose?
- What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- Does Darunavir have any interaction with other drugs?
- Does Darunavir have any interaction with diseases?
- Where can I get more information?
- Clinical research and current scenario of the drug.
- Darunavir is an antiretroviral drug that is used in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infection.
What is the generic and brand name of the drug?
- The drug is available under generic name Darunavir and brand name
- The drug is pharmaceutically known as TMC114, which was named Darunavir after Arun K. Ghosh, the chemistry professor who was the finder of the molecule at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
- The drug was developed by pharmaceutical company Tibotec and is manufactured by Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Darunavir is a synthetic (man-made) second generation protease inhibitor (PIs) class antiretroviral
Why is this medication prescribed?
- Darunavir is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease.
- The drug is co-administered with Ritonavir in combination therapy and drastically reduces viral load and increases CD4 cell counts.
- Darunavir is recommended as treatment option for treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in antiretroviral treatment-experienced adult patients i.e. patients infected with more than one protease inhibitor resistant HIV-1 strains.
- The drug is also an OARAC prescribed treatment option for treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced adults and adolescents.
- This medicine is also used along with other PIs drugs for the treatment of multiple HIV protease inhibitor resistant strain of HIV-1.
- It may reduce the possibility of the development of AIDS and also diminish the occurrence of other infections or cancer.
- Darunavir inhibits the enzyme activity of protease by binding to its active site and lowering the quantity of virus in the infected person’s blood.
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug.
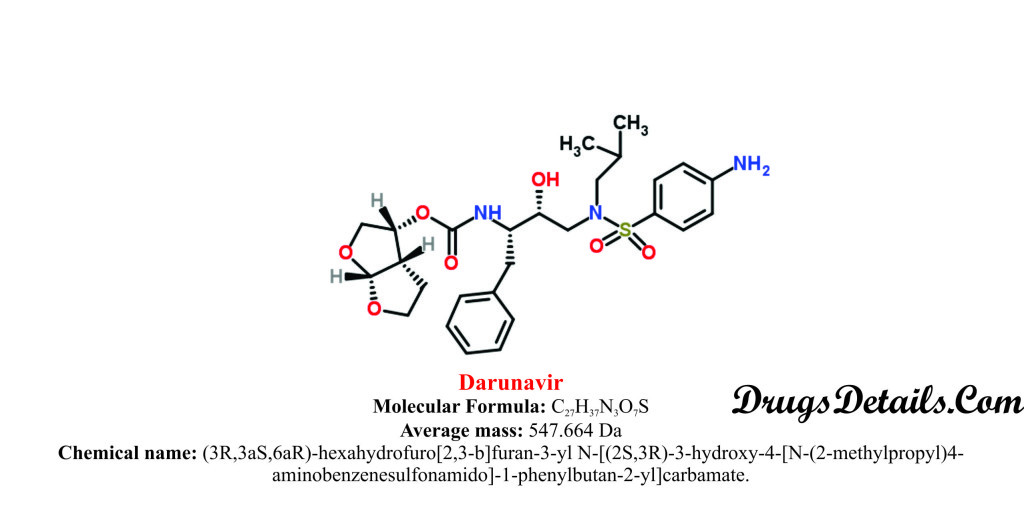
Darunavir chemically belongs to the class of organic compounds which are known as Aminobenzenesulfonamides which are characterized by benzenesulfonamides moiety with an amino group attached to the benzene ring. The detailed chemical classification of Darunavir is described below:
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
| Sub Class | Benzenesulfonamides |
| Direct Parent | Aminobenzenesulfonamides |
Chemical information of the drug.
- It is a synthetic pharmaceutical aromatic heteropolycyclic compound with a molecular formula C27H37N3O7S and molecular weight of 664 Da.
- The drug is chemically known as (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl N-[(2S,3R)-3-hydroxy-4-[N-(2-methylpropyl)4-aminobenzenesulfonamido]-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate.
- Darunavir is available as monoethanolate salt of (3R, 3aS, 6aR)-hexahydrofuro [2, 3-b] furan – 3 – ylN – [(2S, 3R) – 3 – hydroxyl – 4 – [N- (2 – methylpropyl) 4-aminobenzenesulfonamido]-1-phenylbutan-2-yl] carbamate.
