Contents
- What is Erlotinib (Tarceva)
- Erlotinib generic and brand
- What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)
- What does Erlotinib do
- Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
- Chemical information of the drug
- Erlotinib strength
- How does Erlotinib work
- Dose of erlotinib
- When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Erlotinib
- The dose of Erlotinib should be modified under following conditions:
- What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug Erlotinib
- Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Erlotinib
- How to take Erlotinib
- How to store the drug
- How to dispose the medicine
- Does Erlotinib has approval from government / FDA /or any other related agencies
- Other uses of the drug
- What special dietary precautions should I follow
- What special precautions should I follow/ what should I avoid while using Erlotinib
- Erlotinib side effects
- Erlotinib may cause following common side effects
- If any of the under mentioned symptoms are encountered, consult your doctor immediately
- Erlotinib overdose
- Erlotinib missed dose
- Erlotinib drug interactions
- Does Erlotinib have any interaction with Diseases
- Can smoking affect my treatment with Erlotinib
- Where can I get more information?
- Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
What is Erlotinib (Tarceva)
- Erlotinib is a drug that is used for the treatment of cancer.
Erlotinib generic and brand
- The drug is available under generic name Erlotinib or Erlotinib hydrochloride and brand name
- The Erlotinib is marketed in the United States by OSI Pharmaceuticals and Genentech and by Roche elsewhere.
What is the source of the drug (natural or synthetic)
- Erlotinib is a synthetic (man-made) pharmaceutical protein kinase inhibitor.
What does Erlotinib do
Why is this medication prescribed?
- Erlotinib hydrochloride or Erlotinib is widely used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), pancreatic cancer and numerous other types of cancer.
- Erlotinib is approved in several countries to treat locally advanced or metastatic (spread to nearby or other body organs or tissues) non-small cell lung cancer.
- Erlotinib is usually prescribed to patients who have previously been treated with at least one other chemotherapy medication and have not shown improvement as a second- or third-line regimen.
- The drug belongs to the category of medications called tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
- Erlotinib binds in a reversible fashion to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase (protein that signals cancer cells to multiply), thus inhibits the abnormal cellular proliferation/cancer.
- Erlotinib is also prescribed in combination with Gemcitabine (Gemzar, another anti cancer drug) to treat pancreatic cancer.
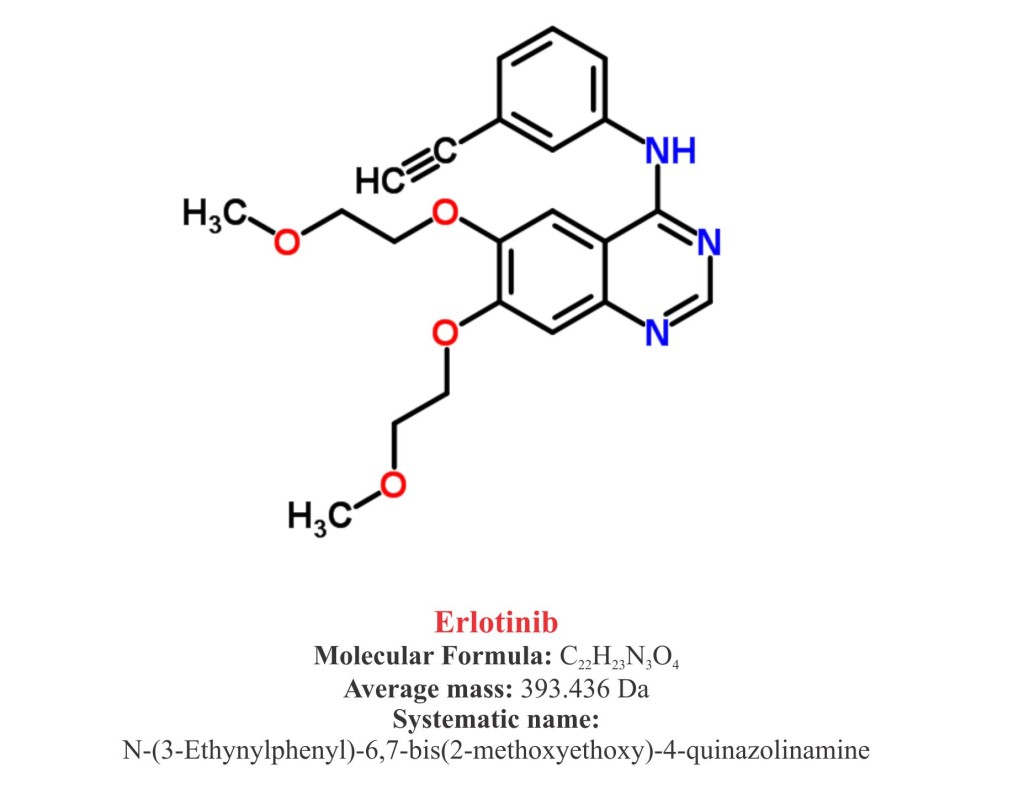
Pharmacophore structure: Information about the chemical structure of the drug
Erlotinib chemically belongs to the class of organic synthetic compounds known as quinazolinamines, a heterocyclic aromatic molecule in which quinazoline moiety is replaced by one or more amine groups. The detailed chemical classification of Erlotinib is as follows.
