Contents
- What is Mupirocin (Bactroban)?
- What is the generic and brand name of the drug?
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Why is this medication prescribed?
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug.
- Chemical information of the drug
- What is the available strength of the drug?
- How the medicine works (mode of action)?
- What are the recommended doses of Mupirocin?
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Mupirocin?
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug?
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Mupirocin?
- How to use the drug?
- How to store the drug?
- How to dispose the medicine?
- Does Mupirocin has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies?
- Other uses of the drug
- What special dietary precautions should I follow?
- What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Mupirocin?
- What are the possible side effects of this drug?
- What should I do in case of overdose?
- Does Mupirocin have any interaction with other drugs?
- Does Mupirocin have any interaction with diseases?
- Where can I get more information?
- Clinical research and current scenario of the drug.
- References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases.
What is Mupirocin (Bactroban)?
- Mupirocin is an antibiotic class of drug that is used for the treatment of primary or secondary bacterial skin infections.
What is the generic and brand name of the drug?
- The drug is available under generic name Mupirocin and brand names Bactroban or Centany.
- GlaxoSmithKline is responsible for the manufacture of Mupirocin and the drug is marketed by SmithKline-Beechem.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)?
- Mupirocin is a naturally synthesized antibiotic agent that is isolated from a strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens (NCIMB 10586, developed by Beecham.)
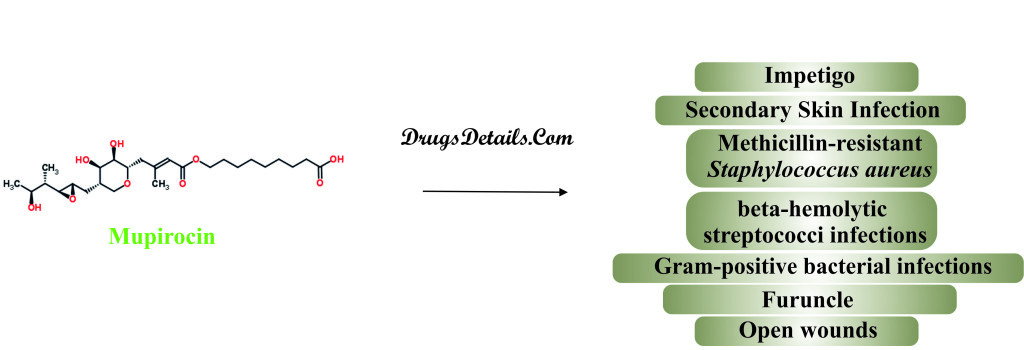
Why is this medication prescribed?
- Mupirocin is ranked among one of the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, which is primarily a list of the most important medications needed in a basic health system.
- Mupirocin is widely used for treatment of complications related to the skin caused by bacteria i.e. Impetigo (blisters or sores on the face, neck, hands, and diaper area), Furuncle (a deep folliculitis, infection of the hair follicle) and open wounds.
- Mupirocin is also used to treat infection caused by gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and beta-hemolytic streptococci including Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Mupirocin is highly effective in the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which is one of the major leading causes of death in hospitalized patients having received systemic antibiotic therapy.
- Mupirocin is also used for the treatment of the nasal infections.
- Mupirocin is bactericidal (acts by killing the bacteria that cause infections) agent at high concentration while it is bacteriostatic (inhibiting the growth or reproduction of bacteria) at low concentrations.
- However, Mupirocin does not provide any protection against fungal, viral and anaerobic bacterial infections.
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug.
Mupirocin chemically belongs to the class of organic compound which are known as monoxycarbolic acid. Monoxycarbolic acid is characterized by aliphatic tail that contains between 4 and 12 carbon atoms. The detailed chemical classification of Mupirocin is described below:
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | Lipid and lipid like molecule |
| Class | Fatty acyls |
| Sub Class | Fatty acid and conjugates |
| Direct Parent | Medium chain fatty acids |
Chemical information of the drug
- Mupirocin is a natural aliphatic heteromonocyclic antibacterial compound, which is represented with a molecular formula C26H44O9.
- Mupirocin is chemically known as 9-[(E)-4-[(2S,3R,4R,5S)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[[(2S,3S)-3-[(2S,3S)-3-hydroxybutan-2-yl]oxiran-2-yl]methyl]oxan-2-yl]-3-metylbut-2-enoyl]oxynonanoic acid.
- The melting point of Mupirocin is 77°C -78 °C and molecular weight is 622g/mol.
- Mupirocin is chemically a mixture of several pseudomonic acids such as seudomonic acid A (90%), pseudomonic acid B, pseudomonic acid C, and pseudomonic acid D.
- Mupirocin is white or off white crystalline powder, solid in texture and freely soluble in acetone, chloroform, methanol and ethyl alcohol.
