Contents
- What is Spirulina?
- Spirulina history of use
- Why is spirulina called a “superfood”?
- NASA and spirulina
- What is spirulina made of?
- Spirulina vs other foods
- Spirulina as an energy and endurance booster for athletes
- Spirulina antioxidant properties
- Spirulina cardiovascular benefits
- Spirulina for better immunity
- Spirulina and cancer prevention
- Spirulina antiviral properties
- Spirulina use for diabetes
- Spirulina use for liver diseases
- Spirulina for chronic fatigue
- Spirulina for Candida infection
- Can Spirulina improve memory and academic performance?
- Spirulina for neurodegenerative diseases
- Spirulina for allergies
- Spirulina for Iron Deficiency
- Is Spirulina good for crash diets?
- Spirulina for chronic arsenic poisoning
- How much Spirulina should I take?
- When is the best time to take Spirulina?
- What is the proper Spirulina composition in dietary supplements?
- How to choose the best Spirulina brand product?
- Precautions and warnings during Spirulina use
- Spirulina side effects
- Cultivated Spirulina safety
- Spirulina interactions with other drugs
- Who should avoid Spirulina?
- Spirulina and Vitamin B12
- Spirulina use for pets, other animals and plants
- Spirulina recipes
What is Spirulina?
Spirulina refers to a dry mass of gram negative, non-toxic cyanobacterium (uni-cellular microalgae) called Arthrospira platensi. It belongs to the groups of Cyanobacteria and Prochlorales. These free-floating filamentous photosynthetic-oxygenic organisms were first considered as algae, until 1962 when these blue-green microalgae were added to prokaryote kingdom and proposed to call as Cyanobacteria. The main cause for this classification was that algae are considered to be a very large and diverse group of eukaryotic organisms.
Spirulina got its name because of bacterial helical (spiral) shaped trichomes of varying size. The filaments are solitary and are reproduced by binary fission whereas the cells of the trichomes vary in size from 2 μm to 12 μm to the maximal of 16 μm.
Arthrospira platensis grows in fresh and salty water as well as in brackish bodies of water. It grows best in a highly alkaline environment with pH values 10-12. Best natural conditions for its growth currently exist in certain lakes in Sub-Saharan Africa (Chad area) as well as in California, Mexico and Central America. It is cultivated worldwide and it is used as a dietary supplement but also as a whole food.
It is available as a supplement in tablet and powder form and can be used as a feed supplement in the aquarium, aquaculture and poultry industries. The largest commercial producers of spirulina are: the United States, India, Taiwan, Thailand, China, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Myanmar, Greece, and Chile.

Despite spirulina’s fast growing reputation of a superfood, its nutritional wealth status might not necessarily lead to better health. Its benefits are still researching. However, patients with various health issues swear by Spirulina that it does promote their overall health and well-being.
Spirulina history of use
Spirulina has been used for centuries due to its nutritional and health properties in various cultures including: Aztecs, Toltecs, Mayas, Kanembu people of Lake Chad, and other ancient cultures.
In Aztec’s tradition spirulina was very prized. It grew wild in the great soda lakes of Central Mexico. When Bernal Díaz del Castillo (soldier and writer) come with the conqueror Cortes to Mexico in 16th century, he discovered tecuitlatl, a small cakes of Spirulina, which the Aztecs traded literally in the same way as the Europeans traded cheese.
He was puzzled how this “blue-green mud” was appreciated in their culture and how Aztecs found it delicious. They made it into bread, which tasted somewhat similar to cheese, mixed it with some grain dishes and sauces. The Aztecs collected Spirulina from the lakes surface with fine meshed nets. On shore, they will smooth the earth into flat beds and then spread the Spirulina out to dry on the sun. The wet paste, which was about 3-4cm thick, would be dried to a thickness of 2-3 mm.
There are stories about how the great Montezuma loved to eat fish. Unluckily, his palace was 180 miles away from the Gulf of Mexico. So, he ordered marathon runners to provide him fresh fish every day. These athletes will run up to 100 miles a day, and Spirulina was a crucial part of their diet. Stopping for a brief rest, they would take some Spirulina and mix up with water to give them energy, endurance and fast recovery.
There are also evidences that the Mayas, who lived in Central America, cultivated Spirulina in the network of waterways that was also used for irrigating crops.
Spirulina has been used as main source of nutrition for centuries by the Kanembu people living at the shores of Lake Chad. It remains one of their main sources of protein. They dry spirulina on the warm sand and sun, mixed it with water and transform into the paste which will then be dried into biscuit, known as dihé. Dihé was eaten plain by pregnant women, who believed that its color will “protect their unborn babies from the eyes of magus”.
Why is spirulina called a “superfood”?
Spirulina is the most nutritious whole food known to humankind. It also might have amazing health benefits such as: blood sugar regulation, blood pressure and cholesterol regulation, pain relief from inflammation, antioxidant activity that guards against life threatening diseases such as heart disease and stroke, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, spirulina can protect the liver and kidneys and remove radiation from the body; it can also improve the immune system, increase mood and endurance, alleviates allergies, fight many different viruses; helps your eyes and brain functioning; help you lose weight, improve digestion and increase bacterial flora in intestines.
Spirulina is an ideal food supplement for people of all ages and lifestyles. It provides athletes long-lasting energy, endurance, strength and reduces recovery time. It is helpful in people and patients who have digestion and elimination problems.
It also satisfies the appetite giving essential nutrients to those who are on weight-reduce diets. It also supports children and others who don’t eat enough vegetables to eat their greens by taking a few tablets and it helps busy people who don’t have time for regular, balanced meals to nourish themselves.
