Contents
- What is Memantine
- Memantine brand name
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- What does Memantine do
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
- Chemical information of the drug
- Memantine available strength
- How does memantine work
- What are the recommended doses of Memantine
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Memantine
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Memantine
- How to take Memantine
- How to store Memantine
- How to dispose the medicine
- Does Memantine has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies
- Other uses of the drug
- What special dietary precautions should I follow
- What special precautions should I follow while using Memantine
- Memantine side effects
- In some cases side effects can be serious and needs immediate medical attention and emergency help
- Memantine overdose
- Memantine missed dose
- Memantine drug interaction
- Does Memantine use interfere with other diseases
What is Memantine
- Memantine or Namenda belongs to the category of medication used to treat the symptoms of Alzheimer disease (a brain disease that deteriorate memory, mood, behaviour and ability to perform daily chores).
Memantine brand name
What is the generic and brand name of the Drug?
- The drug is available under generic name Memantine/Memantine HCl and brand names Axura,Akatinol, Namenda, Ebixa, Abixa, and Memox.
- The drug is marketed by Merz, Forest, Lundbek, and Unipharm.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Memantine is a synthetic (man-made) pharmaceutical N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-receptor antagonist.
What does Memantine do
Why is this medication prescribed?
- Memantine is an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-receptor (glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells) antagonist used to reduce the symptoms associated with the Alzheimer’s disease.
- It is recommended for people suffering from moderate to severe stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Excessive amount or activity of glutamate is responsible for bringing about the damage to the brain cells in the people afflicted with Alzheimer’s disease.
- It works by diminishing the concentration and thus the action of neurotransmitter (brain chemical) known as glutamate.
- However, Memantine is not a cure for Alzheimer’s disease rather it slows the associated symptoms.
- Memantine is usually prescribed for individuals who are unable to take medicines (due to some reasons) specifically recommended for Alzheimer’s disease.
- Memantine is in a class of medications called NMDA receptor antagonists. It works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Memantine may improve the ability to think and remember or may slow the loss of these abilities in people who have AD. However, memantine will not cure AD or prevent the loss of these abilities at some time in the future.
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
Memantine chemically belongs to the class of organic compounds known as cyclohexylamines. These are aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds containing a cyclohexylamine moiety with cyclohexane ring attached to an amine group. The detailed chemical classification of Memantine is as follows.
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Organonitrogen compounds |
| Class | Cyclohexylamines |
| Sub Class | Not Available |
| Direct Parent | Cyclohexylamines |
Chemical information of the drug
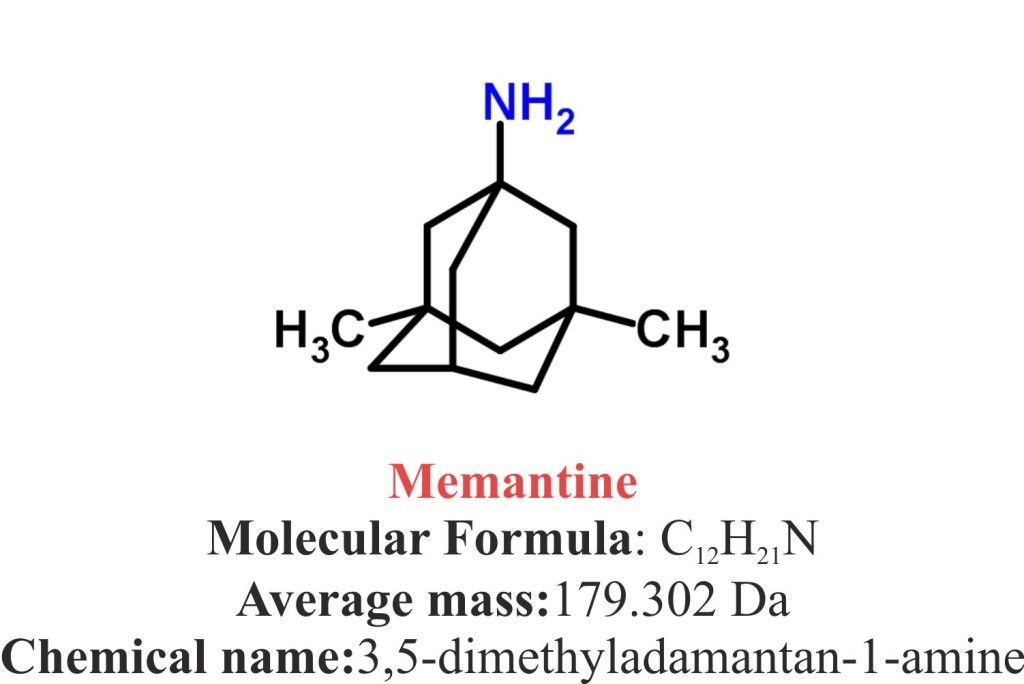
- Memantine (Namenda) is a synthetic pharmaceutical cyclohexylamines compound named as 3,5-dimethyladamantan-1-amine.