- Mupirocin is very slightly soluble in water (0.0265mg/mL) and slightly soluble in ether.
What is the available strength of the drug?
- Mupirocin is available in ointment, and cream form for topical use on skin.
- Mupirocin Nasal solution is also available for the treatment of nasal infections.
- Mupirocin ointment is available in the form of tube of 15 and 30 gm while Mupirocin nasal is available only in the form of 1 gram tube (single use only).
- The Mupirocin ointment/nasal contains 2% w/w Mupirocin (equivalent to 2.15% w/w Mupirocin calcium) as active ingredient in bland water based emulsion.
- Mupirocin ointment contains inactive ingredients such as mineral oil, cetyl alcohol, benzyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, phenoxyethanol, cetomacrrogol 1000, xanthan gum and purified water.
- Mupirocin nasal contains paraffin and mixture of glycerine esters as inactive ingredients.
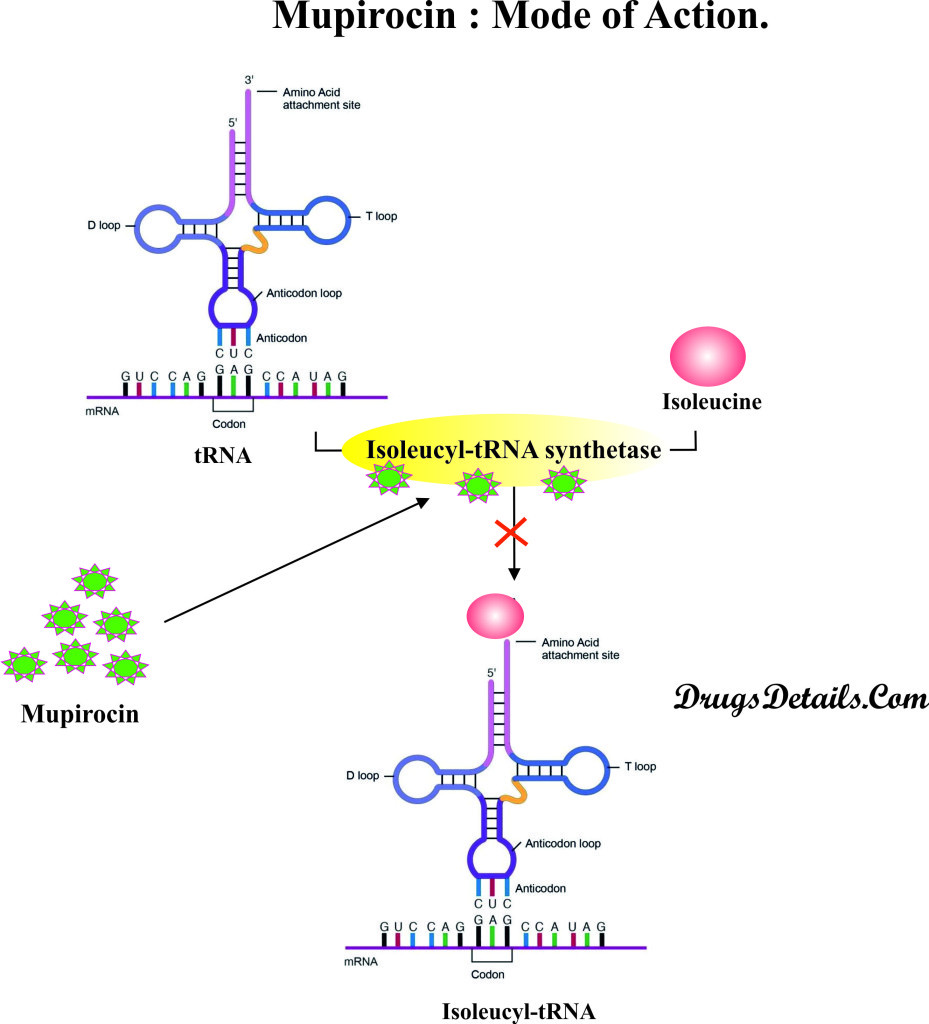
How the medicine works (mode of action)?
- Mupirocin is an antibiotic that acts by reversible binding to the bacterial Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase
- Bacterial Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase enzyme is involved in the formation of Isoleucyl-tRNA from tRNA and isoleucine.
- Inhibition of bacterial Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase enzyme results in the inhibition of RNA and protein synthesis.
- Inhibition of RNA and protein synthesis affects other processes such as cell wall formation, cell division, DNA synthesis and overall bacterial growth and multiplication.
- Due to distinctive mode of action, cross resistance with other class of antimicrobial agents is not established by Mupirocin.
- At low concentrations Mupirocin acts as bacteriostatic agent (substances that inhibits bacterial reproduction, rather than killing), and bactericidal (agent that kill the bacteria) at high concentrations.