According to all stated, Spirulina is a “Superfood”, indeed!

NASA and spirulina
Due to its nutrient’s wealth and health benefits Spirulina has been subjected to NASA research and is being considered as a food to be taken into space. It would be an ideal type of food to be cultivated in closed objects such as a space station because of its special characteristics to grow very quickly, takes up low space, and its nutrient wealth that could be met by recycled waste, in exchange for which it would provide the astronauts with concentrated nutrition and oxygen. NASA found that 1 kg of spirulina had the same amounts nutrients as approxiamtely 1,000 kg of mixed vegetables.
What is spirulina made of?
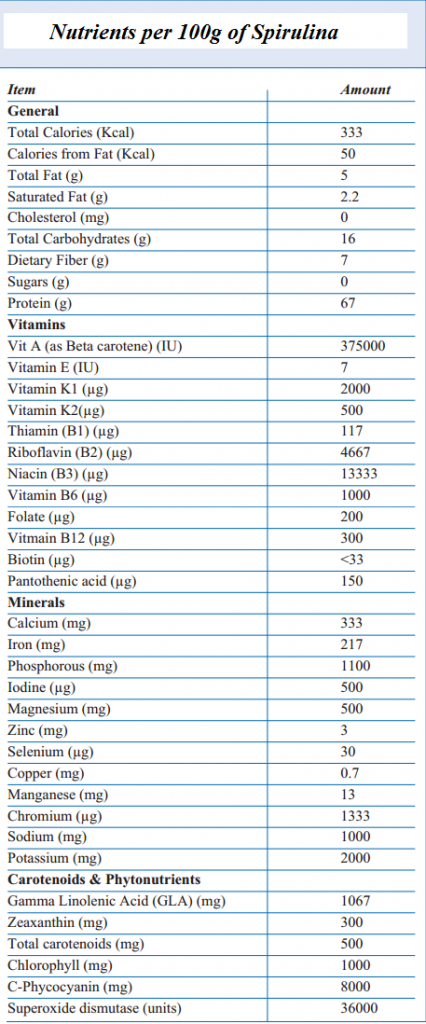
Spirulina is about 60% full and highly digestible protein containing: all essential amino acids, beta-carotene in concentrations higher than any other whole food and gamma linolenic acid (GLA) in very high amounts. Spirulina is also rich in: B complex vitamins, trace elements, minerals, chlorophyll, and enzymes and is plentiful in other nutrients including carotenoids, glycolipids, sulfolipids, phycocyanin, DNK, RNK, superoxide dismutase, etc. Typical nutrient content of a commercially available Spriulina product is shown in picture below:
Besides it wealth composition of basic nutrients including: amino acids, essential fatty acids, vitamins and minerals, Spirulina also contains many different phytonutrients that are lacking in most of our diets. Furthermore, Spirulina supplies common nutrients at very high levels.
Spirulina vs other foods
When Spirulina is compared with other foods it shows its unusual nutrient profile:
- 180% more calcium than whole milk
- 670% more protein than tofu
- 3100% more beta carotene than carrots
- 5100% more iron than spinach
- more antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions in 3 g of Spiurlina than in five servings of fruits and vegetables
- comparing levels of phytonutrient, Spirulina is 31 times more powerful than blueberries, 60 times more potent than spinach and 700 times more powerful than apples
Spirulina as an energy and endurance booster for athletes
Spirulina contains different antioxidants, such as vitamin E, b-carotene, gamma-linolenic acid, polyphenols and phytocyanins, and all of them are able to reduce amounts of exercise-induced reactive oxygen compounds that are usually linked with tiredness, loss of energy, stamina and endurance, muscle fatigue and slow recovery during and after excess physical activity.
Particularly, Maria Kalafati et al study reported for the first time that supplementation with spirulina during 4 weeks improved exercise performance, possibly through the mechanism of an increased fat oxidation rate, and increased GSH (glutathione) levels.
Enhanced performance and increased beta oxidation of fatty acids after spirulina supplementation are yet unknown, thus more research is needed to elucidate this. However, a high content of γ-linolenic acid in spirulina (21.7% of total fats (7%) in dry spirulina) may play an important role in facilitating the reported effects on fat metabolism in the present study
Two smaller studies on humans also found moderate performance improvements and increases in quadriceps force. The most convincing study was animal study on rats in which there were clear, moderate to extremely large improvements in a dose-dependent manner during spirulina intake.
There are also anecdotal evidences suggesting that the Cuban and Chinese Olympic teams have used spirulina daily for many years and have reported their physical and mental improved performances.
Erwin Koeman form Dutch national soccer team stated following: “I use Spirulina simply because it works and it is 100% natural. I feel fitter, have a better resistance and recover more quickly after exertion, whether it is a heavy training session or a match. My last condition test showed clearly that I had more stamina than last year.”
Spirulina antioxidant properties
Spirulina contains: carotenoids, phycocyanin, superoxide dismutase and vitamin C and vitamin E which are all considered as high-effective antioxidants.
