Contents
- What is Meperidine?
- Meperidine history
- Meperidine (Demerol) vs. morphine
- Are meperidine and pethidine the same?
- Meperidine physical properties
- Meperidine chemical name, drug class, structure, molecular formula and weight
- Meperidine FDA approved indications?
- Meperidine dosage
- Meperidine clinical pharmaclology
- Meperidine mechanism of action
- Meperidine effects
- Meperidine absorption, metabolism and elimination
- How should you take Meperidine?
- What happens if I miss a dose of meperidine?
- What happens if I overdose meperidine?
- Special precautions during meperidine use
- Demerol (meperidine) addiction
- Demerol (meperidine) withdrawal
- What are the side effects of Meperidine?
- What other drugs affect the functioning of Meperidine?
- Meperidine drug dependence
- Can Meperidine be taken with CNS depressants?
- How Meperidine is related to head injury and increases intracranial pressure?
- Can Meperidine be given intravenously?
- Can the use of meperidine results in life-threatening respiratory depression?
- Can the intake of Meperidine causes withdrawal syndrome in neonates?
- Can I take meperidine with cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors and inducers?
- What are the risks from continuous use of meperidine with Benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants?
- Is the interaction between MAOIs and meperidine fatal?
- Use of meperidine in chronic pulmonary disease and elderly patients
- Can I take meperidine and amitryptiline together?
- Can meperidne cause adrenal insufficiency?
- What are the risks of meperidine use in patients with GIT problems?
- What are the risks of meperidine use in patients with seizure disorders?
- Can the use of Meperidine result in hypotension?
- Can Meperidine be used in Ambulatory patients?
- Can Meperidine be used in pregnancy and lactating mothers?
- What precautions during meperidine use must be taken in special cases?
- Can I take Meperidine with MAO inhibitors like Phenelzine, linezolid, tranylcypromine?
- Can I take meperidine with CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inhibitors like macrolide antibiotics, Azole antifungal, and protease inhibitors drugs?
- Can I take meperidine with CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers like Rifampicin, phenytoin, carbamazepine?
- Can I take meperidine with benzodiazepines and other CNS depressants?
- Can I take meperidine with antidepressants?
- Can I take meperidine with partial agonist opioid analgesics?
- Can I take meperidine with Muscle relaxants?
- Can I take meperidine with Anticholinergic drugs?
- Can I take meperidine with diuretics?
- Can I take meperidine with Acyclovir?
- Can I take meperidine with Cimetidine?
- Can I take meperidine with alcohol?
- Meperidine Non-clinical toxicology
- What are the Contraindications of meperidine use?
What is Meperidine?
Meperidine is an opioid narcotic drug. It is used to treat moderate to severe pain. The pain includes postoperative pain and pain caused due to labor. It is is classified as a Schedule II (C-II) controlled substance so its prolonged use must be avoided as can lead to dependence.
It is most commonly known under the brand name Demerol. Meperidine is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe pain, and is delivered as a hydrochloride salt in tablets, as a syrup, or by intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intravenous injection. In tablet form, it is available in doses of: 25mg, 50mg, 75mg, 100mg and 150mg.
Meperidine history
Meperidine is synthesized in 1939 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, whereas its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben, Germany. Meperidine is first approved by FDA in 1942 and is originally manufactured by Sanofi Aventis.
Meperidine (Demerol) vs. morphine
Compared with morphine, pethidine was thought to be safer, carry a lower risk of addiction, and to be superior in treating the pain associated with biliary spasm or renal colic due to its putative anticholinergic effects.
These were later discovered to be all myths, as it carries an equal risk of addiction, possesses no advantageous effects on biliary spasm or renal colic compared to other opioids, and due to its toxic metabolite norpethidine is more toxic than other opioids – especially during long-term use. The norpethidine metabolite was found to have serotonergic effects, so pethidine could, unlike most opioids, contribute to serotonin syndrome.
Are meperidine and pethidine the same?
Yes, meperidine and pethidine are names for the same active ingredient.