- The compound has molecular formula C12H21N and the molecular weight of 3018g/mol.
- The melting point of Memantine is 258°C.
- Memantine is available as hydrochloride salt and is powder that is white to off-white in colour.
- Memantine is soluble in water, DMSO and ethanol with solubility of 100 mM, and 43 mg/ml at 25 °C respectively.
Memantine available strength
- Memantine is available as a tablet, a liquid solution, and an extended-release (long-acting) capsule for oral administration.
- Tablets are available in one dosage strength of 5 and 10 mg of Memantine hydrochloride whereas capsule (extended release) as 7, 14, 21 and 28 mg.
- The oral solution consists of 2 mg Memantine hydrochloride per ml.
- Each tablet contains inactive ingredients such as croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, talc, anhydrous lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, and colloidal silicon dioxide.
- Besides, the other inactive ingredients present as the components in the film coating: titanium dioxide, macrogol/polyethylene glycol 4000, FD&C blue #2, hypromellose, iron oxide red and FD&C yellow #6, (5 mg tablets), and FD&C blue #2, titanium dioxide, hypromellose, and polyethylene glycol 4000 / macrogol (10 mg tablets).
How does memantine work
How the medicine works (mode of action)?
- The mode of action of Memantine is completely different from other medications utilized for the treatment of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
- The action of Memantine is independent of the brain chemical acetylcholine and the enzyme acetylcholineesterase, which are the targets for other medicines used for Alzheimer’s disease.
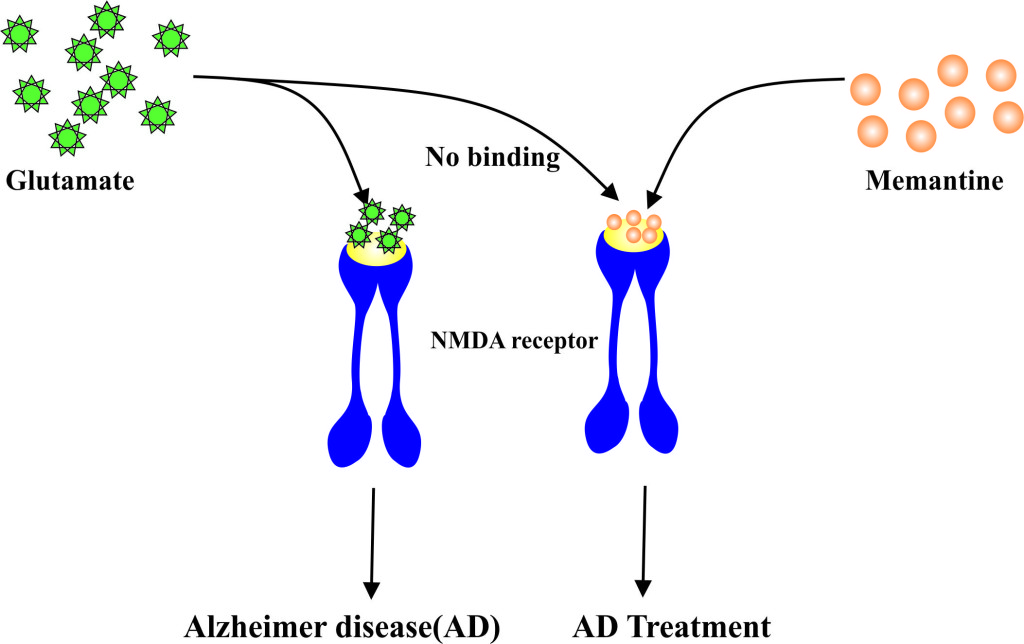
- Memantine basically competes with the amino acid glutamate (main brain chemical secreted by nerve cells) which is responsible for contributing to the symptoms of AD for binding to the receptors on the cells’ surface known as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor.