Carotenoids from Spirulina and its antioxidant properties
Carotenoids are vitally important antioxidants for our health. Numerous studies have been discovered that people who intake a lot of foods rich in carotenoids have lower their risk of developing different types of cancer. Spirulina is a natural source of different carotenoids. There are around 400-600 carotenoids. Almost all studies so far have been focused on beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein, zeaxanthin and most recently astaxanthin. Spirulina is not only rich in beta-carotene, but it also has very important carotenoids such as zeaxanthin and beta-cryptoxanthin aswell as lesser-known carotenoids such as echinenone and myxoxanthophyll. Different carotenoids have various antioxidant functions in the body, e.g.:
- Beta Carotene. Beta carotene is most prevalent carotenoid in Spirulina. There are remarkable and very prospect findings showing that carotenoids are not only the scavengers of active free radicals but also compounds that may affect the way our cells communicate. For example, beta-carotenes are able to stop cancerous cells to receive growth chemical signals from other cells. Beta-carotene is able to open the cell membrane of cancerous and pre-cancerous cells, allowing the body to signal the cancerous line to stop dividing. Beta-carotene seems to play role also in preventing heart disease. It can discourage the formation and oxidation of low-density LDL-cholesterol, thus decreasing the chance of atherosclerosis. Some studies also found that beta carotene may stimulate immunocompetence in healthy individuals and but also it may enhance immune function in patients who are tested HIV positive. Immune system cells are among the most sensitive to oxidation. However, there are some suggestions indicating that beta carotenes work in conjunction with vitamin C to reduce the energy of free radicals. So, in the absence of Vitamin C, beta-carotene can actually form pro-oxidant forms, leading to eventual accelerated cellular damage. It is known that smokers are deficient in Vitamin C so in theory supplementation with beta carotenes in heavy smokers may slightly increase cancer risk.
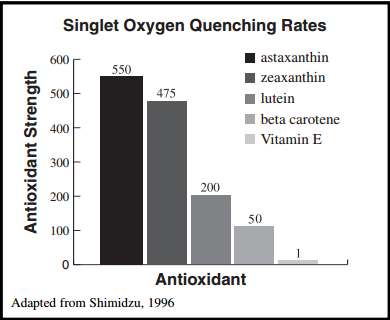
- The second most prevalent carotenoid in Spirulina is zeaxanthin. Zeaxanthin is a very potent and important antioxidant for two reasons: It is very rare antioxidant that can pass the blood brain barrier and bring antioxidant protection to the brain, eyes and CNS in general and the second is its capability of never becoming a pro-oxidant which is not the case with beta carotenes. Zeaxanthin is currently in the process of investigation, and researchers are considering it as the one of the most powerful antioxidant with many benefits. As a powerful antioxidant and filter of the high-energy blue light, Zeaxanthin protects macula and lens of the human eye. Prevention of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, lung cancer, skin conditions related with excessive ultraviolet (UV) light exposure have been also confirmed. Studies found that zeaxanthin is so potent that it beat out all other antioxidants in singlet oxygen reducing rates except for astaxanthin. It beat Vitamin E by over 400 times, as shown in picture below.
Phycocyanin from Spirulina and its antioxidant properties
Phycocyanin is a powerful hydroslouble antioxidant. Pinero et al, 2001 study showed that an phycocyanin is a potent free radical scavenger that inhibits microsomal lipid peroxidation.
The unique nature of phycocyanin will surely make Spirulina a level above other antioxidant foods or formulas. Phycocyanin antioxidant effects have been shown promisable for following health issues: kidney and liver diseases, treating cancer in animals, stimulating the immune system, anti-inflammatory actions, allergies, virus fighting, radioactivity removal and cardiovascular protection.
Superoxide Dismutase from Spirulina and its antioxidant properties
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) or so called “antioxidant catalyst” is considered as the one of the fastest acting and most essential antioxidants in protecting the human body against dangerous oxidative stress. Since it as an enzyme, the biggest problem with exogenous SOD has been that, it is hard to obtain active absorption of this enzyme into the bloodstream and throughout the body.
Enzymes are known to be generally unstable and can’t handle acids of the stomach. However, Spirulina formulations are dissolving into intestines and are able to avoid stomach acid. Superoxide dismutase catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide radicals to hydrogen peroxide. It has been showed that this enzyme play important role in the mechanisms of aging.
Studies showed its benefits for: age-related degeneration such as preventing hearing loss, neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or “Lou Gehrig’s disease). Anti-oxidant activity of SOD have also proved benefits in protecting blood vessels, heart, kidney, lungs and placenta.
Spirulina cardiovascular benefits
Many papers described cardiovascular benefits of Spirulina. One review of spirulina cardiovascular benefits from 2009 suggested that oral administration of spirulina may have beneficial effects in the prevention of cardiovascular events including: increased blood pressure and plasma lipid concentrations, especially tryglicerides and LDL-cholesterol.
Indirectly spirulina may also modify the total cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol levels. A recent study by Torres-Duran PV et al proved antihyperlipidemic and antihypertensive effects of Spirulina. One Korean however smaller study also proved benefits of Spirulina on blood lipid status, as well as on immune markers and antioxidant capacity.
Another study conducted on patients with hyperlipidemic nephrotic syndrome found that total cholesterol was decreased by 65%, LDL-C was decreased by 54% while triglycerides levels saw a decrease of almost 200% more when Spirulina was used in combination with standard therapy than the standard therapy alone. The authors concluded that Spirulina capsules, rich in antioxidants such as amino and fatty acids, GLA, helped to reduce the increased levels of lipids in these profiles.
More studies are needed to confirm spirulina cardiovascular benefits as many scientists believed that there is some specific yet unidentified phyto-anti-cholesterol compound in spirulina dry mass. Some studies have discovered that novel protein C-Phycocyanin can positively influence serum cholesterol concentration and prevent heart and blood vessels.
In animal models, it has been shown that Spirulina or just C-phycocyanin extracted from Spirulina may have preventive actions on drug-induced cardiac side effects such as those with anti-cancer medication doxorubicin as well as a protective effect during heart attack and it better recovery. Moreover, it has been confirmed that phycocyanin is able to decrease infarct size, attenuated creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase release, and suppressed ischemia-reperfusion induced free radical generation.