What are the recommended doses of Mupirocin?
The recommended dose of Mupirocin varies depending upon the age and diseased state of the patient:
Doses for adult patients:
- For the treatment of Impetigo: Apply 2% Mupirocin ointment thrice in a day on affected area.
- For the treatment of Secondary Skin Infection: Apply 2% Mupirocin ointment thrice in a day on affected area for 10 days
- For the treatment of Methicillin resistant Streptococcus aureus Colonization (intranasal): ½ tube in each nostril twice daily for a period of 5 days.
Doses for paediatric patients:
- Treatment of Impetigo: Apply 2% Mupirocin ointment thrice in a day on affected area (not recommended for patients less than 2 months)
- Treatment of Secondary Skin Infection: Apply 2% Mupirocin ointment thrice in a day on affected area for 10 days (not recommended for patients less than 3 months)
- Treatment of Methicillin resistant Streptococcus aureus Colonization (intranasal): ½ tube in each nostril twice daily for 5 days (not recommended for patients less than 12 years)
Doses for geriatric patients:
- There is no significant difference in efficacy and safety of Mupirocin ointment as compared to younger patients. Dosing should be recommended same as adult doses or as prescribed by your pharmacist or doctor.
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Mupirocin?
- The drug is contraindicated in case of pregnancy, breastfeeding or hypersensitive response to any component of the drug.
- Mupirocin should not be used in case of moderate or severe renal impairment.
- Prolong use of Mupirocin should be avoided because it sponsor the infection of other non-susceptible organism.
- Discontinue the use of Mupirocin in case of local irritation or sensitization.
- Mupirocin use should be withheld if you taking other antibacterial drug especially Chloramphenicol.
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug?
- Pharmacokinetic studies suggested that after administration, no measurable systemic absorption of Mupirocin is detected.
- Mupirocin has approximately 97% protein binding.
- Following intravenous or oral administration, Mupirocin is metabolized rapidly into inactive monic acid and eliminated by renal excretion.
- The average median half-life of Mupirocin is 20 to 40 minutes.
- Approximately 1.25% (0.2% – 3.0%) of Mupirocin dose is mainly excreted in urine in the form of monic acid over the period of 24 hour following the last administration.
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Mupirocin?
- The Mupirocin is classified by US FDA pregnancy category: B
- Due to lack of adequate and well-controlled studies the use of Mupirocin in pregnant women is contraindicated and recommended only when benefit justifies the risk.
- Laboratory studies in animals have shown no adverse effect on fetus.
- No data is available that supports the excretion of Mupirocin into human breast milk.
- Despite these facts caution should be exercised when taking Mupirocin.
How to use the drug?
- Mupirocin is available in ointment form for the use on skin only.
- Mupirocin ointment is generally use three times in a day for 7 to 14 days or as prescribed by pharmacist or doctor while Mupirocin nasal should not be used for more than 5 days.
- Mupirocin nasal tubes are only for single use and discard the tube after use.
- Mupirocin is neither applied to burns (unless prescribed by pharmacist) nor to eyes or mouth.
- Mupirocin ointment is not applied in nasal infection while Mupirocin nasal is not use in case of skin infection.
- Mupirocin is applied as a thin film on infected are and may be covered with sterile dressing.
- It is advisable to use Mupirocin exactly as directed and not to use more than three times a day.
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet and use Mupirocin exactly as directed. Ask your pharmacist for any information or any part you are unable to understand.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor, since the dosage is based on patient medical condition, treatment responses and usage with other drugs.
How to store the drug?
- Mupirocin is stored at 25°C (77°F) and excursion permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
- Store the medicine away from heat, moisture and oxidizing agents.
- Container should be closed tightly
- Mupirocin should not be refrigerated.
- The drug should be kept away from children and pets.
How to dispose the medicine?
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used container.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- The drug should neither be flushed down in the toilet nor poured in the drain.
- Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company for proper disposal.
- Mupirocin topical cream/ ointment have received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 1987.
- The intranasal form of Mupirocin has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in October 1995.
- Mupirocin has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 1996 for the treatment of nasal bacterial infection.
Other uses of the drug
- Mupirocin is also used for the treatment of open wounds.
- Mupirocin may also be used for other uses not listed here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special dietary precautions should I follow?
- It is generally recommended to continue with the normal diet, unless and until asked by your doctor.
What special precautions should I follow/ What should I avoid while using Mupirocin?
- Do not use the medicine if you are hypersensitive or allergic to Mupirocin or any component of Mupirocin ointment or Mupirocin nasal that are used as inactive ingredients.
- Mupirocin is not used at central intravenous sites or with intravenous cannulae because it may develop antimicrobial resistance.
