Contents
- What is Sucralfate?
- What are the ingredients of Sucralfate?
- What is Sucralfate molecular formula and weight?
- Sucralfate drug class
- How does Sucralfate work in the body?
- Sucralfate Brand names
- What is Sucralfate used for?
- Sucralfate dosage forms and strengths
- Sucralfate dosage for different indications
- Sucralfate highest dose
- Sucralfate side effects
- How to take Sucralfate?
- Can I abrupt Sucralfate therapy suddenly?
- Sucralfate withdrawal effects
- Precautions and warnings during Sucralfate use
- How long does Sucralfate take to work?
- How does Sucralfate treat ulcers?
- How long does Sucralfate stay in your system, urine, blood, saliva?
- Sucralfate during pregnancy
- Sucralfate during breastfeeding
- Sucralfate Overdosage
- Sucralfate absorption and elimination
- Is it safe to take Sucralfate with alcohol?
- Does Sucralfate cause constipation?
- Sucralfate drug interactions
- Is it safe to take Sucralfate and Lasix together?
- Is it safe to take Sucralfate and Synthroid together?
- Can patients with hypophosphatemia use Sucralfate?
- Can patients with renal dysfunction use Sucralfate?
- Sucralfate and food interactions
- How long do I have to wait to eat after taking Sucralfate?
- Can I take Sucralfate and Pantoprazole together?
- Can I take Sucralfate and Famotidine together?
- Is Sucralfate a proton pump inhibitor?
- Is Sucralfate a painkiller?
- Can I take Sucralfate for Diarrhea?
- Zantac and Sucralfate Drug interaction
- Can I take Sucralfate with Zofran?
- Sucralfate 1 gm tablet for dogs
- Can HIV positive patients take dolutergavir and sucralfate together?
- Can patients with hypothyroidism take paricalcitol and sucralfate together?
- Can diabetics take Insulin and sucralphate together?
- Can Digoxin and sucralfate be taken together?
- Can Allopurinol and sucralfate be taken together?
- Can Metformin and sucralfate be taken together?
- Can Warfarin and sucralfate be taken together?
- Can Tetracycline and sucralfate be taken together?
- Can Quinapril and sucralfate be taken together?
- Can Cipro and sucralfate be taken together?
- Can Atenolol and sucralfate be taken together?
- Can Diclofenac and sucralfate be taken together?
What is Sucralfate?
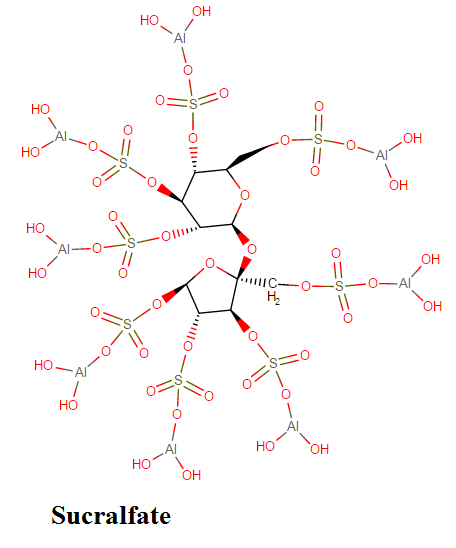
Sucralfate is a generic name for an anti-ulcer, gastro-protective medication that is used to treat and prevent ulcers of the upper GIT. In general, it is a basic aluminum complex of sulfated sucrose.
It works primarily in the lining of the stomach by binding to the active ulcer sites thereby forming a physical barrier that protect the ulcers from acids, enzymes and bile salts. Sucralfate is used to treat an active duodenal ulcer. Sucralfate can heal an active ulcer, but it will not prevent future ulcers from occurring.