The most recent spirulina’s cardioprotective benifical findings are:
- Spirulina water extract may inhibit the intestinal absorption of dietary fat due to pancreatic lipase activity inhibition
- The sulfated polysaccharide called Sodium Spirulan is able to inhibit vascular endothelial cell proliferation.
- Selenium-rich phycocyanin extracted from Spirulina may prevent the development of atherosclerosis
Spirulina for better immunity
There are well-documented proofs showing that Spirulina may improve resistance to viral infections and boost immunity at whole. For many years, spirulina users have anecdotally reported a decrease in colds and flu after its use. Several animal studies have also shown good immunostimulatory effects after spirulina testing particularly by stimulating the production of antibodies and cytokines.
Spirulina has been also been shown to activate macrophages, T and B lymphocytes cells. Sulfolipids compounds isolated from Spriulina have been proved effective against HIV infection. There are also positive findings from spirulina extract biomass against herpes virus, influenza virus, cytomegalovirus etc. Spirulina extracts may be also capable of inhibiting carcinogenesis.
In 2008, a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide called Immulina has been extracted from Spirulina. Denmark researchers found that Immulina is among 100x and 1000x more potent in activating monocytes than other polysaccharide formulas used at the time in clinical settings for cancer immunotherapy. Immulina was found to be very effective against Candida albicans and tetanus toxoid.
Furthermore, Immunlina has been showed significant enhancement of blood immune markers such as: TNF alpha, interferon gamma, and IL-6, after 8 and 14 days of continuous consumption.
Phycocyanin from Spirulina, except described antioxidant properties also poses important immune boosting and anti-viral properties. Studies from Japan indicated that phycocyanin can increase resistance to infection and may have significant effect on immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. It has been concluded that phycocyanin augments biological defense against infectious diseases via supporting functions of the mucosal immune system and by reducing allergic inflammation due to suppression of antigen-specific IgE antibody.
Another study also described that Spirulina can stimulate the secretion of IL-1beta, IL-4 and interferon gamma.
Spirulina and cancer prevention
Even though there are no adequate data from clnical studies on spirulina cancer prevention, there are numerouspre-clinical animal studies showing Spirulina’s great potential to prevent carcinogenesis reduce tumors. First animal studies, from about 30 years ago, showed total tumor regression of about 30% and partial tumor regression of about 70% when Spirulina and Dunaliella extracts was used in combination.
Already, the next year, another study from Harvard revealed that the same combination of extracts could prevent tumor development in rodent mouths. These 2 studies were pioneers of further investigations.
In 1995, Spirulina anticancer effects have been studied on humans, showing complete regression of precancerous oral lesions in 45% of the 44 subjects consuming Spirulina. From that study, it has been suggested that 3 following active ingredients of Spirulina may have the greatest benefits of cancer prevention:
- Polysaccharide called Calcium Spirulan. One study examined its effects on 3 different types of cancers: carcinoma, melanoma and fibrosarcoma. Calcium Spirulan considerably inhibited the invasion of each of these tumor cells. More studies showed that polysaccharides of Spirulina has chemo-protective and radio-protective actions, and may have additional benefits when taken with anti-cancer therapy. Increased levels of IL-1 and IL-3 and TNF-alpha have been also noticed.
- Hot water extracts of Spirulina biomass containing water soluble pigment C-phycocyanin. It has been discovered that C-phycocyanin may enhance antitumor natural killer cells function. Newest studies also found that C-phycocyanin was able to decrease 49% in the proliferation of leukemia cell line, 50% decrease in the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer) cell line, significant reduction in HeLa cells in vitro in cervical cancer cell, antiproliferative actions against human melanoma.
- A blue pigment phycocyanin known to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties.
Unique nutrients found within Spirulina may also play an important role in Spirulina’s function as antiviral actions. Polysaccharide called Calcium Spirulan is considered to have antiviral properties. It has been shown that calcium spirulan can inhibit the replication viruses including: Herpes simplex type 1, cytomegalovirus, influenza A, measles, mumps, and HIV-1.
The proposed mechanism is selective inhibition of the penetration of virus into host cells. Another antiviral agent found in spirulina is proposed to be dextran sulfate. In one comparable study, these 2 carbo-hydrates have been compared for their efficacy.
Calcium Spirulan has been shown to be superior antiviral agent compared to dextran sulfate. It has been concluded that Calcium Spirulan can be a perspective candidate agent for an anti-HIV therapeutic drug.
An interesting finding after antiviral research from Japan proposed that consumption of spirulina at a regular basis may inhibit the replication of HIV virus. The study observed that populations with high algae including spirulina consumption have respectively lower rates of HIV infection.
Such example can be found in Chad where HIV/AIDS reports are significantly lower than in the rest of Africa. A major tribal group in Chad, the Kanemba, eats Spirulina every day, consuming between 3-13 grams per day. Such connection may indicate the link between Spirulina and HIV virus infection.
Simple water extracts of Spirulina as well as dried Spirulina biomass have been both also established antiviral activity. One study found that both the polysaccharide component of Spirulina and the remaining ingredients after the polysaccharides have been removed have antiviral properties. According to this it can be said that anti-viral properties are not only derived from its polysaccharides thus other components in Spirulina may also play an important role in its antiviral activity.
Spirulina use for diabetes
Some animal studies indicated that spirulina is able to reduce blood sugar levels to a great extent. Some of them pointed that spirulina can be as effective as metformin in long-term glycemic control.