- Darunavir ethanolate is represented by molecular formula C27H37N3O7S• C2H5OH and molecular weight of 593.73 Da.
- Darunavir ethanolate is white to off white powder, solid amorphous in texture.
- Darunavir ethanolate is slightly soluble in water and has water solubility of 0.15 mg/mL at 20°C and 8.7 mg/mL at 25°C.
- The melting point of Darunavir ethanolate is 74°C.
What is the available strength of the drug?
- Darunavir is available in both oral suspensions as well as in tablet form for oral administration with food /water / milk.
- The Darunavir tablet is available in varying strength of 75 mg (Caplet-shaped, white in color, film coated), 150 mg (Oval shaped, white in color, film coated), 600 mg (Oval shaped, orange in color, film coated), and 800 mg (Oval shaped, dark red in color, film coated).
- Each tablet contains colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose as inactive ingredients.
- The film coating of each tablet contains OPADRY® Dark Red (iron oxide red) / OPADRY® white (titanium dioxide)/ OPADRY® Orange (FD&C Yellow No. 6), polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, titanium dioxide, and talc.
- Darunavir tablets of 75mg, 150mg, 600mg and 800mg are debossed with “75”, “150”, “600MG” and “800” on one side.
- The another side of Darunavir tablets of 75, 150 and 600 mg are debossed with “TMC” while tablet of 800 mg is debossed with “T”.
- Darunavir oral suspension is white, opaque available in strength of 100 mg/mL for oral administration.
- Darunavir oral suspension contains Darunavir ethanolate as active ingredient and microcrystalline cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, methylparaben sodium, citric acid monohydrate sucralose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment), masking flavour, strawberry cream flavour and purified water as an inactive ingredients.
How the medicine works (mode of action)?
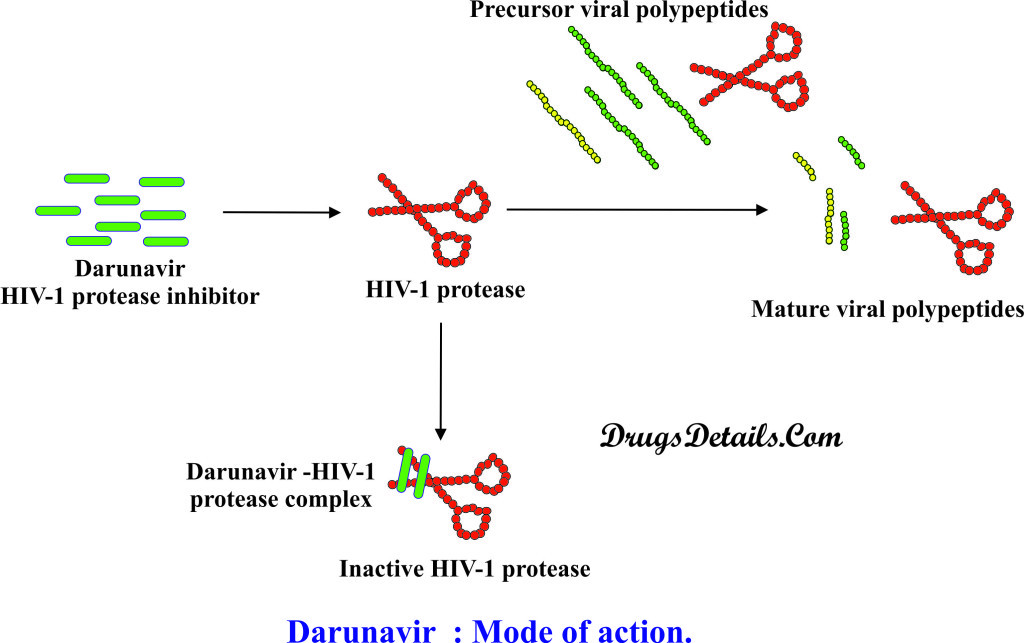
- The mode of action of Darunavir is similar to that of other drugs used for the treatment of retroviral infection.
- Darunavir is the drug of protease inhibitor class that work by inhibiting the HIV-1 aspartyl protease enzyme (enzyme which cleave theHIV polyprotein into its functional fragments) by binding to its active site.
- HIV-1 aspartyl protease enzyme is involved in the formation of infectious viral functional proteins from the viral polyprotein precursors.