Thus, it is commonly used in combination with different anti-ulcer agents. It may also be used to treat or prevent ulcers caused by NSAIDs drugs, to relieve the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and to prevent ulcers linked with physical stress in hospitalized patients. It is available in the form of tablet in dose of 1000mg and in the form of oral suspension in dose of 1000mg/10ml. The most common Brand name for sucralfate is Carafate. FDA approved this drug in 1981 and is originally manufactured by Aptalis Pharma US, Inc.
What are the ingredients of Sucralfate?
Chemically, Sucralfate consists of a complex of the disaccharide sugar, sucrose, sulfate combined with aluminum. The Carafate suspension contains 1g of Sucralfate per 10 mL. It also contains colloidal dioxide NF, glycerin USP, simethicone USP among others.
What is Sucralfate molecular formula and weight?
Sucralfate molecular formula: C12H54Al16O75S8
Sucralfate chemical name: Hexadeca-μ-hydroxytetracosahydroxy[μ8-[1,3,4,6-tetra-O-sulfo-β-Dfructofuranosyl-α-D-glucopyranoside tetrakis(hydrogen sulfato)8-)]]hexadecaaluminum
Sucralfate molecular weight: 2086.75 g/mol
Sucralfate drug class
This drug belongs to the class of chemical entities which are known as disaccharide sulfates which are disaccharides carrying more than one sulfate group on a sugar unit. Therefore, it comes under the class of Organic Oxygen Compounds with its direct parent being disaccharide sulfates.
How does Sucralfate work in the body?
In the body, Sucralfate is a locally acting substance that with its strong negative charge, binds to the positively charged proteins at the base of the ulcers present in the lining of the stomach thereby forming a physical barrier which protects the ulcer surface from further interactions with pepsin and acid. Pepsin, which is an enzyme that breaks apart proteins, is directly inhibited by Sucralfate in the presence of stomach acids.
It reacts with HCL acid in the stomach to form a cross linking, viscous, paste like material capable of acting as a buffer. In addition to this, Sucralfate prevents back diffusion of hydrogen ions, and absorbs both pepsin and bile acids.
Sucralfate may increase prostaglandin production where prostaglandins are enzymes that protect the stomach lining and may also bind epithelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor, both of which enhance the growth and repair mechanism of the stomach lining. It is minimally absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (up to 5% of the disaccharide component and less than 0.02% of aluminum).
Sucralfate Brand names
Sucralfate has many brand names in different parts of the globe, the most common being Carafate. Other brand names include Sucramal, Sucraxol, Ulcogant, Pepsigard, Sucral, Hapifate, Sucralpro, Sutra, Musin, Sulcrate, Ulsanic and Andapsin.
What is Sucralfate used for?
Generally, Sucralfate is used for the treatment of active duodenal ulcers. It can also be used for the short term treatment of gastric ulcer. The drug may be used to prevent ulcers caused by the use of aspirin or any other anti-inflammatory drugs. Additionally, Sucralfate can be used in the following conditions:
- Preventing resolved duodenal ulcers.
- As specified earlier, can be used to treat gastric ulcer with a combination of other drugs while being more cost effective than ranitidine combination group.
- Stress ulcer prevention and stress ulcer prophylaxis
- Preventing stricture formation – It has an inhibitory effect on stricture formation and can also be used in the treatment of corrosive esophageal burns.
- During pregnancy, it can be used to treat the Gastro-esophageal reflux disease.
- After Gastric bypass surgery has been done, Sucralfate can be used in the treatment of anastomotic ulcer.
- During radiation and chemotherapy, it can be used to prevent Aphthous ulcer and Stomatitis
FDA approved indications for sucralfate are:
- Active duodenal ulcer
- Gastric ulcer
- Mucositis
Sucralfate dosage forms and strengths
Sucralfate is most commonly present in two dosage forms, Suspension and Tablet. Both of the forms have to be taken through the oral route and have varying strengths.
The forms along with their varying strengths are given below:
- Oral Suspension – 1g/ 10mL
- Orally administered tablets – 1000mg
- Oral suspension – 100mg
The most common dosage strength is the 1g/10mL or 1g. Each dose should strictly be taken on an empty stomach and about 4 times a day depending on the therapy and instructions of your doctor.