Clinical studies also described that patients with type 2 diabetes who used 2 grams of spirulina per day for 2 months, considerably reduced their blood sugar levels. Glycosilated-hemoglobin – HbA1c, as the most important marker and prognostic factor was also reduced from 9% to 8%. The 1% change of HbA1c is related with the decreased risk of diabetes-related death by 21%.
Spirulina use for liver diseases
Beside many potential benefits, spirulina can be very helpful in patients with chronic liver disease such as those with: liver damage, cirrhosis, hepatitis C viral infection and liver failure.
Spirulina was reported to have: antioxidant effects, harmful metals chelate activity, neutralization of cell-damaging free radicals, and liver damage prevention caused by liver toxin tetrachloride. One more study concluded that spirulina is beneficial for NAFLD patients.
Hepatitis C as a viral infection induces the liver inflammation and may cause liver failure if not discovered in its early phase. Additionally, spirulina possesses immune and antibacterial enhancing properties, which can help with treating the liver illness.
A clinical comparable study that was conducted on 66 people with hepatitis C. 30 of them were treated with the spirulina supplement, whiles the rest were treated with Silymarin. According to the results, the group that was treated with spirulina has a significant improvement in ALT, CLDQ, and ASEX scores, compared to the Silymarin group.
Spirulina for chronic fatigue
Spirulina is known as a “the food of the future” containing specific compounds that may contribute to high energy levels. These energy compounds are carbon-hydrates rhamnose and glycogen and essential fat gama-linolenic acid that are absorbed easily by human cells and help in energy release. Spiriluna has been also shown to increase bacteria healthy microbiota of lactobacillus in the gut, therefore facilitating the production of Vitamin B6 that is also helpful in energy release.
Despite these benefits, the only available placebo-controlled randomized study showed that chronic fatigue reduces were not significantly different between spirulina and placebo. In this study, spirulina taken in doses of 3g per day did not reduce fatigue more than the placebo thus it may have no proper benefits for chronic fatigue. More studies are needed to confirm this.
Spirulina for Candida infection
Spirulina can be very helpful for oral, gut and vaginal Candida albicans infection as several animal studies have proven it to be an effective anti-microbial and antigungal agent, for candida in particular. Furthermore, spirulina has been showed to promote the growth of healthy bacterial flora in the intestines, which inhibits Candida from growing.
Can Spirulina improve memory and academic performance?
Different studies suggest that spirulina may improve both cognitive and memory ability.
One study conducted in Senegal on 549 school children, who were daily administrating 2 g of spirulina for 2 months, showed progress in their academic performance by 10%. It has been proposed that amino acid L-tryptophan found in spirulina which is a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin was responsible for such results. It has been also confirmed that Spirulina can prevent memory loss due to its antioxidant properties by reducing oxidative damage.
Spirulina for neurodegenerative diseases
Findings showed that spirulina, because of its antioxidant properties may also protect the CNS from degenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Spirulina’s protein extract and phycocyanin poses antioxidant activity and work by protecting the cellular antioxidant enzymes and by increasing reduced glutathione in cells against oxidative stress induced by iron.
One animal study discovered that when animals were treated with blueberry, spinach, or spirulina, they had significantly reduced activity of caspase-3 enzyme in the ischemic hemisphere, suggesting that chronic thrapy may reduce ischemia-induced apoptosis and cerebral infarction.
Also, spirulina will not only protect the brain from degeneration, but also sharpen your mind and focus. Some findings suggest that taking spirulina daily will induce productivity and concentration in children with ADHD.
Spirulina for allergies
Spirulina may exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-allergy properties by inhibiting the release of histamine from mast cells.
Recent well-designed study on participants with allergic rhinitis who used Spirulina for 12 weeks found that 2g per day of Spirulina significantly reduced cytokine IL-4 levels by 32%, which is significant in regulating IgE-mediated allergy. This study proved that Spirulina may be high effective for treating allergic rhinitis and other manifestations of seasonal allergies.
Ishii et al. studied the Spirulina influence on immunoglobulin IgA levels in saliva and revealed that it enhances production of, suggesting a potential role of Spirulina for mucosal immunity.
Japanese team also described an important impact of Spirulina water extract to IFN-γ production and Natural Killer (NK) cell that are essential in allergy development.
A placebo-controlled double-blind trial from Turkey evaluated the efficacy and safety of Spirulina for treating allergic rhinitis. It has been found that Spirulina intake significantly reduced symptoms of allergy rhinitis such as: nasal discharge, sneezing, nasal congestion and itching.
Nutrient deficiency may be most significant predisposed factors that are involved in changes of the production of T-cells, IgA antibody response, interleukins and NK-cell activity. The above studies proposed that Spirulina may modulate the immune system by its important role in covering nutritional deficiencies.
Spirulina for Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency can be commonly caused in women, because of iron loss during menstruation, but also because their low-iron diet. Vegetarian women are especially prone to anemia due to iron deficiency. Although the body only needs 1.5 mg of iron per day, the RDA for iron is 15 mg for women and 30 mg for pregnant women. However, only 10 % of dietary iron is absorbed.
The characteristic American diet contains 6-7 mg of iron for every 1000 calories. Six tablets or 3g of Spirulina contain 6.5 mg iron which is equivalent to 80 grams of liver or nearly two cups of raw spinach which are known to be the best sources of iron. However, the iron in Spirulina is easily absorbed by the body, making it more bioavailable.
Is Spirulina good for crash diets?