- Blockage of the receptor and thereby the effects of glutamate by Memantine may protect nerve cells of the brain from excessive stimulation by glutamate.
- Studies have shown that Memantine does not influence the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by other medications of AD such as tacrine, donepezil, or galantamine.
What are the recommended doses of Memantine
- Memantine medication in the form of tablet, solution or capsule is administered orally with or without food.
- The dosage depends upon the medical condition and the response of the patient to the drug.
- The capsule is taken once whereas solution and tablets are usually taken once or twice a day.
- This medication is started at a low dose of 5 mg (2.5 mL) once daily which is gradually increased in 5 mg increments to 10 mg/day (2.5 mL twice daily), 15 mg/day (2.5 mL and 5 mL as separate doses), and 20 mg/day (5 mL twice daily).
- The permissive time interval for dose increment is one week.
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Memantine
- In case of special population, patients with severe renal impairment and hepatic impairment a dose of 5 mg twice daily and a dose with caution should be administered respectively.
- In case of patients with severe renal impairment the dose may be switched from immediate-release (5 mg twice a day) to extended-release (14 mg once a day) the day following the last dose of 5 mg.
- The medication should be discontinued if a patient is allergic to any of the ingredients of the drug.
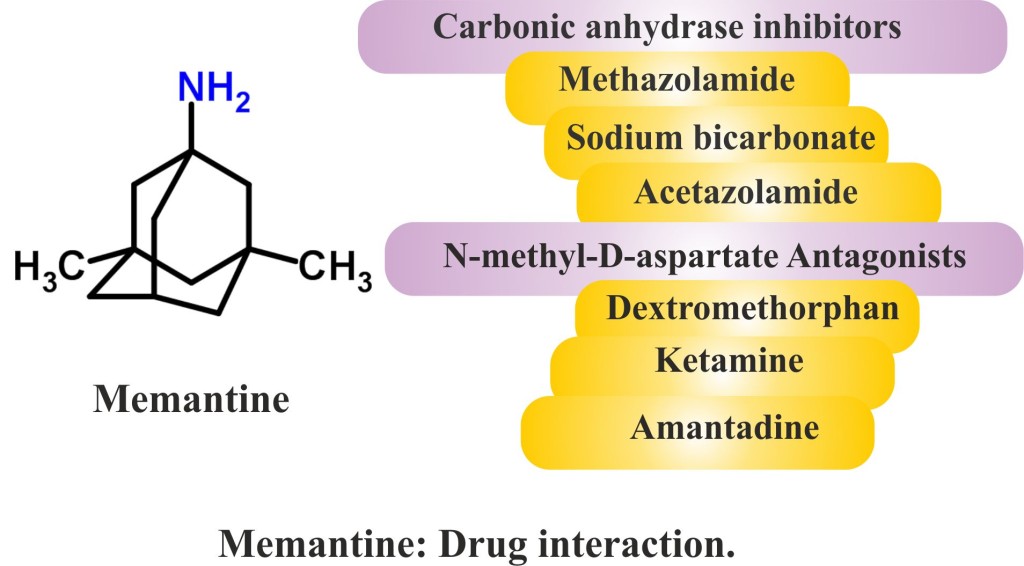
- Co-administration of Memantine with other NMDA receptor blockers likeketamine, amantadine and dextromethorphan should be done cautiously.
- No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment and renal impairment.
- In patients with a history of neurological conditions, Memantine should be used with caution.
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggested that after oral administration, Mermantine is rapidly absorbed and achieves peak plasma concentration within 3-7 hours.
- Food has no implication on drug absorption.