Sucralfate dosage for different indications
The dosage may vary depending on the indications and duration of therapy.
- Usual Adult Dose for Duodenal Ulcer – It is recommended that Sucralfate be taken 1g orally 4 times a day for the duration of 4-8 weeks where each does is taken on an empty stomach. Thereafter, for the maintenance of therapy, it must be taken at a reduced dosage of 1g twice a day after the acute ulcers have healed.
- Usual Adult Dose for Duodenal Ulcer Prophylaxis – 1g orally twice a day should be taken for the duration of up to 1 year.
Elderly patients should be started on the low end of the dosing range.
Sucralfate highest dose
Generally, for the short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer 1g taken 4 times a day is a maximal daily dose.
Sucralfate side effects
Usage of Sucralfate may cause a number of minor side effects that may not need any specific medical attention. The side effects include:
- Constipation (2-3%) – Most common
Less common or rare ones are:
- Backache
- diarrhea
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- dryness of mouth
- indigestion
- nausea
- skin rash, hives, or itching
- stomach cramps or pain
People with chronic kidney failure should avoid taking this drug as it may cause aluminum accumulation and toxicity.
Some of the serious side effects include an unusual feeling of fullness in the stomach, difficulty in swallowing, nausea, and vomiting and stomach pain.
How to take Sucralfate?
- The medicine should generally be taken on an empty stomach at least an hour before eating.
- It is advised that an antacid should not be taken before or after taking Sucralfate for at least 30 minutes.
- It is important to continue the dosage of this medicine even after you don’t feel the ulcer pains and the usage should not be stopped before consulting your doctor.
- Sucralfate should be taken by mouth 2-4 times daily for a period of 4-8 weeks.
- Regular usages are recommended and to help you remember the timings, use it at the same time each day.
- Certain medications may not work well if you take them at the same as Sucralfate. Try to keep a difference of at least 2 hours between medicines.
- Multiple doses of Sucralfate are not recommended. A missed dose should be taken as soon as possible.
- More than 4 doses should not be taken in a day and the therapy period should not be extended than the prescribed duration by your doctor.
Can I abrupt Sucralfate therapy suddenly?
It is not advised to stop your Sucralfate medication suddenly. It is important that you continue your dosage even after you don’t feel any ulcer pains. Your therapy must continue for 4-8 weeks during the presence of ulcers. After that, a reduced dosage should be taken for the maintenance of your therapy. A therapy should only be stopped after proper consultation with your doctor.
Sucralfate withdrawal effects
Withdrawal effects have been reported for very few people out of the total patients who opted out of the medication therapy of Sucralfate. The most common effects after a certain time period are listed below:
- Abdominal Pain Upper (23%)
- Pain (18%)
- Nausea and Vomiting (18%)
- Injury (14%)
- Gallstones (14%)
- Cholecystitis Chronic (14%)
- Nausea (9%)
Other notable effects include a headache, fever, anxiety, high blood pressure, and mood swings.
Precautions and warnings during Sucralfate use
- Sucralfate may contain inactive ingredients which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Therefore it is advised to tell your doctor about your previous medical history including allergies, kidney problems, and stomach/intestine problems.
- The functioning of kidneys declines as you grow older. Sucralfate contains aluminum which is normally removed by the kidneys. Therefore, elderly people are at a higher risk of developing high aluminum levels while using this drug.
- Sucralfate should be used with caution by patients who have known conditions of respiratory complications as it may impair swallowing, tracheotomy and may alter cough and gag reflexes.
- It is not found if this medicine is found in breast milk. If you are or will be breast-feeding, please consult with your doctor about any possible risks.
- The usage of Sucralfate should not be coupled with any other medicine that has aluminum in it too.
How long does Sucralfate take to work?