Meperidine physical properties
It is a white crystalline substance having 186-189 degree Celsius melting point. It is soluble in water and has slightly bitter taste. PH is 3.5-6
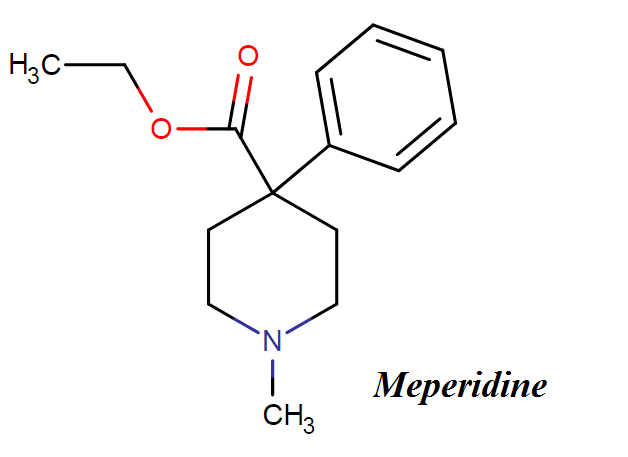
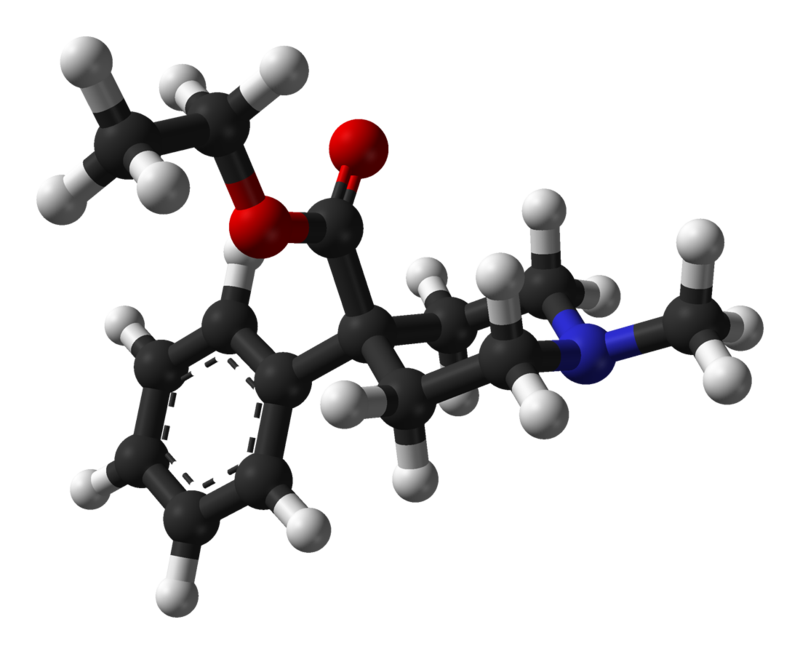
Meperidine chemical name, drug class, structure, molecular formula and weight
Meperidine (pethidine) belongs to the class of chemical entities known as phenylpiperidines. These are compounds containing a phenylpiperidine skeleton, which consists of a piperidine bound to a phenyl group.
Meperidine molecular formula: C15H21NO2
Meperidine molecular weight: 247.338g/mol
Meperidine chemical (IUPAC) Name- ethyl 1-methyl-4-phenylpiperidine-4-carboxylate
Meperidine structure and 3D formula are shown below:
Meperidine FDA approved indications?
Meperidine FDA approved (labeled) indications are:
- Severe pain
- Moderate pain
Meperidine dosage
Following doses are recommended for following indications:
- For relief of pain
Dosage is titrated according to the severity of the pain and response of the patient. Subcutaneous administration is done for occasional use. IV administration is done in the case of repeated doses. In intravenous injection, dosage is decreased and injection is prepared from the diluted solution. The dose of Meperidine is reduced when given with Phenothiazine and other tranquilizers. These drugs can potentiate the action of Meperidine
Adults
The average dose prescribed is 50- 150 mg IM or sub cutaneous in every 3-4 hours as required. Elderly people must be given the drug in lower doses.