- Following absorption, only 45% of the drug is bound to plasma proteins.
- The bioavailability of Memantine is approximately 100%. .
- The drug is metabolized partially via hepatic metabolism and also by renal clearance.
- Approximately 48% of the total drug is excreted without any change in urine while the remaining being converted to 1-nitroso-deaminated Memantine, 6-hydroxy Memantine, and N-glucuronide conjugate.
- The terminal elimination half-life of Memantine varies from 60 to 80 hours.
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Memantine
- Memantine is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: B
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women the use of Memantine is contraindicated and recommended only when benefit overweighs the risk.
- Laboratory animal studies show no adverse effect on the fetus.
- No adequate data is available on excretion of Memantine into human breast milk.
- The effects of Memantine in the nursing infant are unknown.
- Despite these facts caution should be exercised when taking Memantine.
How to take Memantine
- Memantine is available in tablet, solution or capsule form to be administered orally.
- It can be consumed with or without food.
- The drug should be taken at around same time every day.
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on printed information leaflet and take Memantine exactly as directed by the doctor.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor. Since, the dosage is based on patient medical condition and treatment response.
- Doses of the oral medicine should be measured using the dose pump which is supplied with the drug. Do not use household spoons to avoid incorrect dosing.
- The extended-release capsules should be swallowed as a whole and not chewed or crushed.
How to store Memantine
- Memantine should be stored at room temperature (77 ° F /25 ° C).
- Brief storage can be done at temperatures between 59 and 86 ° F (15 and 30 °C).
- The drug should be kept in the container it came in and should be tightly closed.
- It should be kept away from heat, light and moisture.
- It should not be stored in the bathroom.
- The medication should be out of reach of children and pets.
- Do not store the medication after three months once the bottle is opened.
How to dispose the medicine
- Discard away outdated or no longer used medication.
- The drug should neither be flushed down in the toilet nor poured in the drain
- Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company for proper disposal.
- Memantine has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of patients suffering from moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease.
- It had been approved in the year 2003.
- The drug has also received approval from the European Medicines Agency for treatment of moderate-to-severe form of Alzheimer’s disease.
- It has now received recommendation by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in UK for patients who do not respond to other treatment options.
Other uses of the drug
- Memantine may also be prescribed for other uses apart from Alzheimer’s disease. It is advisable to consult the doctor or pharmacist for detailed information.
What special dietary precautions should I follow
- A patient should not modify any normal diet unless and until asked by doctor to do so.
What special precautions should I follow while using Memantine
- Doctor or pharmacist should be consulted in case of consumption of prescription and nonprescription medications, herbal products, nutritional supplements, and vitamins such as potassium or sodium citrate, citric acid, sodium bicarbonate, methazolamide, acetazolamide, amantadine.
- A patient should avoid alcoholic beverages and not drive or perform any chore that require vigilance due to the side effect of dizziness.
- Avoid taking Memantine if you are allergic to any of the inactive ingredients of the drug
- Before taking Memantine, tell your doctor about your medical history preferentially if you have any kind of liver disease, kidney disease, severe urinary tract infection or difficulty in urination, change in diet, and seizures etc.
- Check with your doctor in case of pregnancy or breast feeding due to lack of information about its excretion in milk.
- In case of surgery including dental surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the prescription/ nonprescription drugs and herbal products that you are taking.
- Regular appointments should be made with your doctor so as to assess the progress.
Memantine side effects
Along with the useful effects Memantine may be associated with some unwanted side effects which range from common to severe ones. Common ones affect less than 1 in 10 patients who take this medication. These include:
- Dizziness
- Vomiting
- Cough
- Headache
- Body pain
- Weight gain
- Sleepiness
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Constipation
If any of these symptoms persist and become troublesome consult with your doctor or pharmacist.
In some cases side effects can be serious and needs immediate medical attention and emergency help
- Hallucinations
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Breath shortness
- Severe allergic reactions including rashes; itching; swelling of the mouth, face or lips
- Difficulty in breathing
- Chest pain
- Fainting
- Severe or persistent weakness
- Urination problems
- Mood, or behaviour changes including depression, anxiety, aggressiveness
- Weakness at one-side
- Blistered, peeling, swollen, or red skin
- Persistent or severe dizziness /headache
- swelling of the feet, or hands
- Changes in speech and vision
Memantine overdose
What should I do in case of overdose?