- Darunavir interacts with catalytic aspartates (Asp25 and Asp30) through hydrogen bonding in active site of HIV-1 aspartyl protease.
- Binding of Darunavir with protease enzyme active site results in inhibition of dimerization and the catalytic activity of the HIV-1.
- Due to the inhibition of HIV-1 aspartyl protease enzyme, processing of viral Gag-Pol polyprotein gets inhibited, which results into the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles.
- Darunavir in combination with Ritonavir play an important role in increasing the number of CD4+ cells (immune system cells), thus improving the immune system to fight against HIV infection.
- Besides this, some of the in vivo studies showed that Darunavir also inhibits p-glycoprotein (p-gp) transporters.
The prescribed dose of Darunavir varies depending upon the age and diseased state of the patient.
- Adult dose:
- Treatment-naive patients: 800 mg Darunavir + 100 mg Ritonavir orally once a day or 8 ml Darunavir + 1.25 ml Ritonavir (80 mg/mL) orally once a day with food.
- Treatment-experienced patients:
- Without Darunavir resistant associated mutations: 800 mg Darunavir + 100 mg Ritonavir orally once daily or 8 ml Darunavir + 1.25 ml Ritonavir (80 mg/mL) orally once daily with food.
- With at least one Darunavir resistant associated mutations: 600 mg Darunavir + 100 mg Ritonavir orally twice daily or 6 ml Darunavir + 1.25 ml Ritonavir (80 mg/mL) orally twice daily with food.
- Paediatric dose:
- Treatment-naive and Treatment-experienced patients without Darunavir resistant associated mutations:
- More than 10 and less than 15 kg: 35 mg/kg Darunavir + 7 mg/kg Ritonavir as an oral suspension once daily with food.
- More than 15 and less than 30 kg: 600 mg Darunavir + 100 mg Ritonavir once daily (oral suspension or tablet) with food.
- More than 30 and less than 40 kg: 675 mg Darunavir + 100 mg Ritonavir once daily (oral suspension or tablet) with food.
- 40 kg or more: 800 mg Darunavir + 100 mg Ritonavir once daily (oral suspension or tablet) with food.
- Treatment-experienced patients with at least one Darunavir resistant associated mutations:
- More than 10 and less than 15 kg: 20 mg/kg Darunavir + 3 mg/kg Ritonavir as an oral suspension twice daily with food.
- More than 15 and less than 30 kg: 375 mg Darunavir + 48 mg Ritonavir twice daily (oral suspension or tablet) with food.
- More than 30 and less than 40 kg: 450 mg Darunavir + 60 mg Ritonavir twice daily (oral suspension or tablet) with food.
- 40 kg or more: 600 mg Darunavir + 100 mg Ritonavir twice daily (oral suspension or tablet) with food.
- The drug can be taken orally in presence of food with water.
- Treatment-naive and Treatment-experienced patients without Darunavir resistant associated mutations:
- The usual dosing of the drug may vary depending upon the efficiency and side effects of the drug in a particular individual.
- Do not use the medicine if you are hypersensitive or allergic to any of the ingredients of Darunavir/ Ritonavir or any other sulfa medications.
- Darunavir should not be used with the ergot type medication (dihydroergotamine, ergotamine and methylergonovine), cholesterol lowering medications (Lovastatin, Simvastatin), Midazolam, Triazolam, Pimozide, Rifampin, Alfuzosin, or Sildenafil.
- Darunavir is not recommended for children under 3 year of age (or less than 22 pounds).
- Dose adjustment is required during the medication with Didanosine (take Didanosine 2 hour after or 1 hour before taking Darunavir).
- Seek advice from your pharmacist or doctor if you ever had Diabetes or Haemophilia, Pneumonia, Tuberculosis or Hepatitis.
- Consult with your doctor and pharmacist if you are taking any prescription and non-prescription medications or herbal products.
- In case of hepatic and renal impairment, the dosing recommendations are as follows:
- Dose in hepatic impairment: no dose adjustment required, take dose as prescribed by pharmacist or doctor. Darunavir is not recommended for severe cases of hepatic impairment.
- Dose in renal impairment: No need to alter the dose.
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug?