Children
The average dose varies from 0.5 mg/lb to 0.8 mg/ lb IM or subcutaneously. This can be administer in every 3-4 hours as required.
- For anesthesia support
Repeatedly slow IV injections of 10 mg/ml or continuous IV injection of 1mg/ml can be administered. The doses can be titrated according to the needs and specifications of the patients. It will depend on the premedication and type of anesthesia used. Elderly patients must be given the lower dose and must be strictly observed.
- For obstetrical Analgesia
The average dose is 50 mg to 100 mg IM or subcutaneously. It may be repeated every 1-3 hours as required.
Meperidine clinical pharmaclology
Meperidine is a synthetic opiate agonist. It belongs to the class of phenylpiperidine. Meperidine is a narcotic analgesic. It has similar function to morphine. It act on CNS and smooth muscle.
According to studies, Meperidine can cause less smooth muscle, spasm, constipation and depression. The onset of action is rapid and duration of action is shorter as compared with morphine. It is less effective by the oral route as compared with the parenteral route.
Meperidine mechanism of action
Meperidine is primarily a kappa-opiate receptor agonist and also has local anesthetic effects. Meperidine has more affinity for the kappa-receptor than morphine. Opiate receptors are coupled with G-protein receptors and function as both positive and negative regulators of synaptic transmission via G-proteins that activate effector proteins.
Binding of the opiate stimulates the exchange of GTP for GDP on the G-protein complex. As the effector system is adenylate cyclase and cAMP located at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, opioids decrease intracellular cAMP by inhibiting adenylate cyclase. Subsequently, the release of nociceptive neurotransmitters such as substance P, GABA, dopamine, acetylcholine and noradrenaline is inhibited.
Opioids also inhibit the release of vasopressin, somatostatin, insulin and glucagon. Opioids close N-type voltage-operated calcium channels (OP2-receptor agonist) and open calcium-dependent inwardly rectifying potassium channels (OP3 and OP1 receptor agonist). This results in hyperpolarization and reduced neuronal excitability.
Meperidine effects
-
Effects on CNS
Meperidine directly acts on brain stem respiration points. It produces respiratory depression that results in the reduction in the response of respiratory brain centers. This creates the increase in carbon dioxide tension and electrical stimulation. It can result in eye miosis or total darkness.
-
Effect on GIT and other smooth muscles
Meperidine results reduction in motility that causes increase in the tone of smooth muscles of the stomach and duodenum. It causes delayed digestion of food in small intestine. Propulsive contractions are decreases resulting in constipation.
-
Effects on the cardiovascular system
Meperidine causes vasodilation that results in orthostatic hypotension. With the release of histamine, you can suffer from flushing, red eyes, and sweating.
-
Effects on Endocrine System
Meperidine inhibits the secretion of ACTH, cortisol and LH. They stimulate to release prolactin, growth hormone, secretion of insulin and glucagon.
-
Effects on the immune system
Meperidine exhibits immunosuppressive effects.
Meperidine absorption, metabolism and elimination
- Absorption- Bioavailability of Meperidine is 50%.
- Metabolism- it gets metabolized by the transformation. In vitro data shows that Meperidine is metabolized to nor-Meperidine in liver.
- Excretion-Both Meperidine and non- Meperidine is excreted by kidneys.
- Elimination-The half-life is 3-8 hours. There is only one bioactive metabolite called nor-Meperidine. It has an elimination half-life of 20.6 hours.
How should you take Meperidine?
- Take Meperidine as prescribed by the doctor. You are advised to follow all the instruction mentioned on the prescription.
- This drug can affects your breathing when you start taking this medicine.
- Don’t take it in large amounts or more than the prescribed duration.
- Be in touch with the doctor if you are not getting relieve in pain.
- It can be habit forming.
- Don’t advise another person to take this medicine without consulting doctor.
- Misuse of this medicine can result in overdose, death, and addiction.