Crash diets are never recommendable. But, for someone who is a 100 or more pounds overweight, it can be very hard to try to lose weight step by step, thus obese and overweight patients take all sorts of various non-healthy measures to lose as much weight as possible most commonly not thinking about the body’s nutritional needs.
Those who decide to try crash diets, must know the importance of taking food supplements in order to satisfy body nutritional needs. The concentrated nutrition of Spirulina supplements can certainly help to counteract such an assault on the body by providing much of the nutrition that the body needs.
However, even when people lose their weight during crash diets, they usually put the weight back. Constant weight changes are never good and may put a strain on the system thus they are not recommended for good health.
Spirulina for chronic arsenic poisoning
Many people worldwide are at high risk of chronic arsenic poisoning because of polluted water they are consuming. There are millions of chronic arsenic poisoning cases mostly reported in: Bangladesh, Taiwan, India and Chile and the biggest problem is that there is no specific treatment.
However, one well-controlled study has been found that spirulina extract in combination with zinc may become the treatment of choice for chronic arsenic poisoning. In this study, participants have been used spirulina extract in doses of 250 mg in combination with 2 mg of zinc, twice daily for 16 weeks. Additionally, each patient was supplied with arsenic-safe drinking water by installing water filter at household level.
Efficacy of Spirulina extract/zinc combination was evaluated by comparing modifications in skin manifestations and arsenic concentrations in urine and hair. Results showed that this combination may be useful for the management of chronic arsenic poisoning with melanosis and keratosis. More studies are needed but the results are promising.
How much Spirulina should I take?
As a dietary supplement, the recommended minimum amount is 3 grams per day. So it is approximately 1 teaspoon of powder or six 500 mg tablets. Since it is a pure and natural food, and considered safe, you may safely take more.
Patients commonly ask whether they should take all 6 tablets at once or take 2 tablets 3 times a day. The actual answer is that it truly doesn’t matter. Reports have been showed that people are having benefits no matter how they take it. Also, many Spirulina nutrients are insoluble in water and will not be eliminated from the body with urination, taking all 6 doses of Spirulina at once rather than throughout the day do not present any issues.
The maximum dose of Spirulina during the day should not exceed 20 tablets or 10g especially if you are taking it for the first time, since it is really something new for your body and may cause potential gastrointestinal side effects. Rarely, in approximately 1 – 2% of cases, during first few days of use, patients may experience minor issues in their digestive system when taking Spirulina.
These changes usually don’t last long, and after a few days are back to normal and some people used to claim that they usually report feeling much better than ever due to all the positive benefits of Spirulina.
There are reports that body builders and other athletes intake Spirulina in doses of even 50g a day in order to obtain best sport results, without having any significant reported side effect. Many people can get goodresults by varying the amount they take.
For example if you are under a lot of stress, by working long hours, or you have spent a lot of physical energy, you can freely increase your dose. Patients who are on reduction diets may like to experiment Spirulina dose until they find the optimum quantity that helps to satisfy their appetites.
When is the best time to take Spirulina?
Because high-protein foods are known to increase alertness and Spirulina is one of the richest whole food sources of protein, it may be best to take Spirulina at least 4 hours before going to bed. On the other hand, you can take Spirulina whenever you like, before, or between meals, before or after training or whenever your energy level is low.
What is the proper Spirulina composition in dietary supplements?
3 grams of Spirulina powder (1 teaspoon) or 6 tablets of 500 mg tablet or capsule should contain following composition:
General Composition:
- Protein: 53-62%
- Carbohydrates: 17-25%
- Lipids: 4-6%
- Minerals: 8-13%
- Moisture: 3-6%
Vitamins:
- Vitamin A (100% as Beta-Carotene): 11,250 IU
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine): 3.5 mcg
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): 140 mcg
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin): 400 mcg
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): 30 mcg
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin): 9.0 mcg
- Vitamin E (d-a-tocopherol): 285 mcg I
- Inositol: 1.7 mcg
- Biotin (Vitamin H): 0.5 mcg
- Folic Acid: 6.2 mcg
- Pantothenic Acid: 4.5 mcg
- Vitamin K1: 60 mcg
- Vitamin K2: 15 mcg
Minerals:
- Calcium: 10 mg
- Magnesium: 15 mg
- Iron: 6.5 mg
- Phosphorus: 33 mg
- Potassium: 60 mg
- Sodium: 30 mg
- Manganese: 400 mcg
- Zinc: 90 mcg
- Boron: 22 mcg
- Copper: 20 mcg
- Selenium: 0.9 mcg
- Iodine: 15 mcg
Phytonutrients:
- Beta-Carotene: 6.8 mg
- Zeaxanthin: 9 mg
- Chlorophyll: 30 mg
- Total Carotenoids: 15 mg
- C-Phycocyanin: 240 mg
- Total Phycocyanins: 519 mg
- Superoxide Dismutase: 1080 unit
Fatty Acids (Total 48 mg per gram):
Omega 6 Family:
- Gamma Linolenic (GLA): 32 mg
- Essential Linoleic: 33 mg
- Dihomogamma Linolenic: 1.59 mg
Omega 3 Family:
- Alpha Linolenic: 0.0435 mg
- Docosahexaenoic (DHA): 0.0435 mg
Monoenoic Family:
- Palmitoleic: 5.94 mg
- Oleic: 0.51 mg
- Erucic: 0.072 mg
Other Fatty Acids:
- Palmitic Acid: 61 mg
- Myristic acid: 0.4 mg
- Stearic Acid: 2.5 mg
- Arachidonic Acid: 0.2 mg
- Behenic Acid: 0.144 mg
- Lignoceric Acid: 0.072 mg
Proteins:
Spirulina is a great source of dietary protein containing up to 60% of highly digestible protein, with all essential amino acids.