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggested that after oral administration, Darunavir (600 mg) along with Ritonavir (100 mg) is rapidly absorbed by the body and has a bio-availability of approximately 82% while administration of Darunavir alone (600 mg) has a bio-availability of 37%.
- When Darunavir is taken with food, it decreases the pharmacokinetic variability and increases the bioavailability.
- Following absorption the majority (95%) of the drug is bound to plasma proteins primarily with Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AAG).
- It has been observed that following a 600 mg dose of the drug along with 100 mg Ritonavir dose, maximum (or peak) plasma concentration (3930 ng/ml) is achieved in 5 – 4 hours in the fasted state.
- The drug is largely metabolized in liver primarily by CYP3A4
- The average median half-life of Darunavir is 15
- The average steady state volume of distribution of the Darunavir is approximately 131 L.
- Darunavir is mainly excreted in the feces (approximately 80% in which 41% is uncharged drug) and very little amount in the urine (14% in which 8% is uncharged drug).
- The Darunavir is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: C.
- Darunavir is used for only those pregnant women who are infected with HIV-1 strain.
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies the use of Darunavir in pregnant women is contraindicated and recommended only when benefit justifies the risk.
- Laboratory animal studies have shown no adverse effect on fetus.
- Studies support the excretion of the drug into animal milk. However, no adequate data is available on excretion of Darunavir into human breast milk. It is advisable that HIV infected women should not breast-feed the baby.
- Despite these facts caution should be exercised when taking Darunavir.
How to use the drug?
- Darunavir is available in oral suspension and film coated tablet form for oral administration by mouth with food and water.
- Darunavir is used in the combination therapy with Ritonavir. The drug Darunavir should not be recommended to use alone or without Ritonavir.
- Darunavir should be taken each day at about the same time.
- Do not chew, split or crush the Darunavir tablets. It is recommended to swallow the whole tablet.
- Darunavir oral suspension is taken by oral dosing syringe.
- The time duration between the drug uses should be at least 24 hour (for once daily) or 12 hours (for twice daily).
- Darunavir should be taken with water (one glass or more) or milk at same time each day.
- It is advisable not to take more than one or two tablet daily.
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet and take Darunavir exactly as directed.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor. Since, the dosage is based on patient medical condition, treatment responses and usage with other drugs.
How to store the drug?
- Darunavir is stored at 25°C (77°F) and excursion permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
- Store the medicine away from light and moisture.
- Medicine should not be stored in the bathroom.
- Darunavir oral suspension should not be refrigerated (precipitated on refrigeration).
- The drug should be kept away from children and pets.
How to dispose the medicine?
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used container.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- Darunavir should not be disposed in the household garbage, sink or in wastewater.
- Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company for proper disposal.
- Darunavir was approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration on June 23, 2006 for the treatment of protease inhibitor resistant strain of HIV-1 in combination with Ritonavir.
- In 2008, Darunavir received official approval for the treatment of HIV-1 in both treatment-naive and treatment-experienced adults and in children of 6 year age and older.
- Darunavir is also approved by OARAC (Office of AIDS Research Advisory Council) for treatment-naive and treatment-experienced adults.
- In year 2011, Darunavir was also approved by U.S. FDA for the treatment of the HIV-1 in children of 3 year age and older.
Other uses of the drug.
- Darunavir may also be used for preventing the infection of HIV in people who are accidently exposed.
- Darunavir may also be used for other uses not listed here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special dietary precautions should I follow?
- Alcoholic beverages, grapefruit, or grapefruit juice should be avoided. Consult your doctor or pharmacist regarding the use of grapefruit products.
- Alcohol consumption can also enhance some side effects of the drug.
What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Darunavir?
- First of all inform your doctor if you are allergic to any Sulfa drug, Darunavir or Ritonavir or any of the ingredients present in the product. Ask your pharmacist or check the prescription leaflet carefully for a list of the ingredients.
- It has been observed that food can significantly enhance the absorption of the drug; therefore, it is recommended to take Darunavir with food to achieve the desired antiviral effect.
- Darunavir is used as an adjunct therapy with low dose Ritonavir. Ritonavir is an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A), therefore, it increases the bioavailability and half life of Darunavir.
- Before taking Darunavir, tell your doctor about your medical history preferentially if you have any kind of liver disease, renal disorder, heart disease, eye disorders, bleeding disorders, or blood pressure problems.