- Don’t consume Meperidine without consulting the doctor.
- If you are taking liquid medicine measure it from dosing syringe or measuring spoon or medicine cup.
- If you stop taking Meperidine after long use, it can result in withdrawal symptoms.
- Store the medicine away from heat and moisture.
- In the case of leftover drugs, ask your pharmacist how to dispose the leftover medicines.
- In the case of unused tablets or liquid flush them
- This is required to prevent the overdose or misuse of the drug.
Don’t misuse the drug, it leads to death and other serious conditions.
- Don’t crush or break the tablet. Never inhale its powder.
- Don’t mix the powder into liquid and inject the drug.
- These all practices can lead to death with its misuse.
- Keep track of the use of medicine from your bottle. In this way you will be have the information that someone is not using your medicine.
What happens if I miss a dose of meperidine?
As Meperidine is used to treat the pain, it can happen that you missed the dose. If you remember the missed dose and it is almost the time of next dose. Don’t take extra medicine to make up the misses dose. Just take the scheduled medicine.
What happens if I overdose meperidine?
Consult your doctor immediately. An overdose can be fatal. It is very dangerous in the case of child or the person who is consuming this medicine without prescription. Overdose symptoms are slow breathing, irregular slow heart rate, muscle weakness, severe drowsiness, fainting, coma and blue color skin & lips.
Special precautions during meperidine use
Don’t combine alcohol with this medicine. The combination can have very serious side effects like death. This medicine can impair your thinking and decision making skills. Don’t drive any machine if you have consumed this combination. It can result in serious accidents due to dizziness or drowsiness.
Tell your doctor if you are suffering from any of the following conditions
- Severe or acute kidney disease
- If you are suffering from any liver disease
- Asthma, sleep apnea and other breathing problems
- History of head injury and brain tumor
- Thyroid disease
- Fluctuation in blood pressure
- Seizures or epilepsy
- Diseases of gall bladder
- Sickle cell Anemia
- Disorders of adrenal gland or Addison’s disease.
- Urination problems
- History of alcohol or drug addiction
Demerol (meperidine) addiction
On the street, Demerol is often called “Dillies,” “D” “Dust or“Juice,.”
Demerol functions by altering the body’s perception of pain by working on the central nervous system of the body. In addition to the powerful analgesic properties of Demerol, the narcotic also produces feelings of pleasure and giddiness, which can lead many individuals to use this narcotic for nonmedical reasons. Some use Demerol to escape a troubling situation, to numb emotional pain, or to cope with extraordinary stressors.
When used in an uncontrolled setting, such as on the streets, Demerol can be highly addictive and individuals may take more and more of the drug to achieve greater feelings of pleasure. It can be extremely difficult to overcome Demerol abuse without proper professional treatment.
When Demerol is used outside the normal treatment parameters of the hospital for recreational abuse, it can wreak havoc on an individual’s life. Many individuals abuse Demerol for the blissful high it causes. However, the longer an individual abuses Demerol, the more likely it is that their body will become physically and psychologically dependent upon the drug, which can lead to intense withdrawal symptoms if drug use is ceased.
In addition, while meperidine is offered in pill, oral liquid form, and IV injectable doses, it is the injectable form of Demerol that produces the most intense high. The consequences of long-term drug IV drug use are unimaginable.
Demerol (meperidine) withdrawal
The effects of withdrawal from Demerol can be excruciatingly uncomfortable for people who have been addicted to the drug for a long period of time. Demerol should not be discontinued without the express supervision of trained medical personnel in a rehab or hospital setting. Withdrawal effects include:
- Bone and muscle pain
- Tremors
- Anxiety and agitation
- Fever and chills
- Diarrhea and vomiting
- Insomnia
- Restlessness and irritability
What are the side effects of Meperidine?
Immediately call your doctor if you have signs of an allergic reaction to this medicine. The symptoms of allergic reactions are swelling on face, lips, throat & tongue, difficulty in breathing and hives.
Stop using Meperidine if the following side-effects occur
- Slow heartbeat and shallow breathing
- Feeling that you will pass out or severe drowsiness.