- Consult with your doctor and pharmacist if you are taking any prescription and non-prescription medications or herbal products.
- Consult your doctor in case of any query.
- It is recommended to avoid use of other antibacterial or antimicrobial drugs during Mupirocin therapy.
- It is recommended to avoid use of cosmetic product on the affected and treated surface.
What are the possible side effects of this drug?
In addition to the associated benefits, Mupirocin also is accompanied with the side effects some of which are more common, others less common whereas some that fade away with time while you take the drug. It is always recommended to consult a doctor if you encounter any of the side effects.
Some of the less commonly occurring side effects but requiring medical attention is outlined as:
- Burning
- Pain on the site of application
- Rashes
- Stinging
Some side effects are rare but requiring medical attention is outlined as:
- Blistering on skin
- Canker sores
- Dry, cracked or scaly skin
- Irritation, itching and reddening of the skin
- Ulcers, white spots or sores inside the mouth
- White spots and sores on tongue or lips
There are some adverse effects that disappear while consuming the drug with time. If you have any query about these symptoms consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
- Headache
- Nausea
Mupirocin may not be associated with following symptoms. If you take any other medication along with Mupirocin and you feel following side effect, consult to your doctor.
- Tenderness in stomach or abdomen
- Cough
- Difficulty with swallowing
- Fast heartbeat
- Dizziness
- Fever
- Hive like swelling on lips, face, eyelids, tongue, throat, hand, legs or sex organ
- Pain and severe abdominal and stomach cramps
- Tightness of chest
- Severe bloody diarrhoea
What should I do in case of overdose?
- If you overdose the drug contact with your doctor or pharmacist for symptomatic and supportive measures.
- Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- Apply a missed dose as soon as possible.
- To make up the missed dose, do not apply extra ointment on infected area.
- Avoid applying the missed dose if it is about time for your next dose.
Does Mupirocin have any interaction with other drugs?
- The concomitant application of Mupirocin ointment and other drugs has not been evaluated.
- However, other topical medications may result a change in the skin absorption pattern of Mupirocin.
- It is therefore recommended to avoid application of other topical drug simultaneously with Mupirocin topical on the same area unless asked by your doctor.
- Other nasal drugs may also affect the working or absorption of Mupirocin nasal and hence should not be used together.
- Some other drugs may also interact with Mupirocin nasal including prescription, non- prescription, herbal products, and vitamin.
Does Mupirocin have any interaction with diseases?
Before you begin to take Mupirocin, it is necessary to discuss any medical condition or allergies you have or any other significant fact. It has been observed that following medical conditions (disease) may interact with Mupirocin:
- Allergy: Use of Mupirocin should be avoided in people who are allergic to Mupirocin or any other drugs especially Chloramphenicol.
- Renal dysfunction: Moderate or severe renal impairment leads to absorption of large quantities of polyethylene glycol (PEG). Mupirocin ointment is formulated in PEG base whose lipophilic properties allow it to readily enter the lipid bilayer and exert its cytotoxic effects.
- Severe burns or large open wounds: Polyethylene glycol from Mupirocin ointment and not cream or nasal ointment can be absorbed from open wounds, severe burns and damaged skin to be excreted by the kidney where it may also produce serious cytotoxic effects.
Where can I get more information?
Your pharmacist or health care provider can provide more information about Mupirocin.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug.
- Reproduction studies with subcutaneously administered Mupirocin in rats (male/ female) at doses up to 14 times the human topical dose (approximately 60 mg Mupirocin/day) revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or reproductive performance.
- The safety and efficacy of Mupirocin ointment (2%) have been established in the paediatric population (2 months to 16 years).
- Clinical studies regarding the evaluation of carcinogenic potential of Mupirocin have not been conducted in animals.
- Reproduction studies with Mupirocin in rats and rabbits at subcutaneous dose (greater than 22 and 43 times the human topical dose) revealed no evidence of toxicity to the fetus.
- Clinical studies indicate the efficacy and safety of concomitant topical use of Fluticasone propionate 0.005% and Mupirocin 2.0% ointment in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
- Clinical studies advocate the long term use of low but bactericidal concentrations of Mupirocin in healing wounds without impairment of fibroblasts growth.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases.
- Mupirocin. Medline plus information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a688004.html.
- Mupirocin.Drug Bank Information (DB00410). http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00410.
- Mupirocin. ChemSpider Information. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.393914.html.
- Mupirocin.Pubmed Health. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0001225/.
- Nasal decolonization of Staphylococcus aureus with mupirocin: strengths, weaknesses and future prospects. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19451132.
- Mupirocin ointment for preventing Staphylococcus aureus infections in nasal carriers. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18843708.
Read about,
“Clopidogrel, drug class, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
“Enoxaparin, drug class, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“