Try to avoid taking the overdose of the drug. Symptoms include unconsciousness, hallucinations, impatience, lethargy and personality change.
- In case you or some other person has taken overdose of this medication contact your local poison control centre at 1-800-222-1222 or emergency room immediately.
- Call local emergency services at 911 in case a patient collapses or faces difficulty in breathing.
- General supportive measures should be employed in any case of overdose.
- Enhance the expulsion of the drug by urine acidification.
Memantine missed dose
What should I do in case of missing a dose?
- In case you miss a dose, take it as soon as it comes to your mind and continue a regular dosing schedule.
- Skip the missed dose if it is near the time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind not to double the dose to catch up.
Memantine drug interaction
Some drugs may interact with Memantine and hence care should be taken while consuming these medications together.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (such as acetazolamide, methazolamide) and sodium bicarbonate: These drugs/products responsible for making urine alkaline affect the working of the medicine and increase the risk for serious side effects. The clearance of Memantine diminishes around 80% and accumulates with increased risk of adverse effects under these conditions.
- N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) Antagonists (drugs that blocks or reduces the biological effect): The use of Memantine with other NMDA antagonists such as dextromethorphen, ketamine, and amantadine has not been thoroughly investigated and therefore should be approached with high precaution. These possibly may be responsible for augmenting the levels and thereby adverse effects of Memantine and also increased risk of central nervous system adverse effects.
Does Memantine use interfere with other diseases
Some diseased state may interact with the use of this medication. Hence, the use of Memantine under such conditions is contradicted and not recommended.
- Liver function:The use of Memantine in patients with severely reduced liver function has not been evaluated and hence not recommended. Consult with your doctor under such situation about the probable side effect, modification in the dosage and need for special monitoring.
- Kidney function:Memantine is not prescribed for patients with severe kidney disorders as this may lead to accumulation of Memantine in the body with increased side effects.
- Reduced elimination from the body:The removal of Memantine from the body get reduced in certain conditions including change in diet, use of certain medications such as sodium bicarbonate, acetazolamide etc., renal tubular acidosis, or infection in urinary tract. Your doctor needs to examine your condition strictly under such circumstances.
- Seizures:Memantine effect has not been studied in people having seizures. Discuss with your doctor on the use of Memantine, its dosage and effectiveness and how this medication may affect your medical condition, with special monitoring if needed.
- Heart disease:Memantine may lead to an increase in blood pressure, slowed heartbeat and sometimes, heart failure. In case of patients with heart problems, Memantine use should be done with caution.
Where can I get more information
Your pharmacist or health care provider can provide complete information about Memantine its use, benefits and the associated risks.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug.
- The double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial studies of Memantine on care dependent patients suffering with severe form of dementia have shown the use of Memantine in functional improvement and reduction in care dependence.
- The efficacy of Memantine in advanced stages of dementia has also been studied in the first large-scale systematic and prospective clinical trial of therapeutic intervention of Memantine.
- Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials across 32 sites in the United States have shown functional improvement of patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer disease.
- The efficacy and safety of Memantine was also proven in randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, clinical trial of Memantine in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.
- Role of Memantine is also under study fora number of disorders/diseases including anxiety disorder, epilepsy, depression, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), glaucoma, pervasive developmental disorders, HIV associated dementia, multiple sclerosis, migraine, Down syndrome and for protection of cognitive function during whole brain radiation etc. and for protection of cognitive function during whole brain radiation etc.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
- Memantine . Wikipedia information. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Memantine
- DrugBank: Memantine (DB01043). www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01043
- Memantine: MedlinePlus Drug Information.
- http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a604006.html
- Memantine | C12H21N | ChemSpider. chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.3914.html
- MEMANTINE HCl – Food and Drug Administration. http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/briefing/3979B1_01_ForestLabs-Memantine.PDF
- Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12672860
“Erlotinib, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
“Furosemide, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