- Hallucinations, mood fluctuations, confusion and agitation
- Seizure, tremors and uncontrolled muscle movements
- Irregular menstrual periods, infertility
- Loss of interest in sex, impotence and sexual problems
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tiredness and weakness
- Loss of appetite and dizziness
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
- Less urination
- itching
Immediately seek medical help if you are experiencing these side effects. In elderly patients this medicine can cause severe breathing problems, headache, sweating and dizziness.
What other drugs affect the functioning of Meperidine?
This medicine can interact with various other drugs. It can cause serious side effects or death. Tell your doctor if you are using following drugs.
- Other narcotic medicines like another opioid medicine
- Drugs that affects you’re sleeping and breathing. These medicines can be sedative, muscle relaxant, sleeping pill, tranquilizer and antipsychotic medicines.
- Drugs affective serotonin levels like medicines to treat depression, Parkinson, migraine, infections, headaches and vomiting.
Meperidine drug dependence
Meperidine results in drug dependence. It creates psychic dependence and physical dependence. Tolerance develops on the repeated use. It must be prescribed and administered under the doctor’s guidance.
Can Meperidine be taken with CNS depressants?
It must be used with a great caution. The dose titration is required if the patients are using other narcotic analgesics, general anesthetics, phenothiazine and other tranquilizers. It must not be given with sedative-hypnotics, tricyclic antidepressants, and other CNS depressant drugs. It can result in hypotension, respiratory depression and coma.
Meperidine causes respiratory depressant effects and elevate cerebrospinal fluid in the case of head injury. Use of Meperidine must be under great caution if there is any head injury. It can also result in intracranial lesions or pressure. This drug adversely affects the patients with the head injury.
Can Meperidine be given intravenously?
The injection IV can be given in the dilated form slowly. Rapid intake of Meperidine can result in increase in adverse reaction like apnea, hypotension, severe respiratory depression, cardiac arrest and peripheral circulatory collapse. It must not be administered IV under the absence of narcotic antagonist and emergency facilities. The patient must be in the lying state while giving Meperidine IV.
Can the use of meperidine results in life-threatening respiratory depression?
With the administration of meperidine fatal respiratory depression has been recorded. If this is not treated at once, it can result into death or respiratory arrest. Respiratory depression can be managed by using opioid antagonists, supportive measures and close observation.
The respiratory depression can occur at any time but it is at high risk at the initial stage of therapy and on the increase of the dose. You are advised to monitor the patient closely for 24-72 hours after initiating the therapy. To reduce the risk, proper titration of the dose is must. Accidental ingestion of meperidine tablets by children can result in death. Keep the drug away from the reach of children.
Can the intake of Meperidine causes withdrawal syndrome in neonates?
Prolonged use of meperidine tablets in pregnancy can result in withdrawal in neonates. It can be life-threatening for neonates. Observe any signs of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage it.
Can I take meperidine with cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors and inducers?
Continuous prolong use of meperidine with azole- antifungal agents, protease inhibitor and macrolide antibiotics can increase plasma concentration of meperidine and adverse reactions. Discontinuation of the CYP3A4 inducers like phenytoin, rifampicin and carbamazepine can result in the meperidine concentration in the patients.
While using both these kind of drugs, monitor the patient at the regular intervals. It can lead to the withdrawal symptoms.
What are the risks from continuous use of meperidine with Benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants?
The risks are sedation, coma, respiratory depression and death. Studies have shown that continuous use of meperidine with either benzodiazepines or CNS depressants can result in drug related motility. In order to manage the harmful effects, the lower doses of these drugs can be taken. Titration of the dose is required according the clinical response to the drug.
Under this therapy, you are advised not to operate heavy machinery or drive any vehicle.
Is the interaction between MAOIs and meperidine fatal?
The use of Meperidine is contraindicated in the patients who are already consuming meperidine. This combination can result in the severe adverse reaction within 14 days. It can cause coma, depression, hypotension, and cyanosis. It can also result in other effects like tachycardia, convulsions, and hyper- excitability.