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Super Class | L-Organoheterocyclic compounds |
| Class | Naphthyridines |
| Sub Class | Quinazolines |
| Direct Parent | Quinazolinamines |
Chemical information of the drug
- Erlotinib is a synthetic pharmaceutical heterocyclic aromatic quinazolinamine named as N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine.
- It is available as hydrochloride salt with a molecular formula C22H23 N3OHCl.
- Molecular weight of Erlotinib is 90 g/mol and melting point is 167-180 ºC.
- Erlotinib is a white crystalline solid, granular or powder and slightly soluble in water and methanol.
- It is practically insoluble in other organic solvents such as acetone, acetonitrile and ethyl acetate.
- Erlotinib has a pKa (the number that denotes the pH) of 5.42 at 25°C. Solubility of Erlotinib in water is primarily dependent on pH.
- In low pH (>5) it show better solubility.
- The maximal solubility of Erlotinib is ~ 0.4 mg/ml at a pH of approximately 2.
Erlotinib strength
- Erlotinib is available for oral administration in tablet form.
- Erlotinib is available in three dosage strength which contain different dosage of Erlotinib hydrochloride (27.3 mg, 109.3 mg and 163.9 mg), respectively.
- These dosages are equivalent to 25 mg, 100 mg and 150 mg of Erlotinib.
- The formulation contains Erlotinib and lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose, sodium lauryl sulphate, magnesium stearate, sodium starch glycolate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, and titanium dioxide.
- The Erlotinib tablets also contain a very small amount of FD&C Yellow #6 as a colour additive for product identification.
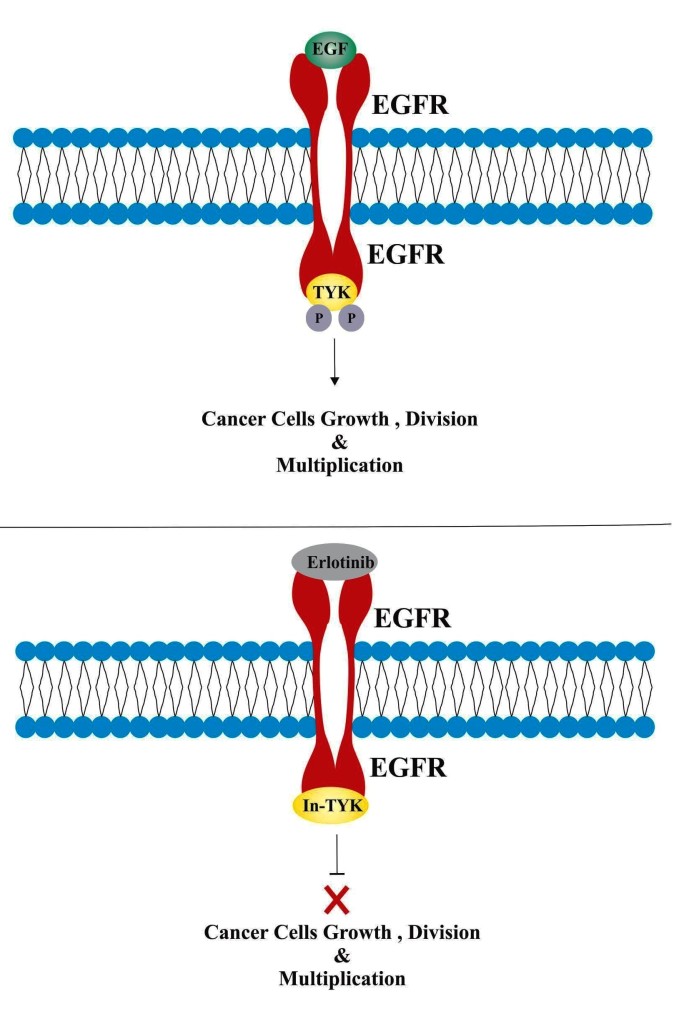
How does Erlotinib work
Mode of action
- Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a protein that is normally produced by the body and involved in promoting cellular growth and multiplication.