The onset of effect is generally within 1-2 hours (initial onset for peptic ulcer disease). The absorption is less than 5% orally and the duration is up to 6 hours primarily due to high affinity for defective mucosa. For best effects Sucralfate should be taken at least an hour before eating.
How does Sucralfate treat ulcers?
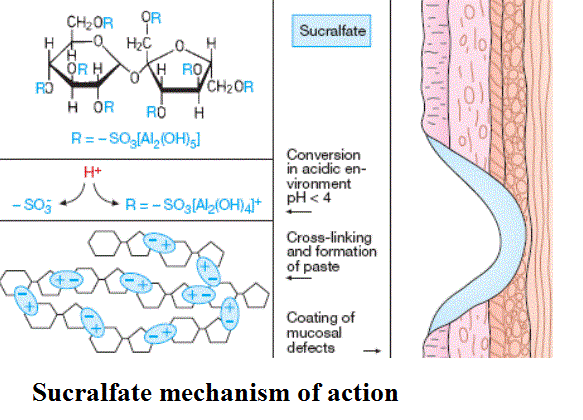
Sucralfate is a locally acting substance that reacts with hydrochloric acid in an acidic environment (pH<4) in the stomach and forms a cross-linking, paste like coating on the ulcers that acts as an barrier and protects the ulcer surface from further interactions with pepsin and acid.
This barrier is formed because Sucralfate has strong negative charges that bind to the exposed positively-charged proteins at the base of ulcers thereby resulting in the formation of this ‘acid buffer’. Thus, due to the formation of this barrier the ulcers are protected from further damage and the healing process starts slowly.
Sucralfate also prevents back diffusion of H2 ions thereby inhibiting pepsin which is an enzyme that breaks apart proteins. It also binds bile salts from the liver via the bile and thus neutralizes any injury that could’ve been caused to the stomach lining by the bile acids.
Sucralfate has also been found to increase the production of prostaglandins which are known to protect the stomach lining. Prostaglandins bind epithelial growth factor which enhances the growth and repair mechanism of the stomach lining. Therefore, Sucralfate also facilitates in the maintenance of an ulcer-free environment
How long does Sucralfate stay in your system, urine, blood, saliva?
Sucralfate stays in your system for a maximum of 6 hours after duration of its effect. After which, the small amounts of the drug absorbed are excreted primarily through urine in an unchanged form.
Sucralfate during pregnancy
Sucralfate falls in the Pregnancy Category of B which means that no risks were found in other studies. Animal reproduction studies have failed to demonstrate any risks to the fetus and insufficient data is available in the case of pregnant women. It can also mean that adequate and controlled tests failed to demonstrate any risks to the fetus in pregnant women in any trimester.
Therefore, Sucralfate has been termed as ‘Possibly Safe’ during pregnancy and usage is recommended only if it is clearly needed. It is advised to consult with your doctor if you are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant as you will need to discuss the benefits and risks of taking Sucralfate during your pregnancy.
Sucralfate during breastfeeding
No tests have clearly determined whether Sucralfate is found in breast milk or not. The drug has been termed to potentially safe due to limited maternal absorption and most authorities find it acceptable. No special precautions are required. It is advisable to consult with your doctor if you are will be breast-feeding while you take Sucralfate.
Sucralfate Overdosage
There is limited experience in humans with overdosage of sucralfate. Sucralfate is only minimally absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and thus risks associated with acute over dosage should be minimal. In rare reports describing sucralfate overdose, most patients remained asymptomatic. Few reports in which adverse events were described included symptoms of nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain.
Sucralfate absorption and elimination
Sucralfate is minutely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The absorption measures up to less than 5% orally which constitutes up to 5% of the disaccharide component and less than 0.02% of aluminum. The drug isn’t metabolized and the small amounts of sulfated disaccharide that are absorbed are eliminated in urine in the form of the unchanged drug.
Is it safe to take Sucralfate with alcohol?