Use of meperidine in chronic pulmonary disease and elderly patients
The use of meperidine in the patient suffering from chronic pulmonary disease can result in hypoxia, hypercapnia, apnea and respiratory depression.
Can I take meperidine and amitryptiline together?
Using meperidine together with amitriptyline can increase the risk of a rare but serious condition called the serotonin syndrome, which may include symptoms such as confusion, hallucination, seizure, extreme changes in blood pressure, increased heart rate, fever, excessive sweating, shivering or shaking, blurred vision, muscle spasm or stiffness, tremor, incoordination, stomach cramp, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Severe cases may result in coma and even death. You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience these symptoms while taking the medications. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns. Your doctor may already be aware of the risks, but has determined that this is the best course of treatment for you and has taken appropriate precautions and is monitoring you closely for any potential complications.
It is important to tell your doctor about all other medications you use, including vitamins and herbs. Do not stop using any medications without first talking to your doctor.
Can meperidne cause adrenal insufficiency?
Many cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with the use of meperidine. The signs of adrenal insufficiency are anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness and low blood pressure. Perform the test for adrenal insufficiency. If the result is positive, then treat it with replacement doses of corticosteroids.
What are the risks of meperidine use in patients with GIT problems?
Meperidine is contraindicated in patients to the person who are suffering from gastro-intestinal obstruction. Meperidine may cause spasm in sphincter of oddi, biliary tract disease, acute pancreatitis and other worst symptoms.
What are the risks of meperidine use in patients with seizure disorders?
Meperidine results in increase in the frequency of seizures in patients who have the problem of seizures. If the dose is given above the permissible limits, then it can result in seizures in patients without the history of seizures. So, these patients must be monitored carefully.
Can the use of Meperidine result in hypotension?
Yes, the use of Meperidine can result in severe hypotension in the post-operative patient. It can also result in hypotension in the patient who is compromised by the depleted blood volume by giving drugs like anesthetics and phenothiazine.
Can Meperidine be used in Ambulatory patients?
It can impair the mental and physical abilities. It degrades the performance of work when driving the car or operating the machinery. It results in orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory patients.
Can Meperidine be used in pregnancy and lactating mothers?
It must not be used in pregnant women. It results in the adverse effects on the fetus. If meperidine is given to pregnant women as obstetrical analgesic, it crosses the placental barrier. It can result in depression of respiration and psychophysiology functions in the newborn. It can also appear in the milk of the lactating mothers that can cause adverse effects in the new born.
There are no controlled data in human pregnancy. AU TGA pregnancy category C: Drugs which, owing to their pharmacological effects, have caused or may be suspected of causing, harmful effects on the human fetus or neonate without causing malformations. These effects may be reversible.
Accompanying texts should be consulted for further details. US FDA pregnancy category Not Assigned: The US FDA has amended the pregnancy labeling rule for prescription drug products to require labeling that includes a summary of risk, a discussion of the data supporting that summary, and relevant information to help health care providers make prescribing decisions and counsel women about the use of drugs during pregnancy.
What precautions during meperidine use must be taken in special cases?
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Meperidine must be given with care to the patient who are suffering from atrial flutter and super ventricular tachycardia. There is a possibility of vagolytic action that can increase ventricular response rate.
Convulsions
It may aggravate the convulsions in patients who are already suffering from convulsion disorders. If the dose is increased then convulsions can occur without history of convulsions.
Acute abdominal conditions
It can result in the worsening of abdominal problems if the Meperidine is used.
Special risk patients
Meperidine must be given with caution in the patients suffering from hepatic and renal impairment. It must be given under the doctor’s guidance in hypothyroidism, urinal problems, Addison’s disease.
Geriatric use
It must be given with caution in the elderly patients. Low doses must be administered to the old patients. As the patients who are above the age of 65 years have impaired functions like renal, hepatic and cardiac in the body.