- It is recommended to avoid consuming alcohol as it may increase the risk of bleeding in stomach or intestines.
- It is advisable to discuss with your doctor and pharmacist about what prescription and non-prescription medications, vitamins, and nutritional supplements you are taking or plan to take.
- Alcoholic beverages, grapefruit, or grapefruit juice should be avoided during Darunavir therapy.
- During the treatment of Darunavir, if the symptoms of other infections develop immediately consult to your doctor.
- Avoid sharing razors, toothbrushes, medicine needles and unprotected sex (contact with semen, vaginal secretions or blood).
- Consult with your doctor and pharmacist if you are taking any prescription and non-prescription medications or herbal products.
- Use of Darunavir may increase the body weight. Consult your doctor in case of any query.
- Co-administration or concomitant use of Darunavir/Ritonavir with certain medications may develop or potentiate significant drug interactions, therefore the use of the other drugs prior to and during treatment should be prescribed under professional supervision.
- Darunavir may cause increased bleeding events therefore, the use of the drug should be prescribed under professional supervision in case of patients with haemophilia.
- Darunavir /Ritonavir antiretrovioral therapy should not be used in paediatric population (below 3 years of age) due to associated toxicity and mortality as observed in juvenile rats.
What are the possible side effects of this drug?
In addition to the associated benefits, Darunavir also is accompanied with the side effects some of which are more common, others less common whereas some are more serious. It is always recommended to consult a doctor if you encounter any of the side effects.
Most common side effects caused by Darunavir are as follows:
- Hyperglycaemia (High level of sugar in blood)
- Changes in immune system
- Increased bleeding in patients of haemophilia
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Rashes on skin
There are some adverse effects that fade away while consuming the drug with time. These symptoms do not require any medical attention:
- Gaining weight around face, breast, neck, upper back or waist
- Runny or Stuffy nose
Some common side effects of Darunavir are as follows. If these symptoms persist tell to your doctor:
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Dry, flushed skin
- Fruit like breath odour
- Increase in hunger, thirst and urination
- Rashes on skin
- Sweating
- Uncomfortable breathing
- Unusual weakness or tiredness
- Weight loss
Some side effects caused by Darunavir are exceptional but they also need medical attention. On appearing of these symptoms instantly contact with your doctor:
- Blood in vomiting
- Chills or itching
- Cough and fever
- Cramps in muscle
- Dark urine
- Clay colored stools
- Difficulty with moving
- Dizziness and decreased appetite
- Fast heartbeat and heartburn
- Headache
- Indigestion and excess air or gas in the stomach or intestines
- Irritated red eyes
- Loss of strength
- Pain in joints or muscles
- Peeling, blistering, or loosening of the skin
- Red skin lesions, often with a purple centre
- Sore throat
- Stomach or abdominal pain or tenderness
- Swelling of the feet or lower legs and joints
- Ulcers or white spots in the mouth or on the lips
- Unpleasant breath odour
- Yellow eyes or skin
What should I do in case of overdose?
- Overdose usually occurs when someone by mistake or deliberately takes more than the prescribed limit of this medication.
- In case of overdose, contact with your doctor or emergency room immediately if the victim is not breathing and has collapsed.
- Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule.
- Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind to not use a double dose to make up a missed dose
It has been observed that Darunavir may interact with or increase or decrease the effect of following drugs. Caution should be taken when co administrating Darunavir with one of the following drugs.
- Clinical studies have suggested Darunavir interaction with certain drugs such as drugs used to treat seizures (such as phenytoin, primidone), barbiturates (such as phenobarbital, secobarbital), hepatitis C virus protease inhibitors (telaprevir, simeprevir, boceprevir), and certain combination HIV medication (elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir).
- Coadministration of Darunavir with certain medication can delay the removal of these drugs from body. Some of the common affected drugs are certain “statin” cholesterol drugs (such as lovastatin, simvastatin), tolvaptan, bosutinib, ergot alkaloids (such as dihydroergotamine, ergotamine), lomitapide, pimozide, salmeterol, certain benzodiazepines (triazolam, midazolam), alpha blockers (such as tamsulosin, alfuzosin), certain drugs to treat erectile dysfunction-ED or pulmonary hypertension (such as avanafil, sildenafil), etc.