Essential amino Acids:
- Isoleucine: 5.43% or 32.6 mg/g
- Leucine: 8.15% or 48.9 mg/g
- Lysine: 4.37% or 26.2 mg/g
- Methionine: 2.22% or 13.3 mg/g
- Phenylalanine: 4.35% or 26.1 mg/g
- Threonine: 4.68% or 28.1 mg/g
- Tryptophan: 1.41% or 8.5 mg/g
- Valine: 6.23% or 37.4 mg/g
Non-Essential amino Acids:
- Alanine: 7.74% or 46.6 mg/g
- Arginine: 7.94% or 47.6 mg/g
- Aspartic Acid: 12.14% or 72.8 mg/g
- Cystine: 0.93% or 5.6 mg/g
- Glutamic Acid: 14.07% or 84.4 mg/g
- Glycine: 5.32% or 31.9 mg/g
- Histidine: 2.50% or 15.0 mg/g
- Proline: 4.11% or 24.7 mg/g
- Serine: 4.42% or 26.5 mg/g
- Tyrosine: 3.97% or 23.8 mg/g
How to choose the best Spirulina brand product?
Follow next recommendations when you are buying Spirulina prodcuts:
- Although there are a various products containing spirulina, some of them may only offer a small portion of it. Hence, such products may not have adequate benefits described above
- The first thing you need to look at is to look for a pure product and not a blend. So, if a product says that it “includes” or “features” spirulina, then avoid such products. You don’t want a mixture with different fillers along with already effective supplement.
- You will go for straight spirulina if you want to be sure that you are getting something that is centered only around this.
- Product you are buying should be organic brand as well. This ensures that proper standards were followed and that the highest quality is recognized
- If the product comes from Japan, no matter it is organic or not, then this is not the best choice in brand. The reason for this is that such products are not considered as safe, because spirulina can absorb heavy metals from the waters that it grows in. Such spirulina may contain high concentrations of lead
Most commonly used Spirulina Brands worldwide are following:
- Nutricost Spirulina
- Nutrakey Spirulina
- Now Spirulina
- Pure Planet Spirulina
- Nutrex Hawaii Hawaiian Spirulina
- Earthrise Spirulina Natural
- Doctor’s Best Spirulina
- Nature’s Way Spirulina
- Source Naturals Organic Spirulina
- Gaia Herbs Spirulina
Precautions and warnings during Spirulina use
- Spirulina is considered safe as it is wealth nutrient source of food. But, as with anything else, don’t take it too much. 3g or 2 teaspoons should be your maximal daily dose, especially at the beginning when there is a chance to cause some not so serious side effects such as: nausea, abdominal discomforts or eventually diarrhea. But in most cases it won’t cause any unpleasant side effect if taken in larger doses.
- As mentioned above, be careful about where the spirulina comes from. Spirulina can absorb toxic heavy metals such as lead and mercury that grows within. Waters of Japan and China have been shown to be contaminated with these chemicals, so avoid Spirulina in that case.
- If you are buying Spirulina, always take original, organic product; never take mixtures that between other also contain Spiirulina.
- Be sure of what you are getting with this or any other natural products where the health standards aren’t necessarily in place to mandate the quality that you think you’re getting.
- Consider some time when you begin taking spirulina because you should want to see how your body will react.
- If you are allergic to sea food then don’t take Spirulina
- If you have other health problems, consult your doctor or pharmacist to make sure that spirulina is safe for you to take. For most people, this so called superfood can be an excellent supplement, but just be sure that you don’t have any potential complications that may interfere with its effectiveness.
- At the beginning, general recommendation is to gradually increase your spirulina intake in small quantities in order to be sure that it doesn’t cause an upset stomach.
Spirulina side effects
Spirulina is considered as a very safe supplement for the majority of people, however it isn’t without concerns and side effects. Some people may experience mild side effects after spirulina use including: gastrointestinal upset with symptoms such as bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, then edema (swelling), and allergic reactions to seafood like a rash. Serious side effects in healthy individuals are very rare and unreported for now.
Spirulina contains a richness of proteins, amino-acids and nucleic acids, substances which may produce uric acid after metabolism. If too much uric acid is produced, it will be accumulated in through your body, gout or kidney stones can develop. If you are susceptible to gout attacks or kidney stones, you should avoid spirulina as it may be harmful for you. To avoid excessive uric acid, do not take more than 50 grams of spirulina per day.
Similarly to different cyanobacterium species, it may be possible that spirulina is able to produce toxins such as microcystins, BMAA, and others. There are reports in which some spirulina supplements were contaminated with microcystins, although at levels below the boundary set by the Oregon Health Department.
Microcystins are toxins that can cause gastrointestinal disturbances and if taken too long also the liver damage. The effects of chronic exposure to even very low levels of microcystins are of concern, because of the potential risk of toxicity to several organ systems and possibly cancer. However, original and controlled Spirulina products are considered as microcystin-free.
Cultivated Spirulina safety
Cultivated Spirulina ponds are sampled every day and carefully inspected for any sign of contamination, warranting that the consumer receives a pure product. Scientists believe there are over 30,000 species of microalgae. The huge range of species includes nutritious diversities like Spirulina and Chlorella, as well as potentially hazardous species such as the microcystis strains well-known in Klamath Lake, Oregon, where a commercially sold blue green algae product is harvested.