- EGF binds or attaches with epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR, present on surface of many cells including cancer cells) and activates an enzyme called tyrosine kinase.
- After activation, tyrosine kinase triggers chemical processes that cause the cells to grow, multiply, and spread rapidly.
- It has been observed that in various forms of cancers, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is highly expressed and mutated, thus promoting constitutive activation of tyrosine kinase, which leads to an abnormal cell growth and proliferation.
- Erlotinib is a reversible epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, which binds with tyrosine kinsae domain of EFGR receptors.
- Erlotinib binding with epidermal growth factor receptors block the attachment of EGF and subsequent activation of tyrosine kinase.
- In this manner, Erlotinib block the signal cascades and therefore growth and multiplication of cancer cells.
Dose of erlotinib
What are the recommended doses of Erlotinib?
- The usual prescribed adult dosage of Erlotinib for Pancreatic Cancer is 100 mg orally per day.
- The usual prescribed adult dosage of Erlotinib for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer is150 mg orally once a day.
- Erlotinib administration is usually prescribed on an empty stomach (i.e. at least one hour before or two hours after the snacks/meal).
- Erlotinib treatment should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
When should I discontinue, withhold or modify the dose of Erlotinib
The use of Erlotinib should be discontinued under the following conditions:
- Gastrointestinal perforation
- Corneal perforation or severe ulceration
- Interstitial lung disease (ILD)
- Severe hepatic toxicity that continues more than 3 weeks
- Severe bullous, blistering, or exfoliating skin conditions
The use of Erlotinib should be with hold under following conditions:
- Suspect /possibility of ILD
- Severe renal toxicity
- In patients (without pre-existing hepatic impairment) showing total bilirubin levels greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal (3 x ULN) and/or serum transaminases greater than 5 x ULN .
- In patients (with pre-existing hepatic impairment or biliary obstruction ) showing total bilirubin levels greater than 2 times the upper limit of normal (2 x ULN) and/or serum transaminases greater than 3 x ULN .
- Under conditions of persistent severe diarrhea or severe rashes (not responsive to medical management).
- For keratitis of grade 3-4 or for grade 2 lasting more than 2 weeks
- Under conditions of acute/worsening ocular disorders i.e. eye pain
The dose of Erlotinib should be modified under following conditions:
- Reduce Erlotinib by 50 mg Decrements under conditions of severe reactions following concomitant use of strong CYP450 3A4 inhibitors or when using concomitantly with an inhibitor of CYP450 3A4 and CYP450 1A2.
- Reduce Erlotinib by 50 mg Decrements, when restarting therapy following interruption of treatment for a dose-limiting toxicity that has resolved to baseline or grade less than or equal to 1.
- Increase Erlotinib by 50 mg increments following concomitant use with CYP450 3A4 inducers. The dose should be increased by 50 mg increments every two weeks to a maximum dose of 450 mg. Avoid concomitant use if possible.
- Increase Erlotinib by 50 mg increments under conditions of concurrent cigarette smoking. Increase the dose by 50 mg every two weeks to a maximum dose of 300 mg. However, the dose should be immediately reduced to the recommended dose (150 mg or 100 mg daily) upon cessation of smoking.
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug Erlotinib
- Pharmacokinetic studies with Erlotinib have shown that about 60 % of the drug is absorbed following oral administration.
- The drug has an apparent volume of distribution of 232 litters.