It is very strongly advised to avoid alcohol consumption while you’re taking your Sucralfate dose although, no direct conflicting interactions have been found between Sucralfate and alcohol. One of the side effects of Sucralfate is that it may cause dizziness. This effect will be heightened if you’re consuming it with alcohol and will inhibit your senses.
Does Sucralfate cause constipation?
The most common side effect of Sucralfate is Constipation (2-3%). This is primarily caused due to the fact that Sucralfate directly interacts with the stomach lining and inhibits the digestive processes. Although, the degree of constipation is very minor and it is advised to notify your doctor if the situation persists. Other minor side effects of Sucralfate may include nausea, dizziness, vomiting, dry mouth and stomach gas.
Sucralfate drug interactions
Some medications that may interact with Sucralfate include:
- Antacids that contain aluminum
- Certain antibiotics (quinolones such as levoflaxacin, ciprofloxacin, tetracyclines)
- Digoxin
- Penicillamine
- Quinidine
- Thyroid medications like liothyronine
- Calcium, aluminum, magnesium or Iron supplements
Certain moderately serious drug interactions include:
- Lasix (Furosemide) – Sucralfate may reduce the degree of absorption and effects of oral furosemide.
- Dolutegravir – As Sucralfate contains aluminum, it may affect the absorption of doultegravir and reduce its effectiveness in treating HIV. It is advised to
administer dolutegravir 2 hours before or 6 hours after the Sucralfate dose. - Paricalcitol – Using Sucralfate with paricolcitol is not recommended as it may increase the blood levels of aluminum and may cause bone toxicity.
The mechanism of most of these interactions is non-systematic in nature. In all of the interactions, it was found that Sucralfate could alter the absorption of other medications thereby reducing their effect. Therefore, it’s advised to administer Sucralfate separately from other drugs with a minimal gap of 2 hours in between.
Is it safe to take Sucralfate and Lasix together?
As specified earlier, Lasix (Furosemide) and Sucralfate should not be administered together and Sucralfate reduces the degree of absorption thereby reducing the serum concentration of Lasix and lowers its therapeutic effects. Therefore, it is advised to that their doses be separated by a minimum of 2 hours.
Is it safe to take Sucralfate and Synthroid together?
According to the limited clinical data, Synthroid (Levothyroxine) and Sucralfate may interact in a minor way where Sucralfate may interfere with the absorption of thyroid hormone and reduce the serum concentration of Levothyroxine.
This interaction can be controlled by restricting the dosage of Sucralfate to twice per day and separating thyroid supplements from Sucralfate be eight hours. Therefore, Sucralfate and Synthroid should never be administered together.
Can patients with hypophosphatemia use Sucralfate?
Due to the phosphate binding properties of Sucralfate, it is sometimes used therapeutically. However, it should be noted that hypophosphatemia may occur in some patients, regardless of renal status. Therefore, patients who have preexisting hypophosphatemia should be administered with therapy with Sucralfate cautiously. It is also advised to monitor the phosphate levels in these patients regularly.
Can patients with renal dysfunction use Sucralfate?
Patients who are receiving dialysis or with chronic renal failure have impaired excretion of absorbed aluminum. As the aluminum in the body is removed by the functioning of kidneys, excess levels of aluminum accumulation may occur with patients undergoing dialysis.
In addition, aluminum is unable to cross the dialysis membranes as it is bound together with albumin and transferrin plasma proteins. Patients with renal impairment have been reported with aluminum accumulation and toxicity (aluminum osteodystrophy, osteomalacia, and encephalopathy). Therefore, caution must be taken while administering Sucralfate to patients with chronic renal failure.
Sucralfate and food interactions
It is advised to avoid alcohol along with Sucralfate dosage. Calcium, iron, magnesium and aluminum supplements should not be taken within 2 hours of Sucralfate medication.
Sucralfate should be taken on an empty stomach with a full glass of water 1 hour before or 2 hour after meals. Sucralfate interacts with enteral nutrition by resulting in precipitation and the formation of bezoars which obstruct the feeding tubes. This is due to the formation of an insoluble complex (aluminum-protein) between the aluminum in Sucralfate and protein in the enteral feeding.