- A number of other drugs affect the metabolism and elimination of Darunavir from body. Some of the examples of these drugs are St. John’s Wort, garlic supplements, certain rifamycins (rifampin, rifapentine) etc.
- Darunavir coadministration may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal birth control such as pills, patch, or ring, thus could cause pregnancy. It is advisable to talk your doctor about other birth control, medication.
A detailed comprehensive list of the medication that can interact with Darunavir is as follows. Caution should be taken when co administrating Darunavir with one of the following drugs.
Drugs that severely interact with Darunavir:
- Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors/naloxegol (> 12.5 mg)
- Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors/ranolazine (> 500 mg bid)
- Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors/avanafil (> 50 mg)
- Selected 3A4 inhibitors/cisapride
- Selected 3A4 inhibitors/pimozide
- Selected 3A4 substrates/rifampin
- Selected 3A4 substrates/St. John’s wort
- Protease inhibitors/midazolam; triazolam
- Protease inhibitors/astemizole; terfenadine
- Protease inhibitors/ergot derivatives
- Darunavir/selected anticonvulsants
- Darunavir; fosamprenavir; saquinavir/atorvastatin (>20 mg)
- Selected 3A4 inhibitors/lovastatin; simvastatin
- Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors/lomitapide
- Protease inhibitors & nnrtis/cobicistat-elvitegravir
Drugs that seriously interact with Darunavir:
- Protease Inhibitors/Carbamazepine
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Garlic
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Contraceptives
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Rifabutin; Rifapentine
- Darunavir/Lopinavir; Saquinavir; Ombitas-Paritap-Ritonavir
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Naloxegol (<= 12.5 Mg)
- Moderate 3A4 Inhibitors/Ibrutinib
- Moderate-Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Quetiapine
- Moderate 3A4 &-Or P-GP Inhibitors/Bosutinib
- Strong & Moderate Inhibitors/Eliglustat
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Suvorexant > 10 Mg
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Tolvaptan
- Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Simeprevir/Ivacaftor
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Telaprevir
- Darunavir; Lopinavir/Voriconazole
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Maraviroc
- Protease Inhibitors/Selected Immunosuppressants;Temsirolimus
- Strong 3a4 Inhibitors; P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors/Colchicine
Drugs that moderately interact with Darunavir:
- Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors/suvorexant <= 10 mg
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Avanafil (<= 50 Mg)
- Darunavir; Fosamprenavir; Saquinavir/Atorvastatin (<= 20 Mg)
- Darunavir/Pravastatin
- Slightly Moderate Cyp3a4 Inhibitors/Alfentanil;Fentanyl;Oxycodone
- Moderate CYP3A4; P-GP Inhibitors/Everolimus
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Eplerenone
- Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Ranolazine (<=500 Mg Bid)
- Selected 3A4 Inhibitors/Itraconazole; Ketoconazole
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Selected Antiarrhythmics
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Clarithromycin
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Vardenafil
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Rosuvastatin
- Selected Protease Inhibitors/Didanosine
Before you begin to take Darunavir, it is necessary to discuss any medical condition or allergies you have or any other significant fact related to your health. It has been observed that following medical conditions (disease) may interact with Darunavir:
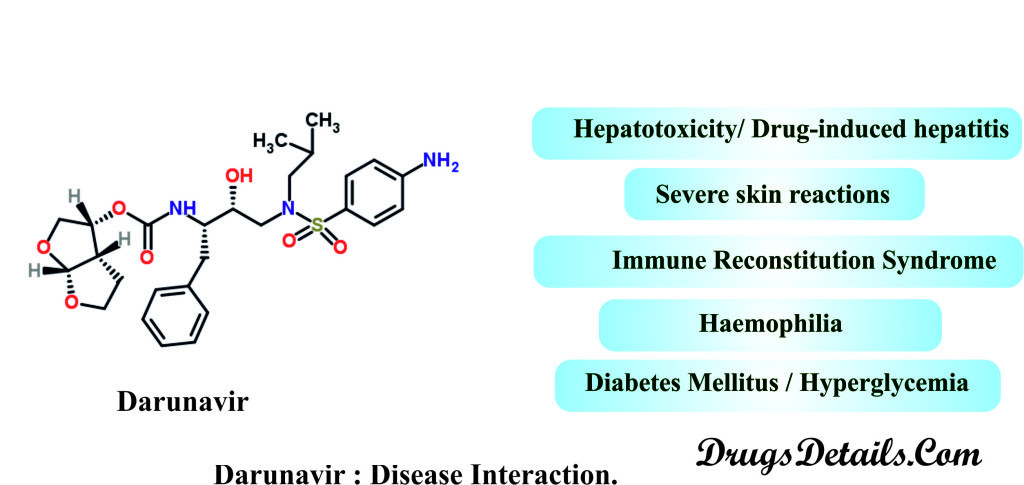
- Hepatotoxicity/ Drug-induced hepatitis: Clinical studies using Darunavir have suggested the occurrence of acute hepatitis and cytolytic hepatitis in patients treated with Darunavir /ritonavir. It is advisable that patients with pre-existing liver dysfunction, chronic active hepatitis B or C, are at higher risk for liver dysfunction or abnormalities including severe hepatic adverse events. In patients with chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or in patients who have pre-treatment elevations of transaminases Darunavir treatment should be under AST/ALT monitoring.