- The bioavailability of Erlotinib is increased significantly to 100% by food.
- The peak plasma level of drug is observed after 4 hours of drug administration.
- The solubility of Erlotinib is inversely proportional to pH i.e. high pH low solubility/low pH high solubility.
- Following absorption the majority (~93%) of the drug is protein bound to plasma albumin and alpha-1 acid glycoprotein.
- The average median half-life of Erlotinib in plasma is 36.2 hours. However, the steady state plasma level of Erlotinib usually takes 7 – 8 days.
- No significant relationship occurs between the drug absorbance and clearance to patient age, body weight or gender. Although smokers show a 24% higher rate of Erlotinib clearance.
- It has been observed that out of 100 mg oral dose of Erlotinib, 91% of the dose is recovered in feaces (83%) and urine (8%).
- Erlotinib is primarily metabolized in liver by CYP3A4. However, a lesser amount of Erlotinib is metabolized by CYP1A2, and the extra-hepatic isoform CYP1A1.
- Cigarette smoking reduces Erlotinib exposure to approximately 2-fold.
Which pregnancy category (A; B; C; D; X) has been assigned to Erlotinib
- Erlotinib use is strictly prohibited in women who are pregnant or contemplating pregnancy.
- As per the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) pregnancy classification, Erlotinib use should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus ( TGA pregnancy category: C)
- Erlotinib is classified by US FDA under pregnancy category: D (Positive evidence of risk)
- Laboratory animal studies have shown extensive toxicity of Erlotinib use during pregnancy such as abortion and embryo-fetal lethality.
- Use of drug prior to mating to early weeks of pregnancy shows an increase in early resorptions and decreased number of live fetuses .
How to take Erlotinib
- Erlotinib is available in tablet form for oral administration.
- Since food leads to significant increase in drug absorption, it is usually recommended on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after eating a meal or snack) per day.
- It is also recommended to take the drug at almost the same time every day.
- Follow the instructions carefully as directed on prescription leaflet and take Erlotinib exactly as directed.
- Do not change the dose of the drug as prescribed by your doctor. The recommended dose may be decreased by the doctor depending upon adverse side effects or medication response.
- If you have any queries about the drug immediately consult to your doctor to explain any part you do not understand.
How to store the drug
- Erlotinib is stored at room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
- The container should be tightly closed and kept away from excessive heat, direct sun light and reach of children.
- Do not freeze or store the medicine at extreme cold temperature.
How to dispose the medicine
- Throw away unused and opened, outdated or no longer used container.
- Also dispose the old medicine after the expiration date.
- Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
- Erlotinib has received its official approval from US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September 1981.
- In 2005, Erlotinib was approved in combination with Gemcitabine (anticancer nucleoside analog used as chemotherapy) for treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer
- The drug was initially approved for use in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (had relapsed after at least one other kind of therapy) by FDA.
- However, in year 2010, the use of drug was expanded for maintenance therapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer whose disease was stable after four cycles of treatment with a platinum-based drug, such as cisplatin or carboplatin.
- In year 2013, FDA has officially approved the use of Erlotinib as a primary therapy for metastasis NSCLC certain types of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations.
Other uses of the drug
- Erlotinib may also be used for other cases not mentioned here. It is advisable to ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special dietary precautions should I follow
- It is generally recommended to avoid eating grapefruit and drinking grapefruit juice during the course of medication.
- To reduce the Erlotinib diarrhoea, it is recommended to drink small sips of a sugar-free sports drink throughout the day.
- Follow a routine diet, eat mild foods and avoid spicy foods.
What special precautions should I follow/ what should I avoid while using Erlotinib
- It is recommended not to use an antacid within several hours before or after Erlotinib use.
- Do not use Erlotinib in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy.
- Skin rashes, dryness, or other irritation are some of the common side effects of Erlotinib, therefore it is advised to stay away from exposure to sunlight or tanning beds. Use protective measures (protective clothes and sunscreen).
- Use of skin commodities that leads to irritation and dryness should be avoided; mild cleanser for cosmetics removal and mild alcohol-free moisturizer and mild soap for skin should be utilized.
- Avoid using tobacco products, smoking can significantly reduce the Erlotinib effect.