In addition, Sucralfate is activated only in an acidic (pH<4) environment and may not be activated in the alkaline pH facilitated by the enteral nutrition products.Therefore, it’s advised to keep a gap of at least 1 hour before and after taking Sucralfate. Alternatives like H2 antagonists or proton pump inhibitors may be considered.
How long do I have to wait to eat after taking Sucralfate?
Sucralfate should be taken at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after each meal to be effective. So, you would have to wait for 1 hour to consume anything after taking Sucralfate.
Can I take Sucralfate and Pantoprazole together?
Pantoprazole is also used to treat stomach and esophagus problems like acid reflux. It also belongs to the class of proton pump inhibitors (PPI).
Though, no known interactions have been found between Sucralfate and pantoprazole, it is advised to take pantoprazole at least 30 minutes before Sucralfate.
Can I take Sucralfate and Famotidine together?
Famotidine, in general, is a drug the blocks the release of stomach acid helping in stopping heartburn and acid indigestion from coming back. Famotidine has no known interactions with Sucralfate so it is generally safe to consume it with Sucralfate. However, just as a precaution, famotidine should be taken 30 minutes before taking Sucralfate.
It is also to be noted that famotidine is known to react with Digoxin/Selected antacids. When both of these are taken together, the body may not absorb digoxin properly thereby decreasing the beneficial effects of digoxin.
Is Sucralfate a proton pump inhibitor?
Sucralfate belongs to the class of chemical entities which are known as disaccharide sulfates which are disaccharides carrying more than one sulfate group on a sugar unit. Therefore, it comes under the class of Organic Oxygen Compounds with its direct parent being disaccharide sulfates.
On the other hand, Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) like Omeprazole and Pantoprazole are drugs whose main action is a long-lasting reduction of stomach acid production. They are the most effective inhibitors of acid secretion available. Other PPIs include rabeprazole, dexlansoprazole, esomeprazole etc. As Sucralfate is primarily an anti-ulcer medication therefore it does not belong to the class of Proton Pump inhibitors.
Is Sucralfate a painkiller?
Painkillers or Analgesics are used to reduce pain by directly acting on peripheral or central nervous system. Pain killers include paracetamol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) etc. As Sucralfate acts on the intestine rather than on the nervous system, it is not considered as a ‘painkiller’.
Can I take Sucralfate for Diarrhea?
Sucralfate is commonly used for the treatment and prevention of stomach ulcers.
Though, Sucralfate can also be prescribed to treat bile diarrhea because it is supposed to coat your insides and prevent any pain and damage from acid and bile. Consequently, diarrhea has also been listed as a minor or less common side effect of Sucralfate.
Zantac and Sucralfate Drug interaction
Minor interactions occur between Zantac (ranitidine) and Sucralfate.
Sucralfate inhibits the absorption of ranitidine and lowers its serum concentration. Moreover, ranitidine can increase the gastric pH and prevent polymerization of Sucralfate as it requires an acidic environment (ph<4) for its functioning.
Therefore, Zantac and Sucralfate are not to be prescribed together and a time period of 30 minutes has to be kept between the consumption.
Can I take Sucralfate with Zofran?
Zofran is a member of the drug class of receptor antagonists and is used to treat conditions like Nausea/Vomiting, Gastroenteritis and alcohol dependence.
No interactions have been found between Sucralfate and Zofran. However, it is advised to consult with your doctor before the consumption of these medications simultaneously.
Sucralfate 1 gm tablet for dogs
It is common for veterinarians to use this as a prescribed medication to treat ulcers in dogs, cats and horses. Sucralfate is available as 1g tablets. For dogs, the usual dosage is half to 1 tablet of Sucralfate 3 times a day orally. It is preferable to give the medication on an empty stomach or 1-2 hours after/before a meal.
Can HIV positive patients take dolutergavir and sucralfate together?