Hepatic Impairment
With the use of meperidine, it results in the accumulation of meperidine and nor-meperidine occur in hepatic impairment patients. Raised serum levels causes CNS excitatory effects. Meperidine must be taken with caution in patients suffering from hepatic impairment. Dose titration is required in this case. The signs of CNS and respiratory depression must be closely monitored.
Renal impairment
Accumulation of meperidine and active metabolite nor-meperidine occur in renal impairment patients. Meperidine must be administered with great caution in patients with renal impairment.
Can I take Meperidine with MAO inhibitors like Phenelzine, linezolid, tranylcypromine?
Meperidine is contraindicated in patients who are taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors. It can result in occasionally fatal reaction within 14 days. Some of the patients suffer from coma, respiratory depression, hypotension, hyper- excitation, convulsions, and tachycardia. Not to use Meperidine Tablets in patients who are taking MAOIs
Can I take meperidine with CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inhibitors like macrolide antibiotics, Azole antifungal, and protease inhibitors drugs?
The simultaneous administration of meperidine and CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inhibitors increases the plasma concentration of meperidine. After stopping these inhibitors, concentration of meperidine decreases resulting in withdrawal syndrome in patients.
Can I take meperidine with CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers like Rifampicin, phenytoin, carbamazepine?
The simultaneous administration of CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers decreases plasma concentration of meperidine. It results in the onset of withdrawal symptom who are physically dependent on meperidine. After stopping these inducers, the concentration of meperidine increases. It results in either the therapeutic effect or adverse reaction.
Can I take meperidine with benzodiazepines and other CNS depressants?
The simultaneous administration of meperidine and these drugs leads to risk of hypotension, sedation, coma, respiratory depression and even death.
Can I take meperidine with antidepressants?
The simultaneous administration of these drugs with meperidine results in serotonin syndrome, thus their use is contraindicated.
Can I take meperidine with partial agonist opioid analgesics?
This combination can lead to reduction in the analgesic effect of meperidine. It can also precipitate withdrawal symptoms.
Can I take meperidine with Muscle relaxants?
Meperidine increases neuromuscular blocking action of muscle relaxants. It increases respiratory depression. This combination should be avoided
Can I take meperidine with Anticholinergic drugs?
This combination the risk of constipation and urinary retention, thus it should be avoided
Can I take meperidine with diuretics?
This combination of meperidine and diuretics induces release of anti-diuretic hormone.
Can I take meperidine with Acyclovir?
The simultaneous administration of acyclovir and meperidine results in the increase in plasma concentration of meperidine and its metabolite non-meperidine.
Can I take meperidine with Cimetidine?
The simultaneous administration of cimetidine and meperidine reduces the clearance and distribution of meperidine.
Can I take meperidine with alcohol?
Never take meperidine and alcohol together. This interaction may increase nervous system side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, lightheadedness, difficulty concentrating, and impairment in thinking and judgment. In severe cases, low blood pressure, respiratory distress, fainting, coma, or even death may occur.
With certain long-acting formulations of narcotic pain medication, consumption of alcohol may also cause rapid release of the drug, resulting in high blood levels that may be potentially lethal. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have questions on how to take this or other medications you are prescribed.
Do not use more than the recommended dose of meperidine, and avoid activities requiring mental alertness such as driving or operating hazardous machinery until you know how the medication affects you. It is important to tell your doctor about all other medications you use, including vitamins and herbs. Do not stop using any medication without first talking to your doctor.
Meperidine Non-clinical toxicology
- Carcinogenesis- Long term studies to analyze carcinogenic potential of meperidine are not conducted on animals.
- Mutagenesis- Studies to analyze the mutagenesis potential of meperidine are not conducted in animals.
- Impairment of fertility- Studies to analyze impairment of fertility are not conducted on animals.
What are the Contraindications of meperidine use?
It is contraindicated in patients with
- Respiratory depression
- Acute and severe bronchial asthma
- Continuous use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors for 14 days.
- Gastro –intestinal obstruction
- Hypersensitivity to meperidine
“Meclizine – Classification, Dosage, Side Effects and Interactions“