- Do not use the medicine if you are hypersensitive to any of the ingredients.
- It is advisable to discuss with your doctor and pharmacist about the prescribed and nonprescribed medications, vitamins, and nutritional supplements.
- Talk with your doctor or pharmacist about what herbal products you are taking, especially St. John’s wort.
- Safety and efficacy of Erlotinib has not been evaluated as first-line treatment in patients with metastatic NSCLC whose tumors have EGFR mutations other than exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitutions.
- Tell your doctor if you are being treated or have recently been treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Inform your doctor if you have or have been previously diagnosed with diverticular disease, lung disease or infection, stomach ulcers, or liver or kidney disease.
- Inform your doctor if you are breastfeeding or pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- Inform your doctor about surgery you have undergone, including dental surgery.
Erlotinib side effects
Long term controlled clinical trial studies with Erlotinib suggested that Erlotinib can cause serious side effects, which include:
- Eye disorders
- Interstitial lung disease, or ILD, events
- Liver and kidney problems
- Serious skin conditions
- Gastrointestinal (GI) perforation
- Cerebro-vascular Accident
- Blood, bleeding, and clotting problems
- Bleeding events when taking warfarin
- Myocardial Infarction/Ischemia
Erlotinib may cause following common side effects
- Weight loss
- Vomiting
- Gas and heartburn
- Hair loss
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Changes in the appearance of the hair and nails
- Constipation
- Stomach pain
- Headache
- Weakness and extreme tiredness
- Anxiety and depression
- Mouth sores
- Darkening of skin
- Loss of appetite
- Bone or muscle pain
If any of the under mentioned symptoms are encountered, consult your doctor immediately
- Burning sensation, softness and Itching of the skin
- Xerostomia (mouth becomes unusually dry)
- Stool colour turning black tarry or accompanied with blood
- Swelling, redness, pain, tenderness in one leg
- Sensation of dizziness or faintness
- Leg or arm becoming weak or numb
- Bruising or bleeding
- Difficulty in speech
- Urine turning dark
- Feeling of pressure, discomfort or pain in chest
- Blood in vomit or coffee colour vomit
- Loss of appetite, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting
- Difficulty in breathing and cough
- Blurred vision and irritation in the eyes
- Growth of eyelashes inside of the eyelid
- Painful, dry, red or sunken eyes
- Skin becoming yellow or pale
- Frequency of urination decreases
- Rashes on the upper portion of the chest, back or face
- Irregular or rapid, irregular heartbeat
- Cracked, peeled, dry or blistered skin
Erlotinib overdose
What should I do in case of overdose?
- Erlotinib overdose usually occurs when someone by mistake or deliberately takes more than the prescribed limit of this medication.
- The common overdose symptoms of Erlotinib include severe diarrhea or severe skin rashes.
- In case of overdose, contact with your doctor or emergency room immediately. Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
Erlotinib missed dose
What should I do in case of missed a dose?
- In case of missed dosage, take it as soon as you remember and maintain a regular dosing schedule. Keep in mind that the missed dose should be taken only on an empty stomach.
- Skip the missed dose if it is time for your next scheduled dose. Keep in mind not to use a double dose to make up a missed dose.
Erlotinib drug interactions
Does Erlotinib have any interaction with drugs?
- The concomitant use of Erlotinib is restricted with drugs affecting gastric pH. The common examples are proton pump inhibitors, H2-receptor antagonist and antacids.
- It is observed that co-administration of Erlotinib with omeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor, decreases the Erlotinib exposure and maximum concentration by 46% and 61%, respectively.
- Some of the common drugs not advised with concomitant use of Erlotinib are as follows.
- Angiogenesis inhibitors such as bevacizumab (Avastin)
- Antifungals such as carbamazepine (Tegretol) and itraconazole (Sporanox),
- Anticoagulants (‘blood thinners’) such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro, Proquin XR); clarithromycin (Biaxin); warfarin (Coumadin); ketoconazole (Nizoral), and voriconazole (Vfend).
- HIV protease inhibitors such as indinavir (Crixivan), atazanavir (Reyataz), ritonavir (Norvir), nelfinavir (Viracept), and saquinavir (Fortovase, Invirase).