Dolutegravir is anti-HIV medicine that should not be taken with sucralfate at the same time. Products that contain calcium, aluminum, iron, magnesium and/or other minerals may interact with the absorption of dolutegravir and reduce its effectiveness in treating HIV infection. The exact mechanism of interaction has not been yet established. You should take dolutegravir at least two hours before or six hours after the sucralfate dose.
Can patients with hypothyroidism take paricalcitol and sucralfate together?
Using sucralfate in combination with paricalcitol is not recommended. Combining these two drugs may increase the levels of aluminum in plasma and cause aluminum bone toxicity. The risk is increased the longer these two drugs are used together.
Can diabetics take Insulin and sucralphate together?
Patients with diagnosed diabetes mellitus should avoid taking sucralphate because of its carbohydrate nature. Due to the carbohydrate content of active and inactive ingredients, especially for sucralfate oral suspension (but not the tablet) may interfere with the therapeutic effects of insulin and other antidiabetic drugs.
Episodes of hyperglycemia have been reported in some patients during treatment with sucralfate oral suspension and insulin.
Can Digoxin and sucralfate be taken together?
Sucralfate may decrease the effects of digoxin by interfering with its absorption, thus these two drugs should not be taken together. Digoxin may be used at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after sucralfate.
Can Allopurinol and sucralfate be taken together?
Aluminum-containing oral medications may decrease the absorption of allopurinol and reduce its therapeutic effects. Allopurinol should be administered at least one hour before or two hours after sucralfate.
Can Metformin and sucralfate be taken together?
Due to the carbohydrate formulation in the excipients, sucralfate oral suspension (but not the tablet) may interact with the therapeutic effects of metformin. Episodes of hyperglycemia may be experience in diabetic patients during treatment with sucralfate oral suspension and metformin.
Can Warfarin and sucralfate be taken together?
Sucralfate may interfere with the warfarin absorption in some patients and may reduce its anticoagulant therapeutic effect. The mechanism is still unknown and clinical data have been conflicting. If your doctor does prescribe these medications together, Warfarin should be administered at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after sucralfate.
Can Tetracycline and sucralfate be taken together?
Sucralfate may interfere with the tetracycline absorption and may reduce its therapeutic effect. The clinical significance of this interaction is however unknown. Tetracycline should be administered at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after sucralfate.
Can Quinapril and sucralfate be taken together?
Quinapril and sucralfate can bind together in the gastrointestinal tract if they are taken at the same time. This may inactivate one or other drug or interfere with the absorption into the bloodstream, possibly reducing effectiveness of both drugs. To avoid or minimize the interaction, you should try to take them at least 2 to 3 hours apart.
Can Cipro and sucralfate be taken together?
Oral preparations containing aluminum such as sucralfate may considerably reduce the gastrointestinal absorption of quinolone antibiotics such as Cipro. The mechanism is chelation of quinolones by polyvalent sucralfate’s cations, forming a complex which is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
The bioavailability of Cipro has been reported to decrease by as much as 90% when administered together with antacids containing aluminum or magnesium hydroxide.
Can Atenolol and sucralfate be taken together?
Cocomitant use of aluminum antacids has been shown to decrease the oral bioavailability of certain beta-blockers, including atenolol. The exact mechanism of interaction is still unknown however it may involve cation binding of beta-blockers or a reduction in the dissolution rate due to increased gastric pH.
Can Diclofenac and sucralfate be taken together?
Sucralfate may delay or reduce the pharmacologic effects of diclofenac. The mechanism may be related to the reduced absorption. Data have been conflicting since many studies suggest that sucralfate may have a protective effect on the gastric mucosa when taken with diclofenac or other NSAIDs. Patients are advised to take diclofenac 2 hours before or 6 hours after sucralfate in order to avoid interaction.
“Dexlansoprazole – Uses, Dosage, Side effects, Interactions, OTC”
“How long should I take omeprazole for gastritis?