- Severe skin reactions: Severe skin reactions, accompanied by fever and/or elevations of transaminases have been reported during Darunavir clinical development program. Furthermore, some cases of drug rash with eosinophilia, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis have been reported.
- Sulfa Allergy: The chemical structure of Darunavir showed that it contains an active sulfonamide moiety. Therefore, use of drug should be under professional guidance in patients with a known sulfonamide allergy.
- Diabetes Mellitus / Hyperglycemia: Clinical studies using Darunavir have reported the exacerbation of pre-existing diabetes mellitus, or diabetic ketoacidosis or new onset of diabetes mellitus, and hyperglycemia following Darunavir therapy. Initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents are necessary for treatment of these events.
- Redistribution/accumulation of body fat: It has been observed that Darunavir therapy may result in central obesity, peripheral wasting, facial wasting, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), breast enlargement, and “cushingoid appearance”. However, the underlying mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are not known.
- Immune reconstitution syndrome: Use of combinational retroviral therapies including Darunavir therapy have shown immune reconstitution syndrome. It has been observed that during the initial phase patients develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (i.e. Cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, Mycobacterium avium infection, or tuberculosis). Besides this, incidence of autoimmune disorders (such as Polymyositis, Graves’ disease and Guillain-Barré syndrome) has also been reported in the setting of immune reconstitution.
- Haemophilia: Studies with haemophilia type A and B patients treated with PIs/Darunavir therapy have reported increased bleeding, including spontaneous skin hematomas and hemarthrosis.
Where can I get more information?
Your pharmacist or health care provider can provide more information about Darunavir.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug.
- Principally Darunavir (a second-generation protease inhibitor (PIs) is designed to conquer the problems associated with the other anti-retroviral agents (PIs). Older agents in this class had experienced a lot of problems such as severe side effects, toxicities, high therapeutic dose, and manufacturer cost and most important high susceptibility to drug resistant mutations. In this view, Darunavir was designed to overcome the problems associated with existing PIs.
- To over-come the drug resistant problem, Darunavir was designed to form robust interactions with the protease enzyme from many strains of HIV, including strains from treatment-experienced patients with multiple resistance mutations to PIs.
- Structural studies with Darunavir suggest that the wide spectrum activity and potency of Darunavir is attributed mainly due to its binding in the main chains of the protease active site amino acids (Asp-29 and Asp-30). The molecular flexibility of Darunavir provides an additional advantage to adapt with changing shape of a protease enzyme.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases.
- Darunavir – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Darunavir
- Darunavir: MedlinePlus Drug Information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a607042.html
- DrugBank: Darunavir (DB01264). http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/db01264
- Darunavir | C27H37N3O7S – PubChem http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Darunavir
- ·Darunavir | C27H37N3O7S | ChemSpider. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.184733.html
- Darunavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV infection in adults. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19323590
- Darunavir: pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18389894
- Clinical pharmacokinetics of darunavir. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17713972
- Pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety of darunavir/ritonavir 800/100 mg once-daily in treatment-naïve and -experienced patients. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19203907
- Darunavir: an overview of an HIV protease inhibitor developed to overcome drug resistance. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17396332
Read about,
“Tadalafil, drug class, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action”
“Rivastigmine, drug class, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