- H2blockers such as famotidine (Pepcid), cimetidine (Tagamet), nizatidine (Axid), and ranitidine (Zantac);
- Medications for acne such as benzoyl peroxide (in Epiduo, in BenzaClin, in Benzamycin, others); midazolam (Versed): nefazodone
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn)
- Oral steroids such as methylprednisolone (Medrol), dexamethasone (Decadron, Dexone), and prednisone (Deltasone); phenobarbital (Luminal, Solfoton); phenytoin (Dilantin)
- Proton pump inhibitors such as lansoprazole (Prevacid), esomeprazole (Nexium), omeprazole (Prilosec), pantoprazole (Protonix), pantoprazole (Protonix), and rabeprazole (AcipHex)
- Taxane medications for cancer such as docetaxel (Taxotere), docetaxel (Taxotere) and paclitaxel (Abraxane, Taxol); telithromycin (Ketek); and troleandomycin (TAO) .
This list does not comprise all the drugs that interact with Erlotinib and there are many other drugs that can interact with Erlotinib. If you start any new medication, first consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Does Erlotinib have any interaction with Diseases
It has been observed that some medical conditions (disease) may also interact with Erlotinib such as:
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD): Studies have shown that Erlotinib use may also be associated with cases of serious ILD, including fatal cases.
- Renal Failure: It has been observed that Erlotinib use may be associated with severe acute renal failure, hepatorenal syndrome, and renal insufficiency.
- Hepatotoxicity: Erlotinib use may also be associated with hepatic failure, hepatorenal syndrome, and baseline hepatic impairment.
- Gastrointestinal Perforation: Gastrointestinal perforation, including fatal cases, can occur with Erlotinib treatment.
- The other medical complications that can be associated with Erlotinib uses are bullous and exfoliative skin disorders, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction (MI)/ischemia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, ocular disorders and hemorrhage in patients consuming warfarin.
Can smoking affect my treatment with Erlotinib
- Yes, Erlotinib treatment is less effective when patient consumes the tobacco products. If you smoke, it is advisable to stop smoking immediately before starting Erlotinib treatment.
- If patient is unable to withdraw smoking, the treatment is needed to be increased /revised.
Where can I get more information?
Your pharmacist can provide more information about Erlotinib.
Clinical research and current scenario of the drug
- A large number of randomized, open, placebo controlled studies have shown the efficacy and safety of Erlotinib.
- Randomized, open-label, clinical trial of Erlotinib as first line treatment (with metastatic NSCLC patients containing EGFR Mutations) have shown significant improvement compared to those randomized chemotherapy.
- The efficacy and safety of Erlotinib was also demonstrated as maintenance treatment of NSCLC in a controlled trial conducted in 26 countries with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC patients whose disease did not progress during first-line platinum-based chemotherapy.
- Furthermore, the efficacy of Erlotinib as NSCLC –Second/Third Line Treatment was also proven effective in patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC after failure of at least one chemotherapy regimen.
- However multicentre placebo-controlled, randomized studies conducted in first-line patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC have shown lack of efficacy of Erlotinib, when administrated concurrently with chemotherapy.
- Randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic pancreatic cancer have shown efficacy and safety of Erlotinib in combination with Gemcitabine as a first-line treatment.
References from chemical, biological and toxicological databases
- Erlotinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: an update for clinicians. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3244201/.
- Drug bank information Erlotinib. http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/db00530.
- Erlotinib: MedlinePlus Drug Information. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a605008.html.
- Tarceva® (erlotinib) Tablets for Advanced-Stage NSCLC http://www.tarceva.com/patient/
- Chemspider information Erlotinib. http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.154044.html.
- FDA Approval for Erlotinib Hydrochloride. http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/treatment/drugs/fda-erlotinib-hydrochloride.
- The SATURN trial: the value of maintenance erlotinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21142856.
- Differential metabolism of gefitinib and erlotinib by human cytochrome P450 enzymes. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17575239.
- Phase II study of erlotinib for acquired resistance to gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24692734.
- Erlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: efficacy and safety findings of the global phase IV Tarceva Lung Cancer Survival Treatment study. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20736854.
Read about,
“Ezetimibe – drug class, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action”
“Memantine, drug class, uses, strength, side effects, mechanism of action“