Microcystis is an alga that has hepatotoxic properties. While microcystis has appeared in wild harvested blue green microalgae products in the past, it has never been found in cultured Spirulina. The microalgae farmer’s “field” is a pond and the “seed” is a live culture. Ponds are lined with food-quality liners covered with a layer of natural calcium carbonate (which coral is composed of).
Paddlewheels gently stir the cultures, ensuring optimum light for each cell and helping the pond to release oxygen. The culture thrives in these ideal conditions, growing several times faster than it would in the wild.
Spirulina interactions with other drugs
There are no scientific data to suggest that spirulina can interact with any conventional drugs. However, it’s possible that the spirulina can interact with immunosuppressive drugs like: cyclosporine (Neoral), adalimumab (Humira), infliximab (Remicade), mycophenolate (CellCept), etanercept (Enbrel), azathioprine (Imuran), leflunomide (Arava), and methotrexate.
Who should avoid Spirulina?
Beside its safety, some patients may need to avoid Spirulina:
- Patients with a metabolic condition called phenylketonuria (PKU) must avoid taking spirulina because they can’t metabolize one of the amino acids it contains.
- Patients with autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, or lupus should consult their doctors whether to take spirulina or not. Theoretically, spirulina can stimulate immune system and make your condition far worse. However, there are no clinical studies that can confirm this.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding woman should also avoid spirulina products since there are no studies on its effects on fetal and infant. Although, it is known that many tribes are taking spirulina safely.
- Spirulina is rich in beta-carotene, which is know that when taken in high doses it may increase the risk of kidney and liver issues and the risk of lung cancer, especially in individuals with Vitamin C deficiency such as smokers. There are no relevant studies to confirm this and it is only theoretically for now.
- Patients with kidney malfunction should also avoid spirulina since it is very high in protein content, thus blood levels of uric acid may be increased, leading to further kidney damage.
- Spirulina grows on the water surface, so there is a risk of potential contamination from toxic bacteria and heavy metals including lead and mercury, which can cause abdominal pain and distention, hepatotoxicity, jaundice, nausea, vomiting, excessive thirst, weakness, rapid and weak pulse, shock, and even death. Original products however, don’t contain heavy metal traces and this data is always on label and/or packaging.
Spirulina and Vitamin B12
Spirulina, naturally, does not contain vitamin B12 naturally therefore spirulina supplements are not considered to be a reliable source of vitamin B12 even if they are added, as they contain predominantly pseudovitamin B12, biologically inactive in humans.
In a 2009 paper on vegetarian diets, the ADA – American Dietetic Association indicated that spirulina is not a reliable source of active vitamin B12. Other literatures similarly guides that spirulina is not suitable as a source of B12.
Spirulina use for pets, other animals and plants
Except for humans Spirulina is also good source of food for your pets, animals but it also good for gardening and plants. It is especially recommended for old cats and dogs with dull, as thinning coats have been shown to develop thick, lustrous coats and pets with stiff joints seem to improve significantly.
Veterinarians often prescribe Spirulina as an aid for recovery, stiffness relief, stamina increase and also for show animals for their general toning, focus, stamina and energy. Prize winning koi carp are commonly fed Spirulina to enhance their color and health.
Bird breeders add Spirulina to the food in order to enhance feathers color and luster. In aquaculture companies spirulina is often used to recover the growth rates, promote disease resistance and survival rates, decrease medication use and improve quality and coloration of numerous fish and shellfish.
Gardeners can use Spirulina as a complete, effective foliar plant food. Homeowners can sprinkle a little Spirulina in the earth around their favorite houseplant and see what a difference it makes. Organic farmers can use Spirulina as a completely natural and healthy fertilizer.
In one case, an organic lettuce grower in Hawaii saw a tremendous increase in the yield and health of his lettuce by fertilizing with Spirulina, while a farmer across the street using conventional fertilizer had lettuce that grew much slower and smaller.
Spirulina recipes
You can use some of following recipes to make your spirulina powder tasty:
4-Ingredient Spirulina Lemonade:
You need:
- 500 ml sparkling water
- 1 fresh lemon
- 6 drops pure stevia
- 1-2 teaspoons Organic Burst Spirulina
Follow next steps:
- Juice the lemon with a lemon juice press and pour into a large jug.
- Add the stevia drops and Organic Burst Spirulina and whisk well to combine.
- Pour in sparkling water and stir if needed to mix.
- Serve straight away.
Spirulina cinnamon cream
You need:
- 1 cup raw cashews, soaked
- ½ teaspoon Organic Burst Spirulina
- ½ cup rice malt syrup
- 1 teaspoon cinnamon
- 2½ cups filtered/mineral water
Follow next steps:
- Soak the cashews for at least 8 hours in 2 cups of water, ideally overnight.
- Drain the water and place the cashews into a blender.
- Add the rice malt syrup, 1/2 cup of water, cinnamon and Organic Burst Spirulina.
- Blend until smooth and creamy.
- Store in a jar in the fridge for up to 5 days
Spirulina pesto
You need:
- 1 cup pine nuts, very lightly toasted
- ½ cup nutritional yeast
- 3 handfuls fresh basil
- 1 clove garlic, chopped
- Sea salt
- Freshly ground black pepper
- 1 tbs extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tsp Organic Burst Spirulina powder
- juice of 1 lemon
Follow next steps:
- Pulse the garlic and basil in food processor.
- Add the pine nuts and olive oil to the mixture and pulse again.
- Stir in the lemon juice, nutritional yeast, and spirulina powder.
- Season to taste. You may add more olive oil to reach the consistency of your liking.
- Serve with gluten-free pasta or courgetti
“What does L-carnitine do for you? L-carnitine benefits, dosages and side effects“